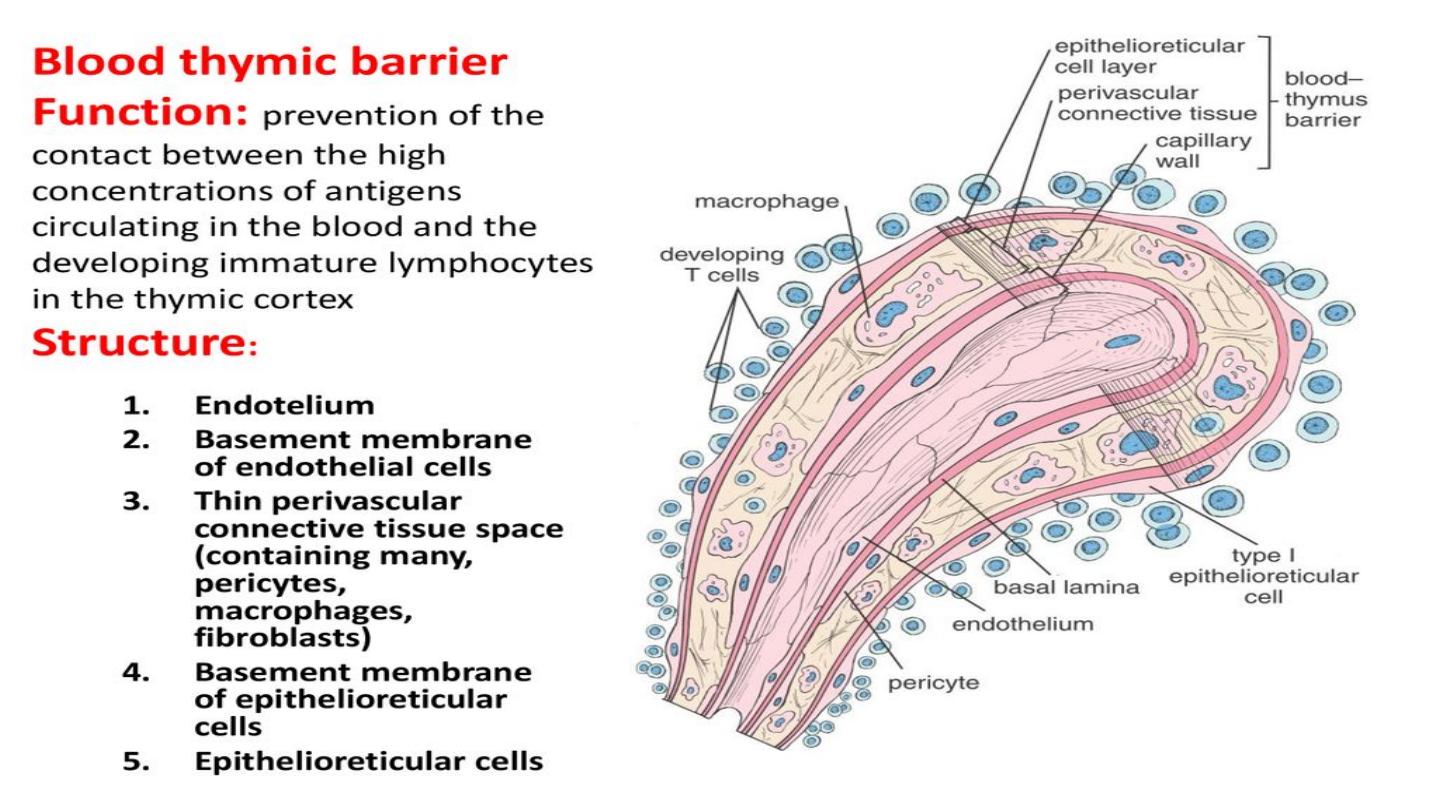
Histology of thymus
2
nd
stage
Dr.Elham majed Al.hadithy
TUCOM
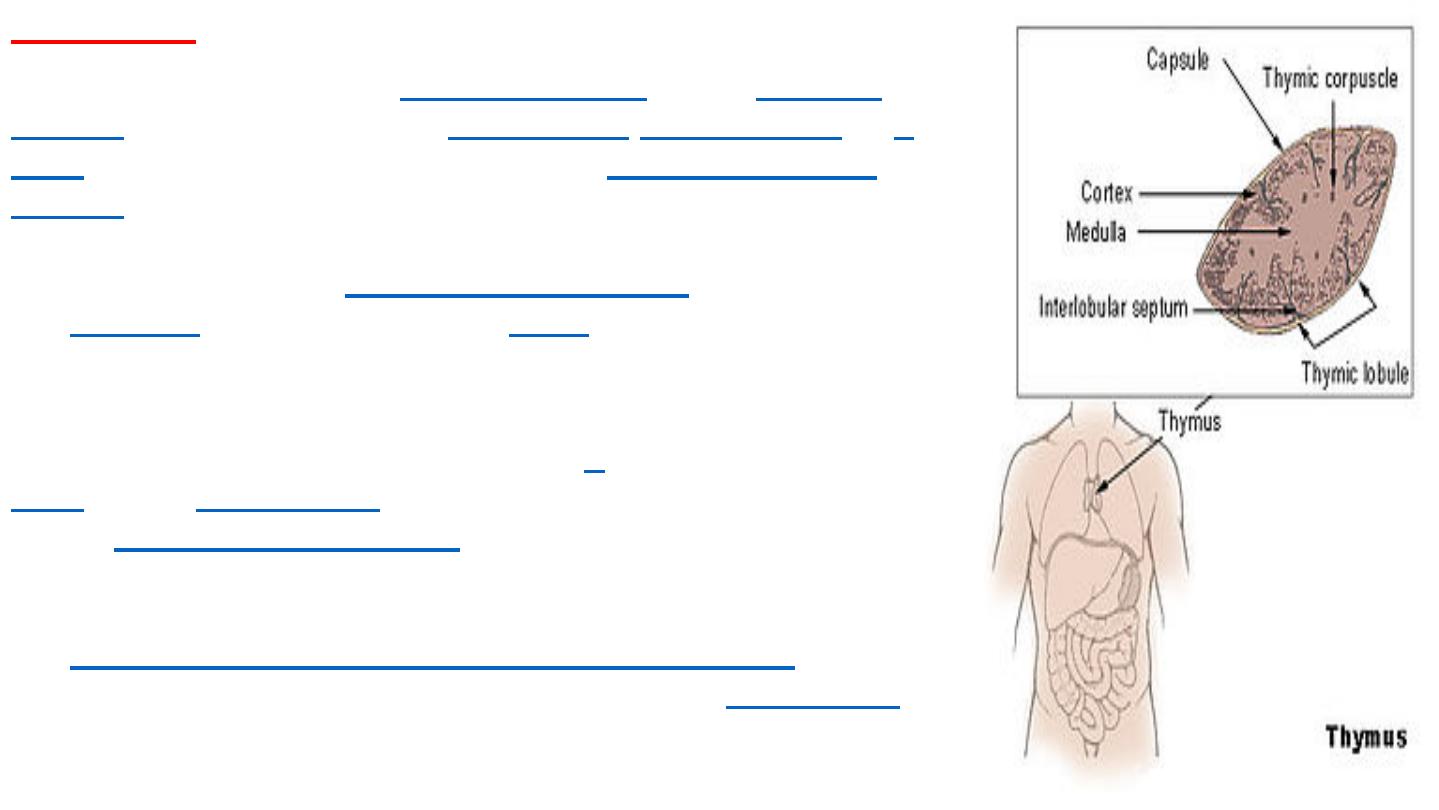
The thymus
is a specialized primary
lymphoid organ
of the
immune
system
. Within the thymus,
thymus cell
lymphocytes
or
T
cells
mature. T cells are critical to the
adaptive immune
system
, where the body adapts specifically to foreign
invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the
chest, in the anterior
superior mediastinum
, behind
the
sternum
, and in front of the
heart
. It is made up of two
lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer
cortex, surrounded by a capsule.
The thymus is made up of immature
T
cells
called
thymocytes
, as well as lining cells
called
epithelial reticulr cells
which help the thymocytes
develop. The thymus is largest and most active during the
neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens,
the
thymus begins to decrease in size and activity
and the
tissue of the thymus is gradually replaced by
fatty tissue
.
