
Lecture four
By Dr. Alaa Al-sahlany
Specialized Connective Tissue
Cartilage
General Features
It is
an avascular
structure nourished by diffusion
No nerves are present (insensitive) in cartilage
Regeneration of cartilage is poor. Its damage results in a scar.
Covered externally by a dense connective tissue sheath known as perichondrium
Components
1)Cells : chondrocytes
2)Extracellular matrix (ECM) which is composed of:
(a) fibers : mainly collagen type II
(b) ground substance
Function
1)Supports soft tissues.
2)Provides gliding area for the joint, facilitating movements
3)Essential for growth of long bones
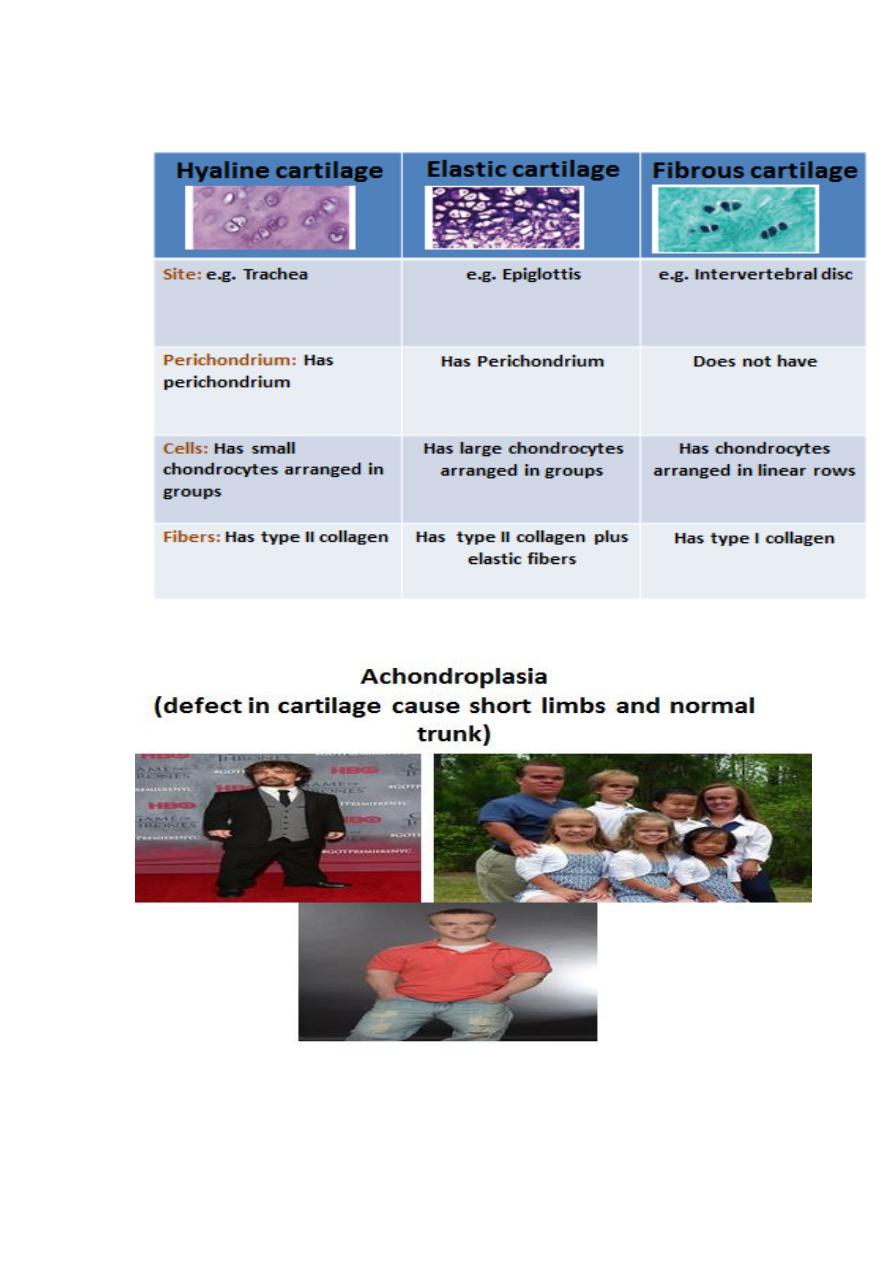
Types of cartilage
Bone
Function
1)It contains bone marrow, which is a haemopoietic tissue
2)Bone stores calcium and phosphate
3)It protects vital organs like brain, heart and lungs
