
2
nd
class /2021-2022
Prof. Dr.Nihad N. Hilal

Objectives: What are the
1. Components of normal cell
2. Causes of cell injury
3. General mechanism of cell injury
4. Factors affecting cell response to injury
5. types of cell injury

Components of normal cell
1. Components essential for survival
• Cell membrane maintain intracellular environment
• Nucleus / nucleolus genetic code/ expression
• Mitochondria energy production/storage
• Endoplasmic reticulum/ribosomeprotein synthesis
• Golgi apparatustransport of products of protein
synthesis
• Lysosomesstorage of hydrolytic enzymes
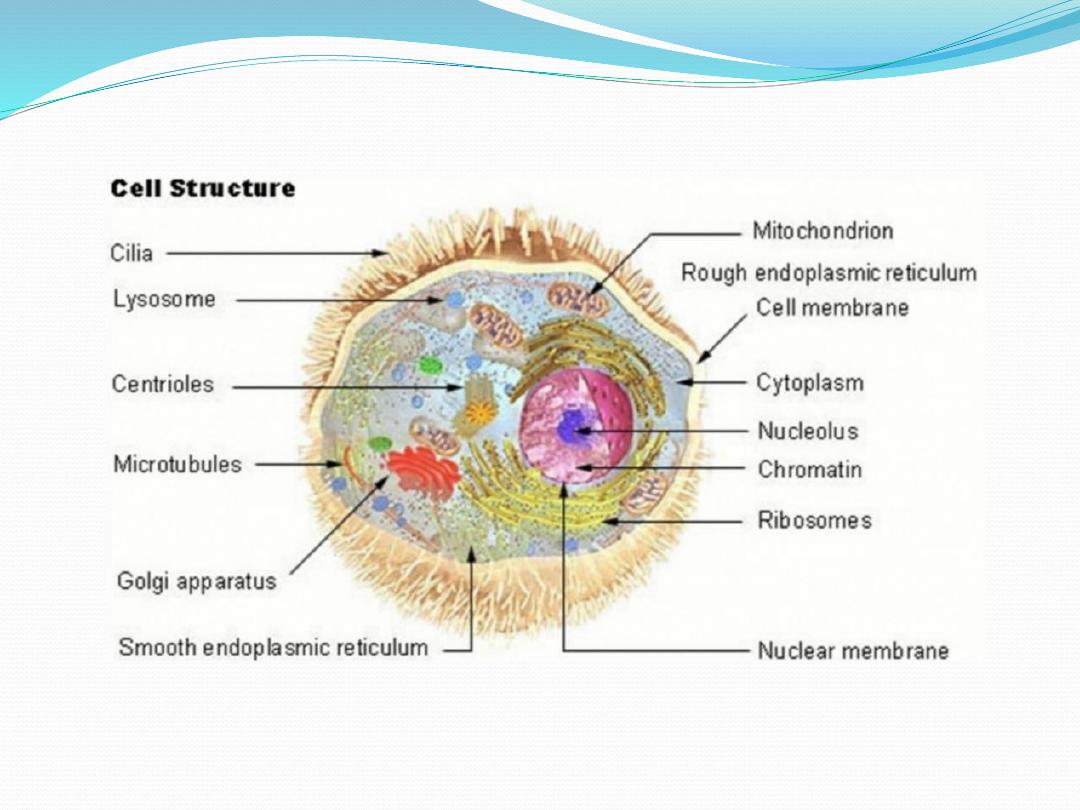

2.