Nevertheless, some T cell development continues
throughout adult life
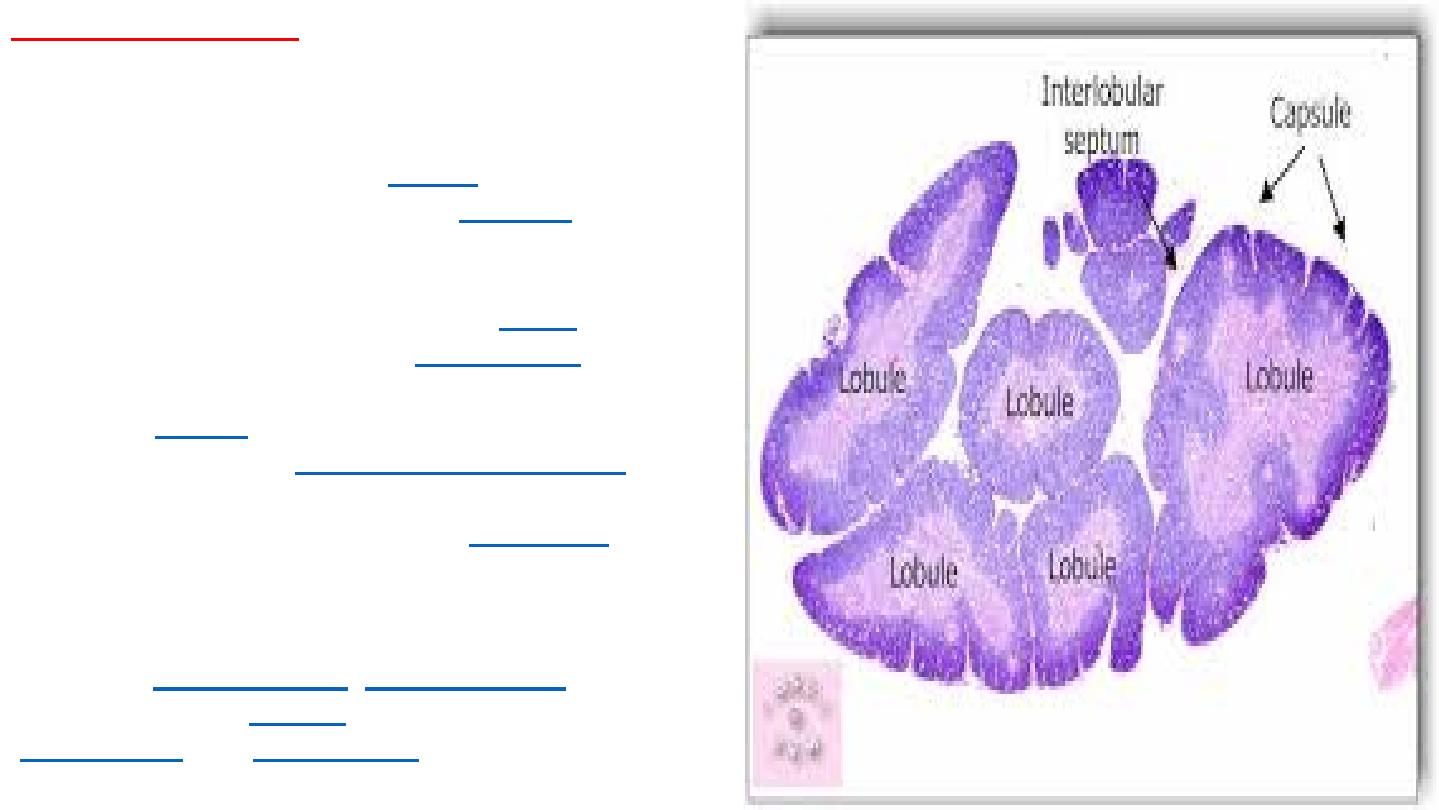
Histology of thymus
The thymus consists of two lobes, merged in the
middle, surrounded by a capsule that extends
with blood vessels into the interior. The lobes
consist of an outer darker
cortex
rich with cells
and an inner less dense lighter
medulla
. The
lobes are divided into smaller lobules 0.5-2mm
diameter, between which extrude radiating
insertions from the capsule along
septa
. The
cortex is mainly made up of
thymocytes
and
epithelial reticular cells. The thymocytes,
immature
T cells
, are supported by a network of
the finely branched
epithelial reticular cells
,
which is continuous with a similar network in the
medulla. This network forms an
adventitia
to the
