
College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
Trichomonas
:
Objectives:
The main objectives of this lecture are:
Trichomonas vaginalis (Biology, transmission, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis,
treatment and prevention).
Other trichomonas as Ttichomonas tenax and Trichomonas hominis
Trichomonas vaginalis:
• Trichomoniasis is the most prevalent non-viral sexually transmitted infection affecting an
estimated 3.7 million persons in USA.
• It is an anerobic, flagellated motile protozoan parasite.
• Alfred Francois Donné (1801-1878) was the first to describe a procedure to diagnose
trichomoniasis through "the microscopic observation of motile protozoa in vaginal or
cervical secretions in 1836.
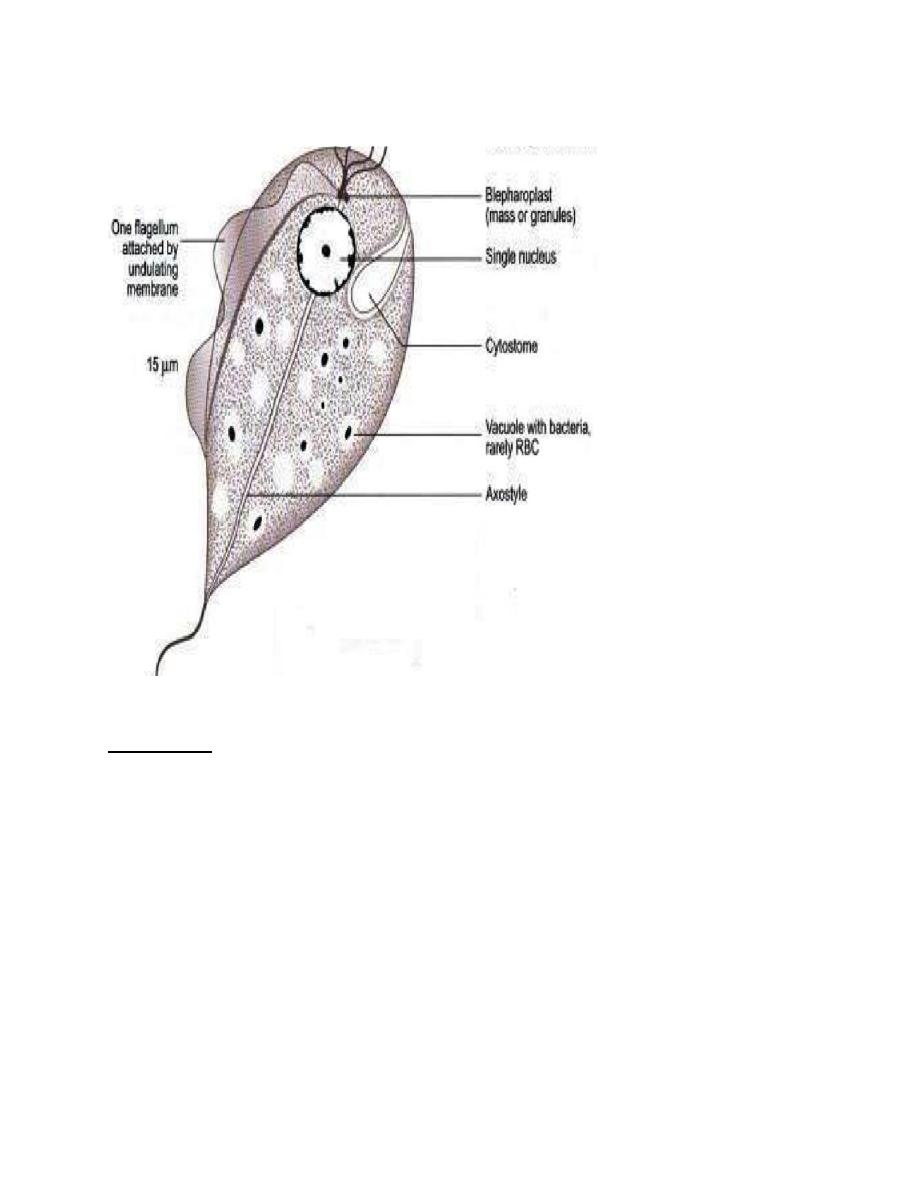
Morphology:
• Trichomonas vaginalis exists in only one morphological stage, a trophozoite that cannot
encyst.
