Blood typing & transfusionPhysiology Lecture Three
ByDr. Suroor Mohammed
Objectives
1. Describe the basis of blood typing2. Know the ABO and Rh systems for blood typing
and their clinical significance.
3. What is the Hemolytic Disease of Newborn HDN?
Basis of Blood grouping or Typing (Multiplicity of Antigens in the blood cells)
At least 30 commonly occurring antigens havebeen found on the cell membrane of RBCs.
These can cause Ag-Ab (antigen-antibody) reaction if
mixed with plasma that contain Ab against these
Ag.
According to presence or absence of these antigens blood is classified into several groups ,Two groups of
Ag can cause transfusion reactions more than others:
ABO and Rh systems of Ag.
Definition:
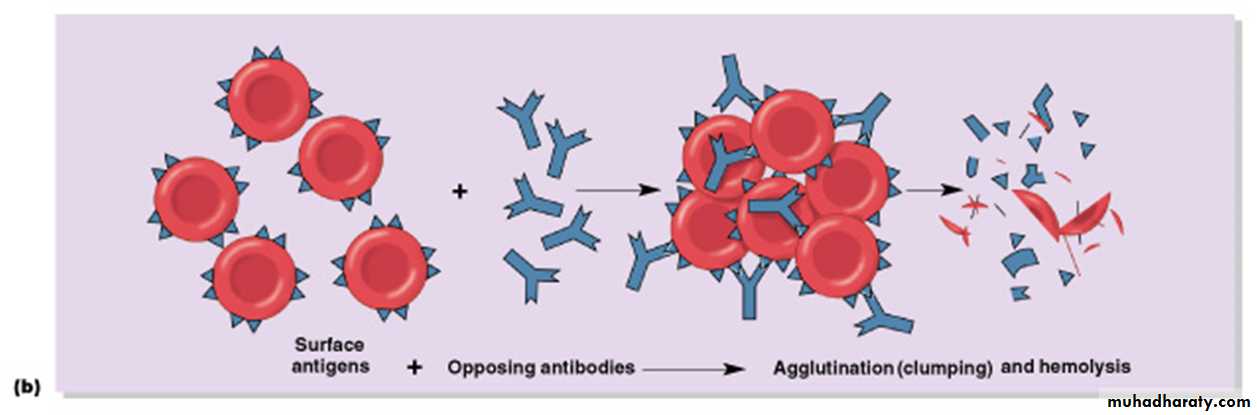
