Lecture - one
Anatomy of the anterior abdominal wallDr. Raya Abdul Ameer
CABHS-RAD , MBCHB• The abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity which located between the diaphragm
above and the pelvic inlet below
Boundaries
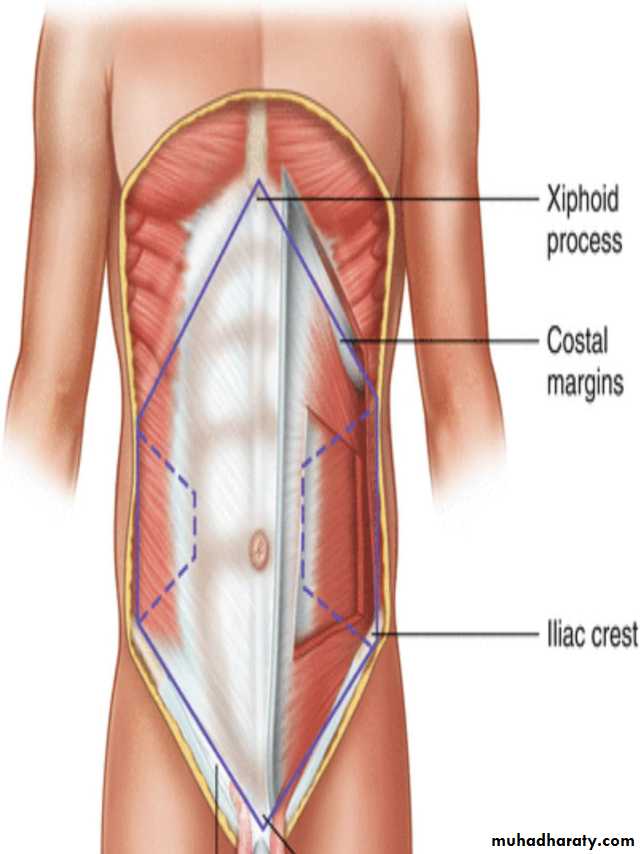
The anterior abdominal wall represent a hexagonal area :
Superiorly
xiphoid process ,
costal cartilage of 7th , 8th ,9th ,and 10th ribs
Laterally
Mid axillary line
Inferiorly
iliac crest , pubis and symphysis pubis .
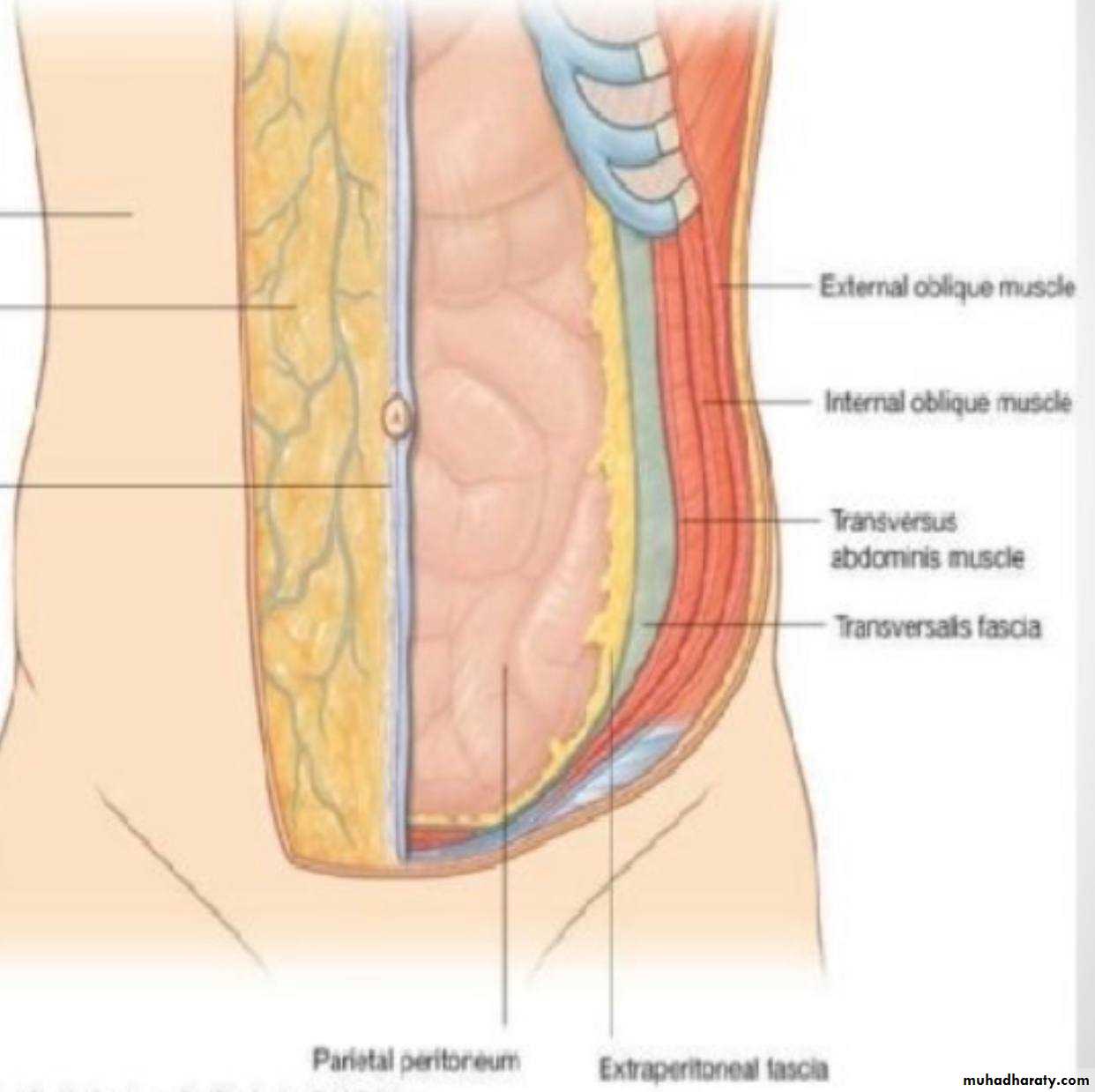
• Structures ( layers ) of the anterior abdominal wall
