
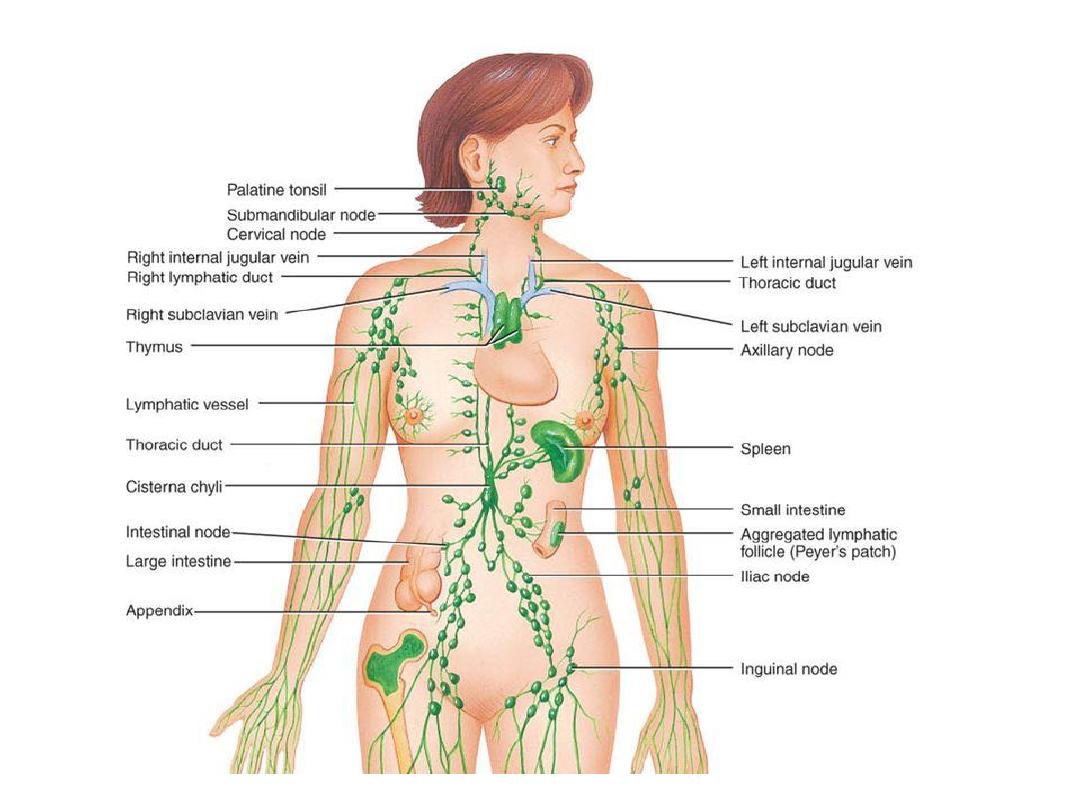
LYMPHOID TISSUE
By
Dr.Alaa Al-sahlany
Boston, USA
Nov. 25
th
, 2021

Lymphoid system consists of tissues and organs
mainly made of lymphocytes, which protect the
body against invasion of microorganisms

Cells of the lymphoid System
Lymphocytes:
1. B lymphocytes
2. T lymphocytes
2. Natural killer (NK) cells
Supporting cells:
1. Macrophages
2. Antigen-presenting cells (APC) such as Langerhans’
cell in skin.
3. Neutrophils.
4. Basophils and eosinophils
Classification of Lymphoid Tissue
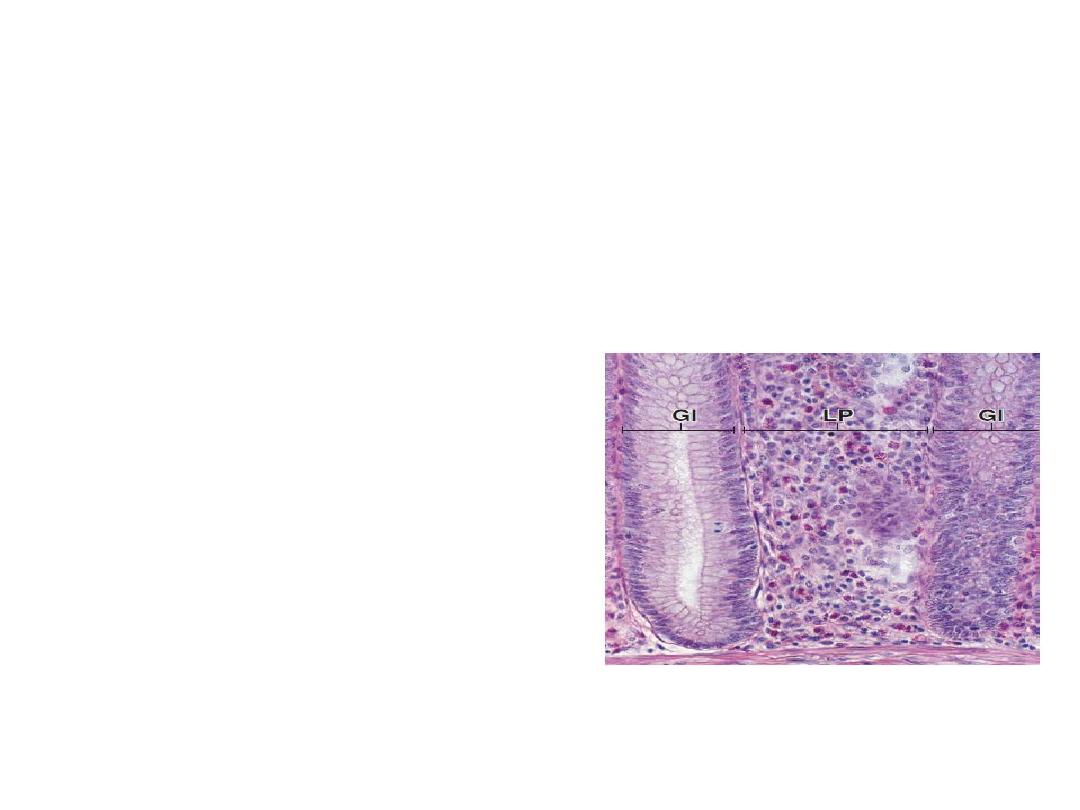
1.Diffuse lymphoid tissue (Mucosa associated
lymphoid tissue MALT)
Lymphocytes deep to epithelium(subepithelium)
in lamina propria of digestive, respiratory
tract
2.Dense lymphoid tissue
lymphocytes arranged in the form of nodules

