
Objectives:
1-Describe the morphology of smooth muscles.
2-Recognize the types of smooth muscles and their properties.
3-List the steps in smooth muscle contraction.
4-Outline the factors affecting smooth muscle contraction.

Morphology:
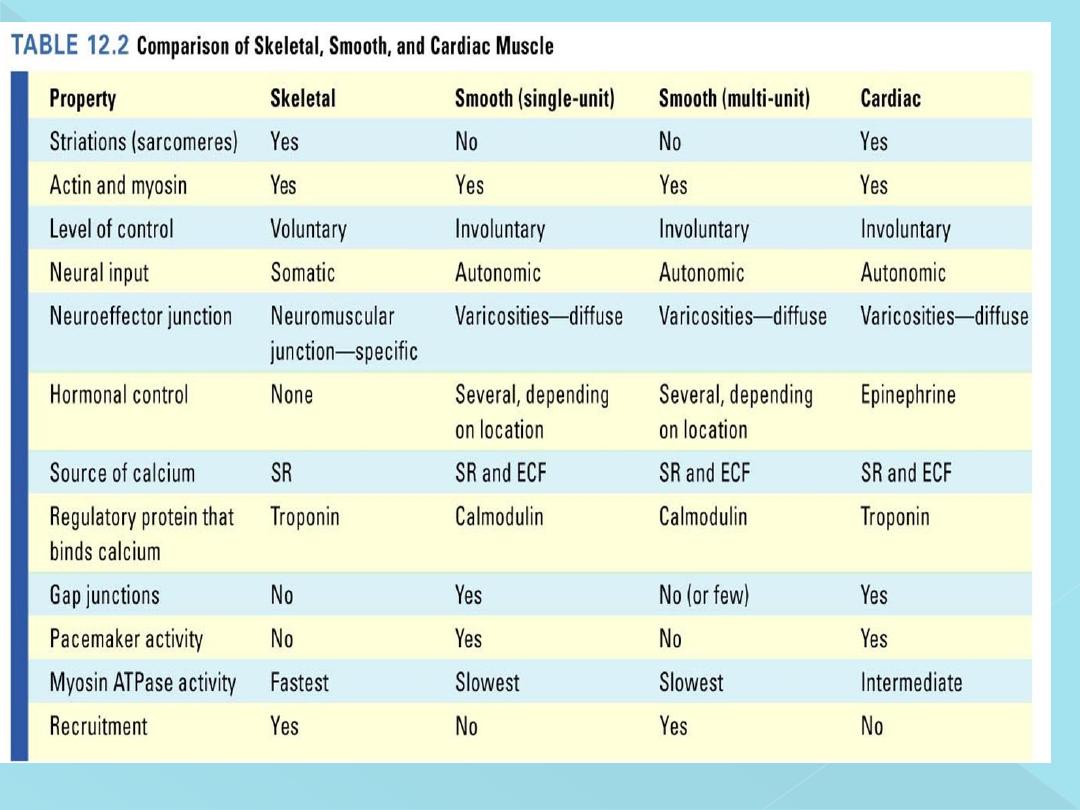
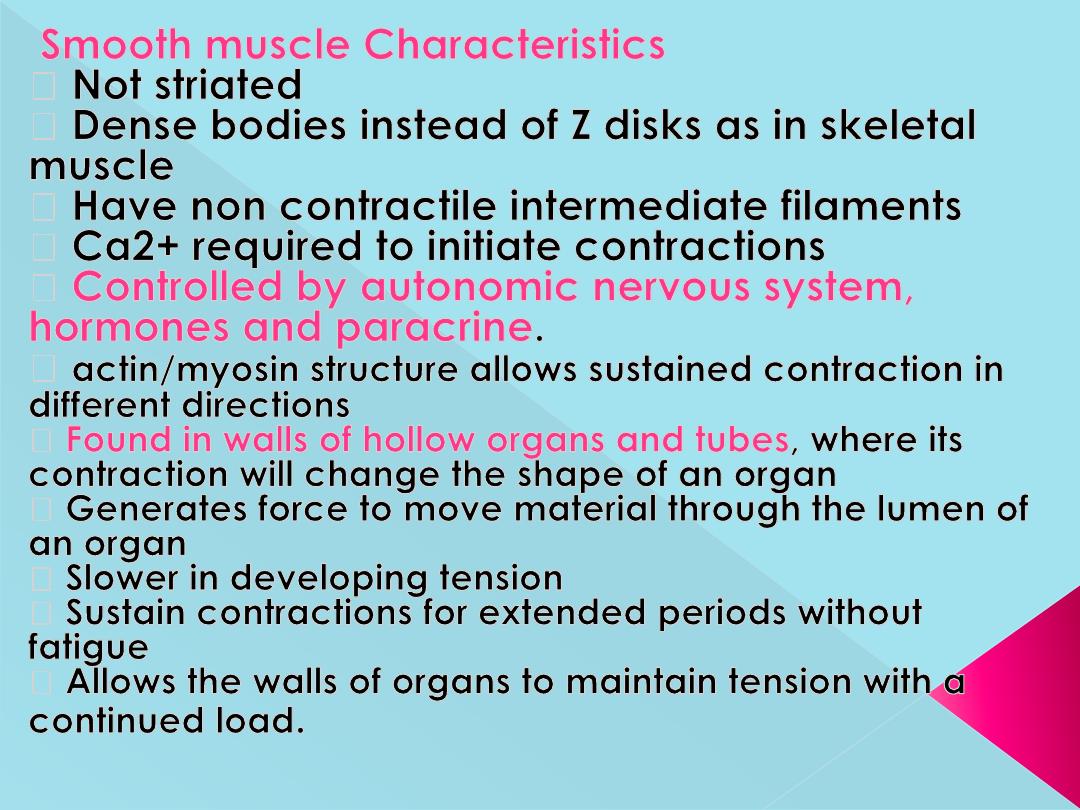
-Lack visible cross striations.