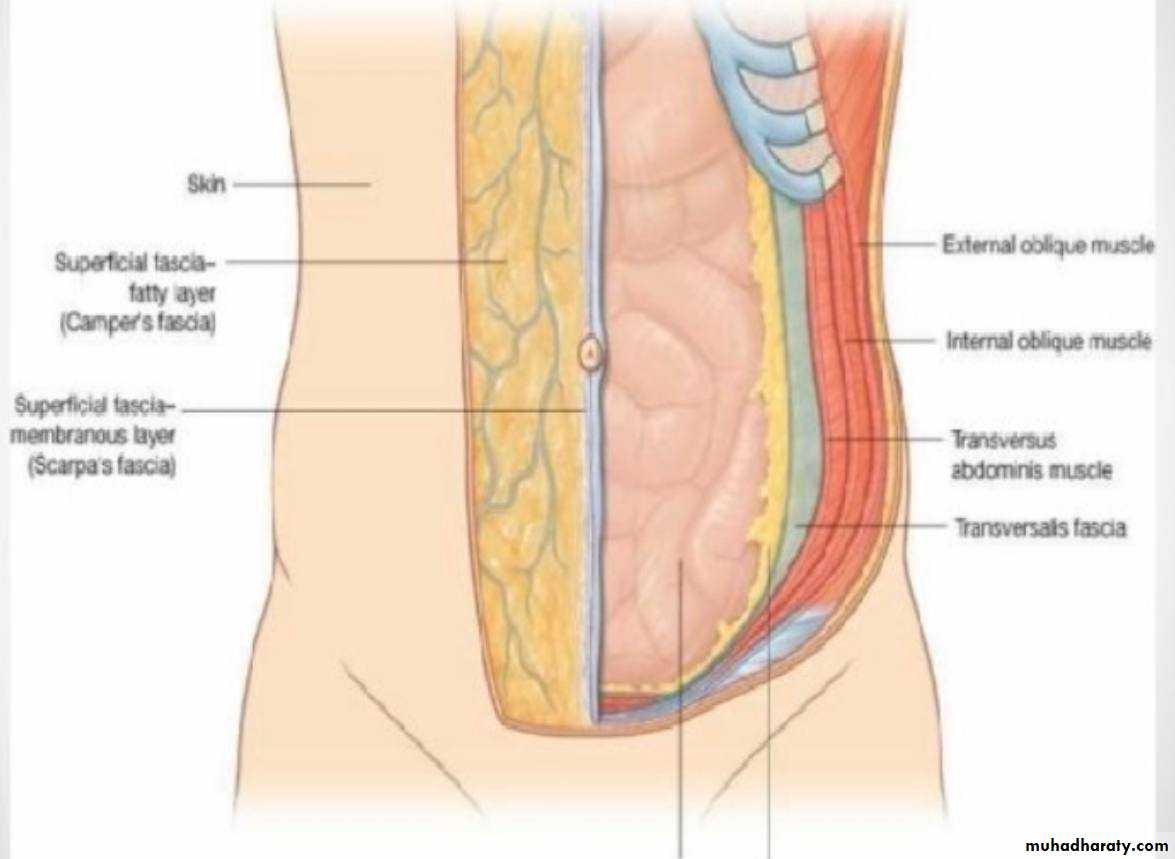
• From out side to inside :• 1-Skin
• 2-Superfiacial fascia
• 3-Deep fascia
• 4-Muscles
• 5-Transversalis fascia
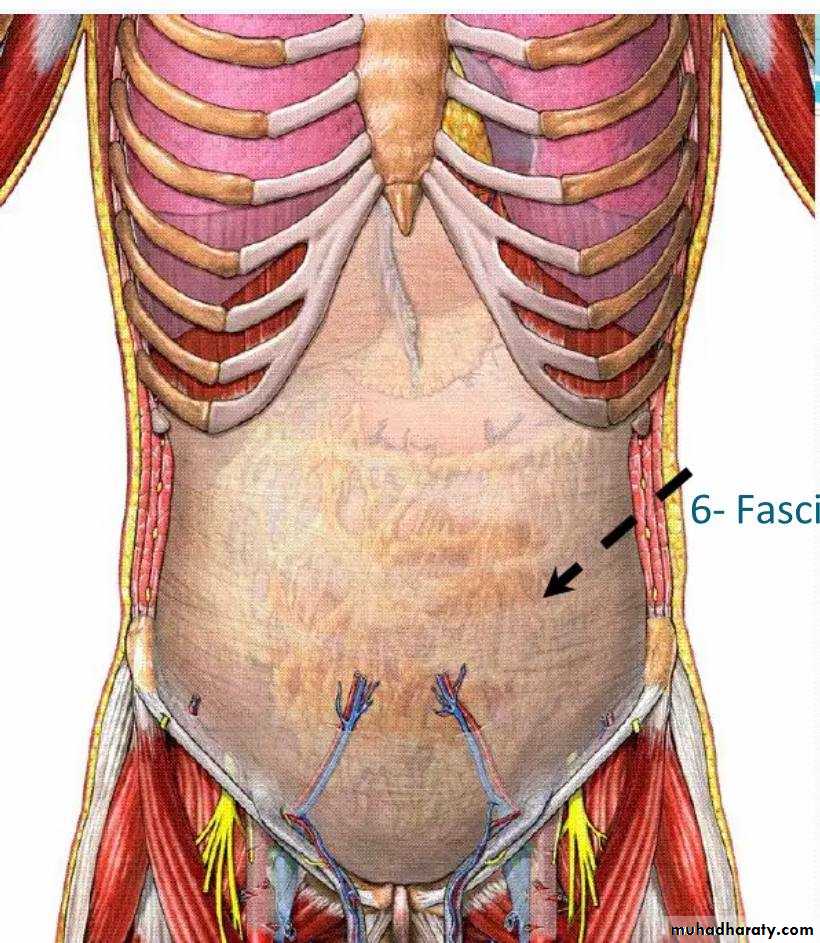
• 6-Extra peritoneal fascia
• 7-Paraietal peritoneum
1-skin of the abdominal wall
The most important characters of skin of abdomen are :--Thin , loosely attaches to the underlying structures except the umbilicus
The umbilicus is a scar representing the
site of attachment of the umbilical cord
in the fetus , it is situated in lines alba .