Dense lymphoid tissue
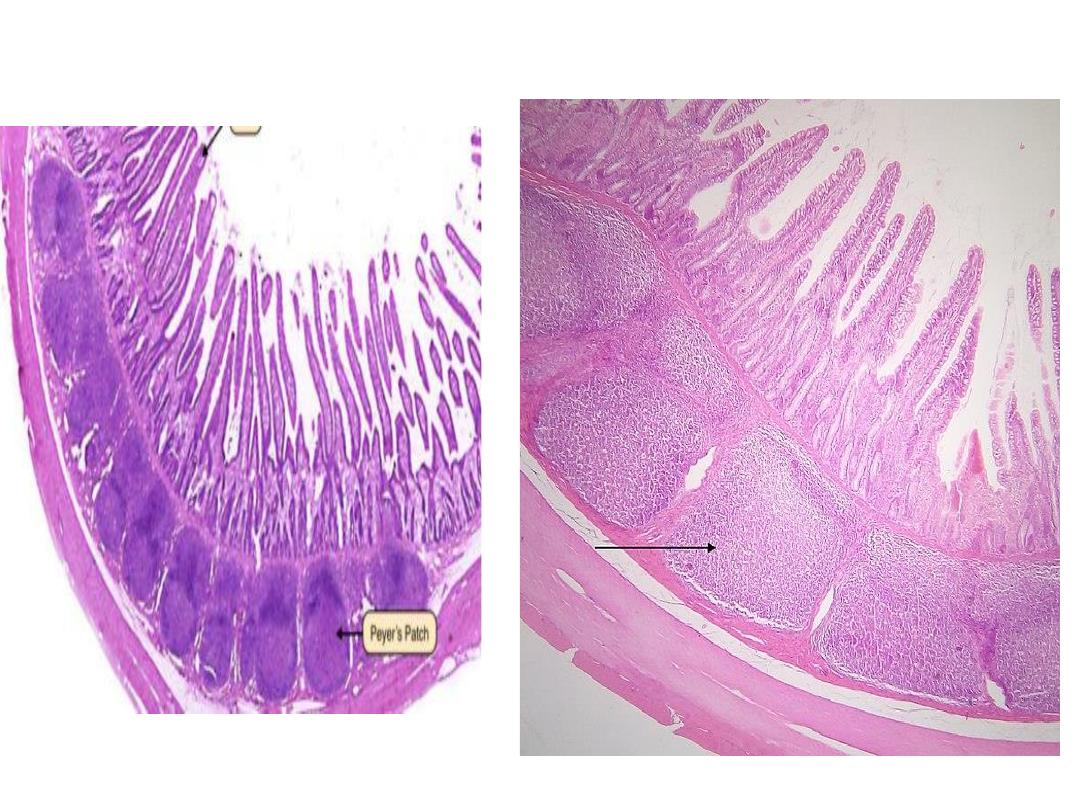
(A) Non-encapsulated: e.g. Aggregated nodules
(Peyer’s patches)
(B)Encapsulated discrete lymphoid organs:
Thymus
Lymph node
Spleen
Peyer patches
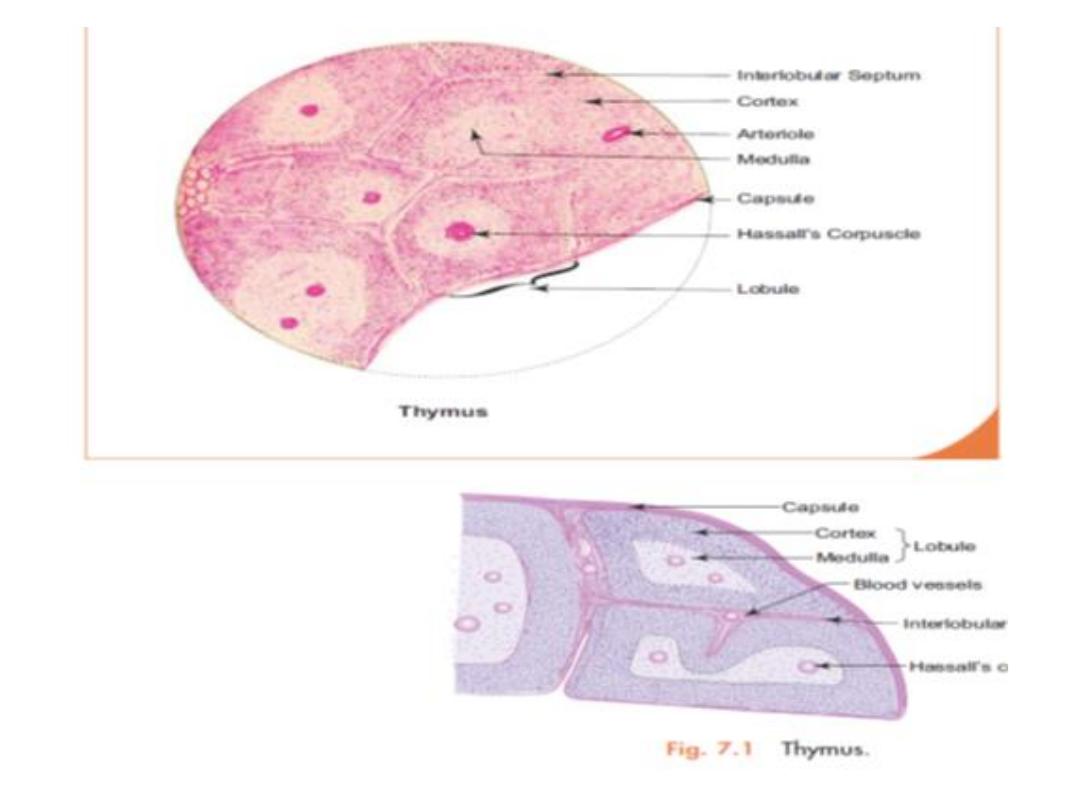
Thymus
Located behind the sternum and in front of the
heart
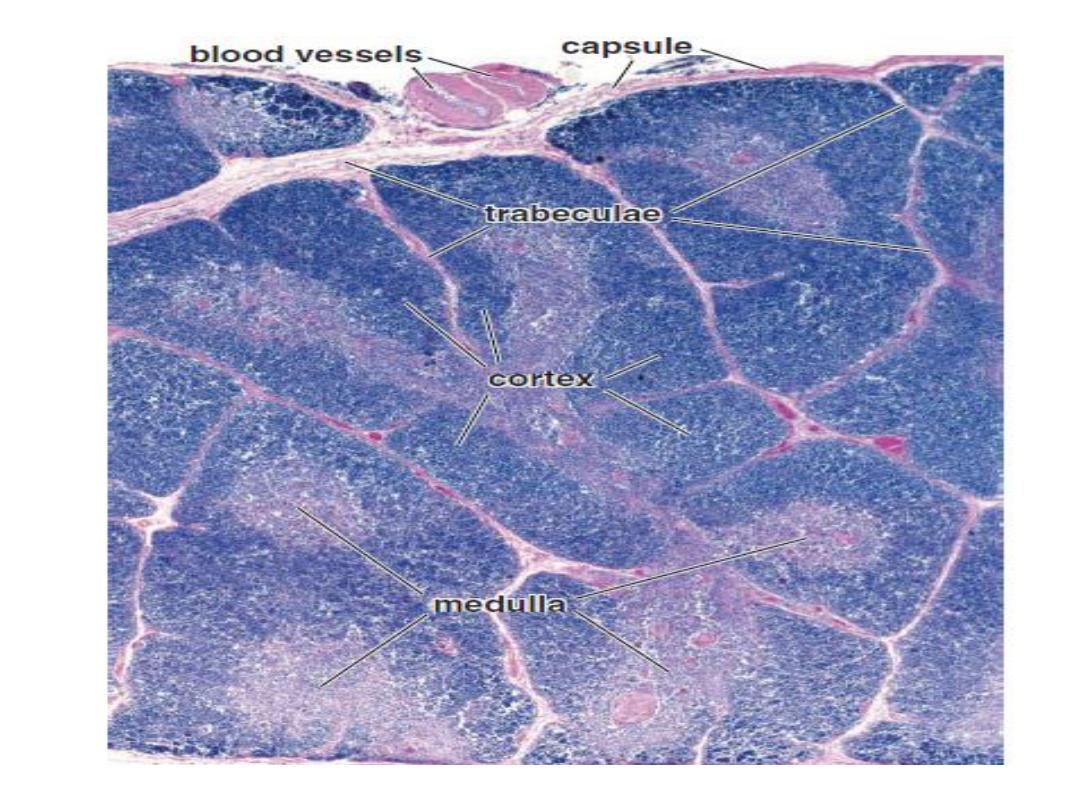
Made up of two lobes, each consisting of a
central medulla and outer cortex surrounded by
capsule

