1
Biochemistry
stage
nd
2
Dr.Lamees Majid Al-Janabi
TRIGLYCERIDES
SYNTHESIS OF TRIGLYCERIDES
fatty acids stored as components of triacylglycerol. Monoacylglycerol,
diacylglycerol, &triacylclycerol formerly called Glycerides. e.g.
Triglyceride consist of one, two, or three molecules of fatty acid.
-Synthesis:- glycerol phosphate is the initial acceptor of fatty acid during
the synthesis of triacylglycerol.
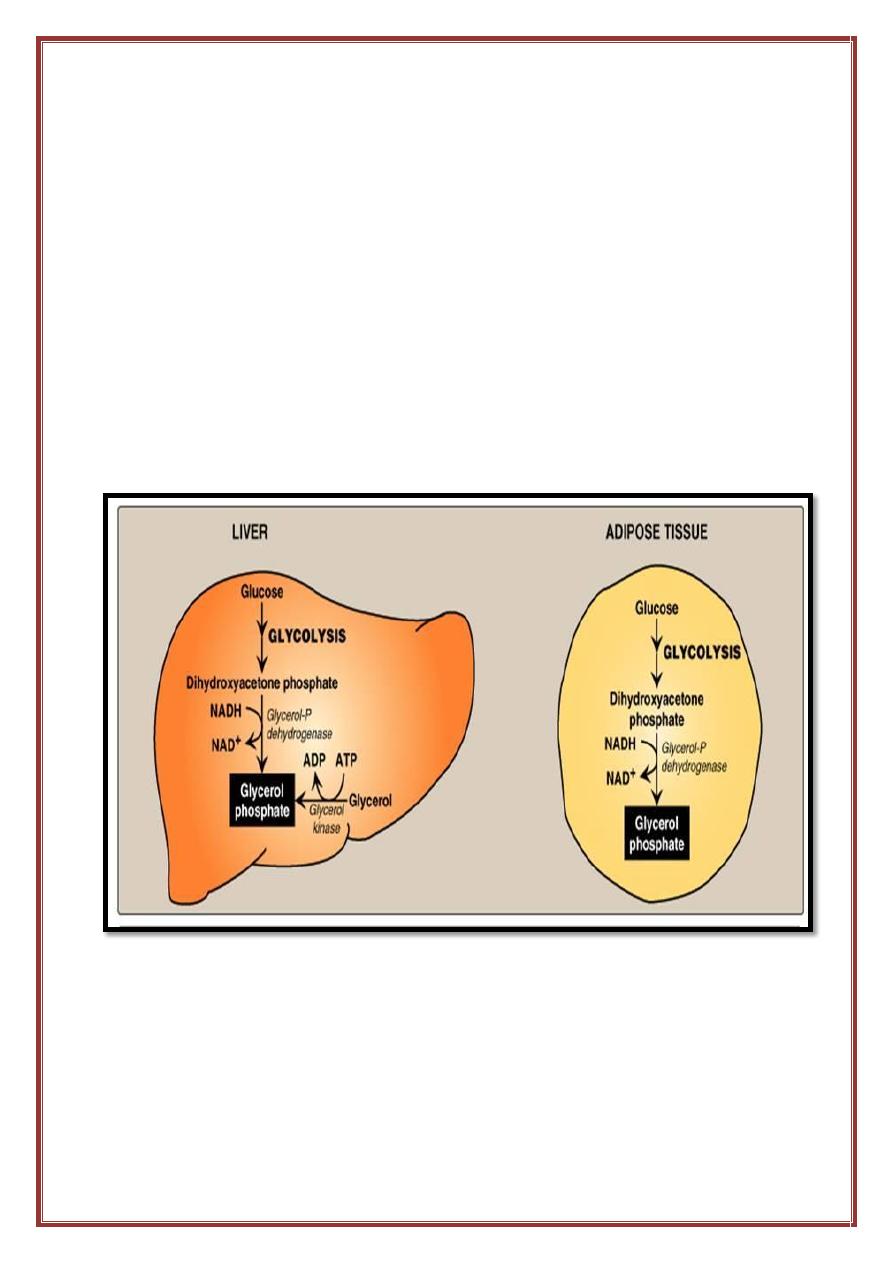
Pathways for production of glycerol phosphate in liver and adipose
tissue
Note:- a- Adipocyte can take up glucose only in the presence of the hormone
insulin. Thus, when plasma glucose—and, therefore, plasma insulin—levels are
low, adipocytes have only a limited ability to synthesize glycerol phosphate,
and cannot produce TAG.]