• 2) Superficial Fascia
• The superficial fascia is divided into two layers:• 1-Superficial fatty layer (Camper's fascia)
• Continue with fascia over thorax and thigh
• In the scrotum, the fatty layer of the superficial fascia
• exists as a thin layer of smooth muscle, the dartos
• muscle
• 2- Deeper membranous layer (Scarpa's fascia)
• *Continue in the perineum as
• surpefacial perineal fascai ..called Colles fascia
• *And continues inferiorly to the fascia of the
• lower limbs and called fascia lata
3 - Deep Fascia
A thin layer of connective tissue covering the muscles. It lies immediately deep to the membranous layer of superficial fascia
4- Muscles
The muscular layers include five bilaterally paired muscles :1 ) Three antero latreral muscles ….
three broad thin sheets of muscle that are most pronounced ( muscular ) posteriorly and laterally and become aponeurotic anteriorly and medially . From exterior ( superficial ) to interior ( deep ):
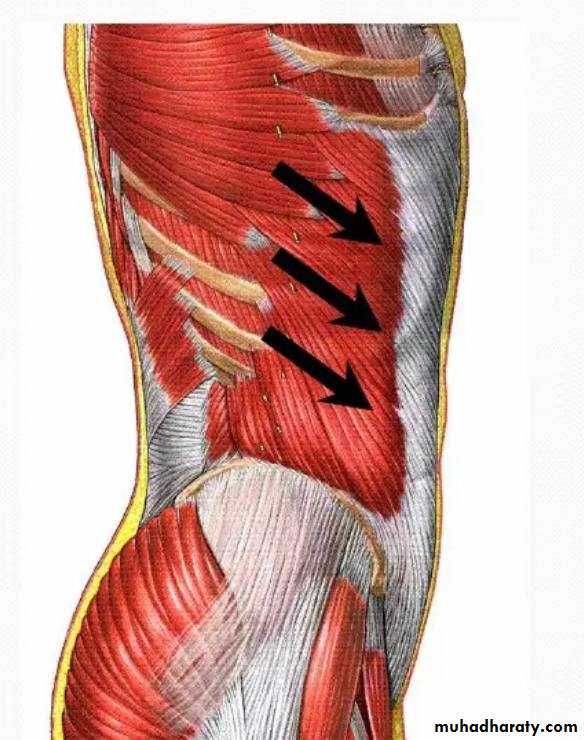
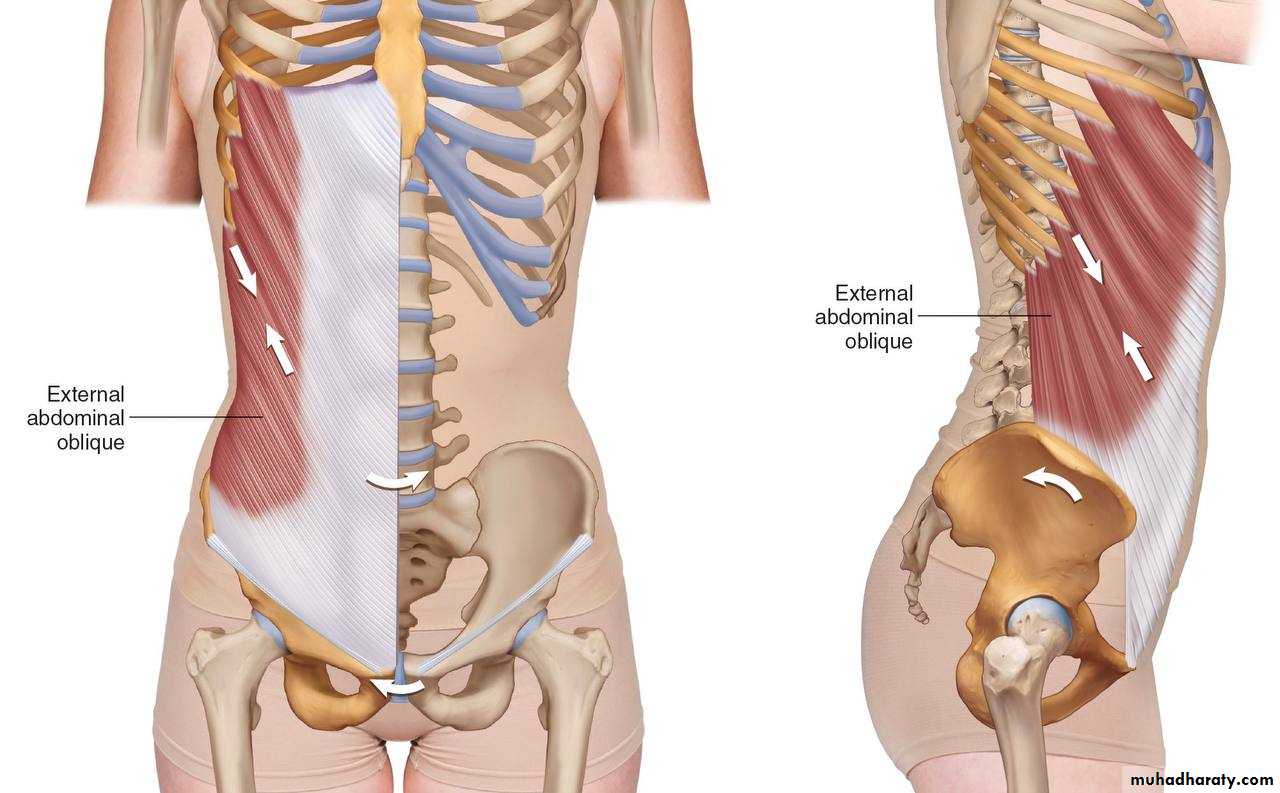
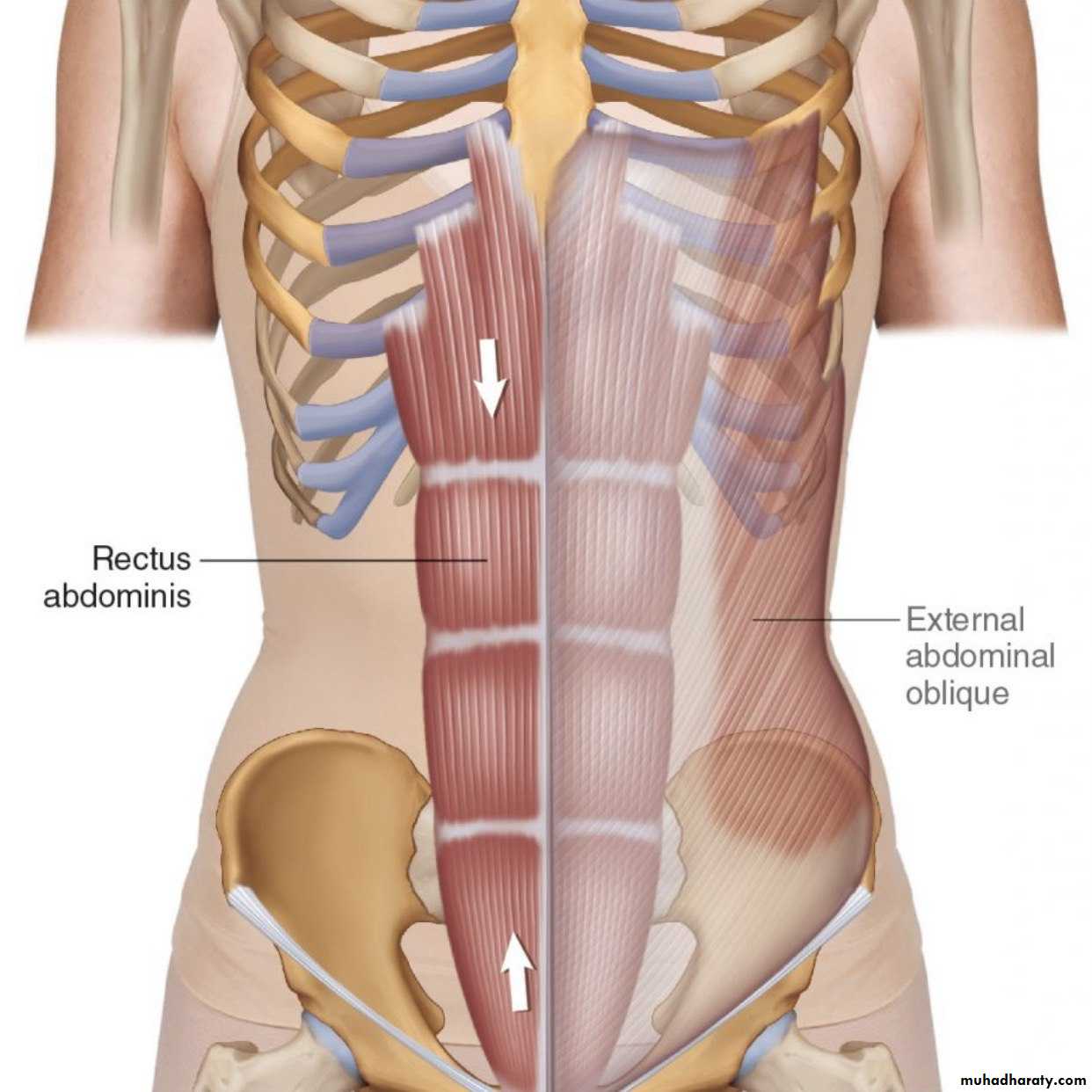
1) External oblique
2) internal oblique
3) Transverse abdominis muscle
2) Two Anterior ( para median muscles ) include :
1 ) Rectus abdominis muscles form wide vertical straps
on either side of the anterior midline
2) Pyramidalis
• Muscles of abdominal wall
• 1) External oblique muscle• Origin:- outer surface and inferior border of the lower eight ribs ( 5-12 )
• Direction of fibers downward , for wards and medially
• Insertion :-Xiphoid Process , Linea alba , pubic crest, pubic tubercle & iliac crest
• N supply :-
• 1- lower 6 thoracic nerves (T7 –T12 )
• 2- ilio-hypogastric and ilio- inguinal nerves ( L1 )
• Actions
• -Supports abdominal contents