Composition
Connective tissue capsule: covers the thymus and
sends septae into the interior dividing the lobe into
lobules.
Parenchyma: Each lobule has a darkly stained
cortex at the periphery and a lightly stained
medulla in the centre that has Hassall’s corpuscles

FUNCTIONS
It is a central lymphoid organ and is essential till
puberty for T cells differentiation and maturation.
After puberty it undergoes involution.
Secrete hormones like thymopoietin, etc., which
are involved in stimulation and differentiation of T
lymphocytes(no B lymphocytes).
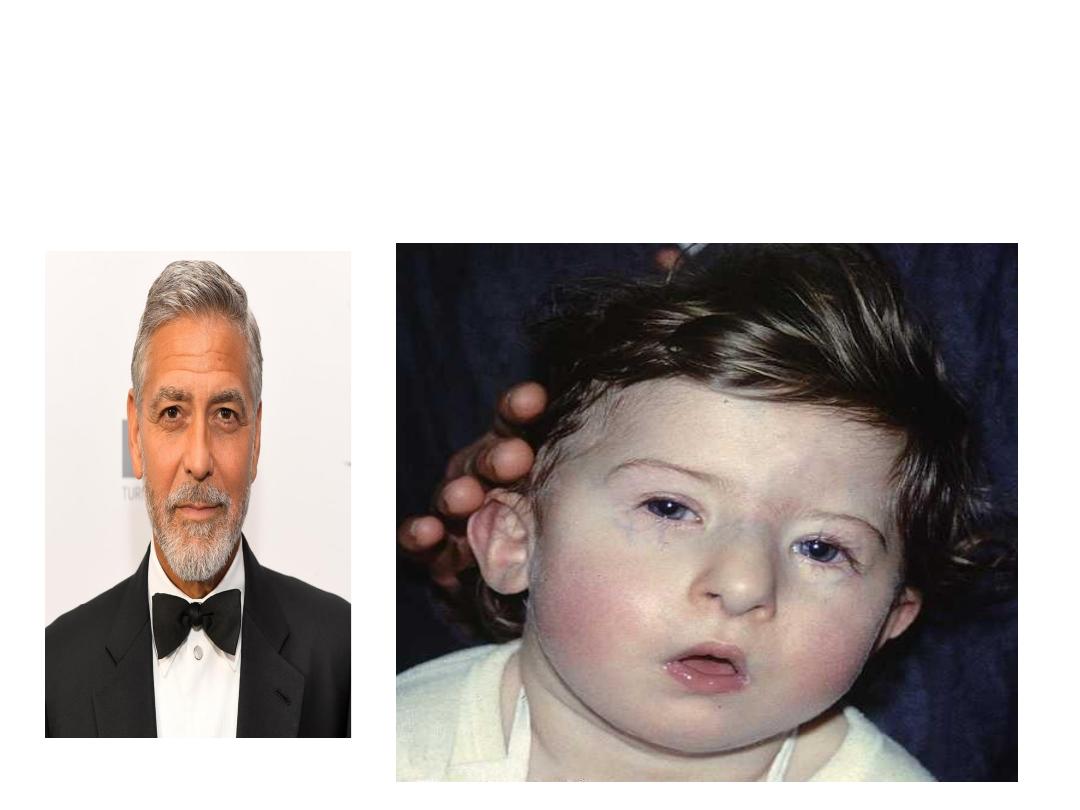
DiGeorge syndome
No thymus cause recurrent infections
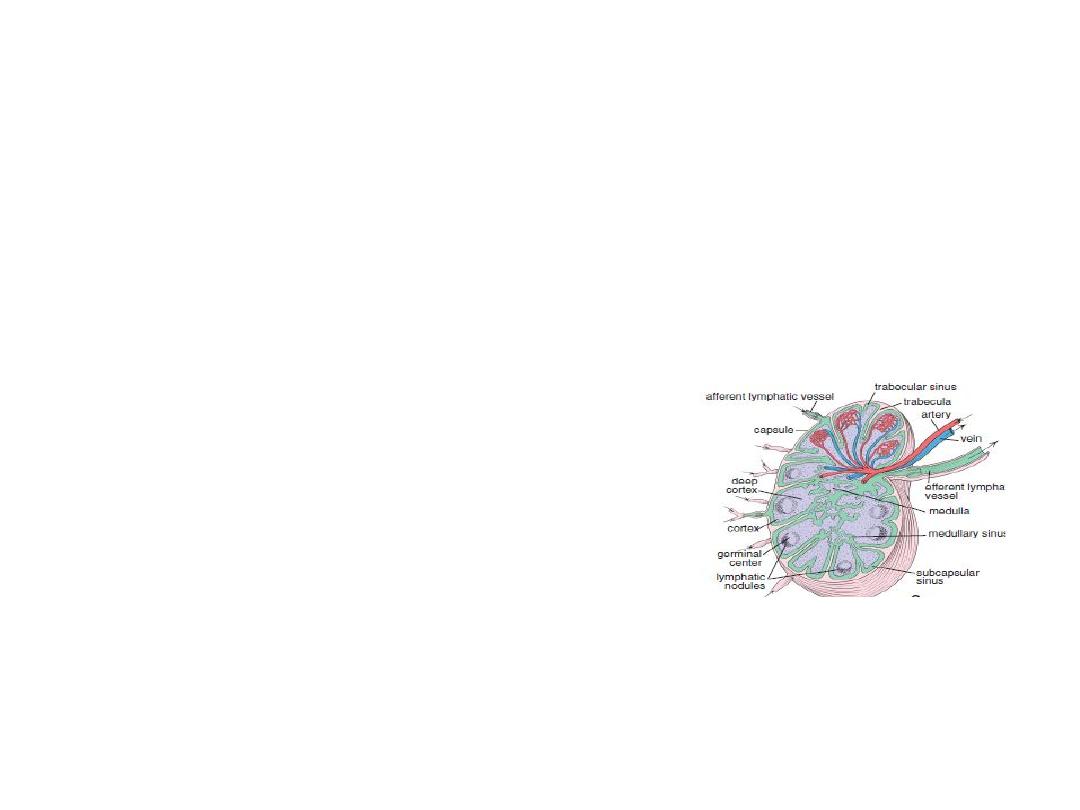
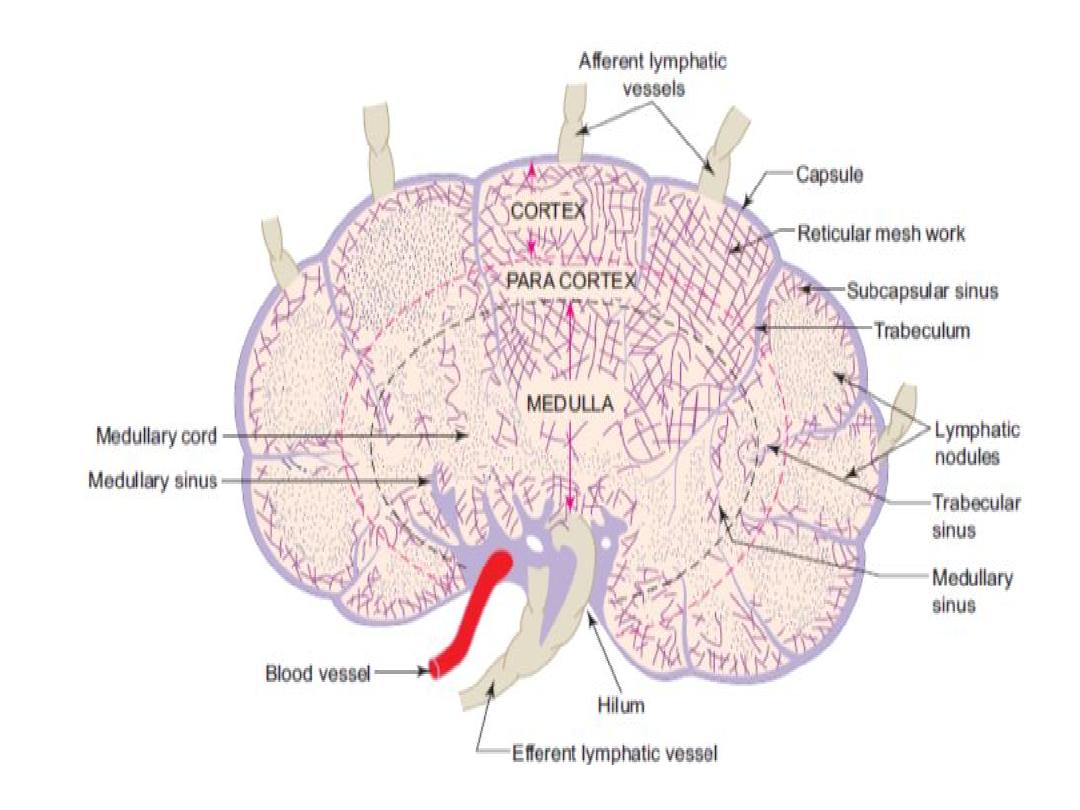
LYMPH NODE
Bean-shaped structures situated along the
course of the lymphatic vessels
Usually found in groups such as in the axilla,
inguinal region
Function:
Localizing and preventing the spread of infection
(defense).

Composition

A. Connective tissue framework
The organ is surrounded by a connective tissue
capsule which sends trabeculae into the interior.