Specialized components
e.g.,
•
Hemoglobin (RBC)
•
Zymogen granules (exocrine cells)
•
Neurofilaments (nerve cells)

Causes of cell injury
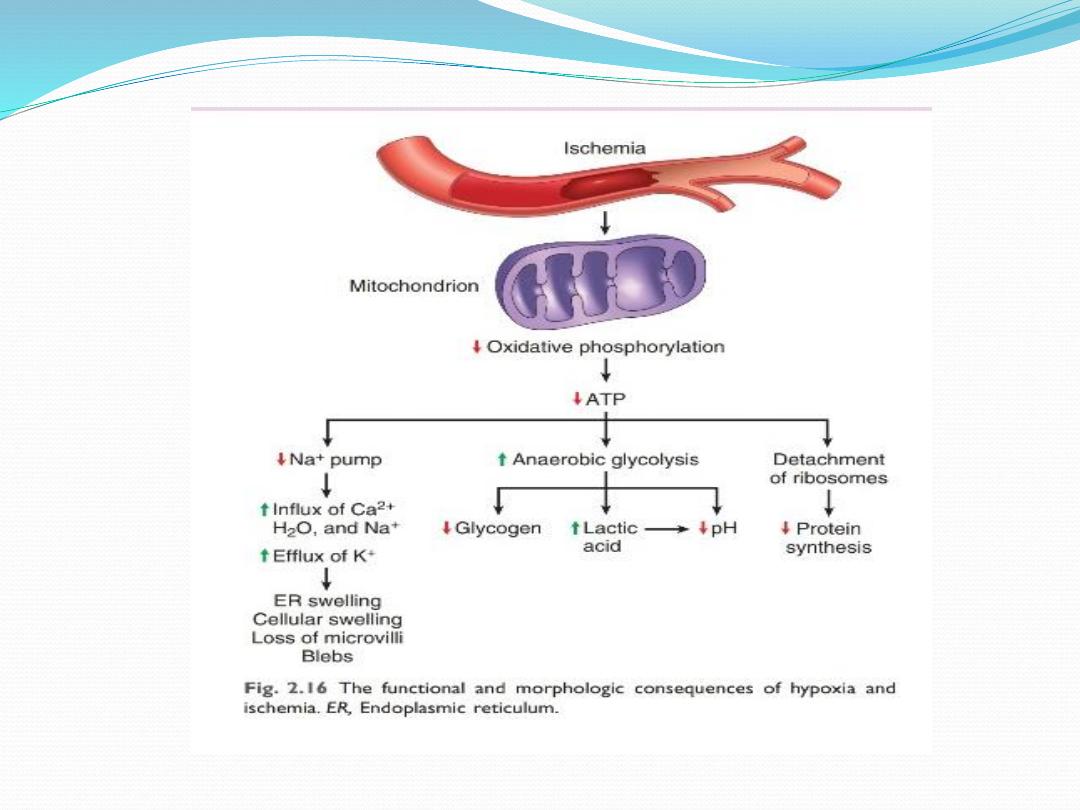
1. Ischemia/hypoxia:
any
↓ O
2
/ ↓ O
2
transport
(anemia), COPD
1. Infection: viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic
2. Physical: heat, cold, radiation, electricity