TYPES OF BONE
Morphologically, bone consists of:
1.compact bone: it is a solid shell of cortical bone. Form the outer layer of bones
2.spongy or cancellous bone : a network of trabeculae separated by marrow
spaces. Form the inner layer of bones
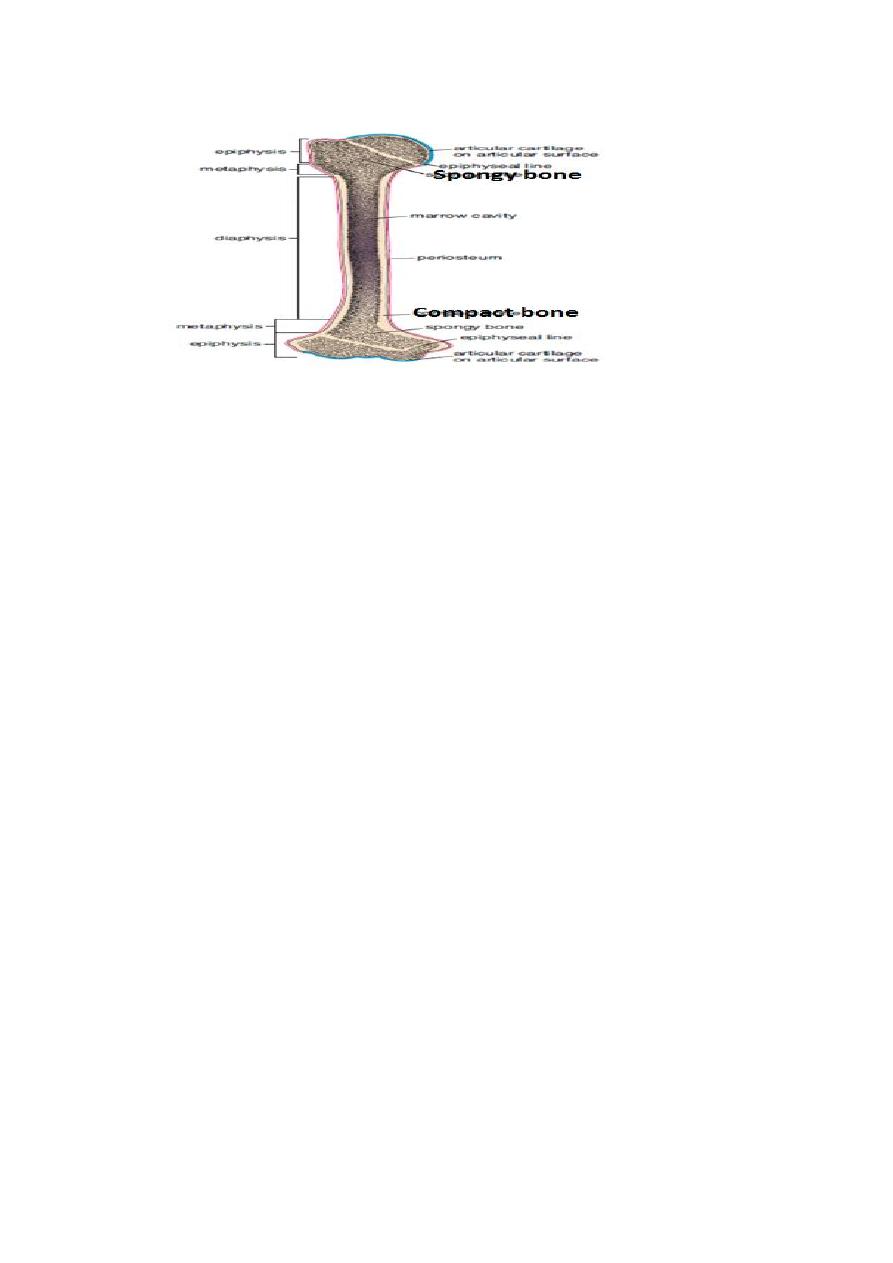
BONE MEMBRANES
1. Periosteum
It is
a dense
connective tissue membrane covering the external surface of bone
It has
rich nerve supply and is very sensitive
It is involved in bone growth and repair
2. Endosteum
It is a membrane of
loose
connective tissue lining the medullary cavity
It is involved in bone growth and repair
Bone composition
1. Cells
(a) Osteoprogenitor cells: they are pluripotential cells derived from mesenchymal
cells
(c) Osteocytes
(b) Osteoblasts
(d) Osteoclasts
2.Extracellular matrix
(a)Fibres :composed of type I collagen.