-Actin and myosin are present.
-There are dense bodies instead of Z lines.
-Contain tropomyosin but toponin absent.
-Poorly developed sarcoplasmic reticulum
-Few mitochondria so depend on glycolysis in their
metabolism
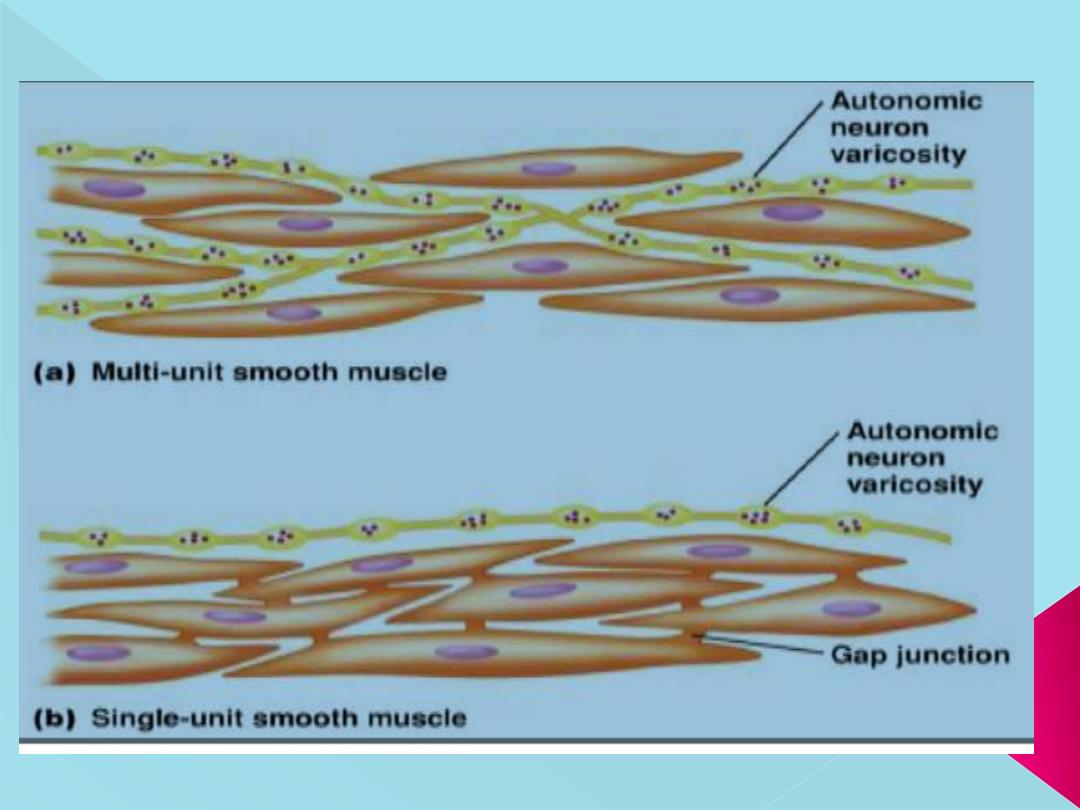
Types of smooth muscles
2 Types:
-Visceral smooth muscle (unitary or single unit).
