Tooth impaction
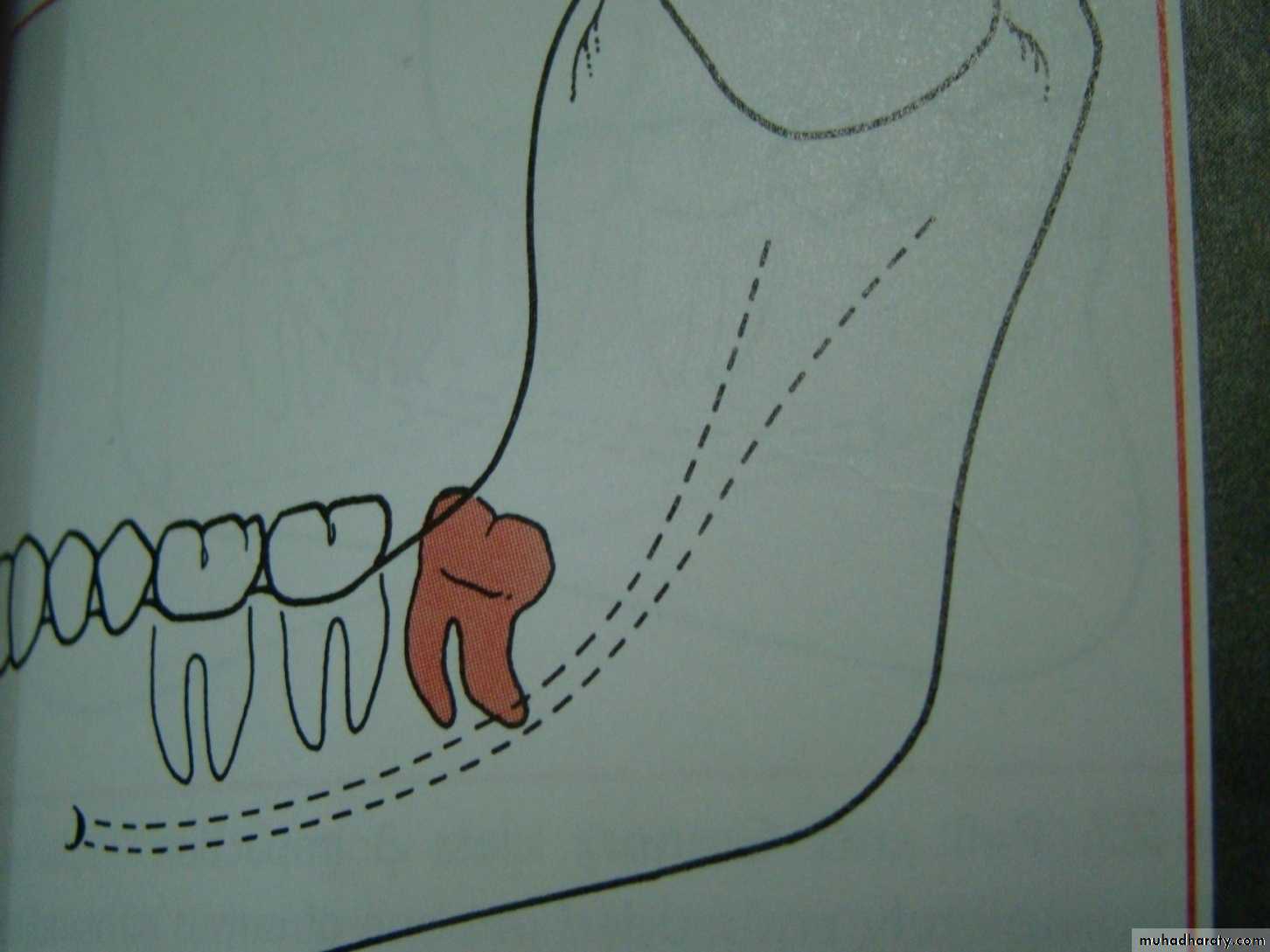
Impacted tooth is a tooth that fails to erupt into its normal functioning position in the dental arch within the expected time of eruption .
unerupted teeth include both impacted teeth and teeth that are in the process of erupting.