B. Parenchyma
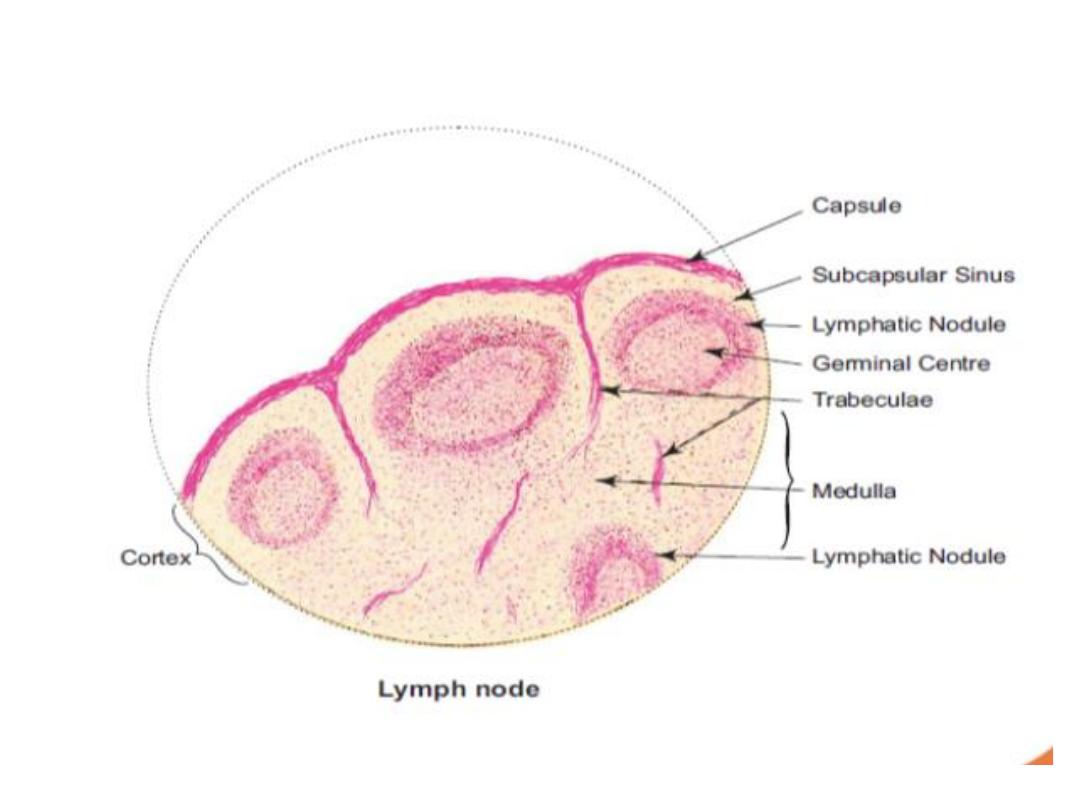
1.Cortex is the peripheral part of the lymph node.
It contains:
(a) Subcapsular sinus
(b) Lymphatic follicles—with or without germinal
centers formed mainly of B lymphocytes.

2.Paracortex(deep cortex)
It consists mainly of T lymphocytes . Part of
cortex lie between lymphatic follicle and medulla
No follicles can be seen

3.Medulla: consist of
(a)The medullary cords are composed of closely
packed lymphocytes
(b)The medullary sinuses lie between the
medullary cords.
The medullary sinuses are lightly stained
compared to the darkly stained medullary cords
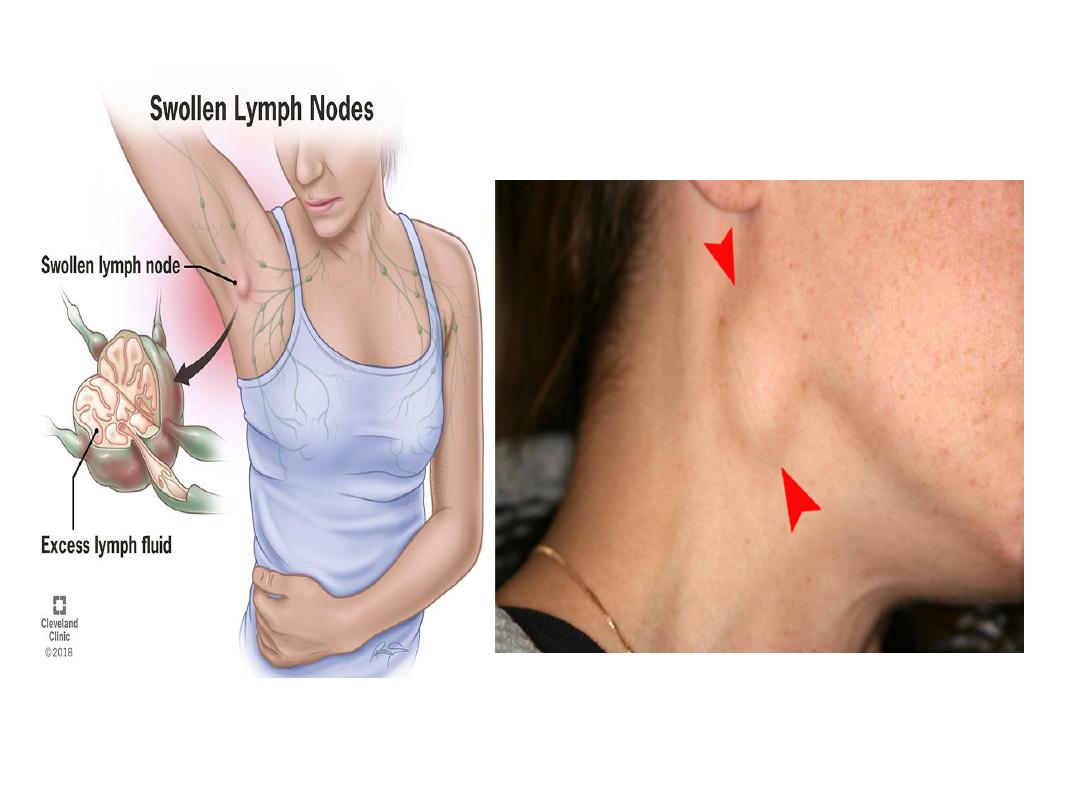
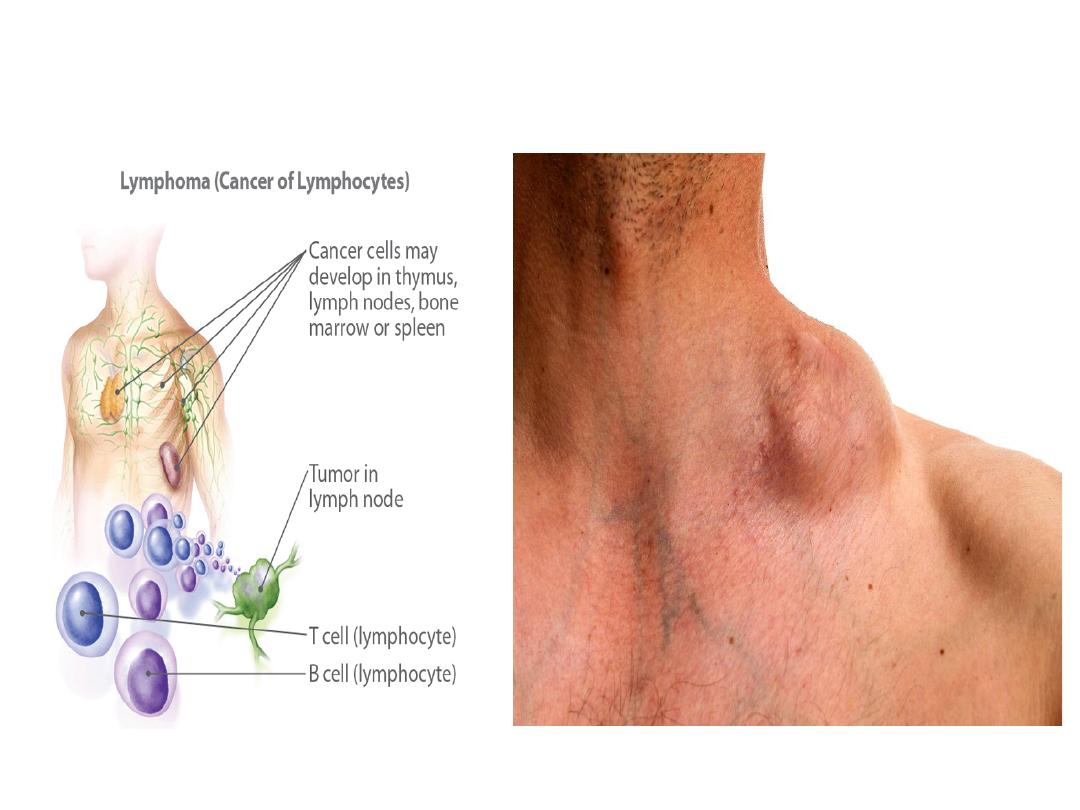
Enlarged lymph node in case of
infection and cancer

