
1
4th stage
جراحة بولية
Lec-5
.د
نعمان
11/10/2015
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
Urology
URETERAL INJURIES
Rare
Etiology
1. External Trauma
Ureteric injuries after external violence are rare, occurring in less than 4% of cases of
penetrating trauma (Gun shot, bullet and shells) and less than 1% of cases of blunt
trauma
Those patients often have significant associated other organs injuries and a devastating
degree of mortality that approaches one third
• .
2. Surgical Injury: Difficult pelvic surgery, gynecological, (hysterectomy & CS), or
vascular surgery.
3. Endoscopic: ureteroscope, TUR & Dormia basket stone extraction.
4. Hyperextension injury of the spine
• Types:
perforation, division or ligation
Ligation:
1- Asymptomatic resulting in renal atrophy.
2- Ureteric colic or pain post operatively with or without fever of UTI, and tender renal
angle.
3- In single kidney: unuria
Ligation of both ureters also result in uremia (obstructive uremia).
• Division & perforation:
Result in urine collection (urinoma) then super added by infection resulting in abscess
formation, fever, rigor and abdominal pain.
ureterocutaneous or
from the wound or vagina (
urine leak
More commonly
ureterovaginal fistula
) about 10
th
post operative day.

2
Clinical presentation
• Hematuria : sometimes
• Delayed presentation of ureteral injuries Fever, leukocytosis, and local peritoneal
irritation (Signs of internal abscess formation (infected urinoma)) are the
most common signs and symptoms of missed ureteral injury and should always
prompt CT scan examination.
•
.
• Post operative colic.
• Post operative urine leak (urinary fistula).
• Post operative uremia.
• Asymptomatic
Diagnosis
A high index of suspicion is required in cases of potential ureteral injury
Laboratory investigations
• GUE : hematuria ?
• Renal function tests: normal, and elevated in uremia.
• CBC : leukocytosis
• Imaging Studies
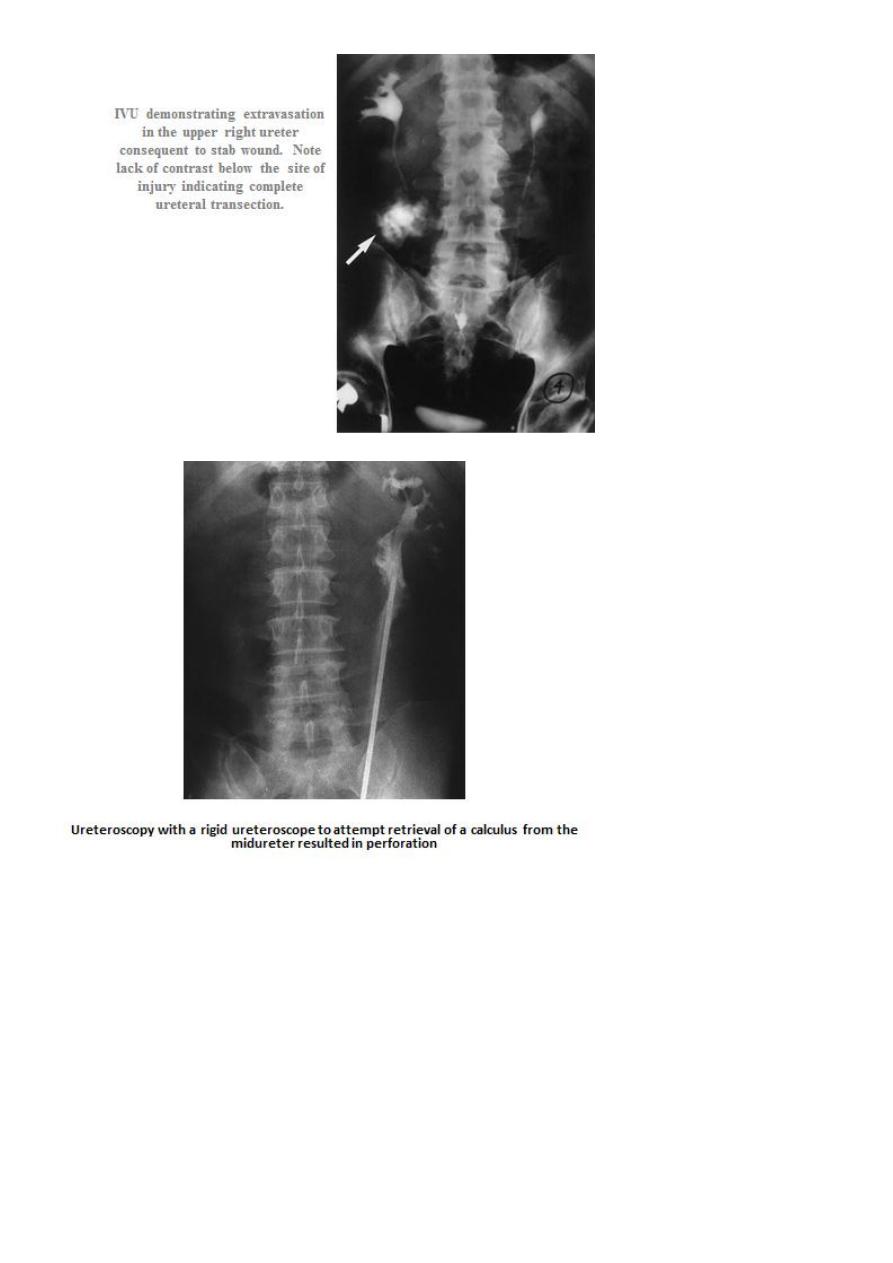
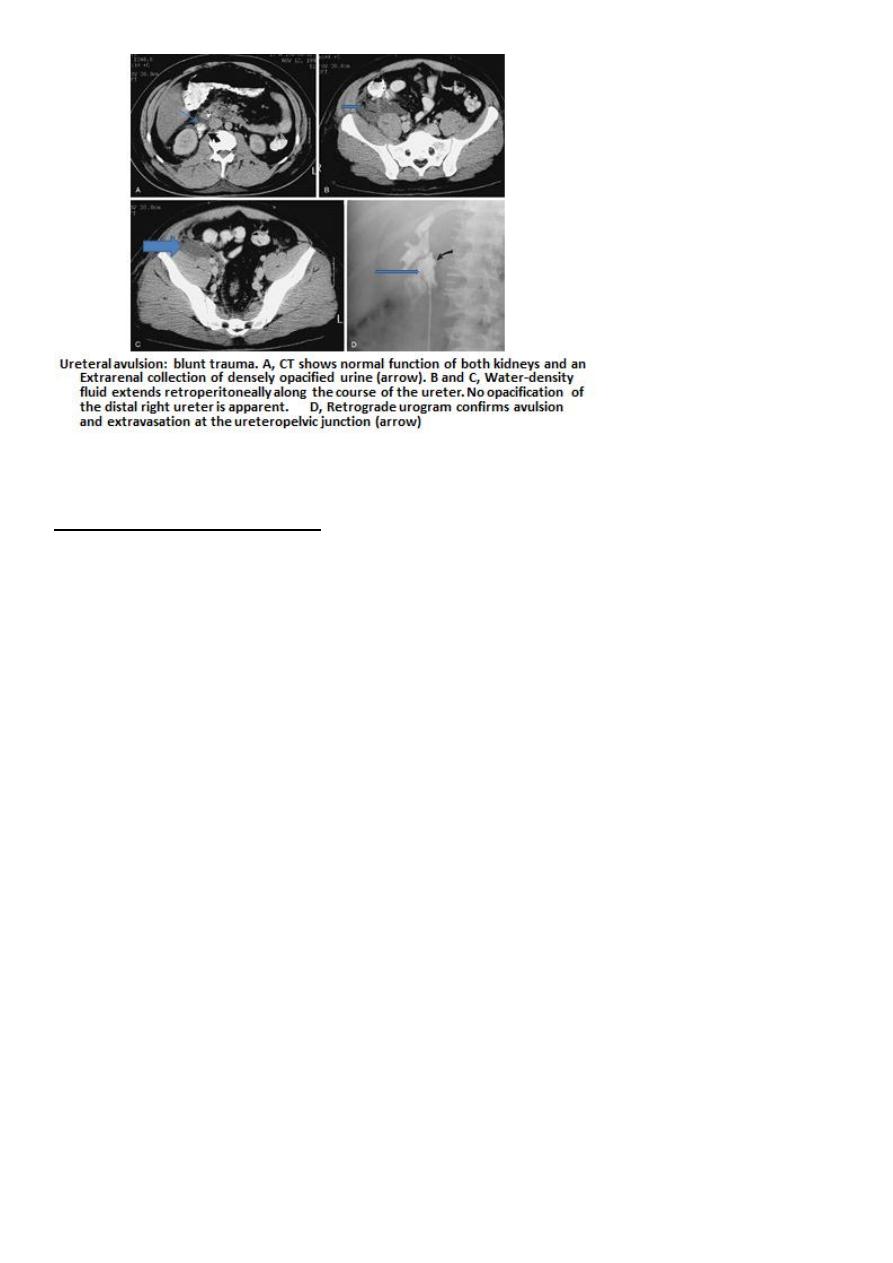
• U/S: hydronephrosis in ligation and urinoma in division.
• IVU contrast leak in division, hydronephrosis or poor function in ligation.
• CT scan with contrast: diagnostic
• Retrograde pyelography: obstruction in ligation and contrast leak in division.
•
3
4
Management of ureteric injury
Prevention is better than treatment.
Proper identification of the ureter before uterine artery ligation in gynecological operations
or pre-operative stenting in pelvic surgeries.
The aim is to regain the continuity of the ureter, preserving renal function and decreasing
the morbidity.