Definition of impacted teeth
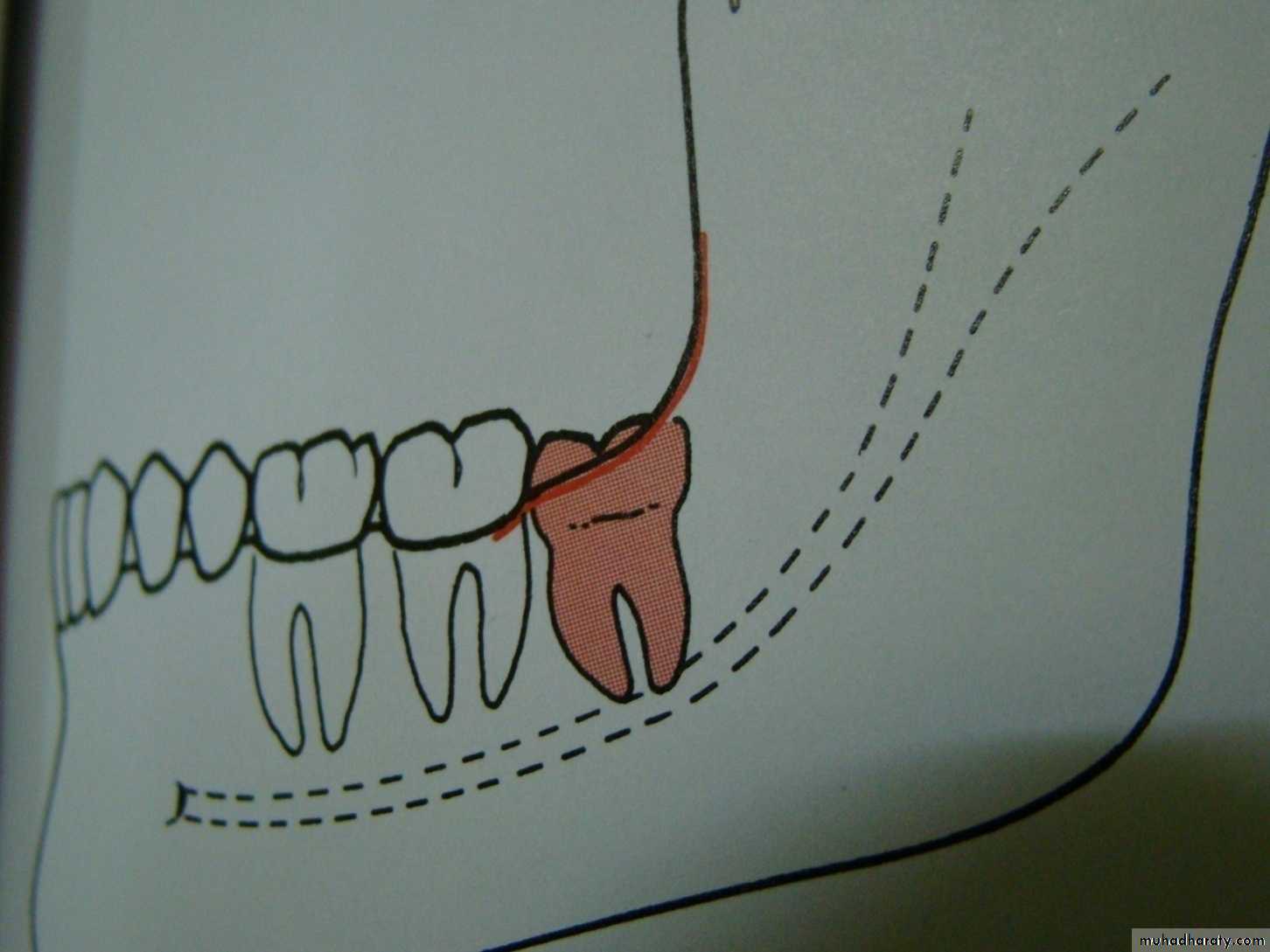
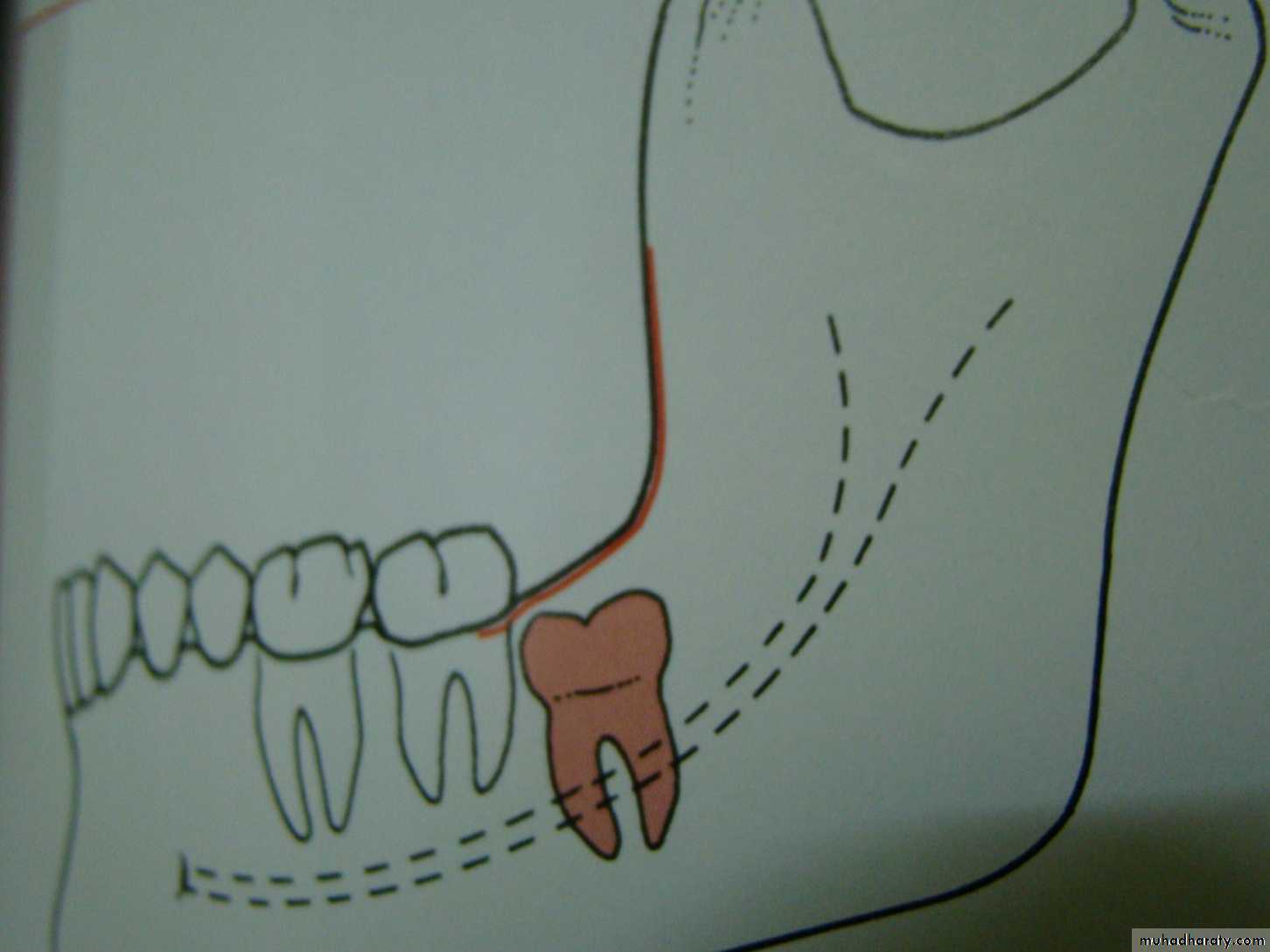
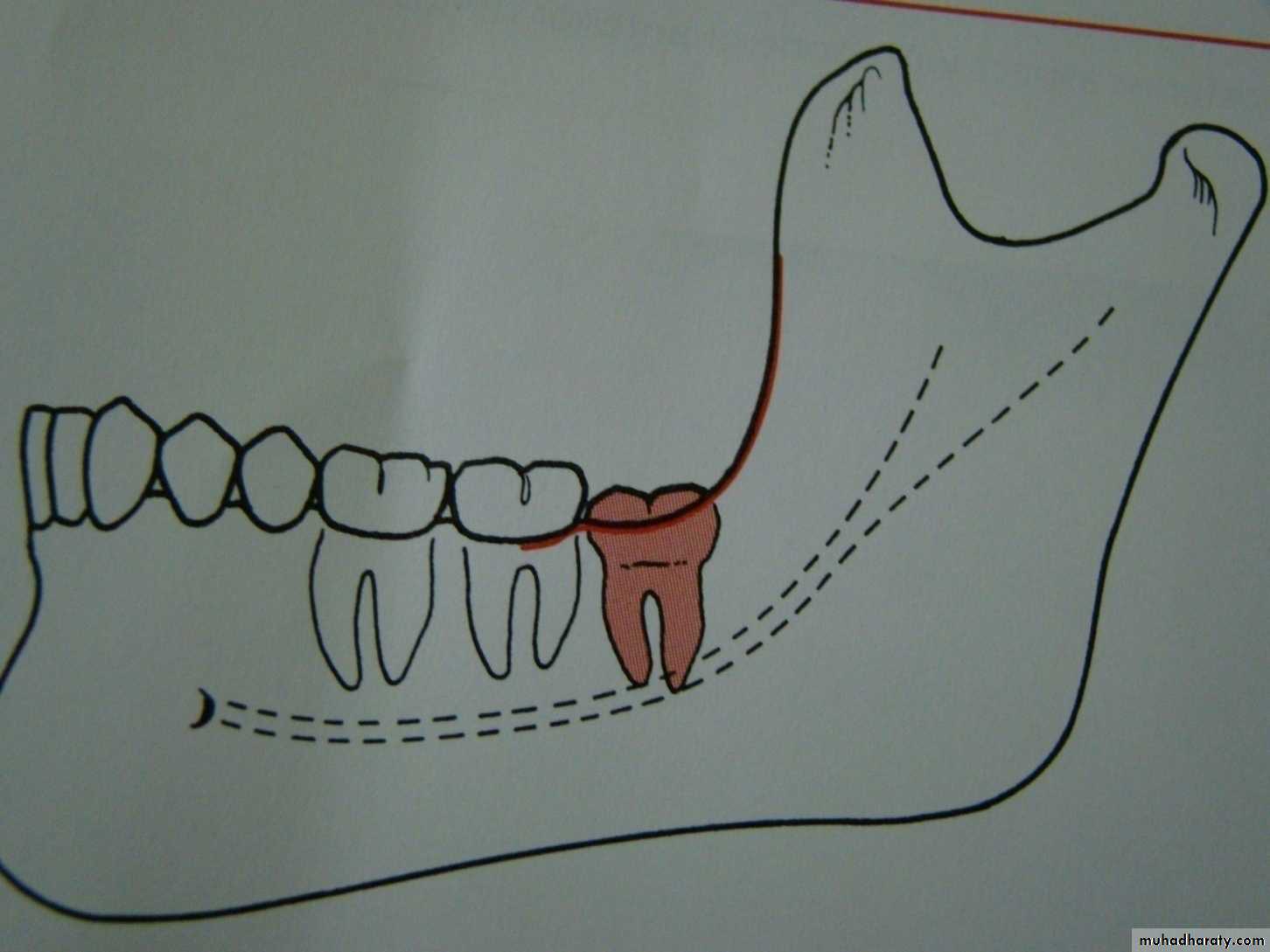
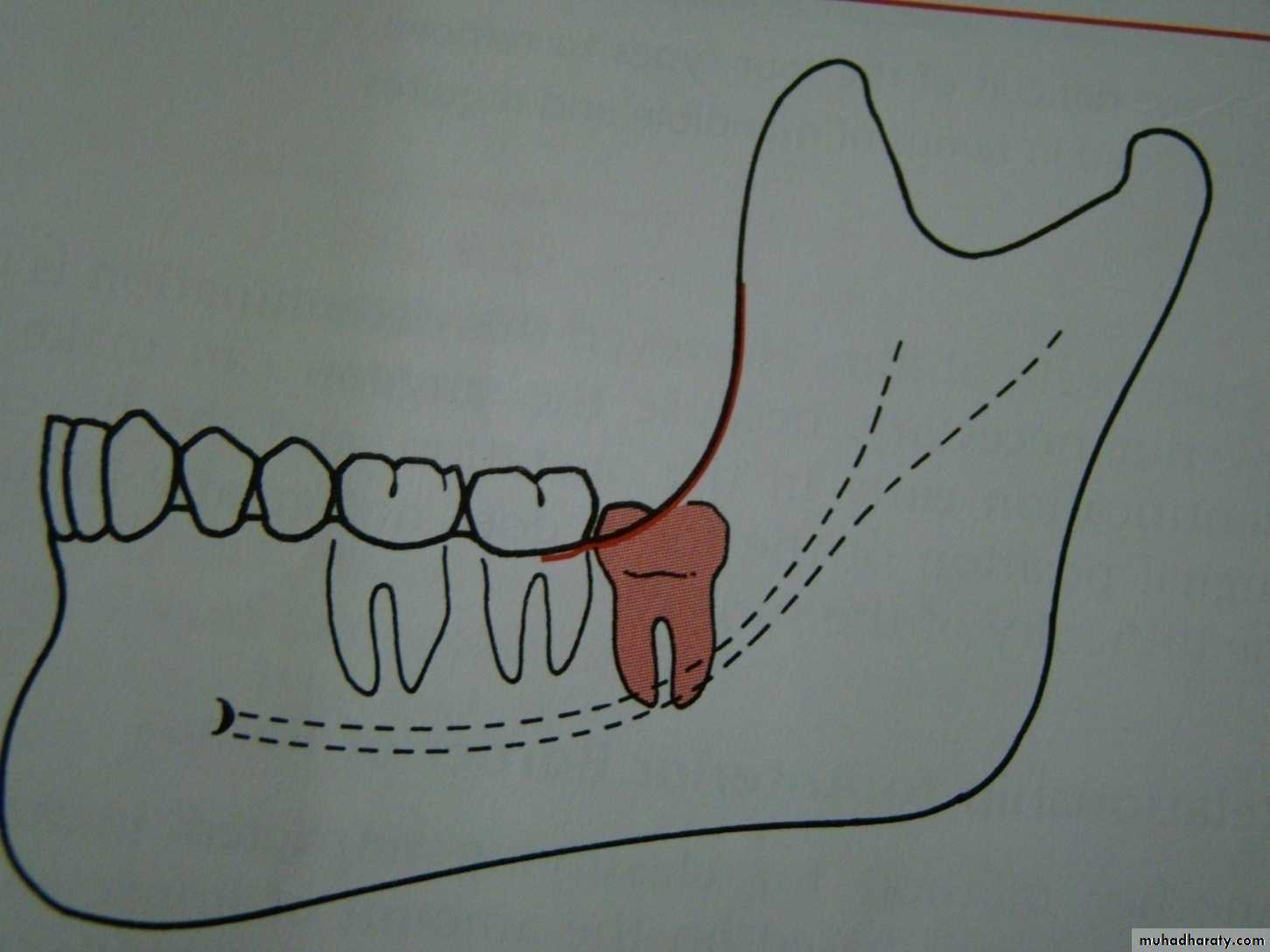
Development of mandibular third molar
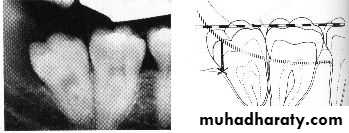
The mandibular third molar tooth germ is usually visible radio graphically by age 9 years and cusp mineralization is completed at age 11 years.At age 11 years the tooth is located within the anterior border of the ramus with it,s occlusal surface facing almost directly anteriorly
.crown formation is usually complete by age 14 years
At age 16 y the roots are approximately 50 % formed
At age 18 years the roots are completely formed with an open apex .