3. Chemical: acid, alkali
4. Immune:
5. Nutritional
6. Genetic: e.g. enzyme defaccumulation of toxic
product (iron in hemochromatosis)
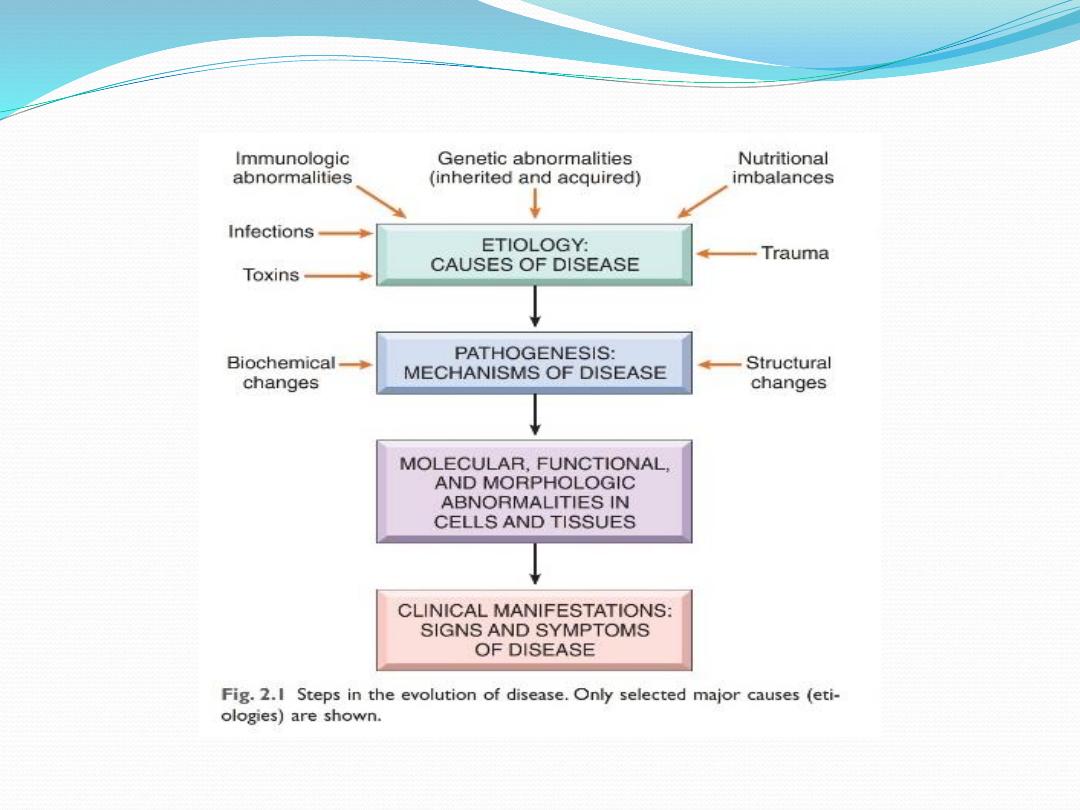

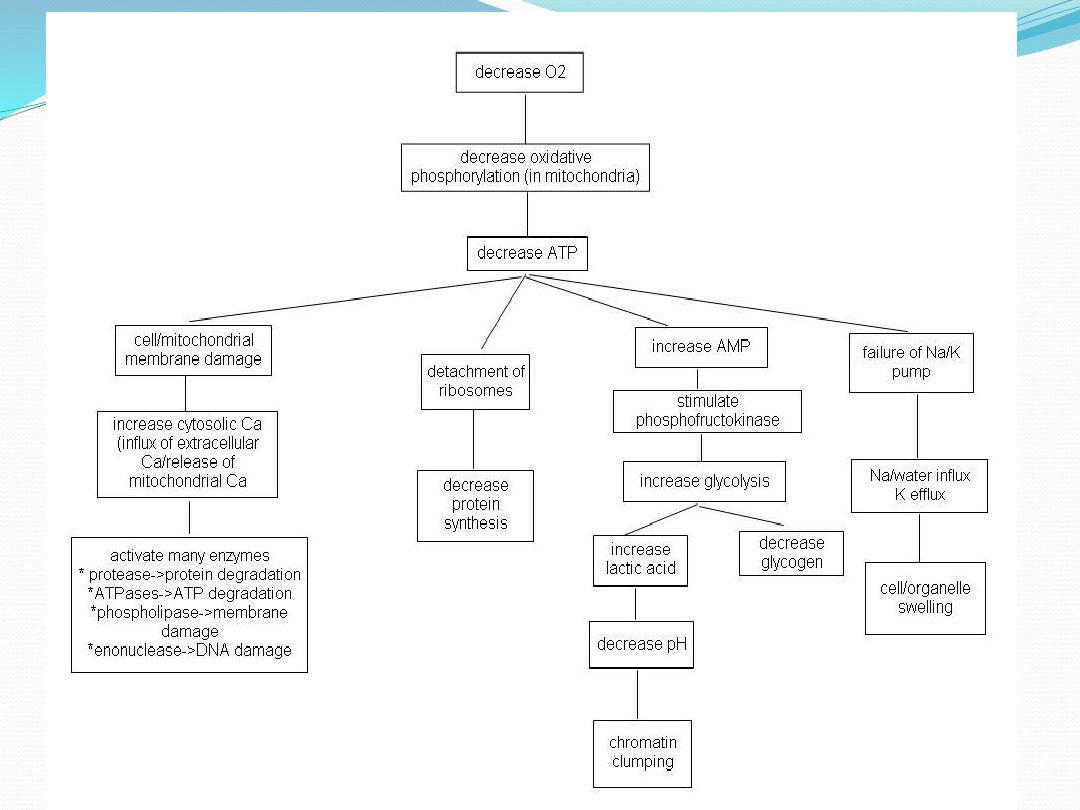
General mechanism of cell injury
i. Free radicalsDamage to DNA, proteins, lipid
ii. ATP depletion
iii ↑ cell membrane permeability
iv. Influx of calcium Activates enzymes