-Multi-unit smooth muscle
.


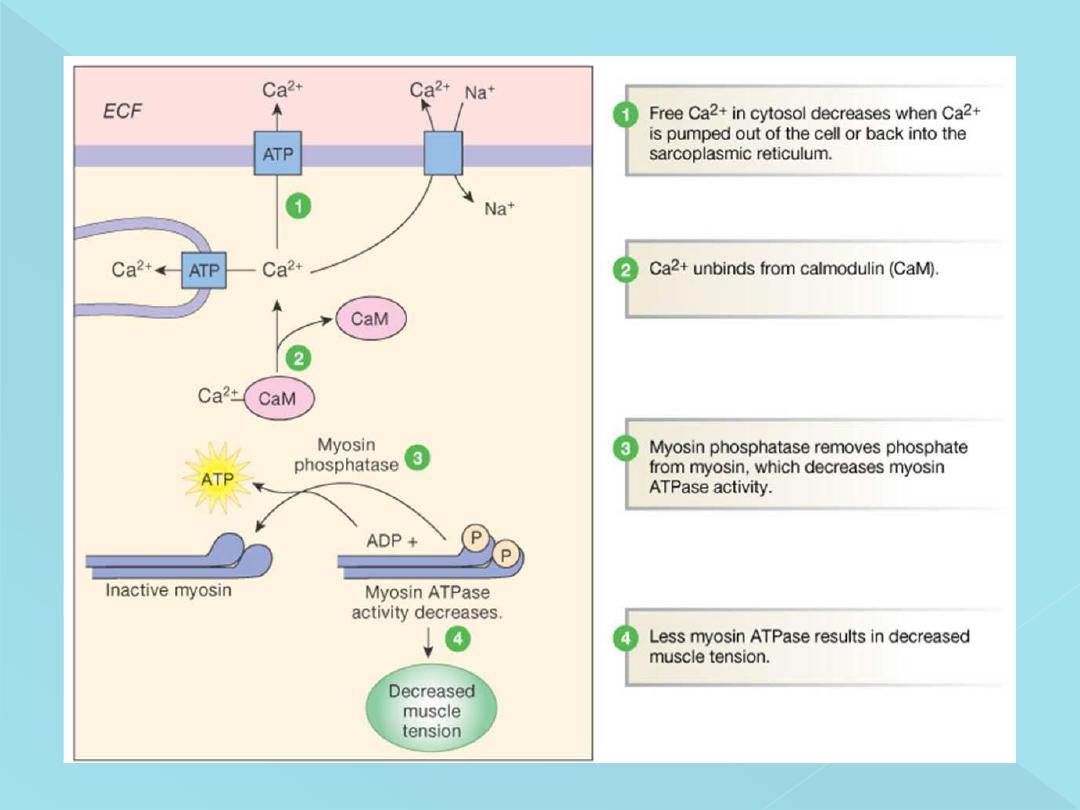
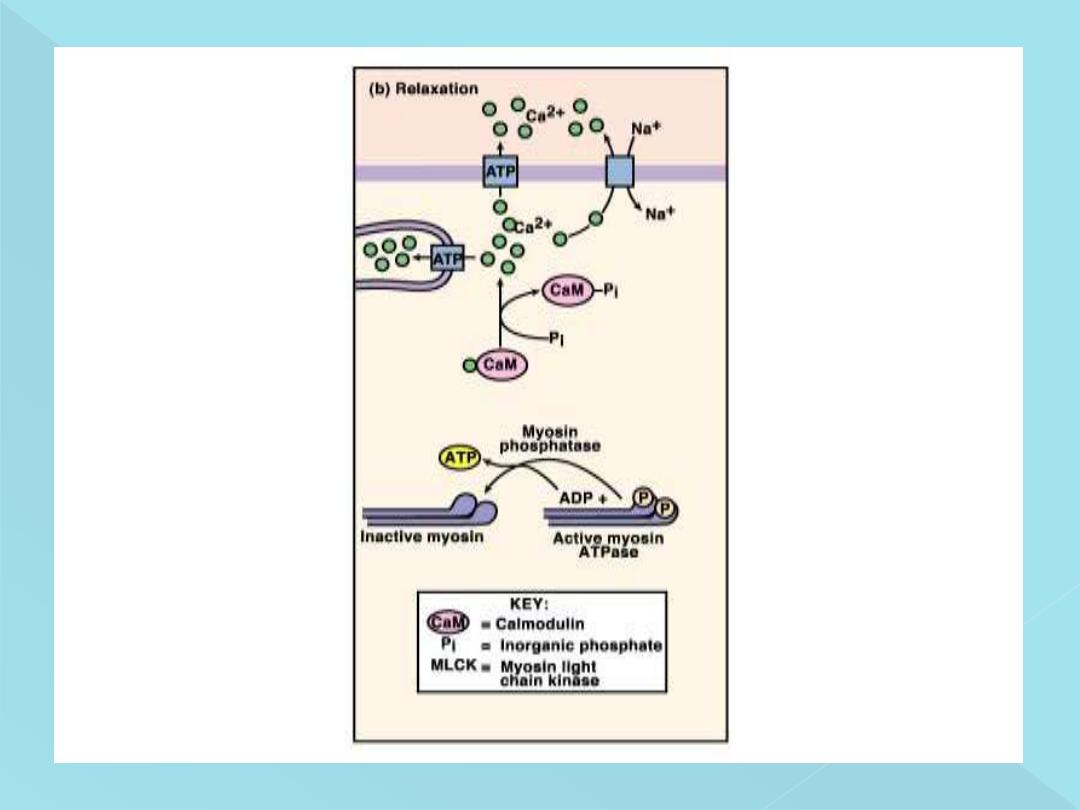
Myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP), located in the fluids of
the smooth muscle cell, which splits the phosphate from the
regulatory light chain. Then the cycling stops and contraction
ceases. The time required for relaxation of muscle contraction,
therefore, is determined to a great extent by the amount of active
و
myosin phosphatase in the cell
Control of Smooth Muscle Contraction
Although skeletal muscle fibers are stimulated exclusively by the nervous
system, smooth muscle can be stimulated to contract by multiple types of
signals: by nervous signals, by hormonal stimulation, chemical factors, by
stretch of the muscle, and in several other ways.
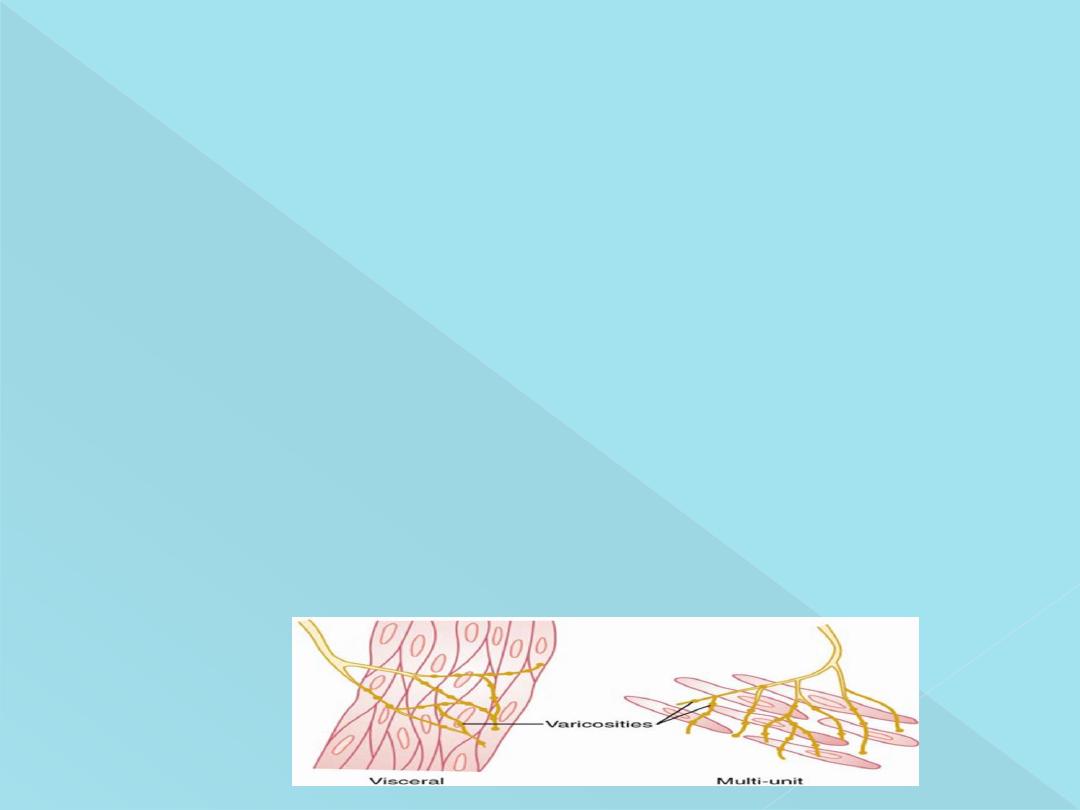
Nervous signals:
Neuromuscular Junctions of the Highly Structured Type
Found on Skeletal Muscle Fibers Are Not Present in Smooth Muscle Instead,
the autonomic nerve fibers that innervate smooth muscle generally branch
diffusely on top of a sheet of muscle fibers, as shown in Figure bellow. In
most instances, these fibers do not make direct contact with the smooth
muscle fiber cell membranes but instead form so-called Diffuse junctions :
These are the sites of transmitter release. that secrete their transmitter
substance into the matrix coating of the smooth muscle; the transmitter
substance then diffuses to the cells.
Varicosities of the axons
: The axons that innervate smooth muscle fibers do
not have typical branching end feet of the type found in the motor nerves
on skeletal muscle fibers. Instead, most of the fine terminal axons have
multiple varicosities that are distributed along their axons. The varicosities
contain vesicles loaded with transmitter substance.
Contact junctions
: In the multi-unit type of smooth muscle, the varicosities lie
directly on the muscle fiber membrane. These so-called contact junctions
have a function similar to that of the skeletal muscle neuromuscular
junctions.

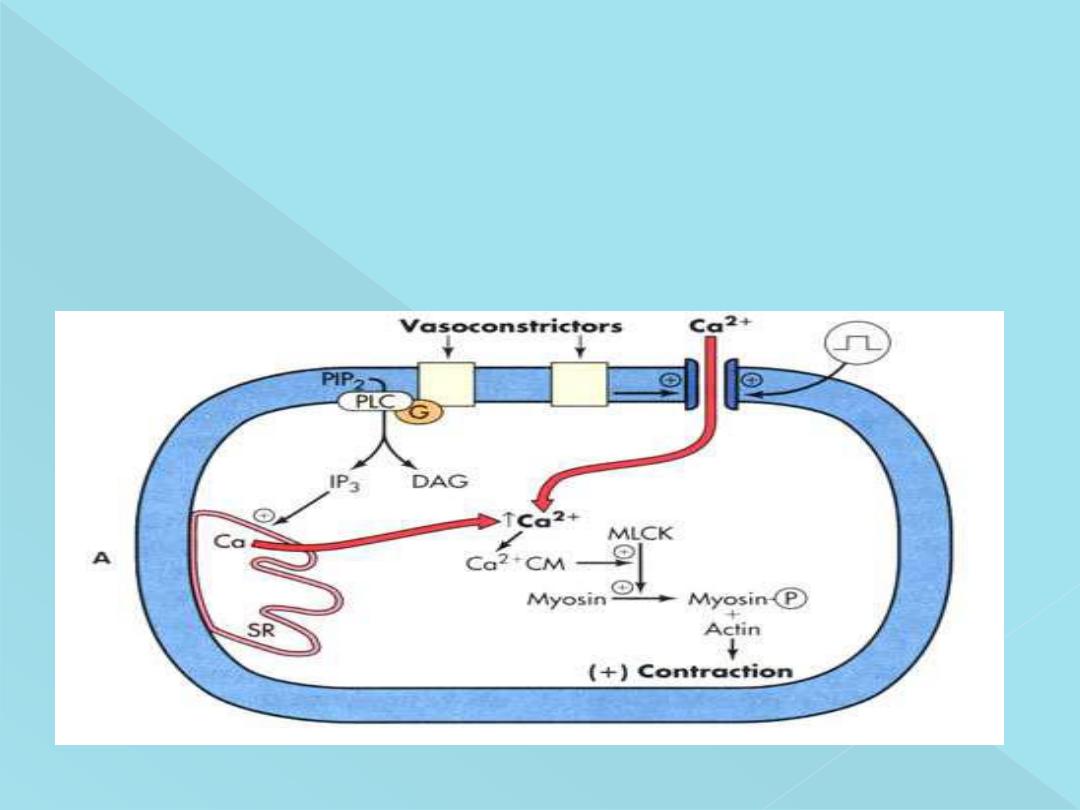
Source of Calcium Ions That Cause Contractio
n
(1) Through the Cell Membrane
(2) From the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Although the contractile process in smooth muscle
،
as in skeletal muscle,
is activated by calcium ions
،
the source of the calcium ions differs; the
difference is that the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which provides virtually all
the calcium ions for skeletal muscle contraction
،
is only slightly
