Dept of Family & Community Medicine
• 3rd stage• Lecture sampling
• By Dr. Muslim N.Saeed
• November 11th , 2021
Sampling
*Population : all the people living in an area, frequently of a country.-In statistics:
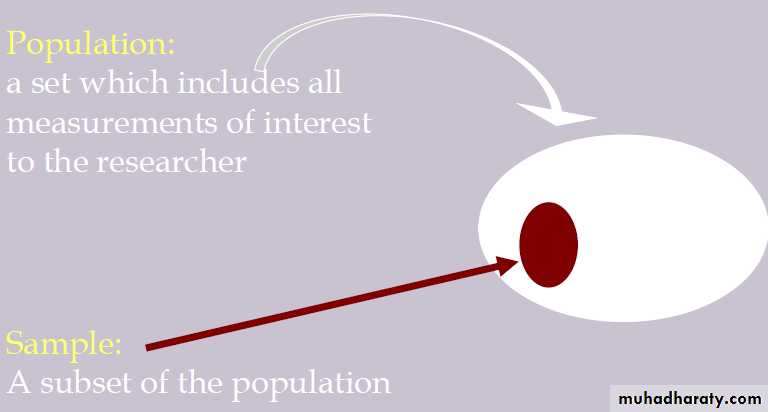
Population:
a set which includes all measurements of interest
to the researcher.
-Imagine that we are going to make studies on:
Percentage of Iraqi population that had access to internet.-The population we would to ask is bigger than 30 million
- Time
-Money
- at time of interview we miss some people
It is better to choose sample in appropriate way so that we can obtain later conclusion.
Sample
A sample is :
A finite part of a population whose properties are studied to gain information about them.
– A set of respondents selected from a larger
population for the purpose of a survey or
experiment.
Sampling:
The process, or technique of selecting asuitable sample, or a representative part of a
population for the purpose of determining
parameters or characteristics of the whole
population.
Target Population:
The population to be studied/ to which the investigator wants to generalize his resultsSampling Unit:
smallest unit from which sample can be selected
Sampling frame
List of all the sampling units from which sample is drawn
Sampling scheme
Method of selecting sampling units from sampling frame
Probability sampling
-Random sampling
-Stratified sampling
-Cluster sampling
-Systematic sampling
- other types of sample technique
Non- probability sampling
-Convenience sampling- Purposive sampling
- snowball
-Quota sample
1-Non-probability sample
-Probability of being chosen is unknown-Cheaper- but unable to generalize
-potential for bias
2-Probability sample
Random sampling
–Each subject has a known probability of being selected
•Allows application of statistical sampling theory to results to:
–Generalise
–Test hypotheses
Conclusion
Probability samples are the best
•they ensure–Representativeness
–Precision
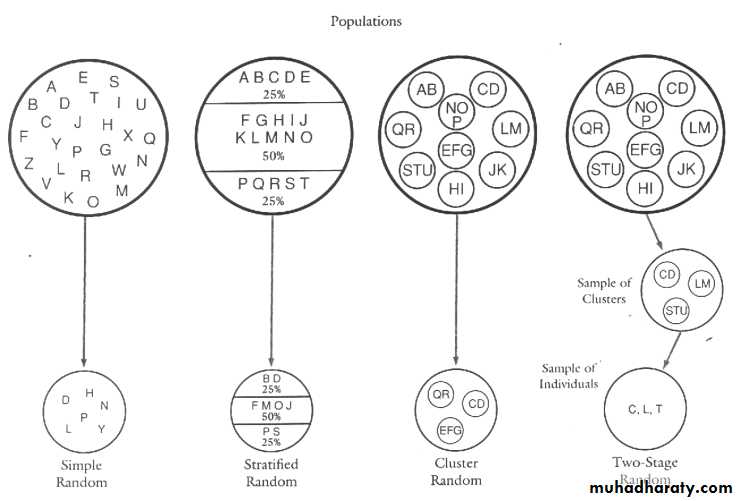