2
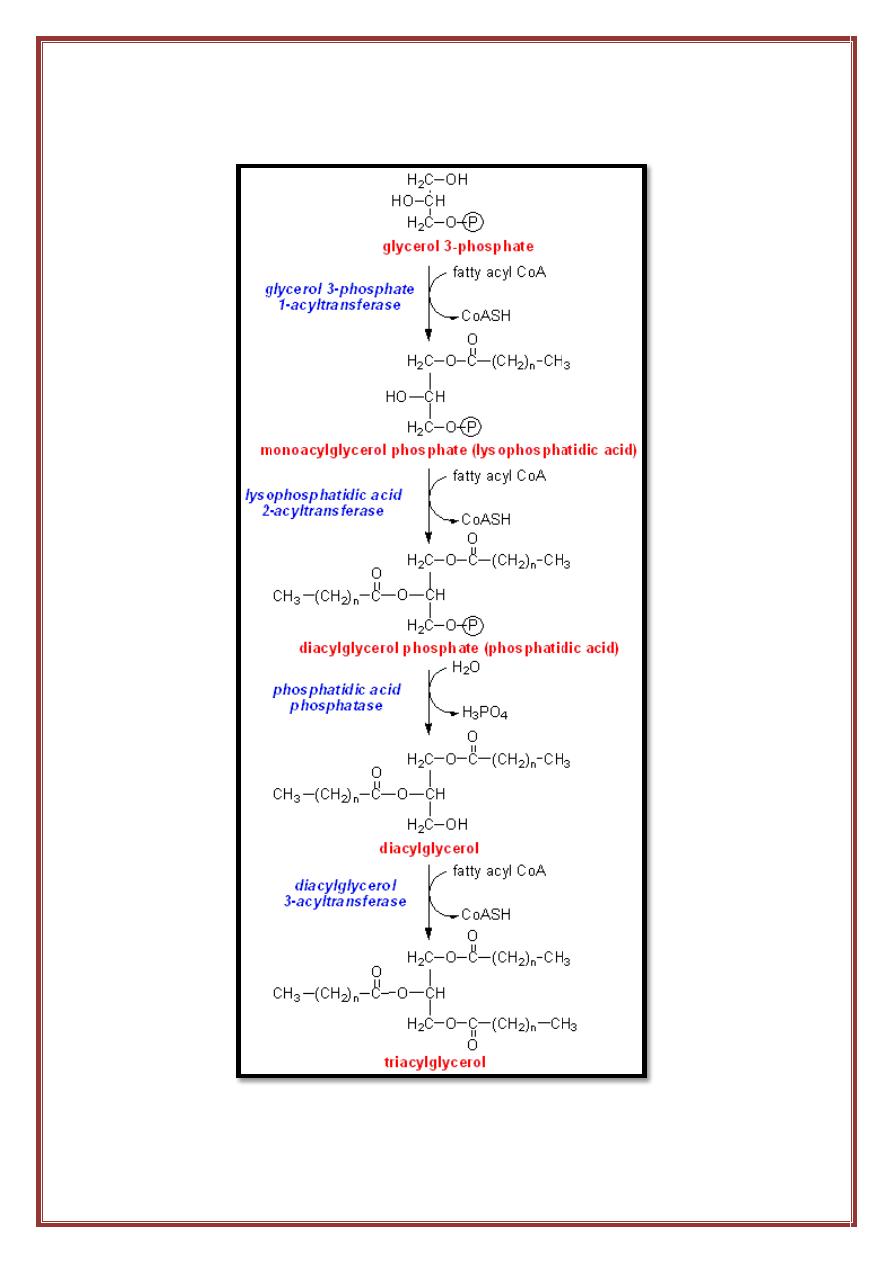
b- A fatty acid must be converted to its activated form(attach to co enzyme A)
before it can participate in triacylglycerol synthesis.
Synthesis of triacylglycerol
3
Typically the fatty acid on carbon no.1 is saturated and on carbon no.2 is
typically unsaturated and the fatty acid on carbon no.3 could be the either
.So the type of the fatty acid on carbon no.3 usually determine the
melting point of TG.
Functions of TG:
The function of TG in the body is energy store. Saturated and
unsaturated fatty acids are store as TG. Mainly the synthesis of TG occur
in the liver and excreted as VLDL or in the adipose tissue and store
there. Fatty acids in the adipose tissue are derived from the VLDL and the
chylomicron by the action of lipoprotein lipase.
- Glycerol 3 phosphate is the initial acceptor of fatty acid during TG
synthesis. There are two sources for glycerol 3-P in the liver :
1. From Dihydroxy acetone phosphate one of the intermediate of
glycolysis which reduces by the NADH in the present of the
enzyme glycerol P- dehydrogenase.
2. In the liver from the glycerol by the action of the enzyme glycerol
kinase.