developed in most smooth muscle. Instead, almost all the calcium ions
that cause contraction enter the muscle cell from the
extracellular fluid
at
the time of the action potential or other stimulus
.
The Figure bellow shows a few slightly developed sarcoplasmic tubules
that lie near the cell membrane in some larger smooth muscle cells.
Smallinvaginations of the cell membrane, called caveolae, about the
surfaces of these tubules. The caveolae
suggest a rudimentary analog of the
transverse tubule system of skeletal muscle
The calcium ions, which are responsible for excitation-contraction coupling, must be
obtained from the extracellular fluid. It makesthe process of excitation-contraction
coupling slow.
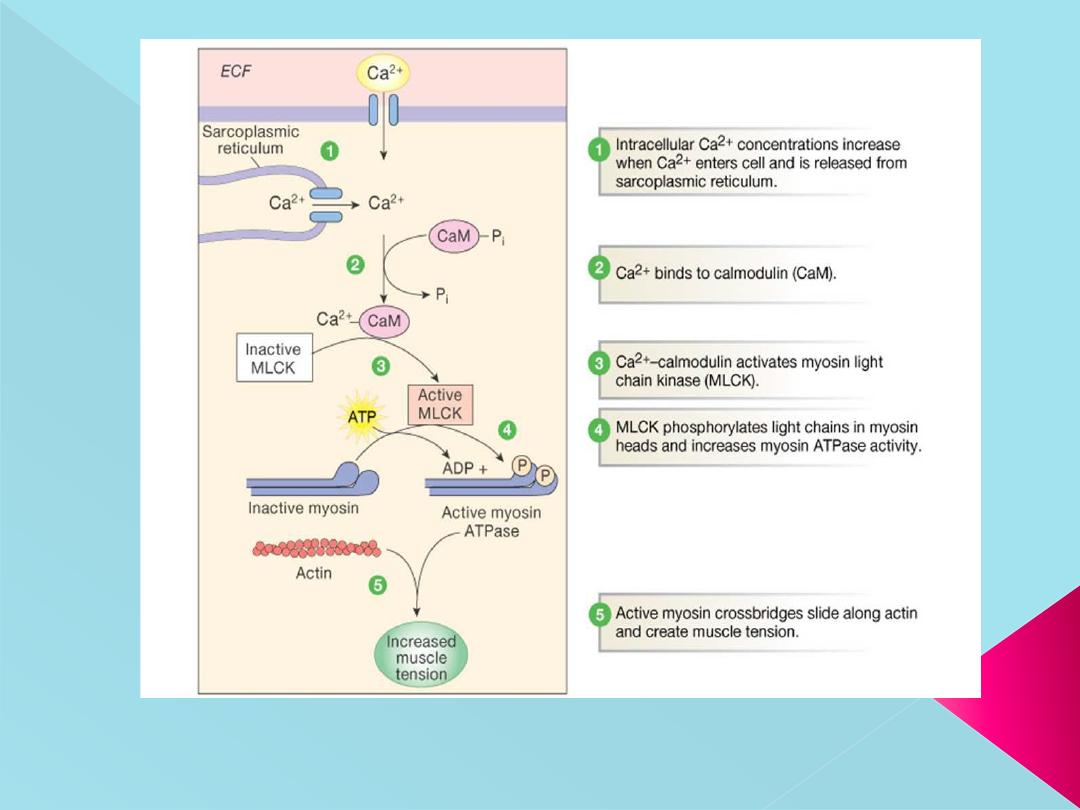
**Calcium-calmodulin Complex
**Stimulation of ATPase activity of myosin in smooth muscle is different from that in the
skeletal muscle.