• The T. vaginalis trophozoite is oval, flagellated, pear shaped as seen on a wet-mount.
• It is slightly larger than a white blood cell, measuring 9 × 7 μm.
• Five flagella arise near the cytostome; four of these immediately extend outside the cell
together, while the fifth flagellum wraps backwards along the surface of the organism. In
addition, a conspicuous barb-like axostyle projects opposite the four-flagella bundle.
• The axostyle may be used for attachment to surfaces and may also participate in the
tissue damage seen in trichomoniasis. While T. vaginalis does not have a cyst form,
organisms can survive for up to 24 hours in urine, semen, or even water samples.
• Trophozoites divide by binary fission.
•
Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoite.(1).
College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
Trophozoite of T. vaginalis (2).
Transmission
• The trophozoite cannot survive outside and so infection has to be transmitted directly
from person-to-person.
• Sexual transmission is the usual mode of infection. Trichomoniasis often coexists with
other sexually transmitted diseases like candidiasis, gonorrhea, syphilis, or human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
• Babies may get infected during birth.
• Vaginal pH of > 4.5 facilitates infection.
• Fomites such as towels may transmit infection.
Habitat
In females, it lives in vagina and cervix, and may also be found in Bartholin 's glands, urethra
and urinary bladder. In males, it occurs mainly in the anterior urethra, but may also be found in
the prostate and preputial sac.
College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
Infective stage:
• The trophozoite itself is the infective form.
Pathogenesis
• T. vaginalis particularly infects squamous epithelium but not columnar epithelium.
• It is an obligate parasite and cannot live without close association with the vaginal,
urethral, or prostatic tissues.
• It secretes cysteine proteases, adhesins, lactic acid and acetic acid, which disrupt the
glycogen and lower the pH of the vaginal fluid.
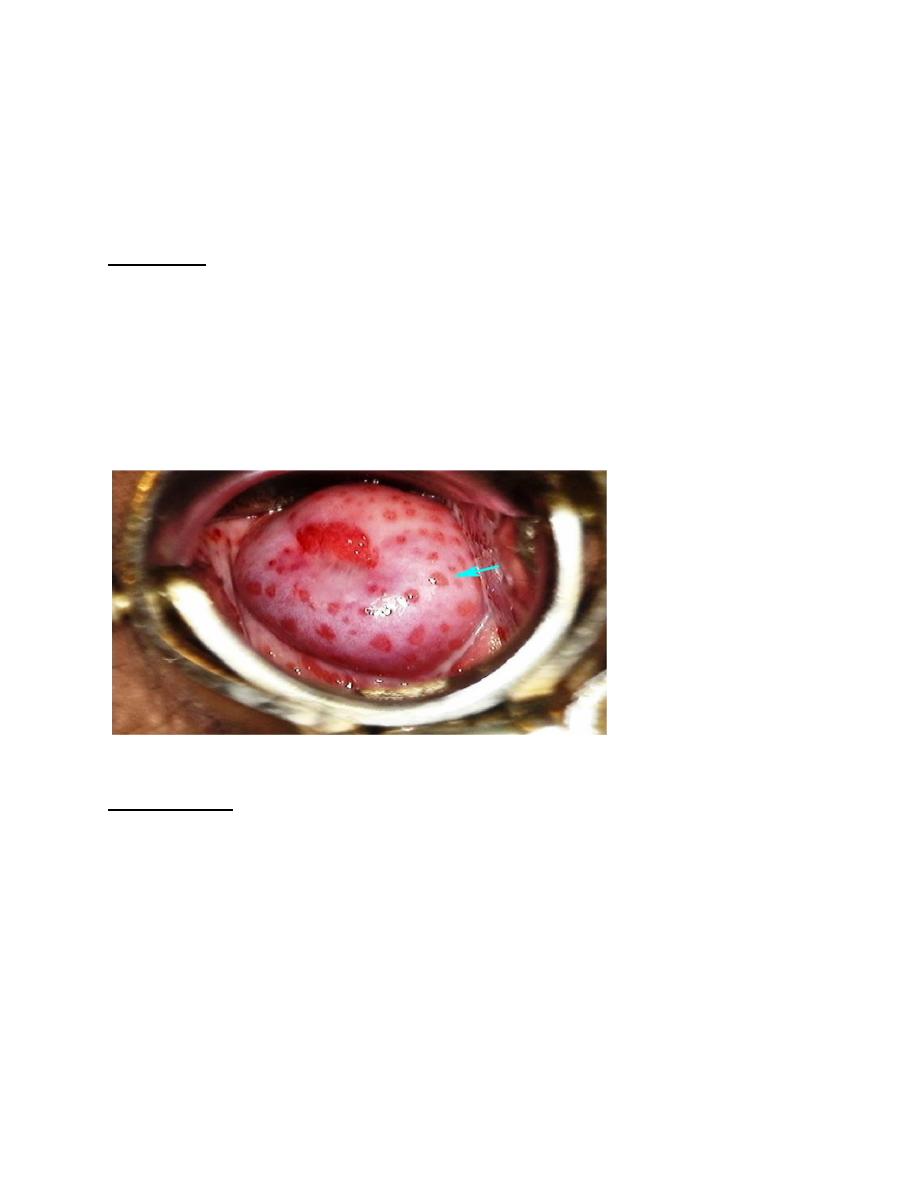
• Parasite causes petechial hemorrhage and mucosal capillary dilation (strawberry
mucosa), metaplastic changes and desquamation of the vaginal epithelium.
• Intracellular edema and so called chicken-like epithelium, which is the characteristic
feature of trichomoniasis.
Strwberry mucosa(3).
Clinical picture:
• The incubation period of trichomoniasis is 4 days to 4 weeks.