At age 24 years 95% of all third molars that will erupt have completed their eruption.Causes of tooth impaction 1- systemic causes2- local causes
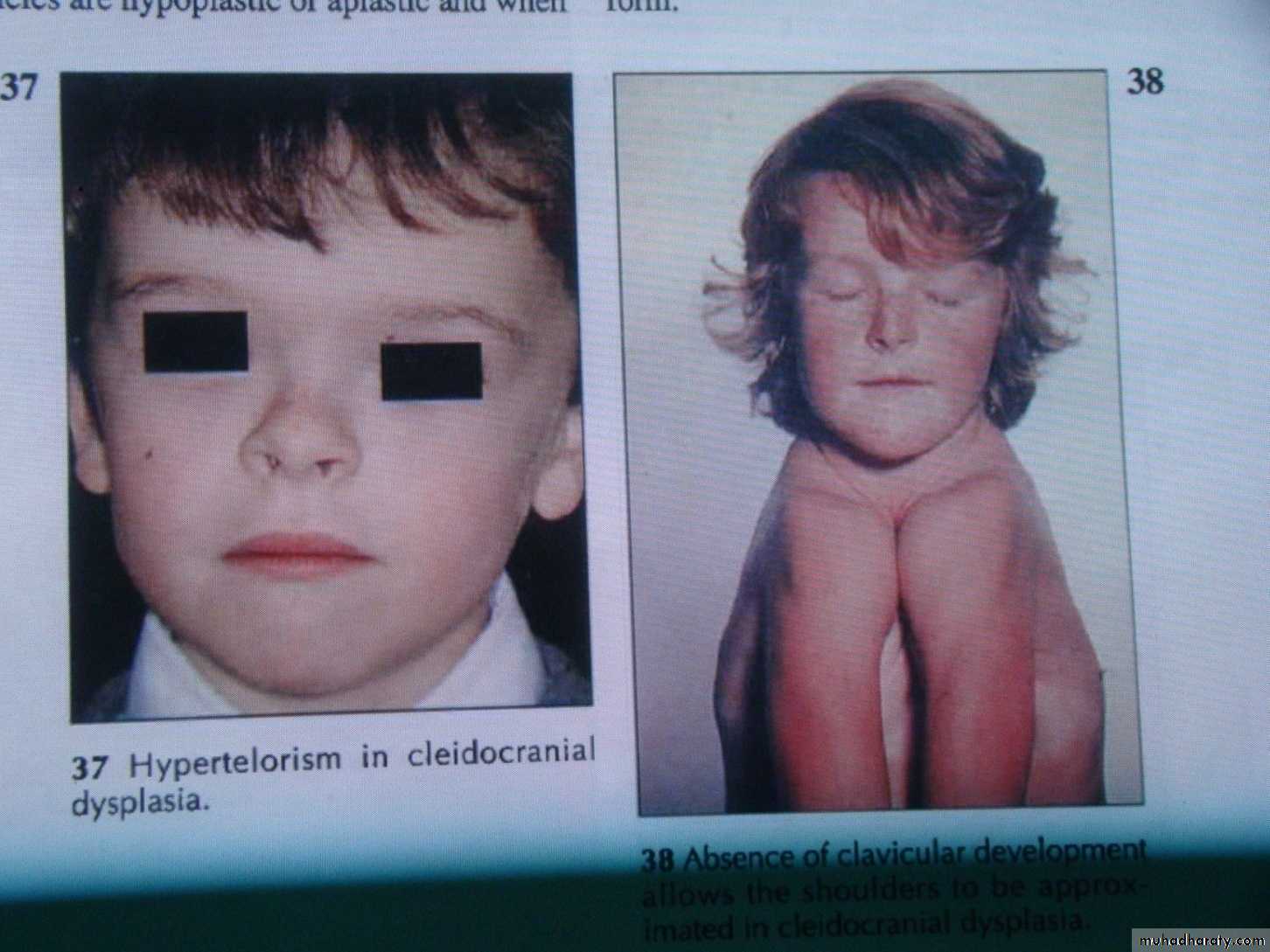
Systemic causes of impaction1- a hereditary syndrome of Cliedo cranial dysostosis2- endocrinal deficiency like hypothyroidism and hypopituitarism3-febrile diseases , downs syndrom, irradiation ( all cause multiple teeth impaction)Local causes of tooth impaction
1 – prolonged retention of deciduous teeth2 – large size teeth with arch length deficiency
3 – odontogenic cyst or odontogenic tumor change the path of eruption
4- cleft lip and cleft palate
5- malposed tooth germ
Frequency of tooth impaction
The frequency of tooth impaction is as follow:
1- lower third molar
2 – upper third molar
3- upper canine