Agglutinogens - glycoproteins on the surface of blood cells causes "agglutination" (clumping)
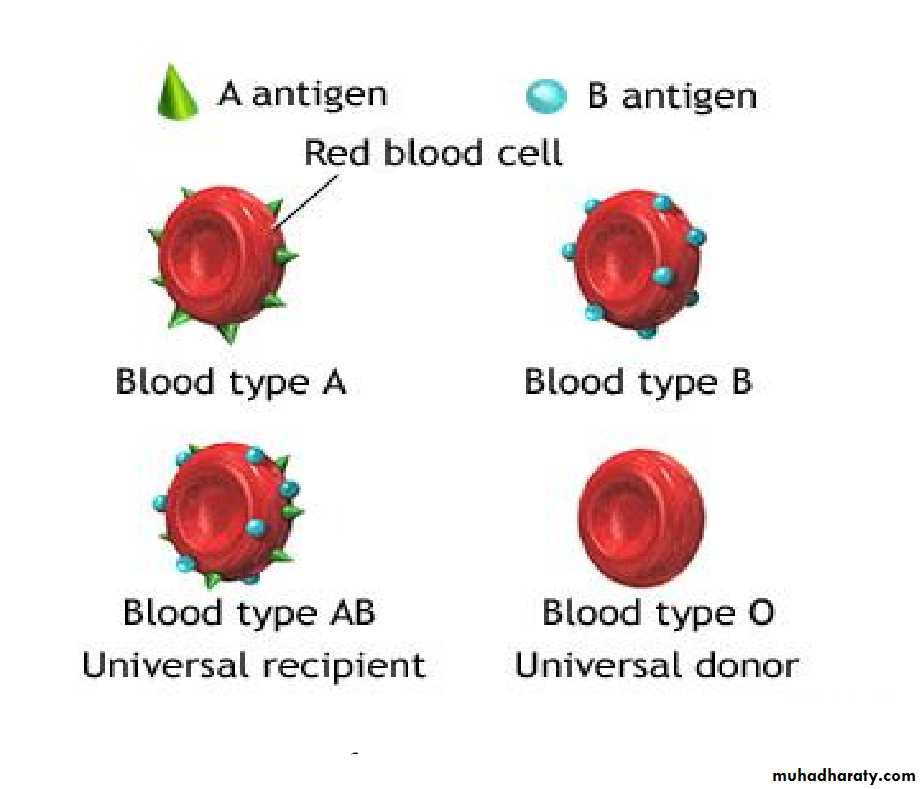
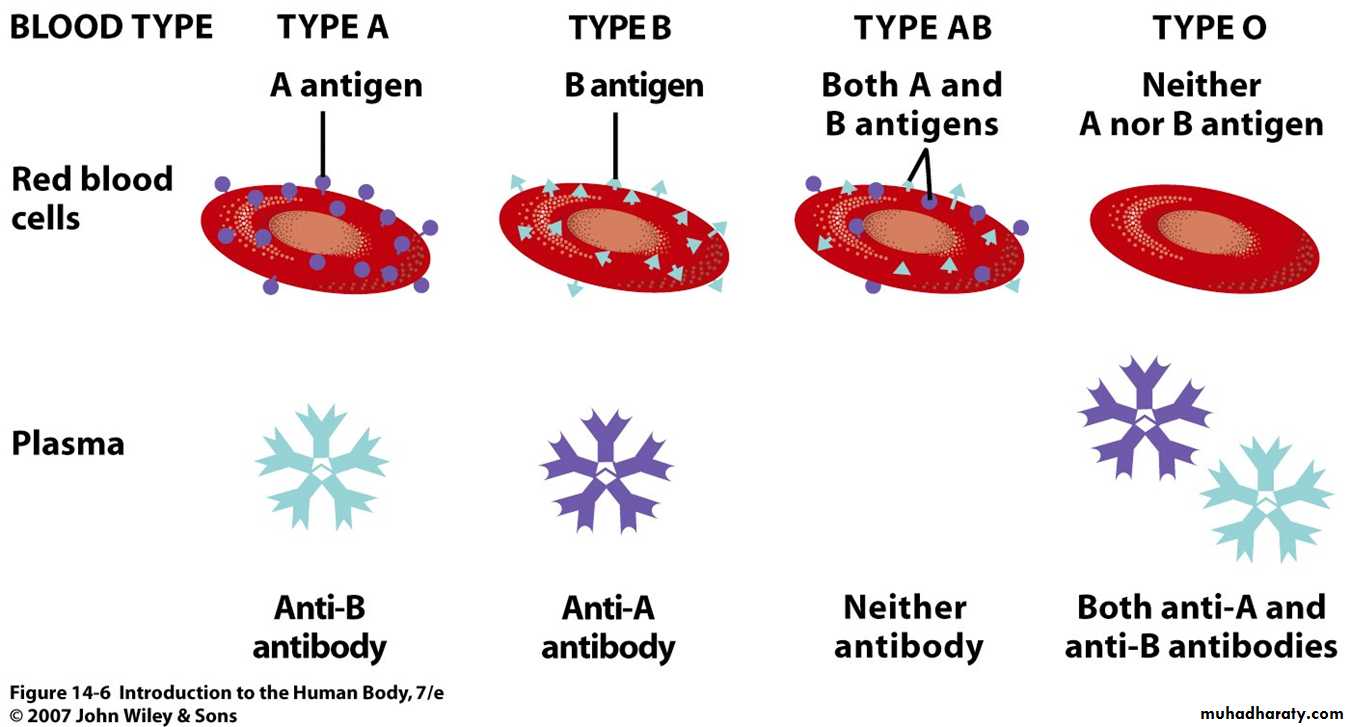
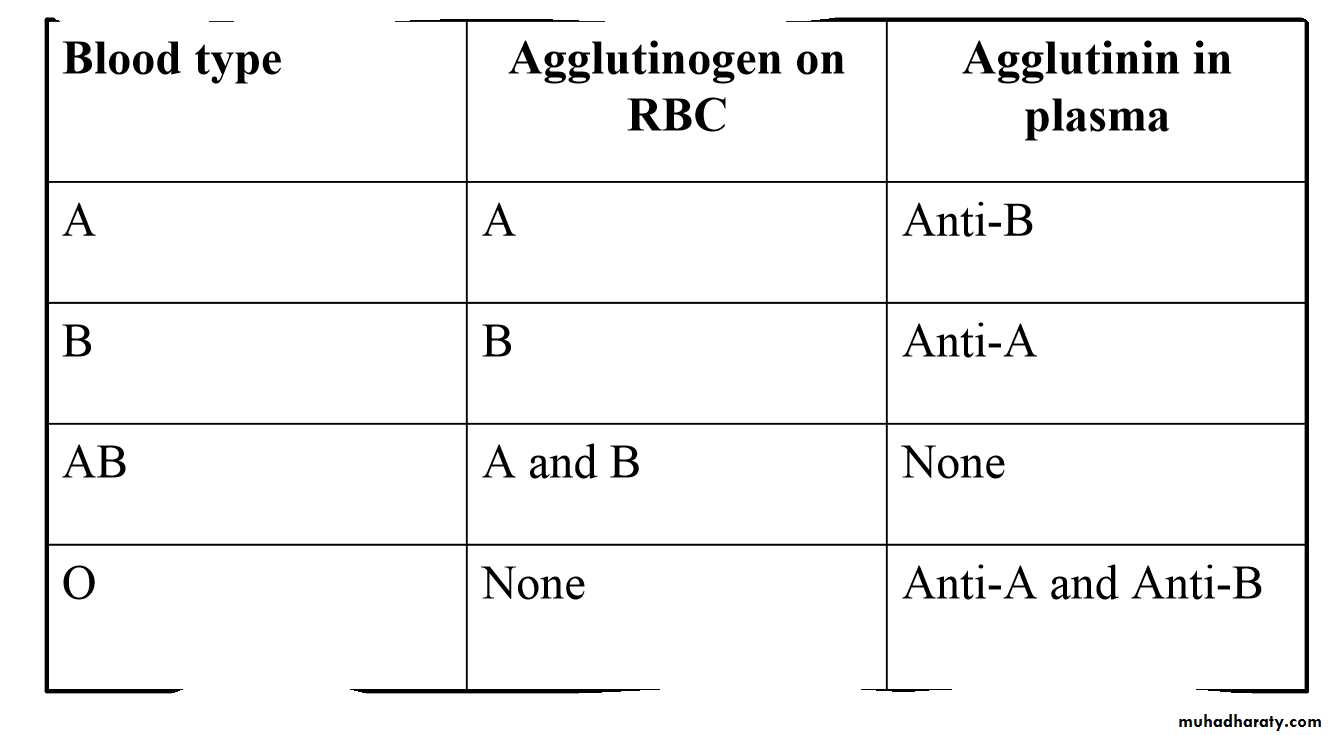
ABO Blood Groups - determined by presence or absence of Type A and Type B agglutinogen proteins on the surface of RBCs cell membrane.