(b) Ground substance
(c) Inorganic components: responsible for rigidity and hardness of bone
include:

(a) Calcium phosphate
(b) Calcium carbonate
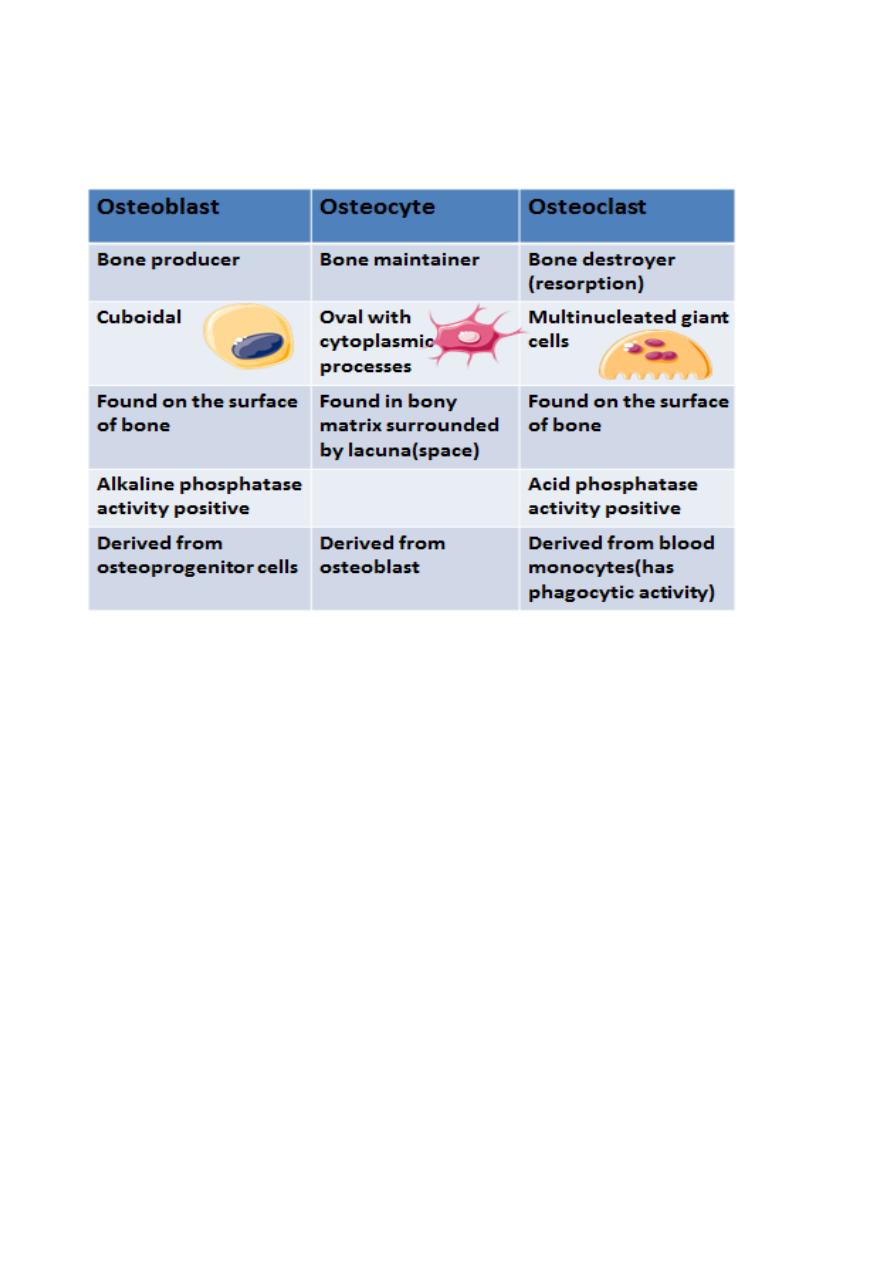
Cells
Structure of the bone
Structure of compact bone
1. Circumferential system
– Outer (near the periosteum)
– Inner (near endosteum)
2. Haversian system or osteon(the main units)
3. Interstitial system(occupying the triangular spaces between Haversian systems)
Haversian system or osteon
Found between the outer and inner circumferential systems
Are long cylindrical structures
Each system consists of a central canal(Haversian canal) surrounded by concentric
lamellae of bone matrix
The canal contains blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics and connective tissue
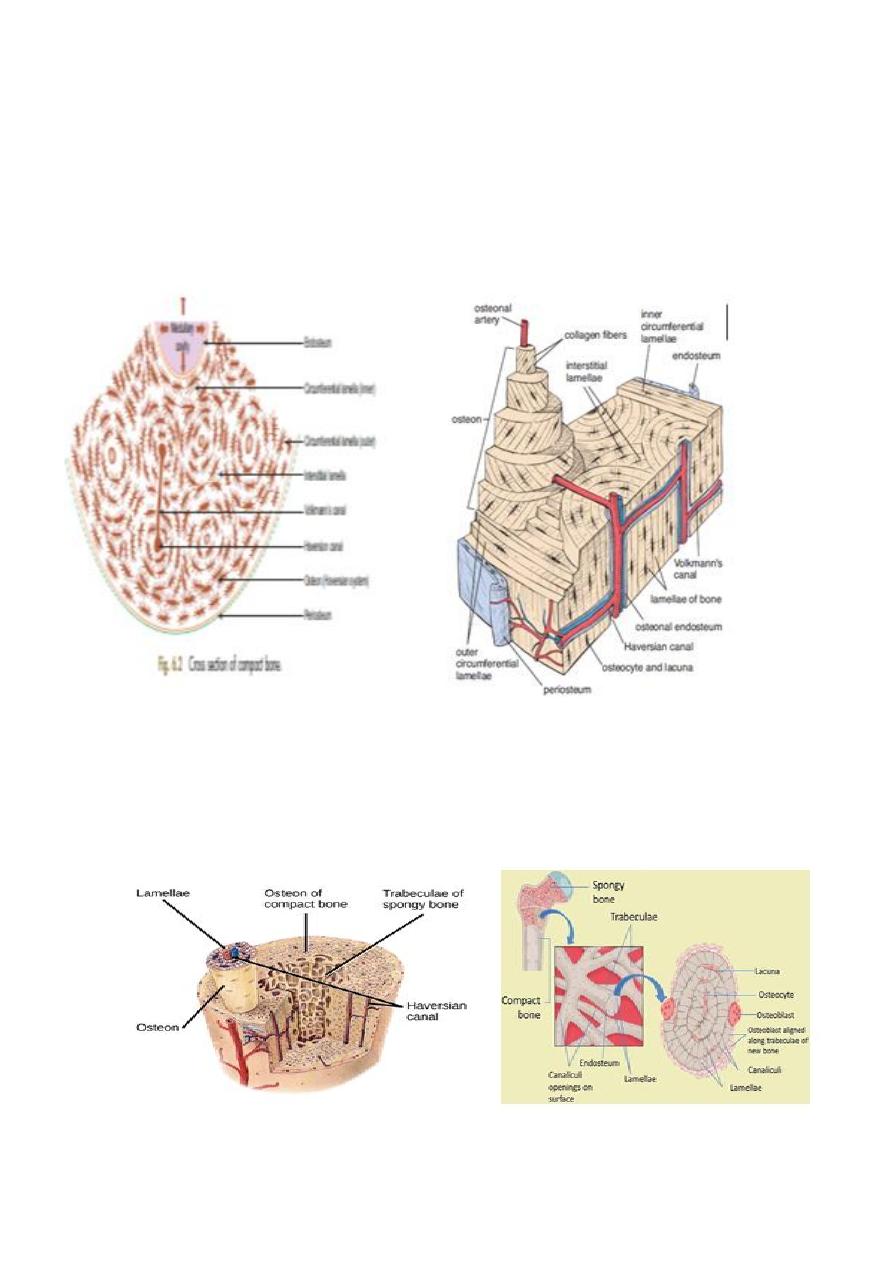
The canals communicate with each other, with the periosteum and with the
internal medullary(marrow) cavity through Volkmann’s canals.
Osteocytes are seen between lamellae in lacunae(spaces)
Interstitial system
Are concentric lamellae occupying the spaces between the osteons
Structure of spongy bone
Spongy bone is made of bony trabeculae that branch and anastomose with one
another surrounding marrow spaces between them which contain bone marrow

Role of Vitamins in Bone Formation
Vitamin D
Necessary for absorption of calcium from small intestine.
Deficiency:
in children → rickets, which is characterized by bowing of long bones due to loss of
rigidity and hardness in the weight-bearing bones.
in adults → osteomalacia, which also causes softening of bone
Role of Hormones in Bone Formation
1.
Parathyroid hormone
—activates osteoclasts to resorb bone → ↑ calcium in
blood.
2.
Calcitonin
—inhibits bone resorption by osteoclasts → ↓ calcium in blood.
3.
Growth hormone
—stimulates the growth of epiphyseal plate
Deficiency of growth hormone → Dwarfism
Excess of growth hormone →
– in children → Gigantism
– in adult → Acromegaly