• -Compress abdominal contents
• -Assists in flexing and rotation of trunk
• -Assists in forced expiration, micturition ,defecation , parturition, and
and vomiting
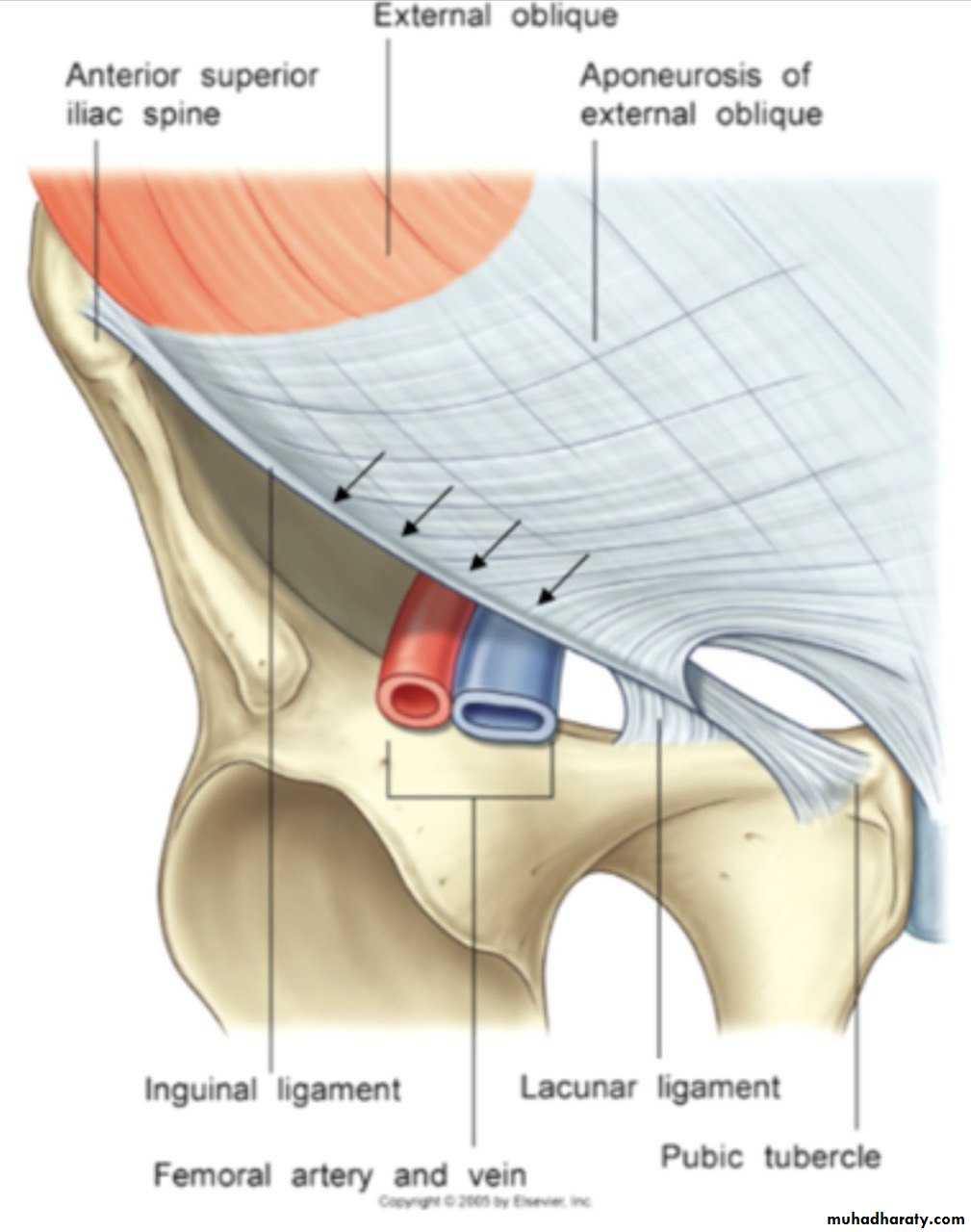
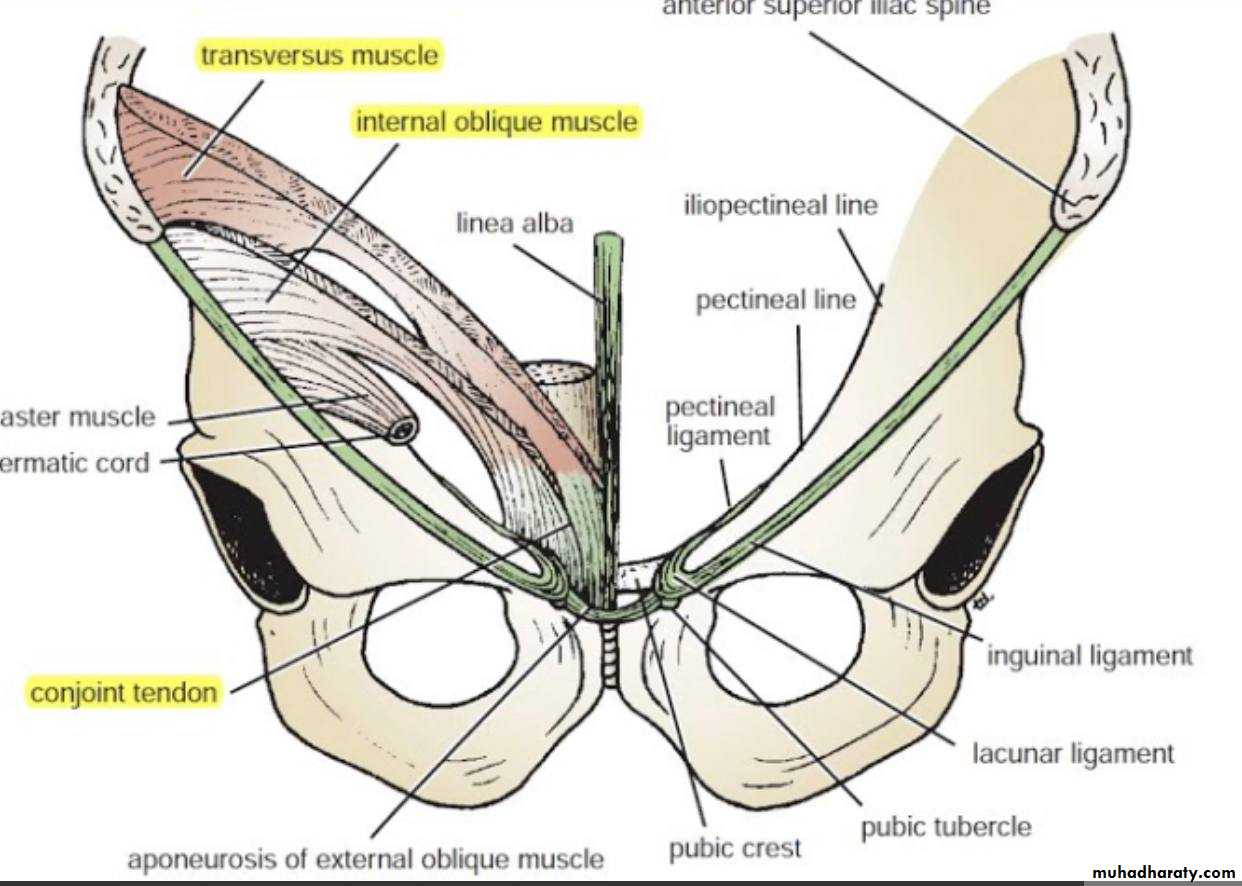
-* A triangular-shaped defect in the external oblique aponeurosis lies Immediately above and medial to the pubic tubercle. Called …superficial inguinal ring .
The spermatic cord (or round ligament of the uterus) passes through this opening
* The lower border of the aponeurosis is folded backward on itself between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic tubercle, forming the inguinal ligament
*The lacunar ligament extends backward and upward from the medial end of the inguinal ligament to the pectineal line on the superior ramus of the pubis , its sharp free edge formed the medial margin of femoral ring .