agglutinins - antibodies against either A or B agglutinogen , when bind agglutinins to RBC antigens, resulting in agglutination (clumping) or hemolysis (rupture) of RBCs
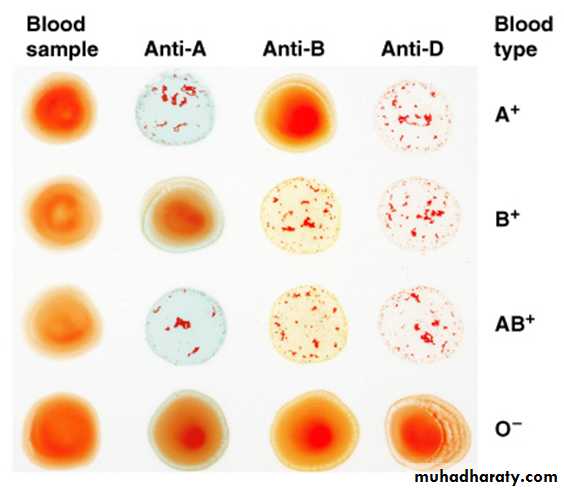
A and B Antigens Agglutinogens
ABO System for Blood TypingABO blood types
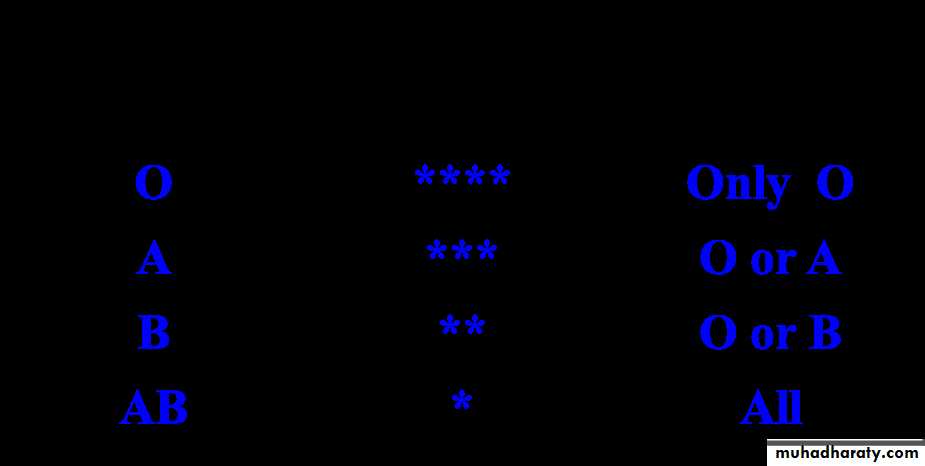
Relative frequency of different blood types:• O 47%
• A 41%
• B 9%
• AB 3%
Agglutinins & agglutinogen
Blood transfusion:
• A person with blood type A can receive blood from a donor with blood type A.The anti-B antibodies in the recipient do not combine with the type A antigens on the red blood cells of the donor.
2. A person with blood type B cannot receive blood from a donor with blood type A.
The anti-B antibodies in the recipient will combine with the type B antigens on the red blood cells of the donor
If the wrong blood type is used, the person’s own immune system immediately attacks the donor’s blood and causes clumps and RBC destruction(hemolysis) that can lead to total kidney failure and death.
Transfusion reaction
Plasma antibody meets its specific surface antigenBlood will agglutinate and hemolysis , If donor and recipient blood types not compatible.
Type AB has no AB antibodies so can receive any ABO type blood called Universal recipients.
Type O have neither antigen so can donate to any other ABO type called Universal donors.
Transfusion Reactions resulting from mismatched
blood types lead to :
Agglutination and delayed hemolysis of donor’s RBC (or immediate intravascular hemolysis)→ Jaundice
Renal failure: Renal tubular blockage by hemoglobin
The term "Rh-positive" means that the individual has agglutinogen D. The "Rh-negative" individual has no D antigen and forms the anti-D agglutinin when injected with D-positive cells.
85% of Caucasians are D-positive and 15% are D-negative; over 99% of Asians are D-positive.
Differences between ABO and Rh Ab?