blood vessels, which enter the cortex via septa
near the junction with the medulla. Other cells are
also present in the thymus,
including
macrophages
,
dendritic cells
, and a
small amount of
B cells
,
neutrophils
and
eosinophils
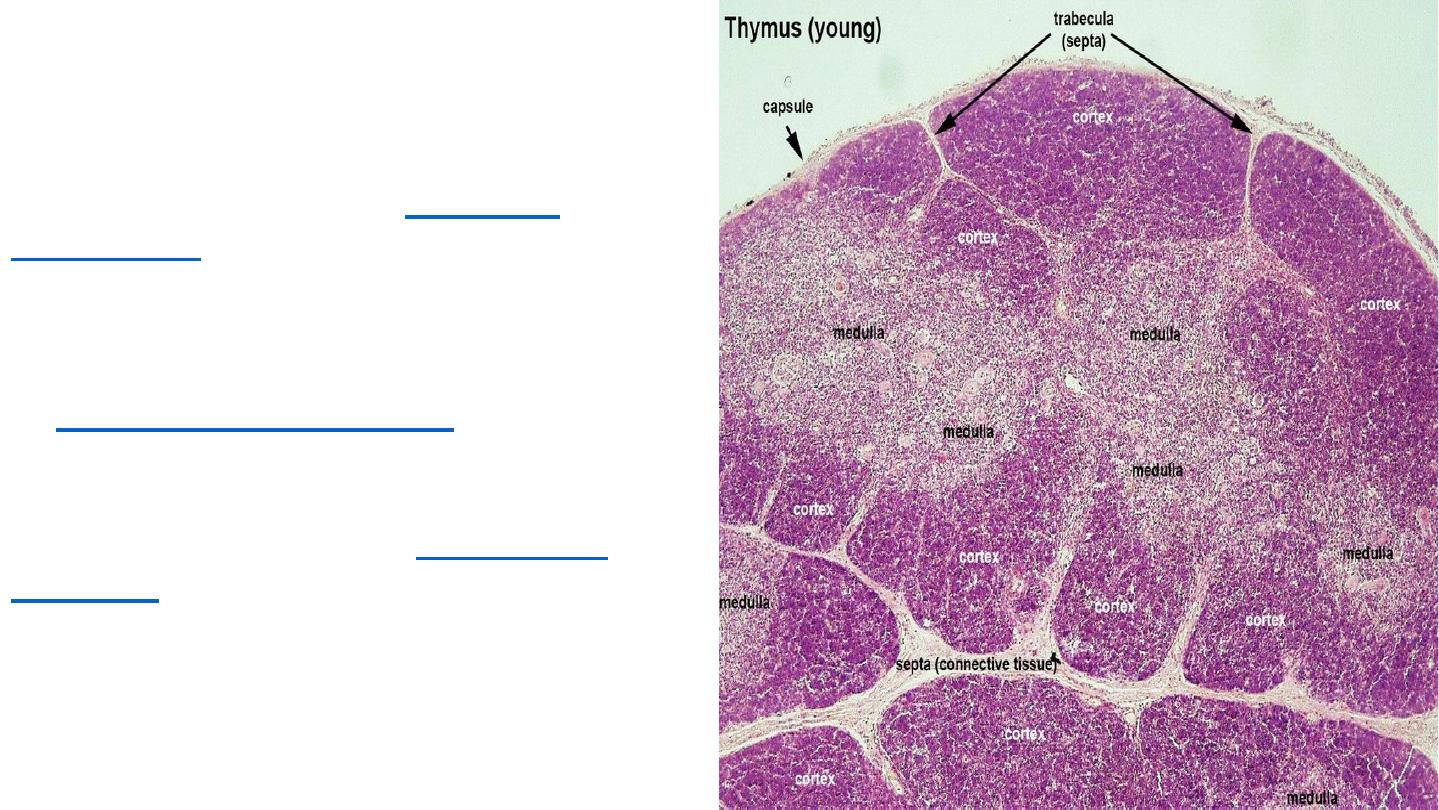
In the medulla, the network of epithelial
reticular cells is coarser than in the
cortex, and the lymphoid cells are
relatively fewer in number. Concentric,
nest-like bodies called
Hassall's
corpuscles
(also called thymic
corpuscles) are formed by aggregations
of the medullary epithelial reticular cells.
These are concentric, layered whorls
of
epithelial reticular cells
that increase
in number throughout life. They are the
remains of the epithelial tubes, which
grow out from the third
pharyngeal
pouches
of the embryo to form the
thymus.