SPLEEN
Is the largest lymphoid organ
Located in the upper left quadrant of the
abdominal cavity
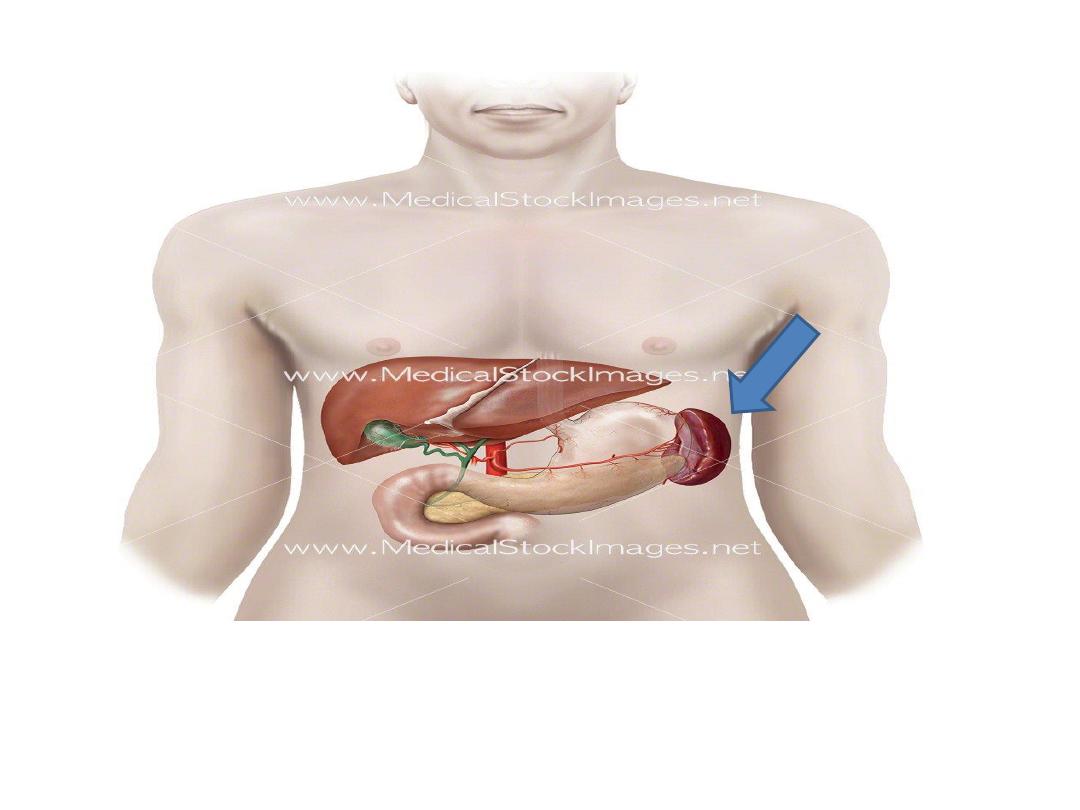

Function
Filtration of blood: filters the blood from antigens,
microorganisms, aged platelets and aged and
abnormal RBCs
Production of lymphocytes (defense of the body)
Acts as haemopoietic organ (in fetal life).