Anti-D (Rh)antibodies do not develop naturally without exposure of a D-negative individual to D-positive red cells by blood transfusion or entrance of fetal blood into the maternal circulation , Rh negative women pregnant with Rh +ve baby.Rh System for Blood Typing
You will receive 2 slides , wood stick and filter paper.• Lable the filter paper in one side with Anti A and the other side anti B
•The second slide is for Anti D .
•Add on drop of blood from your finger to each side of the slide
•Add agglutinin to your sample as labeled
•Mix and wait until 10 min for agglutination to occur
Practical point
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn(HDN)
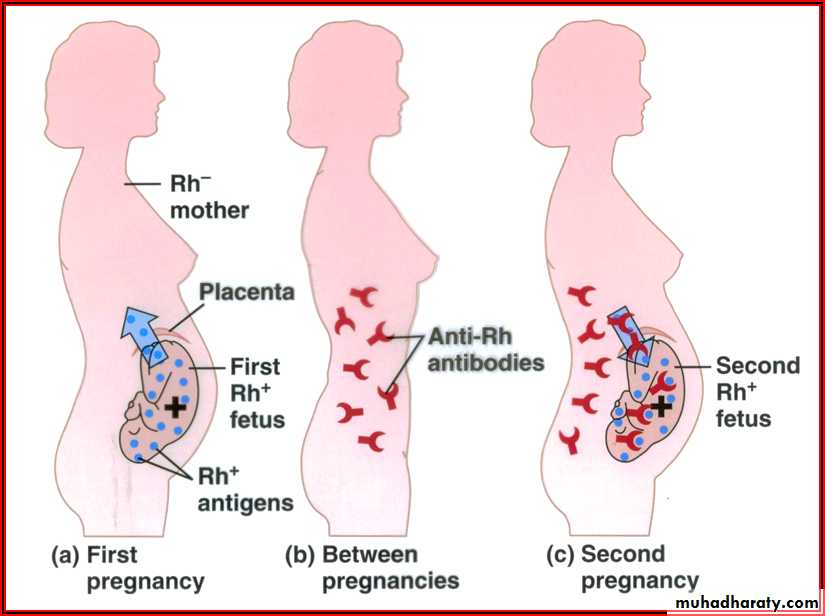
Is most common problem with "Rh incompatibility" arises when an Rh-negative mother carries an Rh-positive fetus.Small amounts of fetal blood leak into the maternal circulation at the time of delivery, and some mothers develop significant titers of anti-Rh agglutinins during the postpartum period. During the next pregnancy, the mother's agglutinins(Abs) cross the placenta to the fetus , cause hemolysis and various forms of hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis).
HDN
If the mother is Rh- and the baby is Rh+, the mother’s immune system begins to produce anti-Rh antibodies.
The mother’s antibodies cross the placenta during the subsequent pregnancy into the fetal blood.
If the second fetus is Rh+, the antigen-antibody reaction causes hemolysis of fetal RBCs and it results in HDN
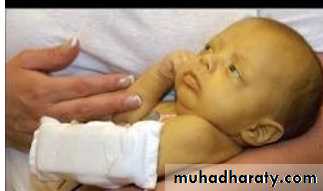
Jaundiced baby due Rh Incompatibility
If hemolysis in the fetus is severe, may die in utero or may develop anemia, severe jaundice, and edema (hydrops fetalis). Kernicterus, a neurologic syndrome in which unconjugated bilirubin is deposited in the basal ganglia.
Prevention by :
by administering a single dose of anti-Rh antibodies in the form of Rh immune globulin during the postpartum period, (anti-D) IG.has reduced the overall incidence of hemolytic disease by more than 90%.
Indicated Anti-D in :
If a woman has Rh- and gives birth to a child, or if she has a miscarriage or abortion, she is given an injection of anti-Rh antibodies called anti-Rh gamma globulin or RhoGAM to prevent HDN.Action of Anti-D:
The antibodies bind to the fetal Rh antigens and inactivates them if they crossed the placenta during birth, and the mother’s immune system does not respond by producing antibodies