*
Proteases protein breakdown
* ATPaseATP depletion;
* Phospholipases cell membrane injury;
* Endonudeases DNA damage
v. Mitochondrial dysfunction
•
↓ Oxidative phosphorylation
• Release of cytochrome c which trigger apoptosis


Factors affecting cell response to injury
1.The type of injury
2.The duration of injury
3.The severity of injury
4.The type of injured cell
5.The cells metabolic state
6.The cell’s ability to adapt
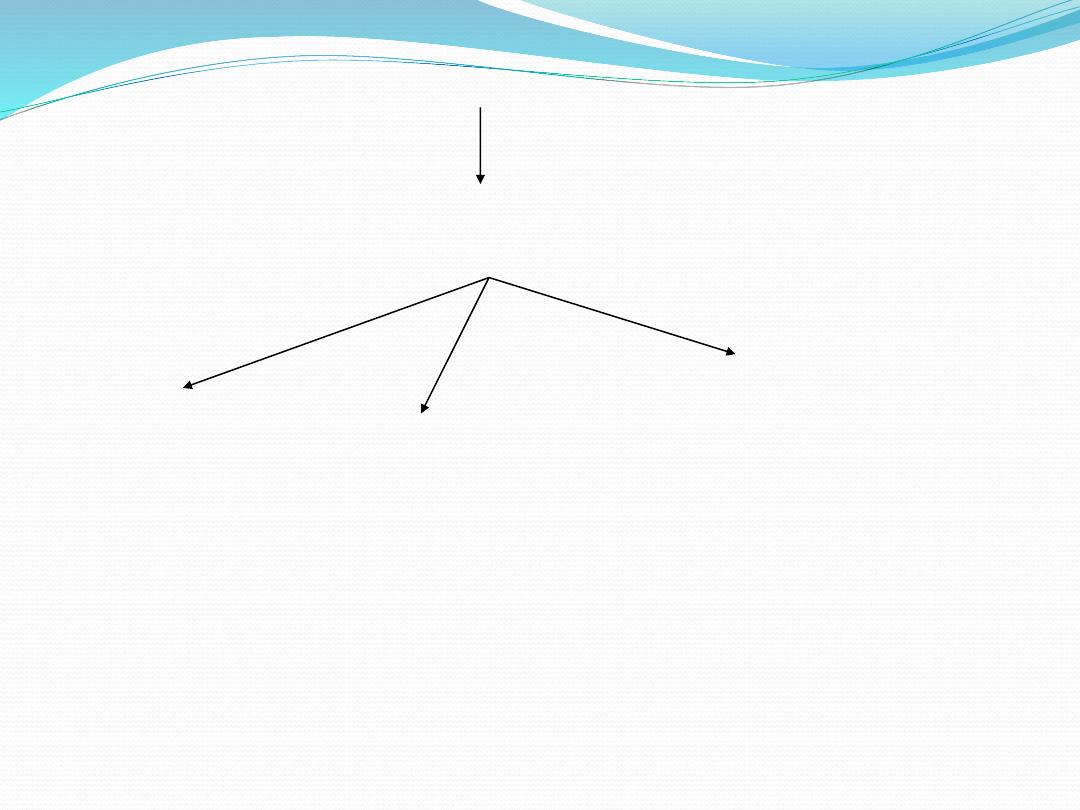
Normal cell
Injurious agent
(ischemic, hypoxic, chemical, physical etc)
Irreversible changes
reversible changes
adaptation
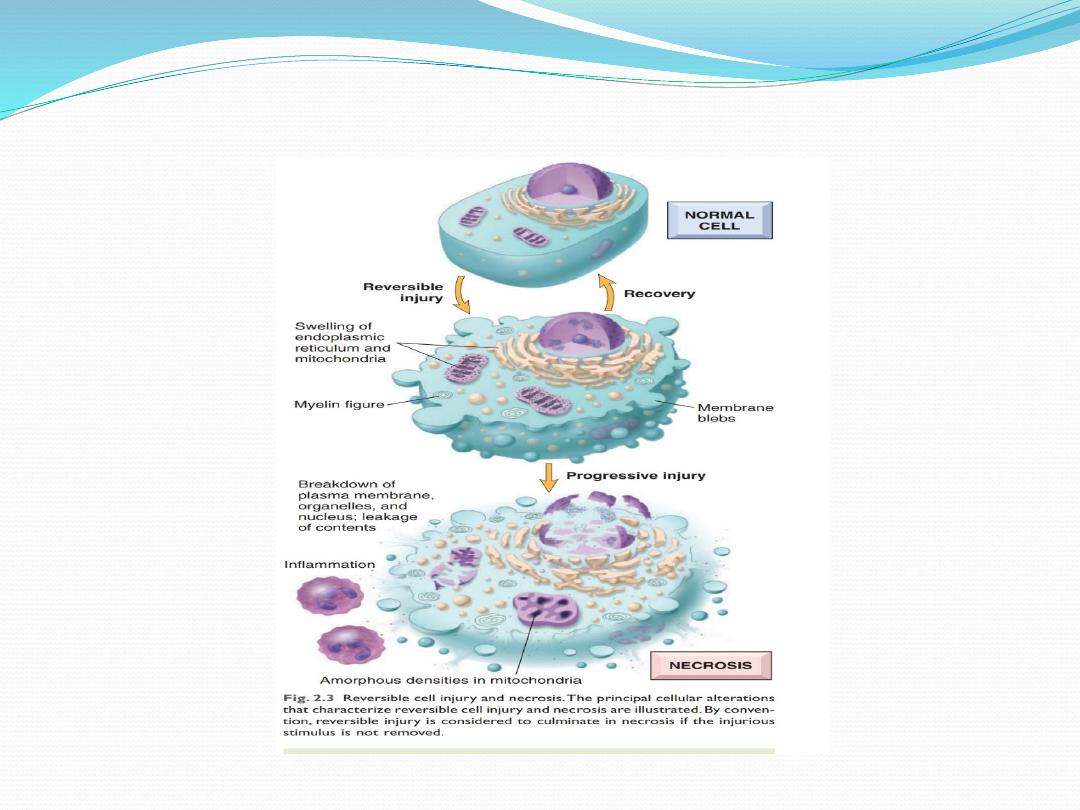
Reversible cell injury

Irreversible cell injury
1. Severe membrane damage (influx of Na/water etc)