4- lower canine
5- lower premolar
6- maxillary premolar
7-maxillary central and lateral incisor
The most common teeth to become impacted are the third molars or "wisdom teeth." Because they erupt so late in life and because most people's jaws are not large enough to accommodate them. Followed by the canines which is the last tooth to erupt in regard to the anterior teeth
Diagnosis of impacted teeth
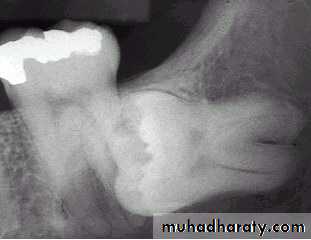
1- clinical inspection to disclose the missing tooth2- radiographic assessment showing the position of the unerupted tooth
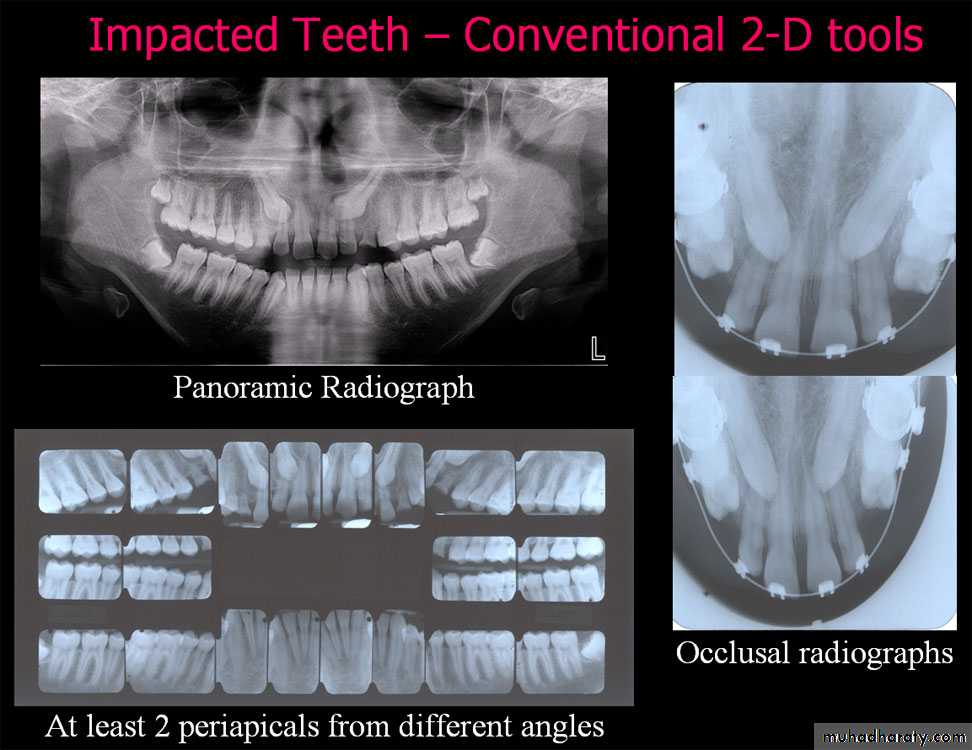
Standard radiographic techs used to localize the unerupted teeth, these include:
a –the tube shift techniqueUses two periapical radiographs, shifting the tube horizontally between exposures.