In smooth muscle, the myosin has to be phosphorylated for the activation of myosin
ATPase.

Phosphorylation of myosin occurs in the following manner
:
1. Calcium, which enters the sarcoplasm from the extracellular fluid
combines with a protein called calmodulin and forms calcium-calmodulin
complex
2. It activates calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase
3. This enzyme in turn causes phosphorylation of myosin followed by
activation of myosin ATPase
4. Now, the sliding of actin filaments starts.
Phosphorylated myosin gets attached to the actin molecule for longer
period. It is called latch-bridge mechanism and it is responsible for the
sustained contraction of the muscle with expenditure of little
energy.
Relaxation of the muscle occurs due to dissociation
of calcium-calmodulin complex

Electrical & Mechanical Activity:
Visceral smooth muscle: It is characterized by the
instability of its membrane potential and by the fact
that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are
independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state
of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is
no true "resting" value for the membrane potential,
but it averages about -50 mV, when the muscle active it
becomes low and high during inhibition.

Two types of action potentials occur in smooth
muscles
:
Spike Potential:
Typical spike action potentials,
such as those seen in skeletal muscle, occur in
most types of unitary smooth muscle. The duration
of this type of action potential is 10 to 50
milliseconds.
Action Potentials with Plateaus:
The onset of this
action potential is similar to that of the typical
spike potential. However, instead of rapid
repolarization of the muscle fiber membrane, the
repolarization is delayed for several hundred to
as much as 1000 milliseconds (1 second). The
importance of the plateau is that it can account
for the prolonged contraction that occurs in some
types of smooth muscle, such as the ureter, the
uterus under some conditions, and certain types
of vascular smooth muscle.

Smooth Muscle Contraction in Response to Local Tissue
Chemical Factors or hormones
The smallest blood vessels have little or no nervous supply. Yet
the smooth muscle is highly contractile, responding rapidly to
changes in local chemical conditions in the surrounding
interstitial fluid.
In the normal resting state, many of these small blood vessels
remain contracted. But when extra blood flow to the tissue is
needed, multiple factors can relax the vessel wall, thus
allowing for increased flow. In this way, a powerful local
feedback control system controls the blood flow to the local
tissue area.
Some of the specific control factors are as follows
:
1 .Lack of oxygen in the local tissues causes smooth muscle
relaxation and, therefore, vasodilatation.
2. Excess carbon dioxide causes vasodilatation.
3. Increased hydrogen ion concentration causes
vasodilatation.
4. increased body temperature can cause local
vasodilatation

Contraction of Visceral Smooth Muscle by Muscle
Stretch
When visceral (unitary) smooth muscle is stretched sufficiently,
spontaneous action potentials usually are generated.
They result from a combination of (1)the normal slow wave potentials
and (2) decrease in overall negativity of the membrane potential
caused by the stretch itself.
This response to stretch allows the gut wall, when excessively
stretched, to contract automatically and rhythmically. For instance,
when the gut is overfilled by intestinal contents, local automatic
contractions often set up peristaltic waves that move the contents
away from the overfilled intestine, usually in the direction of the anus