• Infection is often asymptomatic, particularly in males, although some may develop
urethritis, epididymitis and prostatitis.
• In females, it may produce severe pruritic vaginitis with an offensive, yellowish green,
often frothy discharge, dysuria and dyspareunia.
• Cervical erosion is common.
• Endometritis and pyosalpingitis are infrequent complications.
• Rarely, neonatal pneumonia and conjunctivitis have been reported in infants born to
infected mothers.
• T. vaginalis infection is associated with two to threefold increased risk for HIV
transmission, preterm birth, and other adverse pregnancy outcomes among pregnant
women.

College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
• Among women with HIV infection, T. vaginalis infection is associated with increased
risk for pelvic inflammatory diseases and developing cervical cancer.
Diagnosis
• Diagnostic testing for T. vaginalis should be performed in women seeking care for
vaginal discharge.
• Screening might be considered for persons receiving care in high-prevalence settings
(e.g., sexual transmitted disease clinics) and for asymptomatic persons at high risk for
infection (e.g., persons with multiple sex partners, drug addicts, or a history of STD).
Tests commonly used:
1. Microscopic wet mount examination:
The most common method for T. vaginalis diagnosis might be microscopic evaluation of wet
preparations of genital secretions because of convenience and relatively low cost.
Unfortunately, the sensitivity of wet mount is low (51%–65%) in vaginal specimens and lower in
specimens from men (e.g., urethral specimens, urine sediment, and semen).
Clinicians using wet mounts should attempt to evaluate slides immediately because sensitivity
declines as evaluation is delayed, decreasing by up to 20% within 1 hour after collection
• Organisms lose motility ex vivo because of temperature shock, so slides should be
prepared and read as soon as possible following collection in order to avoid false-
negative results.
• The motile trichomonads move in a characteristic jerky and twitching pattern.
2. Fixed smears: may be stained with acridine orange, Papanicolaou and Giemsa stains.
3. NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test (Aptima Trichomonas vaginalis assay)):
• It is highly sensitive (96.5%) and highly specific (97.5%), often detecting three to five
times more T. vaginalis infections than wet-mount microscopy.
• It is the gold standard test.