Management (Surgical options )
• Perforation: ureteric stenting using DJ stent ( double J or JJ stent ). If it is possible
to insert a stent endoscopically past a partial ureteric obstruction, an open repair
may be avoidable.
• Ligation: excision of the ischemic segment with end to end anastamosis.
• Division or Transection: refreshment of the ends with end to end anastamosis.
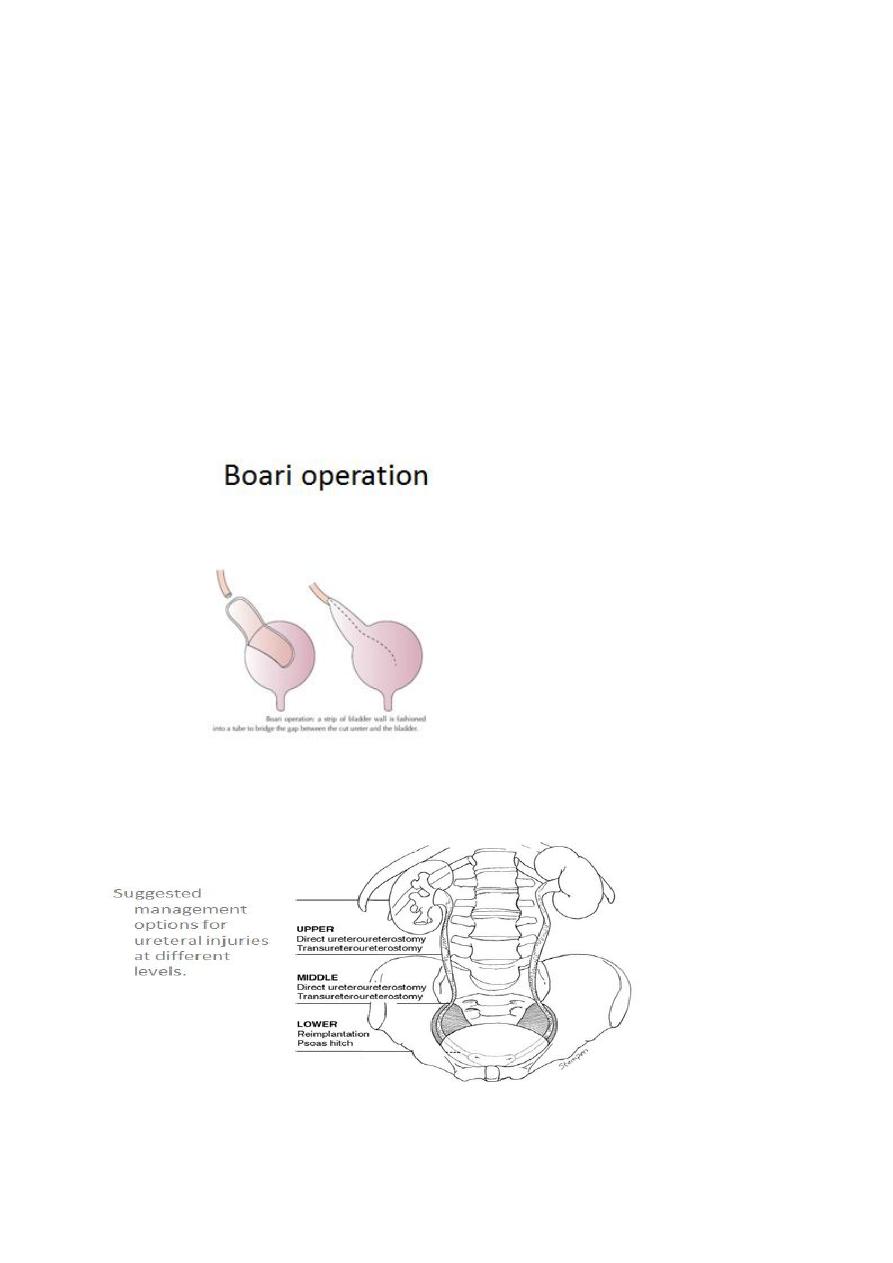
Methods for repairing a damaged ureter
• If there is no loss of length: Spatulation and end-to-end
anastomosis without tension
• If there is little loss of length: Mobilise kidney, Psoas hitch of bladder, Boari
operation
• If there is marked loss of length: Transureteroureterostomy, Interposition of
isolated bowel loop or, mobilised appendix, or Nephrectomy
5
• Upper Ureteral Injuries
Direct Ureteroureterostomy (end to end anastamosis)
Transureteroureterostomy. To the other ureter ( end to side anastamosis
)
Autotransplantation
Bowel Interposition (ileal transposition): Using the appendix to bridge the
defect in the right side
Mid Ureteral Injuries
• Ureteroureterostomy
• Transureteroureterostomy
Lower Ureteral Injuries
• Ureteroneocystostomy (ureteric reimplantation ) with Psoas Bladder Hitch
• Boari Flap