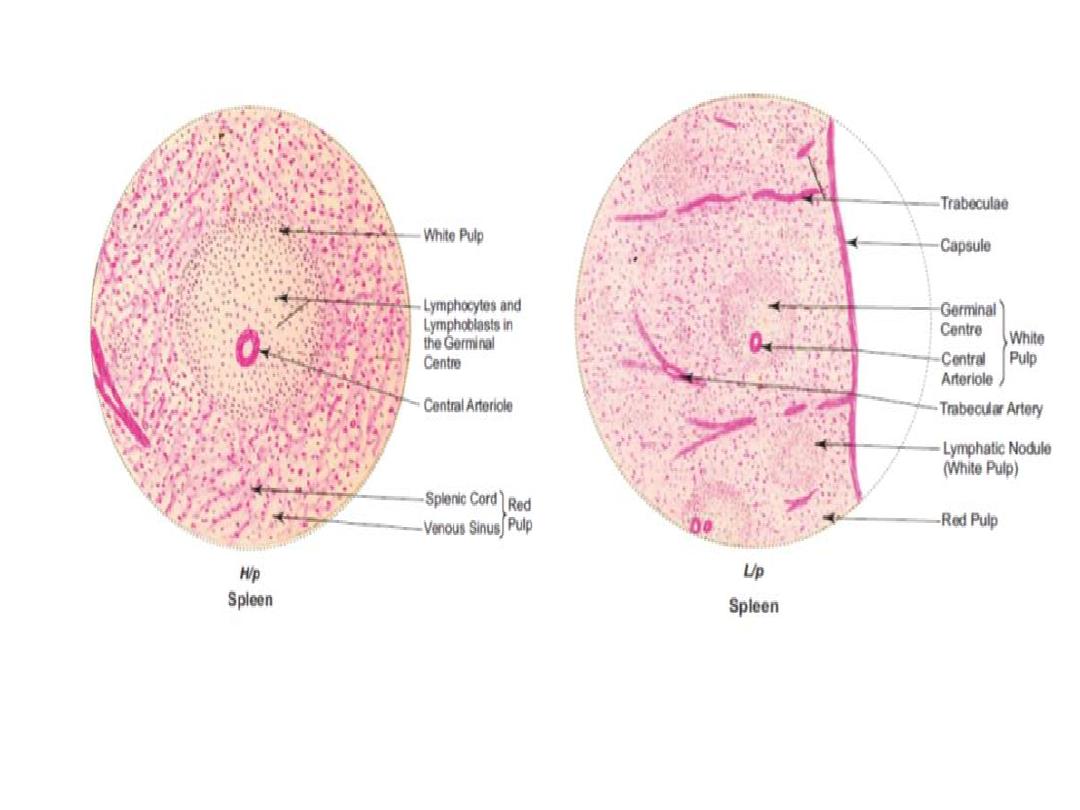
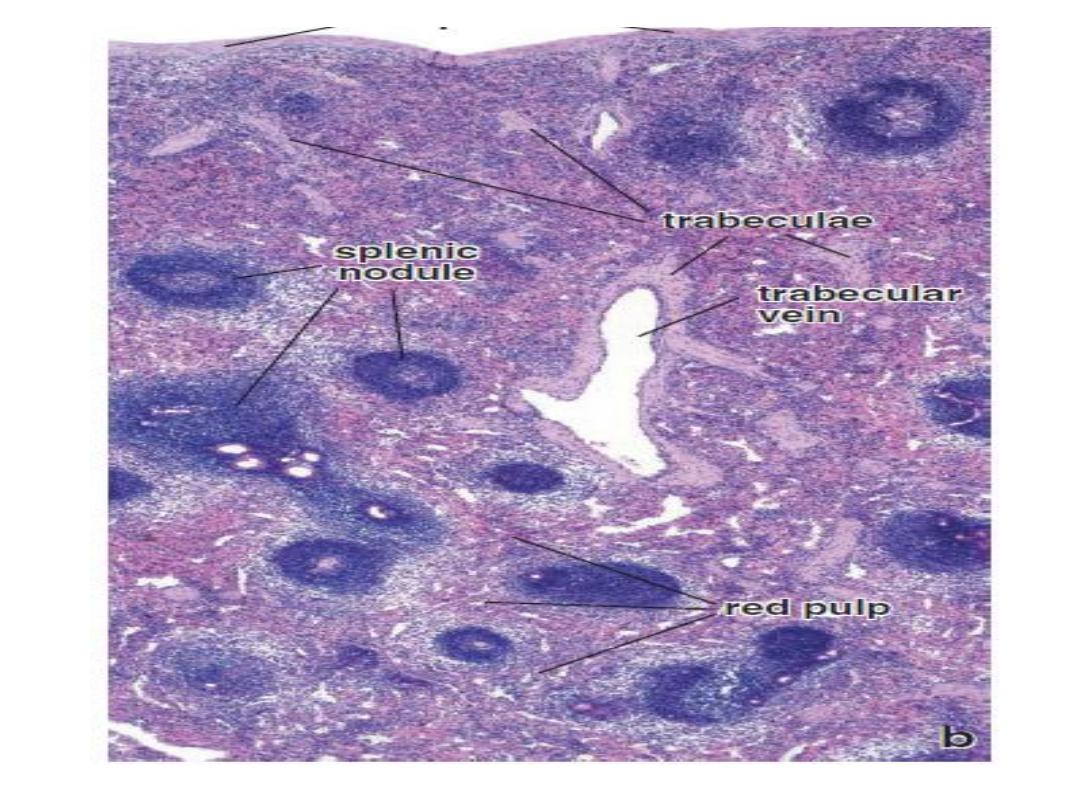
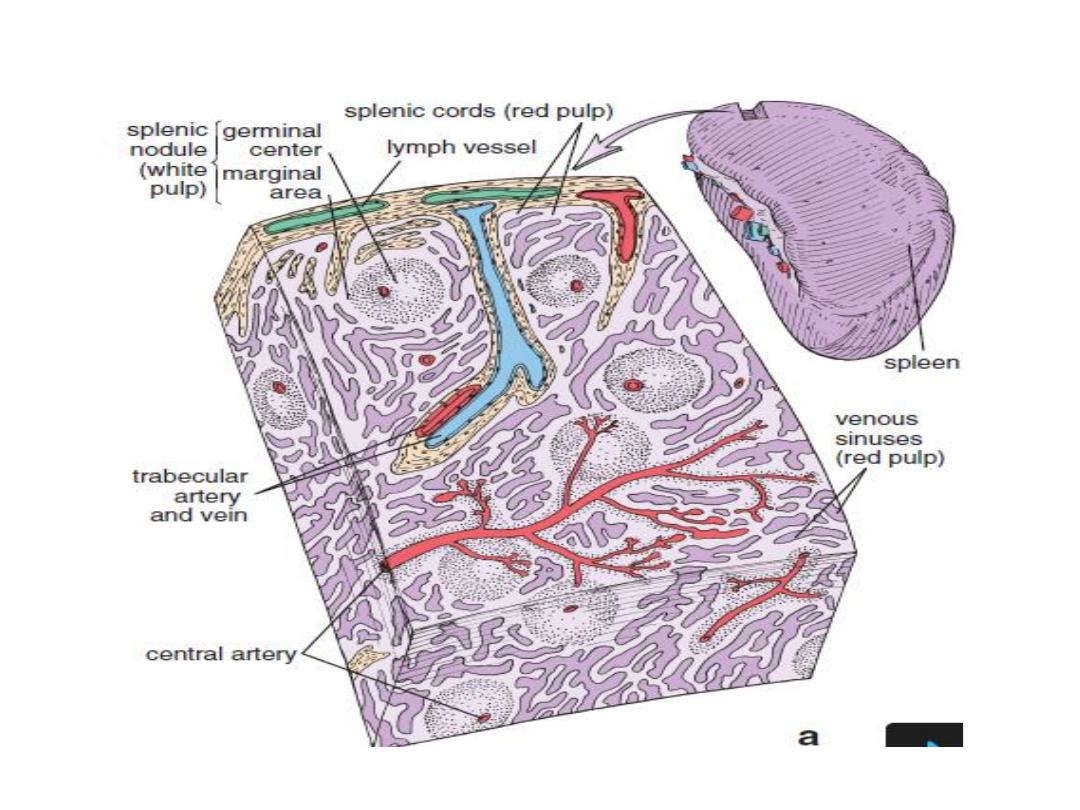
Composition