4. Affirm VPIII: nucleic acid probe test:
• For the diagnosis of T. vaginalis as well as Gardnerella vaginalis and Candida
albicans in females.
• This test can be run and give results in 45 minutes with sensitivity 90-95% and
specificity of 92-100%.
5. OSOM Trichomonas Rapid Test:
• It is used to detect T. vaginalis in vaginal secretions.
• It is an antigen-detection test uses immune chromatographic capillary flow
dipstick technology that can be performed at the point of care.
• The results of the OSOM Trichomonas Rapid Test are available in approximately
10 minutes, with sensitivity 82%–95% and specificity 97%–100%.
• Self-testing might become an option.
6. Culture with a modified diamond medium:
• It was considered as the gold standard method for diagnosing T. vaginalis
infection before start of NAAT.

College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
• Culture has a sensitivity of 75%–96% and a specificity of up to 100%.
• In women, vaginal secretions are the preferred specimen type for culture.
• In men, culture specimens require a urethral swab, urine sediment, and/or semen.
• To improve yield, multiple specimens from men can be used to inoculate a single
culture.
• Cultures are assessed by microscopy of a slide prepared from a drop of the culture
medium daily for up to 7 days.
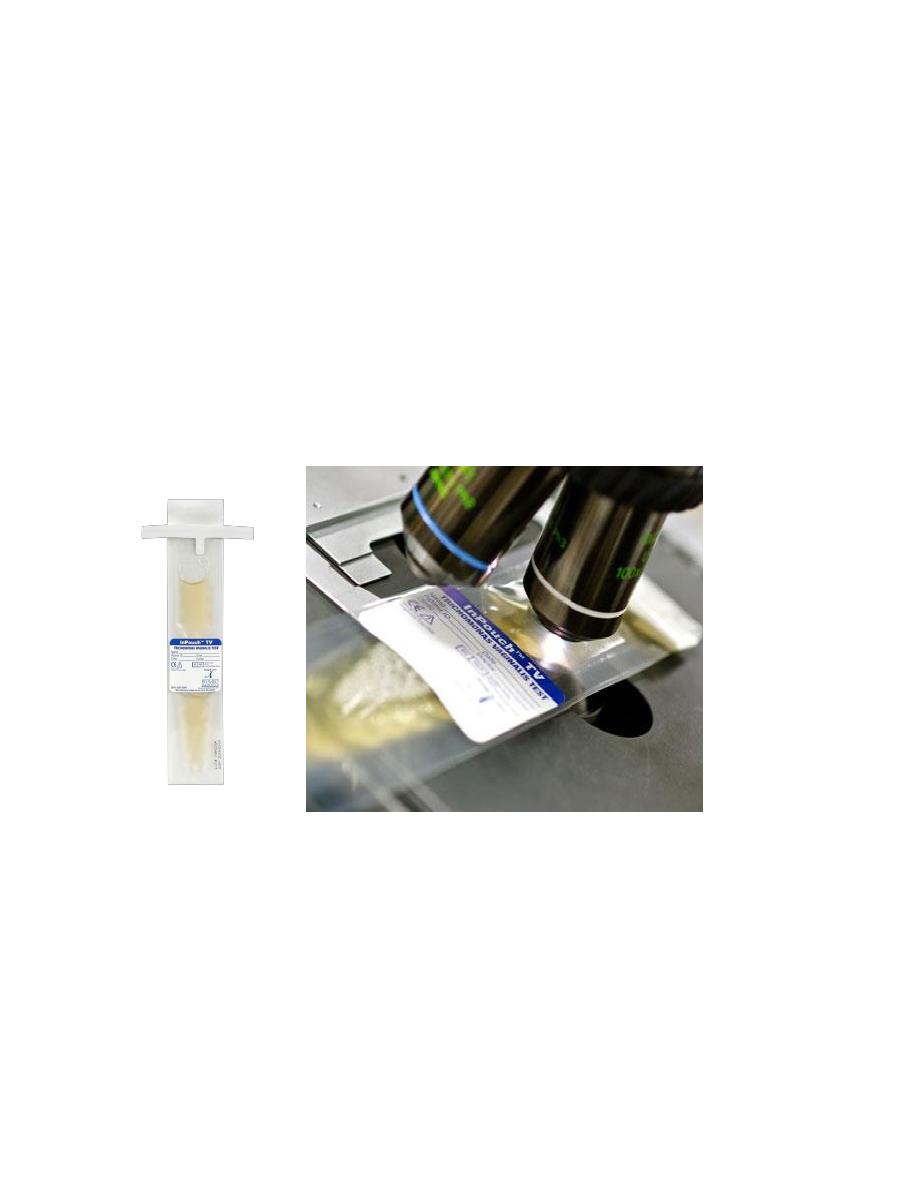
7. The InPouch (Biomed Diag- nostics, Santa Clara, CA) system:
• It contains culture medium in a pouch that can be placed on a microscope stage.