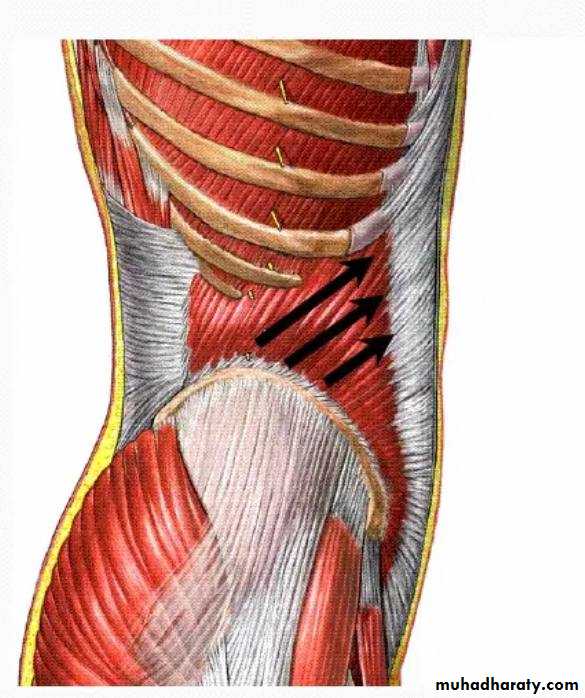
2) Internal oblique muscle
1 ) Origin :Lumbar fascia, iliac crest, lateral 2/3 of inguinal ligament
-Direction : up wards and forward
2) InsertionLower three ribs and costal cartilages , xiphoid process, linea alba, symphysis pubis
• 3 ) NN supply :
• -lower 6 thoracic nn (T7 –T12) ,
• -Ilio hypogastric and ilio inguinal nn ( L1 )
• 4 ) Action :
-Supports abdominal contents
-compresses abdominal contents;
-Assists in flexing and Rotation of trunk
-Assists in forced expiration, micturition, defecation
, parturition, and vomiting
*Near their Insertion, the lowest tendinous fibers are joined by similar fibers from the transversus abdominis to form the conjoint tendon( attach medially to linea alba and has free lateral border )
* As the spermatic cord passes under the lower border
of the internal oblique, it carries some muscle fibers
that are derived from the internal oblique. These fibers
that surround the spermatic cord constitute the cremaster muscle
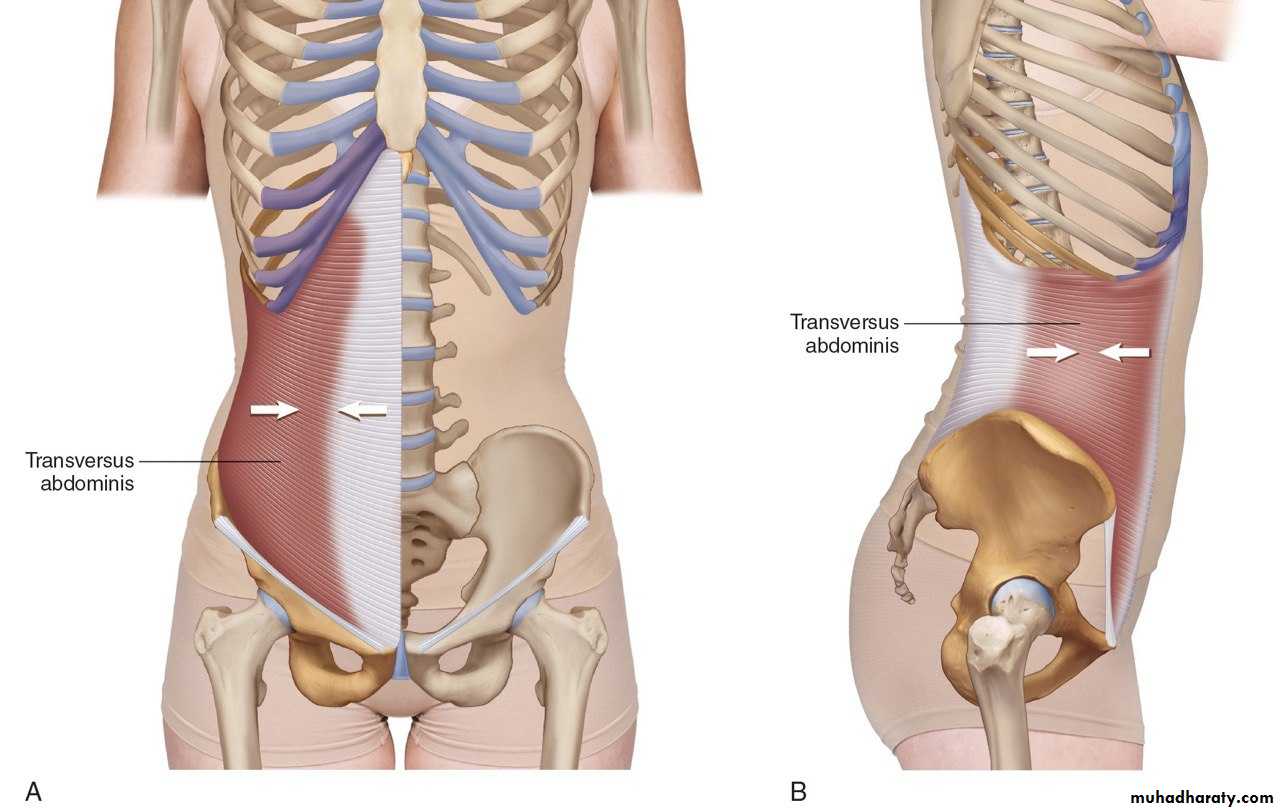
• 3)Transversus abdominis muscle
• Origin:-Lower six costal cartilages, lumbar fascia, iliac crest, lateral third of inguinal ligament
Direction of fibers horizontally and forwards
• Insertion
-Xiphoid process, linea alba, symphysis pubis
N . Supply–
lower 6 thoracic nn &
iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nnL1
Action :
Compresses abdominal contents
• 4) Rectus abdominis muscle
• Longitudinal paramedial m• Origin:- lower end 2 heads
• Med- head symphysis pubis
Lat. head pubic crest
• Insertion:- upper end Front of 5,6,7th costal cartilage & Xiphoid Process
• N supply lower six thoracic n (T7-T12)
• Action :
-Compresses abdominal contents
-Flex vertebral column
-Accessory muscle of expiration
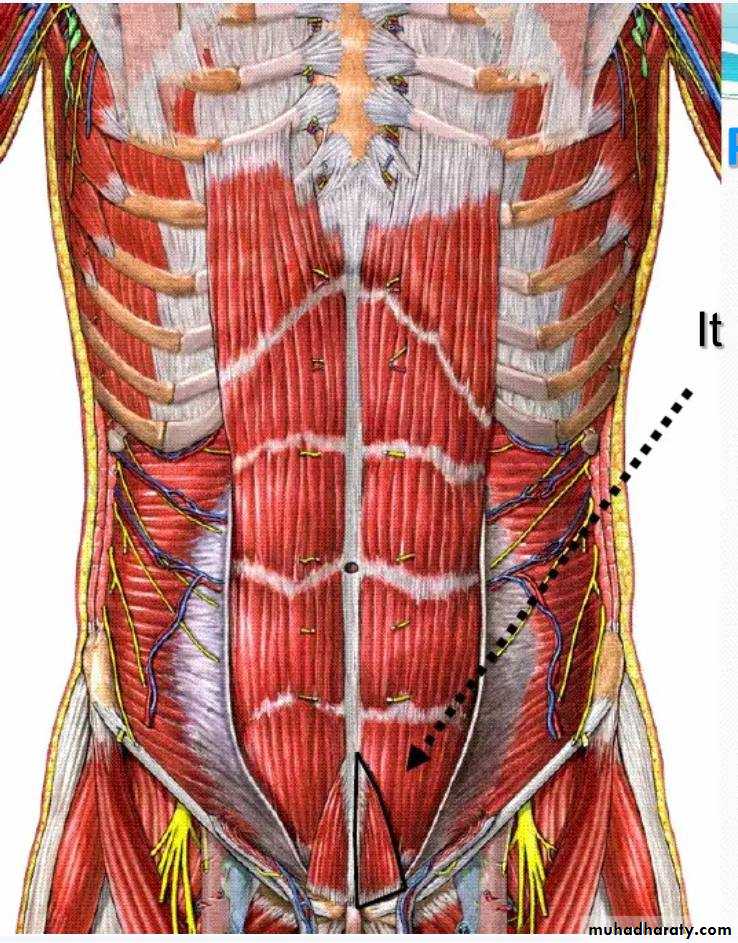
• *tendenous intersection s 3,4 transvers bands
• (xiphoid P, umbilicus, midway bet. Xiphoid &umb, below umb.)
