Biochemistry
2nd stageDr.Lamees Majid Al-Janabi
FATTY ACIDS
SYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACIDSIn mammal fatty acid synthesis occur primarily in the liver & lactating mammary glands & to lesser extent in adipose tissue.
The primary metabolic substrate for synthesis of fatty acid is Acetyl CoA which is generated from the oxidation of pyruvate, and by the catabolism of fatty acids, ketone bodies, and certain amino acids.
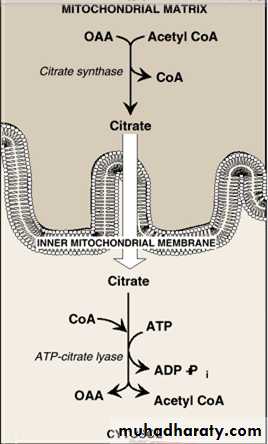
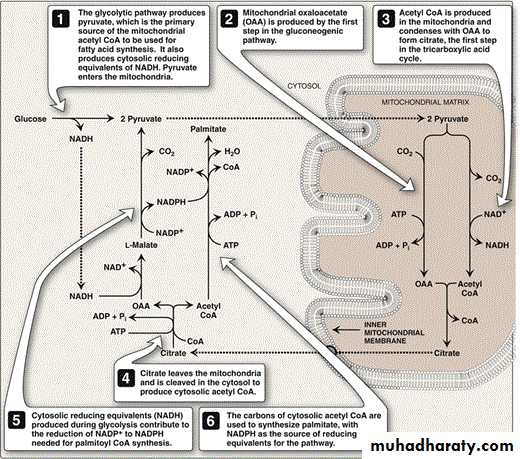
Acetyl Co A from catabolic reaction is generated mainly in the mitochondria. Whereas the fatty acid synthesis occur in the cytoplasm therefore we need a special transport mechanism for transportation of acetyl Co A from the mitochondria to the cytoplasm because the CoA portion of acetyl Co A cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane.
The acetyl Co A will react with oxaloacetate (OA) to form the citrate by the enzyme citrate synthetase. The citrate then will pass the mitochondrial membrane to the cytoplasm where it react with CoA to form acetyl CoA & this step need 1 ATP.
Production of cytosolic acetyl CoA
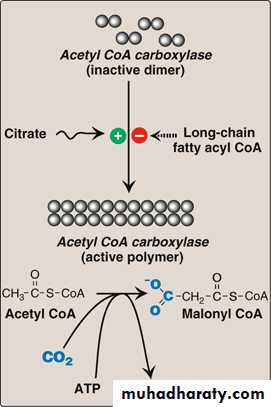
Formation of malonyl CoAIt is the rate limiting step catalyzed by the allosteric enzyme acetyl CoA Carboxylase which is allosterically stimulated by citrate and inhibited by long chain fatty acyl CoA.
Biosynthesis of malonyl-CoA
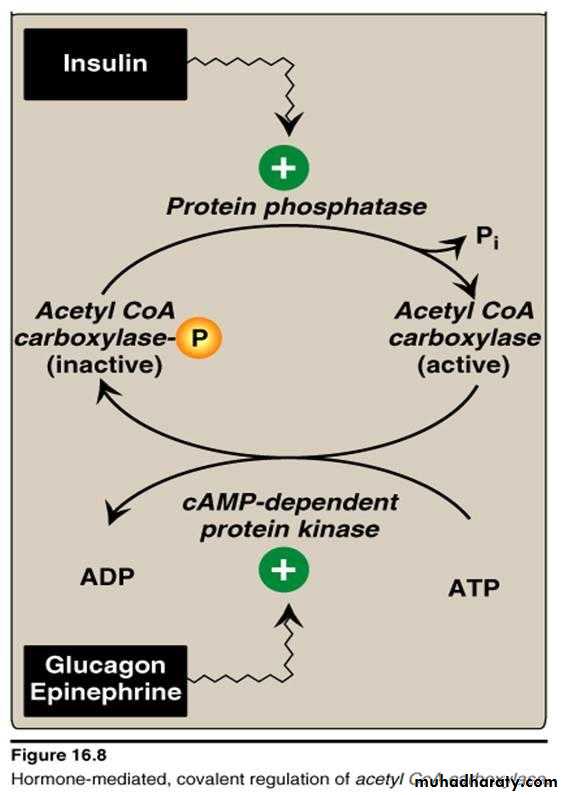
This enzyme also activated by dephosphorylation i.e. adrenalin will reduce the formation of fatty acid , while the insulin will increase the formation of fatty acid .