Covered by capsule which send trabeculae that
carry trabecular vessels
Connective tissue framework

Parenchyma
(1) White pulp: mainly consist of lymphocytes
Composed of two parts:
a)Periarterial lymphatic sheath: made mainly of T
lymphocytes that aggregate around the central
artery (a branch of splenic artery)
b)Lymphatic follicles formed mainly of B
lymphocytes and may contain germinal center

(2)Red pulp : heavily infiltrated with all the cells of
the circulating blood including large number of
RBC, giving a dark red color to this tissue
Consists of two parts:
a)Splenic sinuses (which are sinusoidal
capillaries)
b)Splenic cords ( that has RBC and all types of
WBC including macrophage )
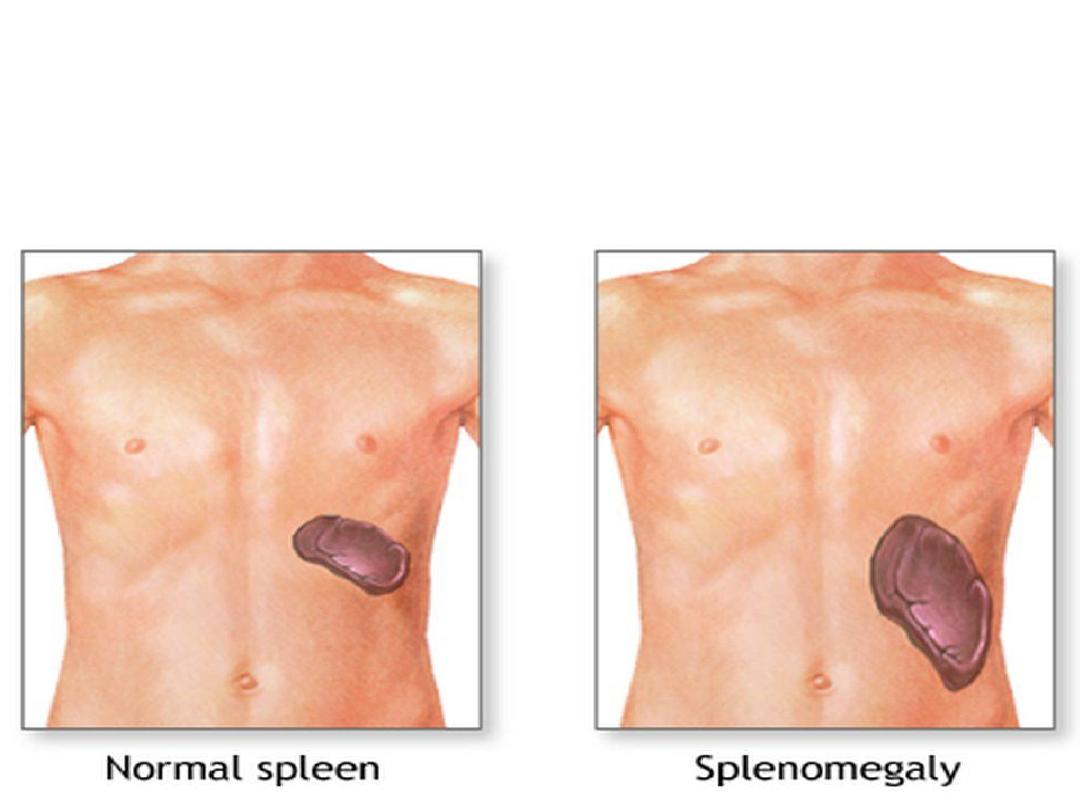
Enlarged spleen
in hemolytic anemia and severe
infection
.
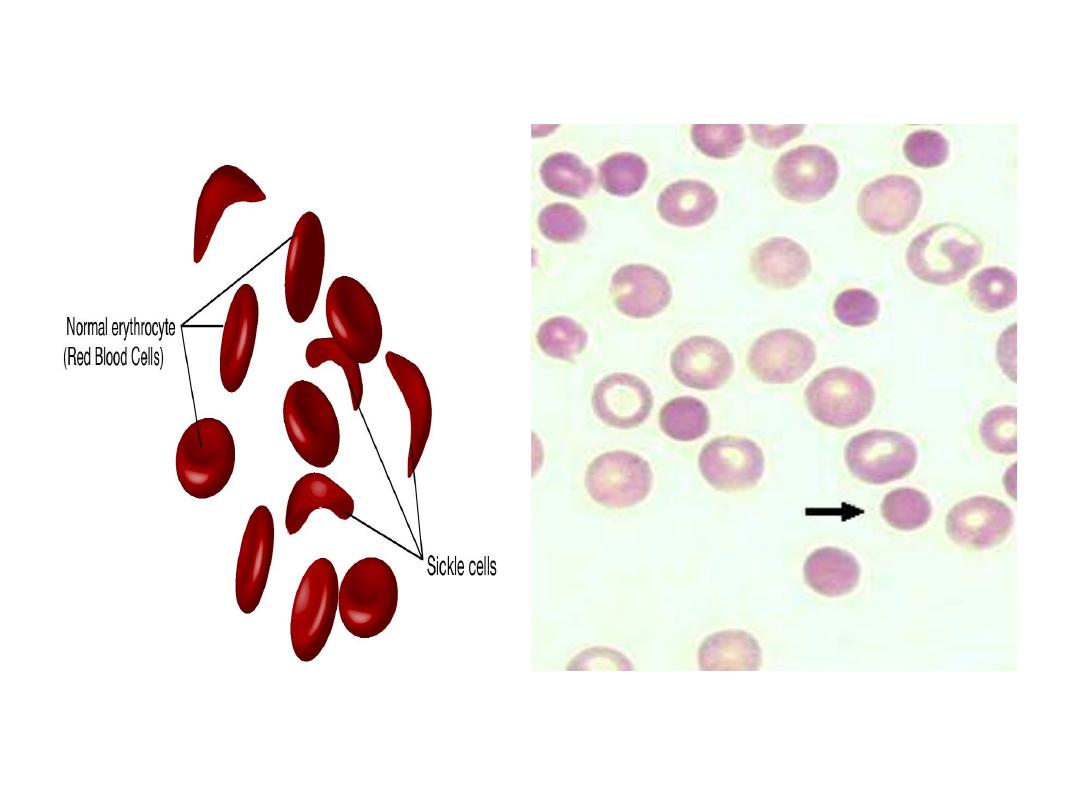
Sick cell anemia cause
splenomegaly
Spherocytosis cause
splenomegaly

Immortality