In adipose tissue dihydroxy acetone phosphate is a source of glycerol 3
phosphate. The intermediate that give us fatty acid is the fatty acyl CoA.
4
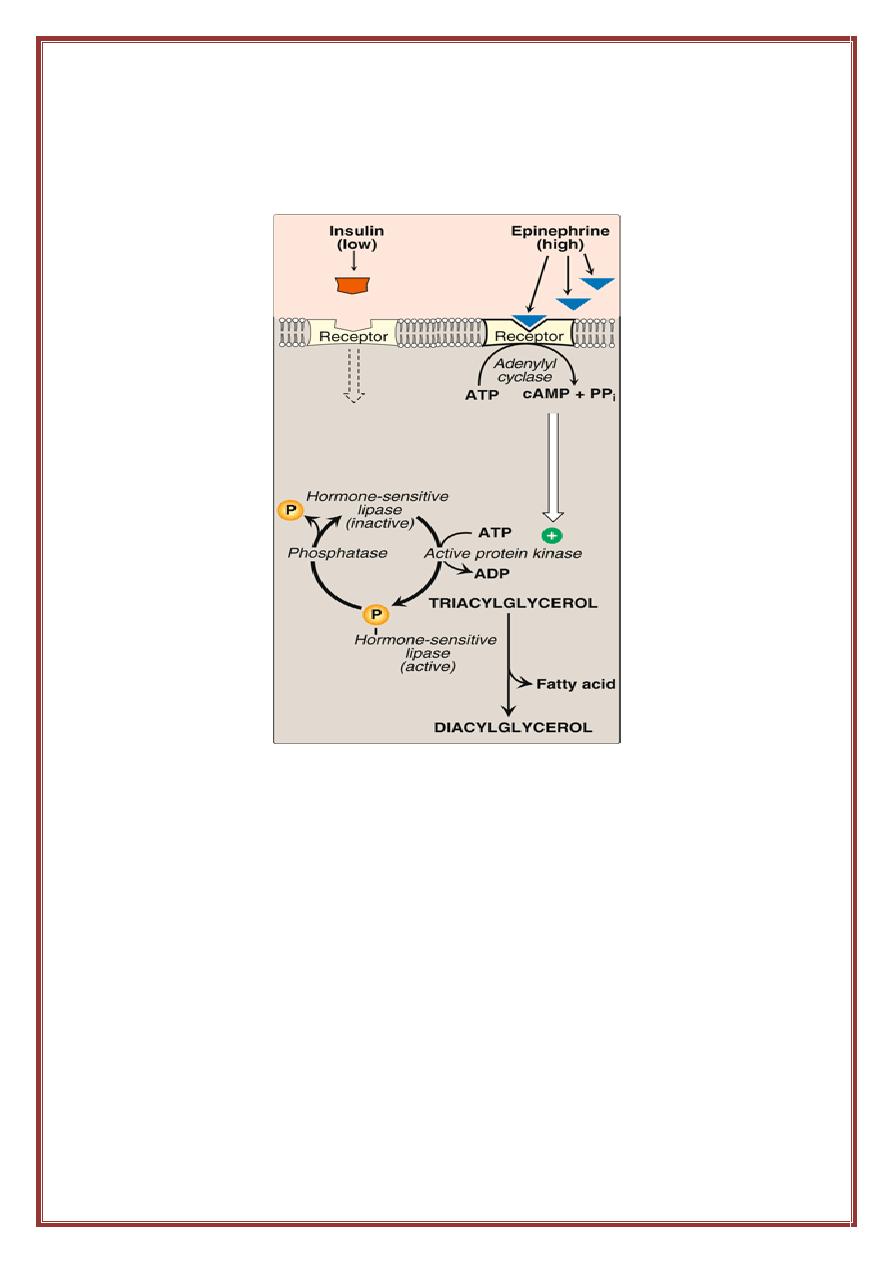
Hormonal regulation of triacylglycerol degradation in the
adipocyte
•
Fate of glycerol:
The glycerol released during TAG degradation
cannot be metabolized by adipocytes because they apparently lack
glycerol kinase. Rather, glycerol is transported through the blood to
the liver, where it can be phosphorylated. The resulting glycerol
phosphate can be used to form TAG in the liver, or can be
converted to DHAP by reversal of the glycerol phosphate
dehydrogenase reaction. DHAP can participate in glycolysis or
gluconeogenesis.
•
Fate of fatty acids:
The free (unesterified) fatty acids move
through the cell membrane of the adipocyte, and immediately bind
to albumin in the plasma. They are transported to the tissues, where
the fatty acids enter cells, get activated to their CoA derivatives,
and are oxidized for energy.