1. Severe mitochondrial dysfunction: cessation of ATP
production
3. Rupture of lysosomes release of hydrolytic
enzymescell lyses
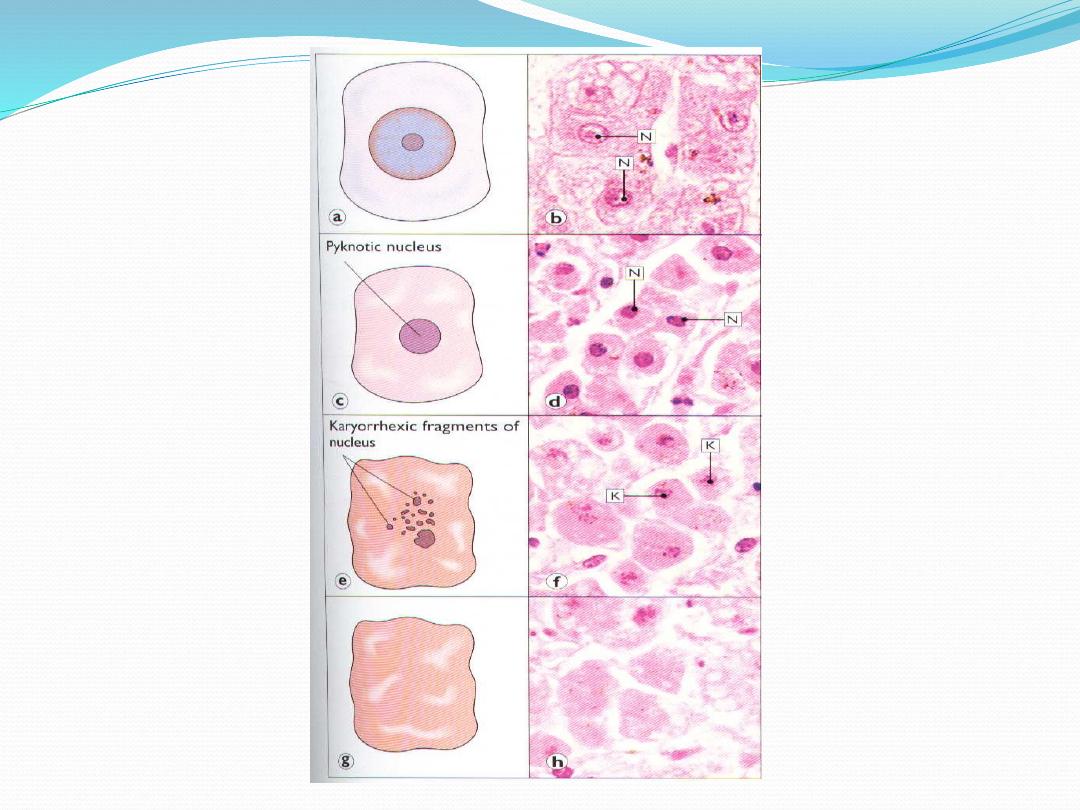
4. Nuclear changes
* pyknosis: condensation chromatin
* karyorhexis: fragmentation of nucleus
* karyolysis: disintegration of nucleus
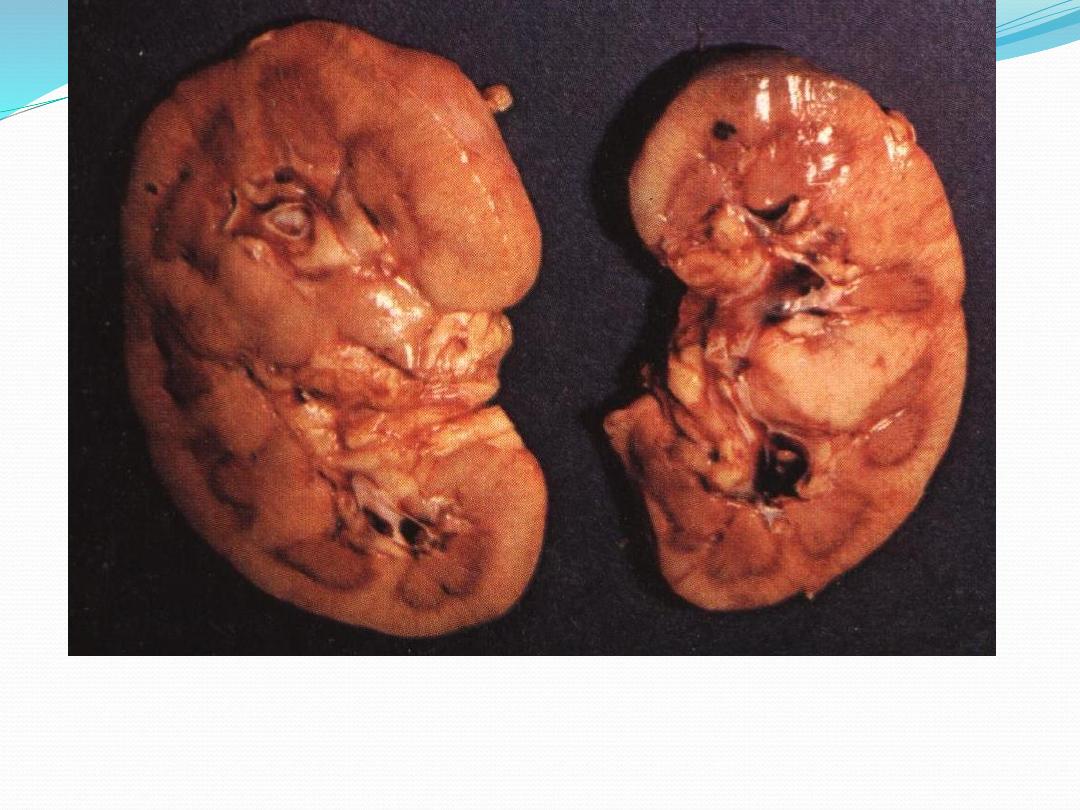
Cut section of kidney showing cloudy swelling