• *Linea semilunaris –shallow curved groove along lateral. border of muscle
• The rectus abdominis is enclosed between the aponeuroses of the external oblique, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis, which form the rectus sheath
• Pyramidalis m
• Small triangular m at the lower end of rectus muscle ,some time absent• Origin –Anterior surface of pubis
• Insertion-- lower part of L alba
• N . Supply –12th thoracic nerve
• Action -- Tenses the linea alba
• 5)The transversalis fascia
• *Is a component of an extensive thin layer of fascia that lies between the muscle layer of the abdominal wall and the parietal Peritoneum (It lines the inner surface of transversus abdominis muscle )*At the midpoint between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis, the spermatic cord pierces the transversalis fascia to form the deep
Inguinal ring
•
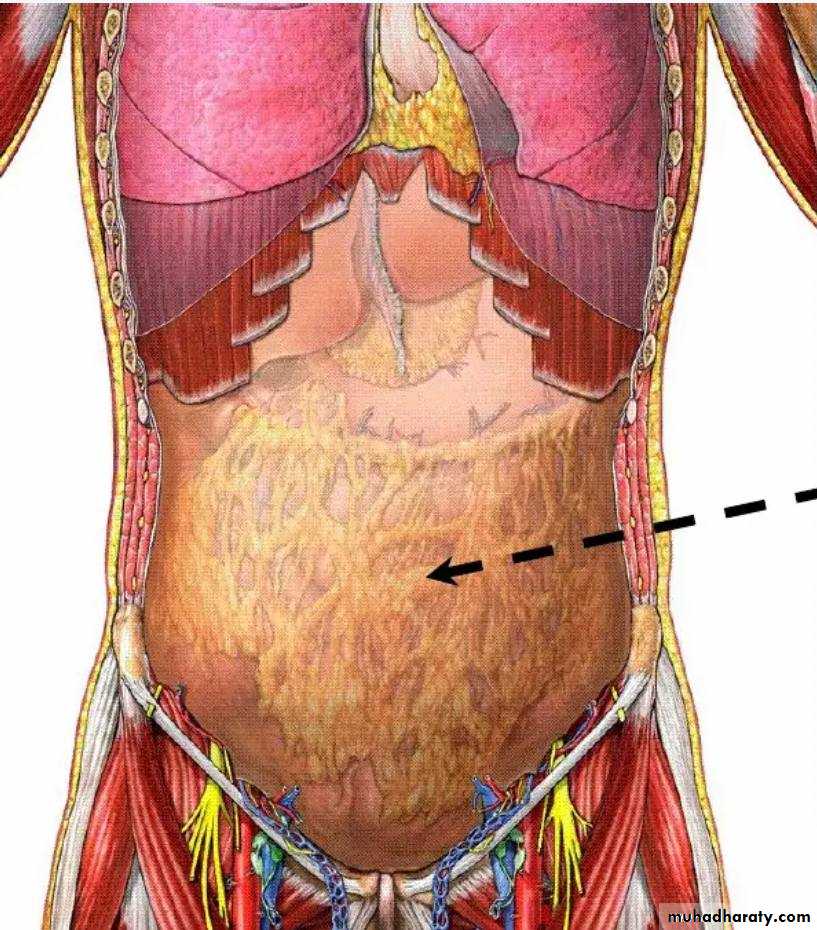
6) Extra peritoneal Fascia
The extra peritoneal fascia is a thin layer of connectivetissue that contains a variable amount of fat. It lies
between the transversalis fascia and the parietal peritoneum
7) Parietal Peritoneum
It lines the internal surface of the abdominal wall .It is a thin serous membrane and is continuous below with the parietal peritoneum lining the pelvis.Arterial supply of the anterior abdominal wall
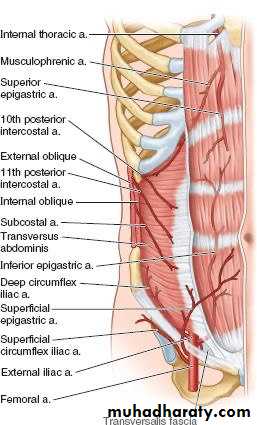
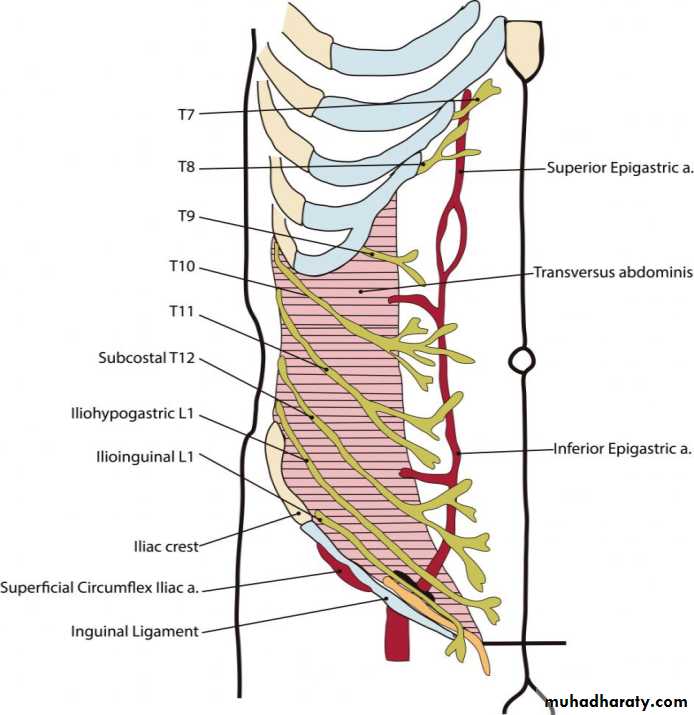
1- from above central part supplied bySuperior epigasteric artery and musculophrenic artery , branches from internal thoracic artery a ( internal mammary a )
• 2- from above and laterally
• --10th, 11th posterior intercostal a & subcostal arteries all are branches from thoracic aorta