• Thus, the entire volume of the culture can be evaluated for the presence of
trichomonads.
• The InPouch system achieved an incremental increase in sensitivity over routine
culture.
• It is used for collection , Transportation, Incubation and observation of the micro
organism
• The Inpouch culture technique is as sensitive and specific as molecular
techniques in detection of TV
Microscopic examination of Inpouch culture(4).

College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
OSOM test(5).
Treatment
• Simultaneous treatment of both partners is recommended as it is an STD.
• Metronidazole 2 g orally as a single dose or 500 mg orally twice a day for 7 days is the
drug of choice.
• In patients not responding to treatment with standard regime, the dose of metronidazole
may be increased or it may be administered parenterally.
• In pregnancy, metronidazole is safe in 2nd and 3
rd
trimesters.
Prevention
• Prevention is same as for other sexually transmitted diseases.
• Avoidance of sexual contact with infected partners and use of barrier method during
intercourse prevent the disease.
• Patient's sexual partner should be tested for T. vaginalis when necessary.
• Treatment of both partners at the same time.
Trichomonas tenax
• T. tenax, also known as T. buccalis, is a harmless commensal which lives in mouth, in the
periodontal pockets, carious tooth cavities and, less often, in tonsillar crypts .
• It is smaller (5-10 μm) than T. vaginalis.
• It is transmitted by kissing, through salivary droplets and fomites.
• There are sporadic reports of its involvement in respiratory infections and thoracic
abscesses especially in severe lung diseases.
• Better oral hygiene rapidly eliminates the infection and no therapy is indicated.

College of Medicine University of Mosul /Department of: Microbiology
Subject: Parasitology Stage: 3
rd
2021-2022
Lecturer: Dr. Ahmed Alharbi Date: 1/12/2021 No.6
Trichomonas Hominis
• T. hominis measures 8- 12 μm, pyriform-shaped, and carries five anterior flagella and an
undulating membrane that extends the full length of the body.
• It is a very harmless commensal of the cecum where the organism feeds on bacteria and
food debris.
• Microscopic examination of stool will reveal motile trophozoite of T. hominis.
• The cysts are lemon-shaped having a spiral projection at the anterior end. It measures 5-
10 μm in length and 4-6 μm in breadth and is surrounded by a thick cyst wall.
• Both trophozoites and cysts are demonstrated in the semi-formed stool.
Summary:
• T. Vaginalis is the most important spp among all trichomonas.
• T. Vaginalis is sexually transmitted parasite.
• The commonest diagnostic method is microscopic examination.
• Treatment should be for both partners.
References:
1. CDC.gov
2. Microbeonline.com/laboratory-diagnosis-trichomonas-vaginalis-infections/
3. Health Jade.com
4. Biomed Diag- nostics, Santa Clara, CA
5. Seckisui diagnostics
6. BURTON J. Bogitsh,Clint E. Carter, and Thomas N. Oeltmann, 2013, Human
parasitology 4
th
edition, USA and UK, Elsevier.
7. Britanica.com
8. Paniker J CK , 2018, Paniker
,
s textbook of medical parasitology, 8
th
edition, Newdelhi,
London , Panama, JAYPEE.
9. Labmedica.com
10. Zeibig A. Elizabeth, 2013, Clinical parasitology, USA, Elsevier