Simple random sample
It requires:1-Sample frame: a numerical list of all observations (or units) composing the population
2-Sample fraction: sample size to the total population
3-Lottery method
-Computer generated random sampling
-Random number table (random digit)
Simple random sampling
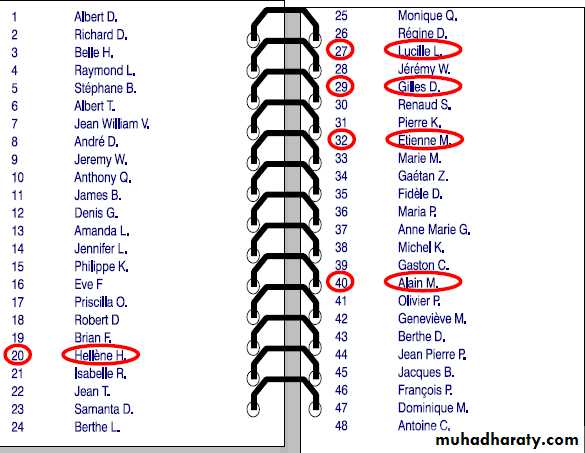
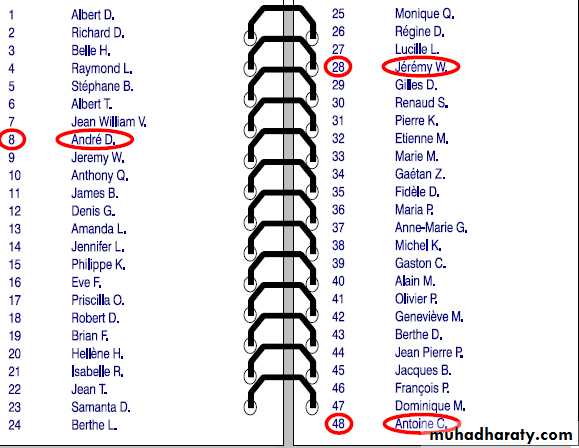
Systematic random sampling
– samples according to a ruleE.g., every fifth person is chosen
Problems: same as simple random. Rule must not lead to bias.
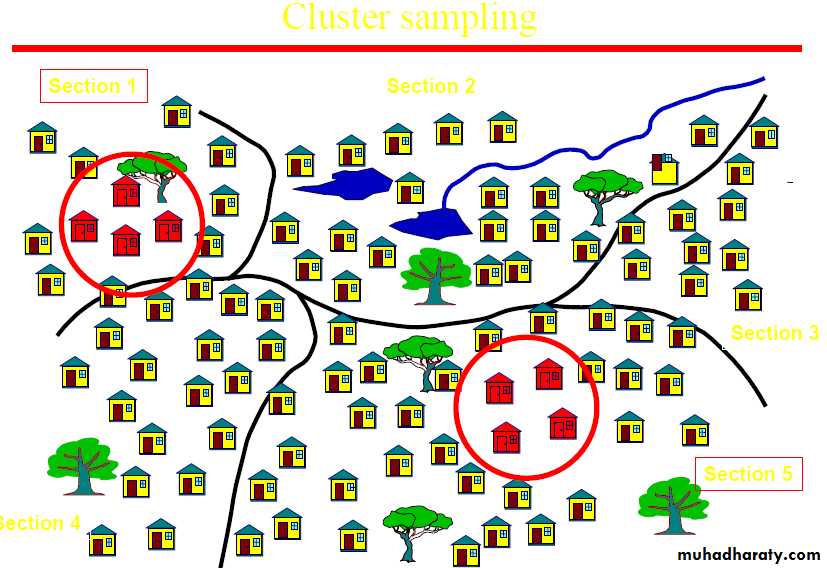
Cluster sampling
Cluster: a group of sampling units close to each other i.e. crowding together in the same area or neighborhoodStratified sampling (multi-stage sampling)
Stratified sampling – break the sample into various subgroups or strata and sample from them.Must have good knowledge of strata
Types of sampling
Non-probability sampling
Qualitative researchers are not as concerned about representativenessRelevance to the research topic
Importance of context
Sample size does not have to be determined in advance.
Selection of cases gradually over time
Important: many statistics assume random sampling
Types of non-probability sampling
1-Convenience sampling (haphazard, accidental) – sample whoever is available.Used by both quantitative and qualitative researchers
Problems
-no representativeness
-It is haphazard, can be very biased
-Not random.
2-Purposive sampling - Use judgment to pick individuals who meet a specific criteria.
-Especially good for exploratory or field research.-Appropriate for at least 3 situations.
1. select cases that are especially informative.
E.g., college coaches and championships
2. desired population for the study is rare or very difficult to locate.
E.g., prostitutes
3. case studies analysis – find important individuals and study them in depth.
Errors in sample
A. Systematic error (or bias)
Inaccurate response (information bias)
Selection bias
B. Sampling error (random error)