Hormone-mediated covalent regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
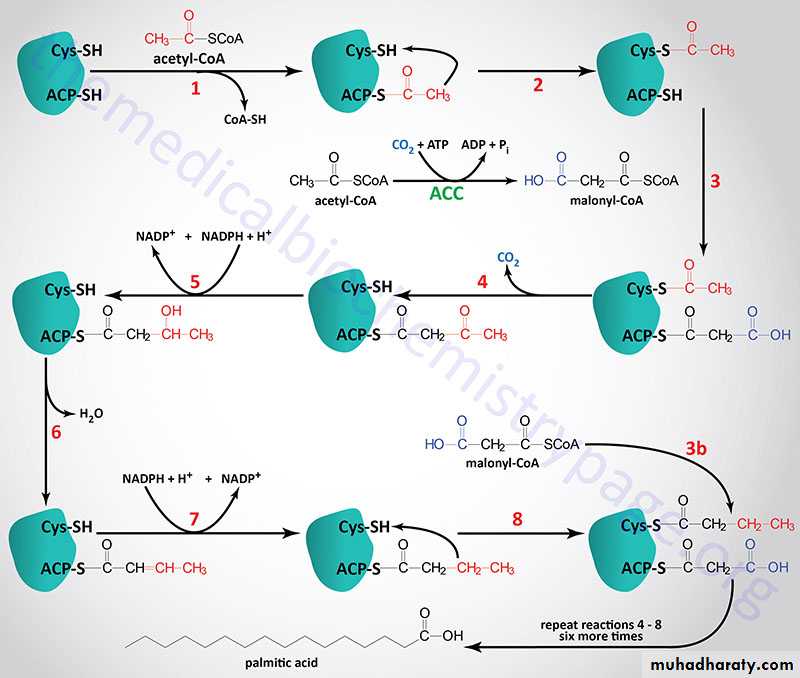
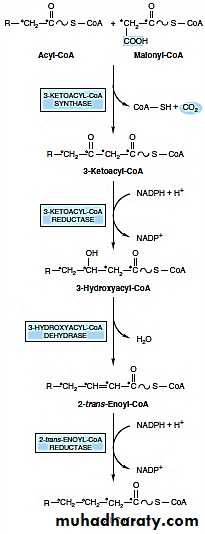
Fatty acid synthase: a multifunctional enzyme in eukaryotesThe remaining series of reactions of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes is catalyzed by the multifunctional, dimeric enzyme, fatty acid synthase. Each fatty acid synthase monomer is a multicatalytic polypeptide with seven different enzymic activities plus a domain that covalently binds a molecule of 4'-phosphopantetheine.
In prokaryotes, fatty acid synthase is a multienzyme complex, and the 4'-phosphopantetheine domain is a separate protein, referred to as the acyl carrier protein (ACP).
Synthesis of palmitate
Major sources of the NADPH required for fatty acid synthesisThe hexose monophosphate pathway.
The cytosolic conversion of malate to pyruvate by cytosolic malic enzyme (NADP+-dependent malate dehydrogenase).
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, producing alpha-ketoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate).
Interrelationship between glucose metabolism and palmitate synthesis
Elongation of the chain
the Chain elongation take place in the endoplasmic reticulum by addition of 2 carbon units as acetyl-CoA to produce stearoyl-SCoA and the intermediate are in the form of CoA derivative. The brain has additional elongation capabilities, allowing it to produce the very-long-chain fatty acids (up to 24 carbons) that are required for synthesis of brain lipids(sphingolipid).Elongation of fatty acid chain
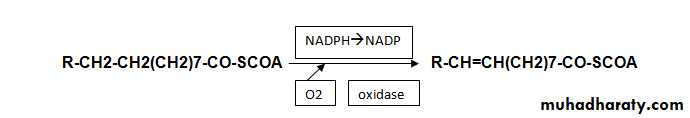
DESATURATION OF THE CHAINAnimals can synthesis fatty acid contain only one unsaturated bond between C9 &C10 .Desaturation of the chain : the cell of the liver and the adipose tissue contain the necessary enzyme for conversion of palmitoyl –SCoA and stearoyl –SCoA to the respected unsaturated palmitoleyl –SCoA and oleyl-SCoA (these enzymes called mix function oxidases).
This reaction occur in the E.R and cytoplasm ,in mammals this enzyme system can only desaturate the fatty acid with double bond between C9-C10 ,therefore, mammals are unable to synthesize polyunsaturated (essential F.A).
-Regulation of lipogenesis:-
The nutritional state of the organism is the main factor regulating the rate of lipogenesis. The rate is high in the well-fed animal whose diet contains a high proportion of carbohydrate. It is depressed under conditions of restricted caloric intake, on a fat diet, or when there is a deficiency of insulin, as in diabetes mellitus.Acetyl co A carboxylase:- is an allosteric enzyme and is the most important enzyme in the regulation of lipogenesis and is activated by citrate.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase:- Acyl co A causes an inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Insulin:- stimulates lipogenesis by increasing acetyl-co A carboxylase activity. It increases the transport of glucose into the cell(e.g. adipose tissue), increasing the availability of both pyruvate for fatty acid synthesis and glycerol 3-phosphate for esterification of the newly formed fatty acid.