note the pale swollen parenchyma
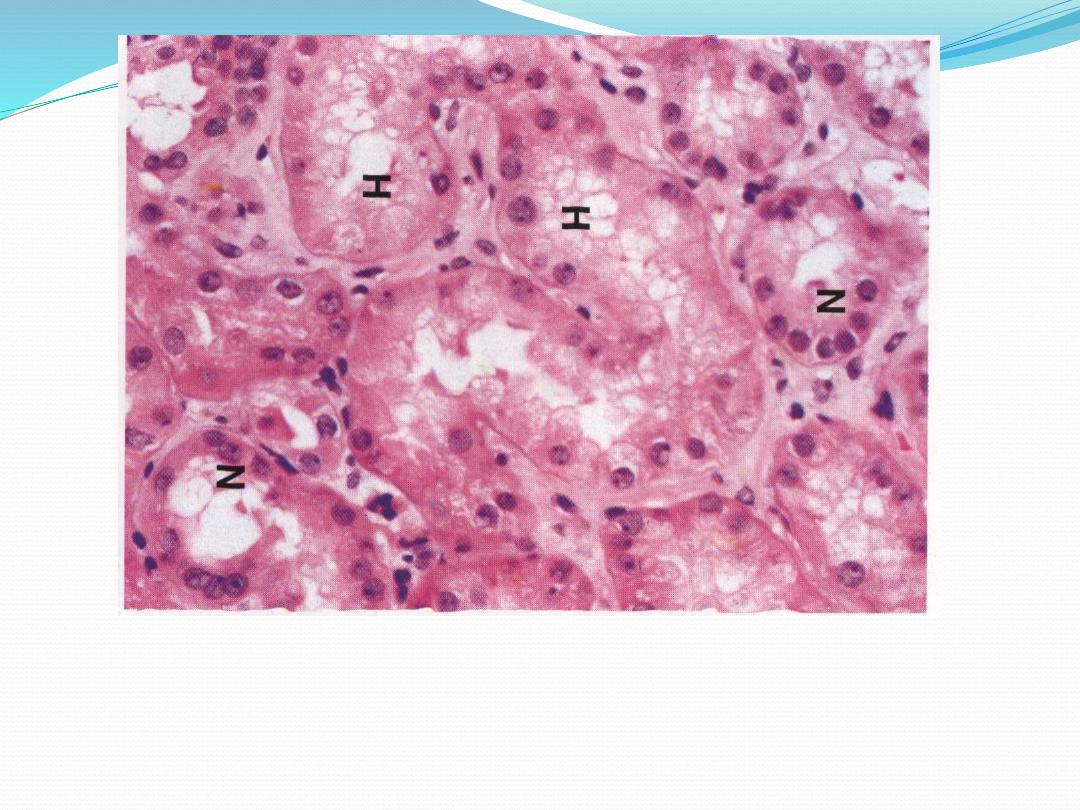
Hydropic degeneration
cells lining renal tubules distended with water,
cytoplasm eosinophilic & less granular than normal
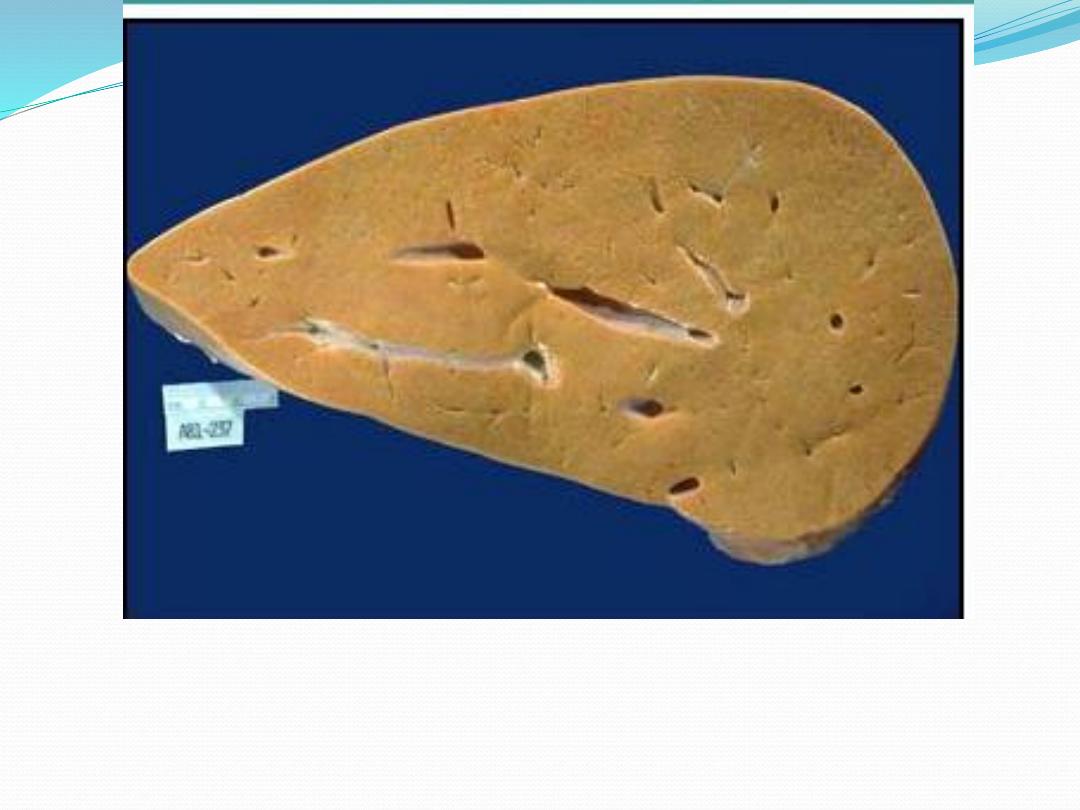
Fatty degeneration: grossly liver enlarged, yellow & waxy
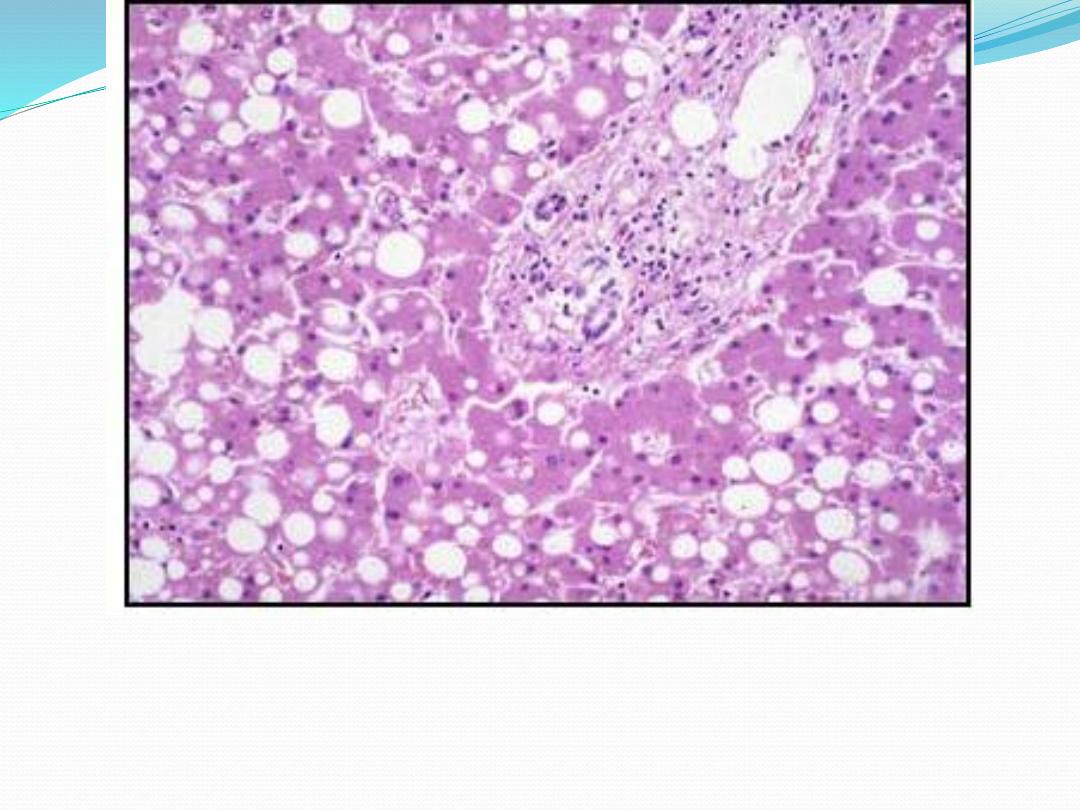