If the unerupted teeth moves in the same direction in which the tube is shifted, its located on the lingual or palatal side
A facial or buccally located tooth moves in the opposite direction to the tube shift.
b – periapical and occlusal film
Uses the periapical radiograph taken with standard technique and an occlusal radiograph to give different views of the impacted tooth
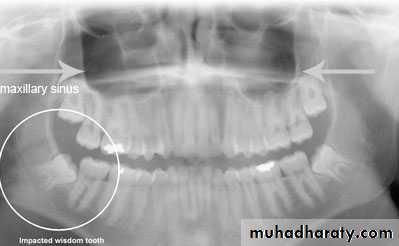
c – panoramic view (OPG)
can be used to assess maxillary canine positiond – CT scan if necessary
Problems of impacted tooth indicating its extraction
The presence of impacted tooth in the jaw cancause a variety of problems or complications ,
so it should be removed as soon as diagnosis is made , these complications may include
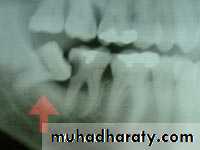
1-Pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is an inflammation of the soft tissues around the crown of partially erupted tooth and is caused by1- the normal oral flora associated with transient decrease in host defense mechanism
2- it may arise secondary to minor trauma from upper third molar .
3- food debris accumulation under the operculum
The soft tissue that cover the occlusal surface of the partially erupted lower third molar known as the operculum which can be traumatized and become swollen ,this can be treated by removal of maxillary third molar.
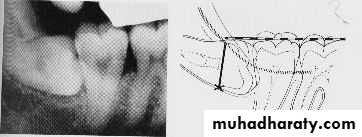
2 – prevention of Dental caries
Dental caries can occur at the lower 8 oradjacent lower 7 . most commonly at the
cervical line due to the inability of the patient
to clean the area thoroughly .
3 - Prevention of Periodontal disease
Food debris accumulation distal to the second molar and difficulty to clean it may lead to periodontal problems4-Prevention of resorption of adjacent tooth root
If external resorption is small in amount the tooth may repair it self by deposition of a layer of cementum over the resorbed area and the formation of secondary dentin . But if the resorption is severe both second and third molar may require removal .5- Pain of unexplained origin
Occasionally patient complain of jaw pain at the area of impacted third molar that has neither clinical nor radiographic signs of pathology . removal of this impacted tooth may relieve this pain .6 - Prevention of odontogenic cysts and tumors
The dental follicle may undergo cystic degeneration like a Dentigerous cysts or odontogenic keratocyst .
Ameloblastoma may develop from epithelium within the dental follicle .
7 - Tooth in the fracture line
Impacted lower third molar may weakens the angle of the mandible and make it more liable to fracture during trauma to the face .Asymptomatic deeply impacted tooth can be safely left in situ but if the bone overlying the tooth is very thin or absent the tooth should be removed before construction of the prosthesis .
8 - Impacted tooth under dental prosthesis
9 - To facilitate orthodontic treatment
1- crowding of mandibular incisors :in fact anterior incisor crowding is associated with arch length deficiency rather than the mere presence of impacted tooth2 – if the orthodontist is attempting to move the molars distally , removal of the impacted third molar may facilitate treatment.
3-interferance with orthognatic surgery especially in mandibular osteotomy or mandibular advancement surgery.
Contra indications for removal of impacted tooth
1 – extreme of age2- compromised medical status
3- probable unnecessary excessive damage to adjacent structures .
4- acute pericoronitis.
Treatment options of impacted teeth
1- leave it insitu
2 –surgical extraction
3 – surgical exposure
4- surgical relocation ( intentional replantation or auto transplantation )
5 – orthodontic treatment
Classification of impacted teeth
This is done to help the dentist in evaluation the extent and difficulty of the surgical procedureClassification of impacted lower third molar
1- Pell and Gregory classification(1933) according to the depth or according to the relation of the impacted tooth to the occlusal plane of the lower second molar2- Pell and Gregory classification(1933) according to the relation ship of the lower second molar to the anterior border of the ramus
3- Winters classification according to the angulations of the long axis of the impacted tooth
4-Based on the Nature of the Overlying Tissue
according to the depth
Level A the highest point of theocclusal surface of the impacted
tooth lie with or above the occlusal
surface of the second molar
Level B the highest point of the
impacted tooth lie below the
occlusal surface but above the
cervical surface of the lower second molar
Level C the highest point of the occlusal surface o f the impacted tooth lie below the cervical line of the lower second molar .
Relation of the impacted tooth to the anterior border of the ramus
Class 1 : the space between the lower second molar and the anterior border of the ramus is sufficient to accommodate the mesio distal dimension of the crown of the impacted lower third molarClass 2 : the space between the lower second molar and the ramus is insufficient to accommodate the crown of the impacted tooth .so part of it in the body and the other part lie in the ramus .
Class 3 the anterior border of the ramus lie near the distal surface of the lower second molar ,so ,the whole impacted tooth lie within the ramus .