• 3- from below
• -- central part by inferior epigastric artery branch from external iliac artery
• -- laterally deep circumflex iliac artery br. from ext. iliac a
• -- inguinal region supplied by superficial circumflex iliac a & superficial epigastric a , branches from femoral artery
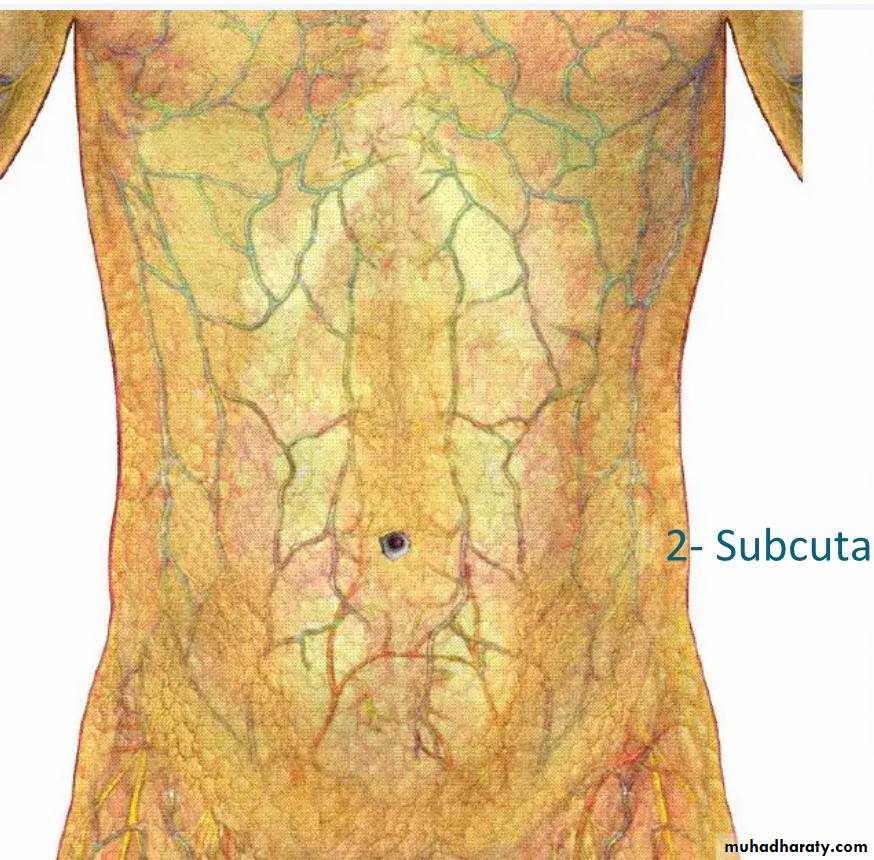
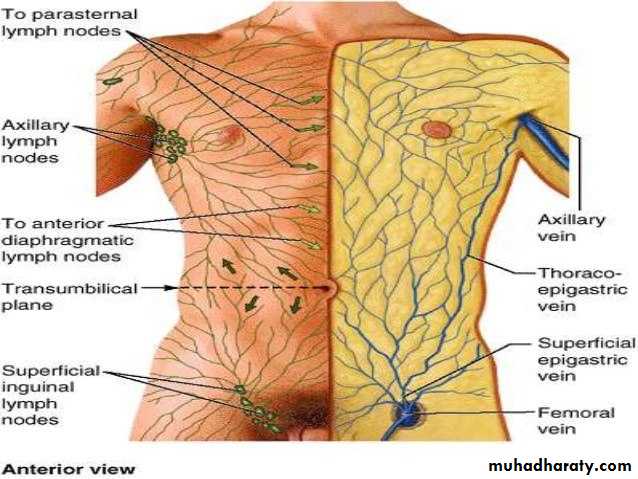
• Venous drainage of the anterior abdominal wall
• Superfacial vein :• Form a net work that radiate out from the umbilicus
• Above the umbilicus
• Drain to the axillary vein via lateral thoracic vein
• Below the umbilicus
• Drain to femoral vein by superficial epigastric vein and great saphenous vein
Deep veins
-Superior epigastrtic vv ..→ internal thoracic vv
-Inferior epigatric and deep circumflex iliac vein → external iliac vv
-Posterior intercostal vv → azygos vv
• Lymphatic drainage of ant. Abd. Wall
• Superficial lymphatic vessels• Above the umbilicus ……axillary lymph nodes
• Below the umbilicus …superficial inguinal lymph nodes
• Deep lymphatic vessels
• Follow the arteries and drain to
• 1-thoracic LN
• 2-external iliac LN
• 3-Posterior mediastinal LN
• 4-para oartic LN
•
• Nerve supply of ant abd. wall
• Derived from the ventral rami of T7 to L1• 1-lower intercostal n(T7- T11)
• 2-subcostal n (T12)
• 3-iliohypogasteric (L1)
• 4-ilioinguinal n(L1)
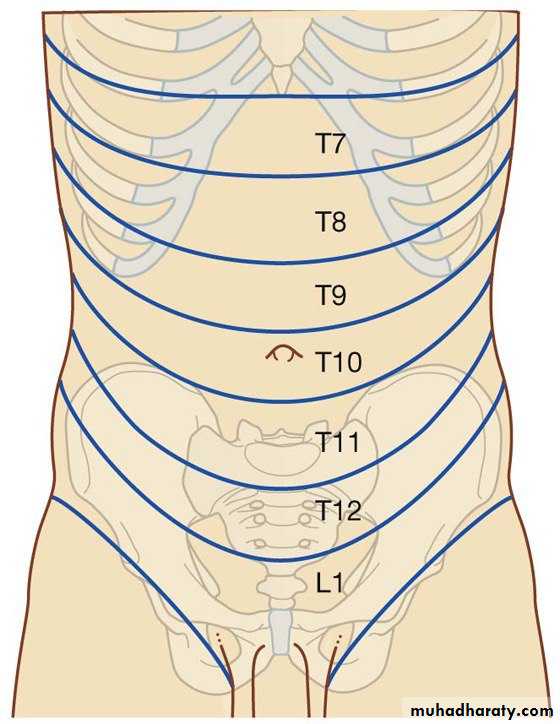
Useful landmarks of The dermatomes of the anterolateral abdominal wall
are :
Superior to umbilicus ( T7,8,T9)
Around umbilicus T10
Inferior to umbilicus T11, T12, L1
• Dermatome T7: xiphoid process
• Dermatome Tl0: umbilicus
• Dermatome L1: pubis
•