Fatty changes: liver: Some hepatocytes filled with fat
& looks empty due to removal of fat during processing
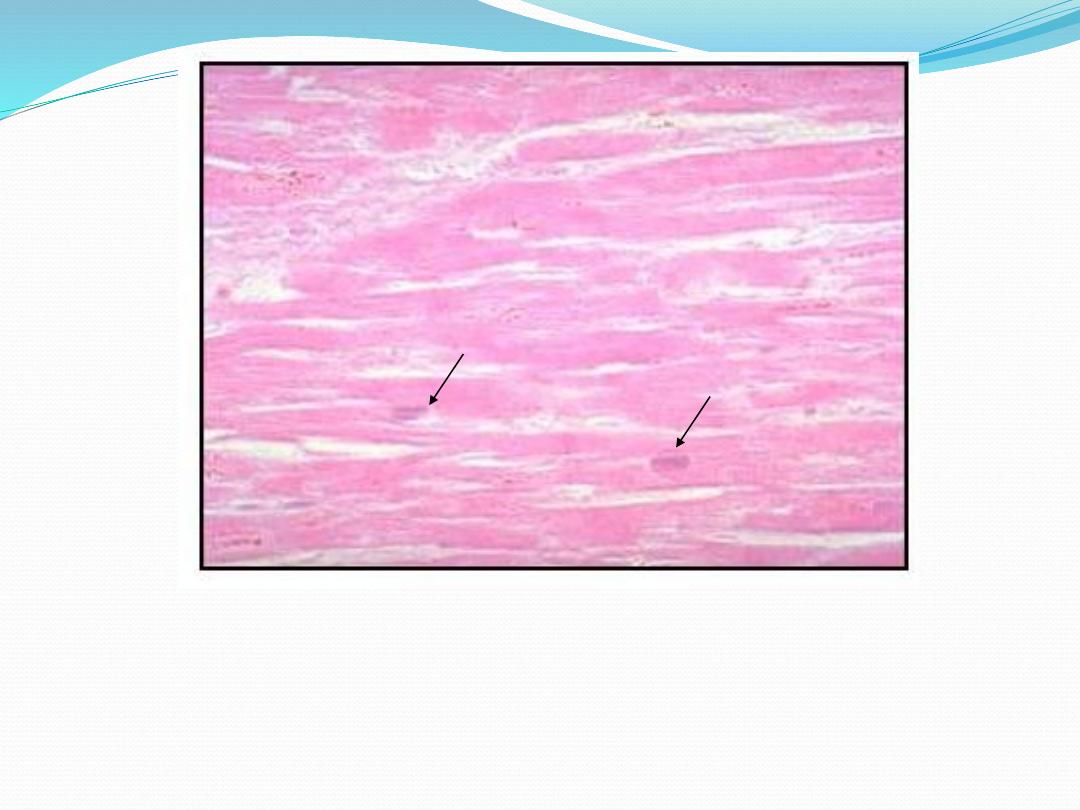
Dead cells: look to pyknotic faded nuclei

References
Textbook: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC: Robbins basic
pathology. 10th edition, Elsevier, 2018.
Currant's Atlas of Histopathology,4th Revised Edition

Thank you