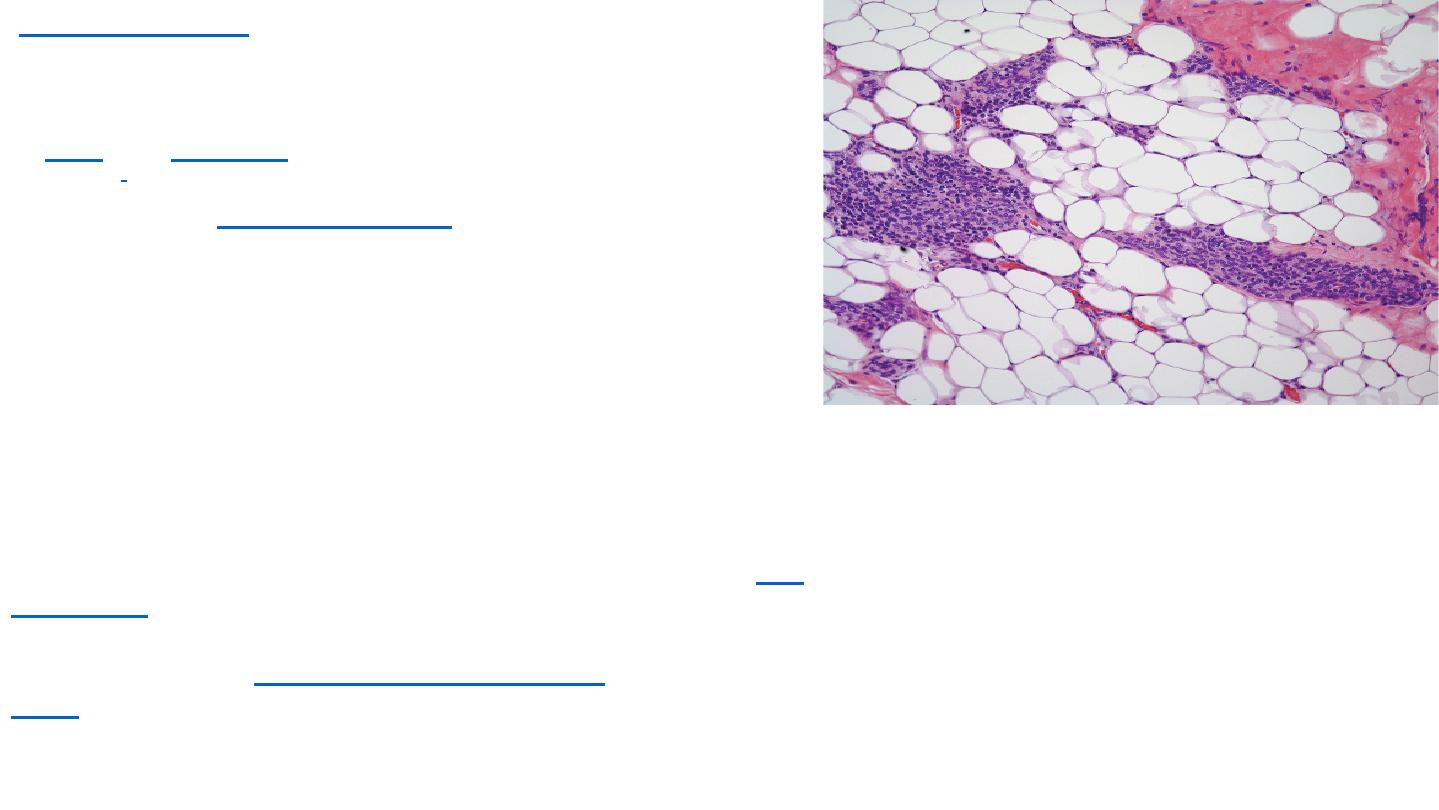
Thymic involution
The thymus continues to grow after the birth reaching the
relative maximum size by puberty. It is most active
in
fetal
and
neonatal
life. It increases to 20 - 50 grams by
puberty.
]
It then begins to decrease in size and activity in a
process called
thymic involution
. After the first year of life
the amount of T cells produced begins to fall. Fat and
connective tissue fills a part of the thymic volume. During
involution, the thymus decreases in size and activity. Fat
cells are present at birth, but increase in size and number
markedly after puberty, invading the gland from the walls
between the lobules first, then into the cortex and medulla.
This process continues into old age, where whether with
a microscope or with the human eye, the thymus may be
difficult to detect. although typically weights 5 - 15 grams.
The atrophy is due to the increased circulating level of
sex
hormones
, and chemical or physical castration of an adult
results in the thymus increasing in size and activity.
Severe illness or
human immunodeficiency
virus
infection may also result in involution.

Thank you for
listening