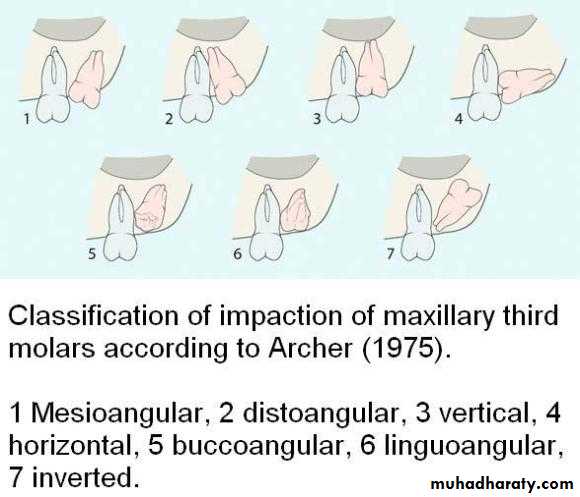
Winters classification of impacted lower third molar
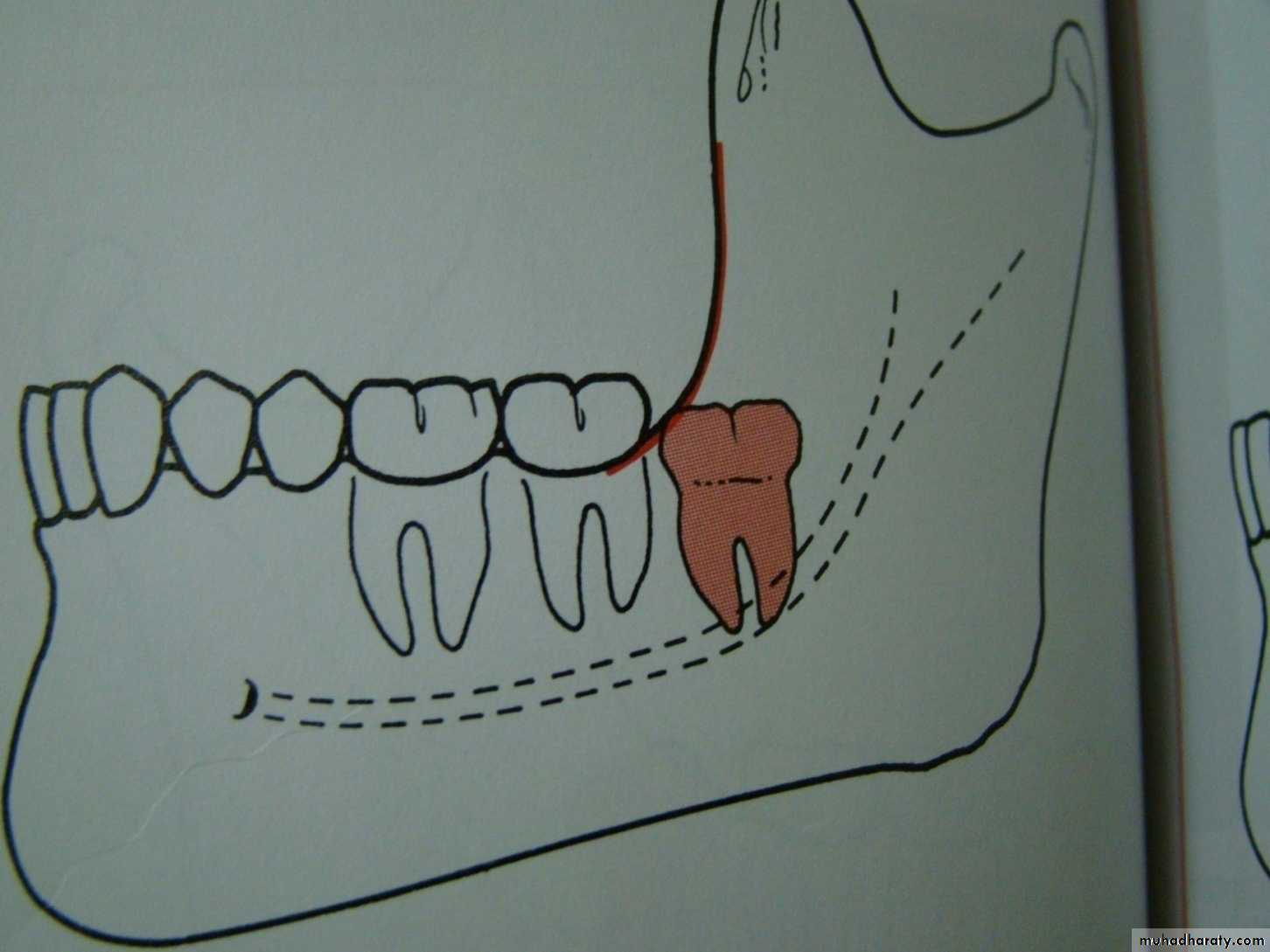
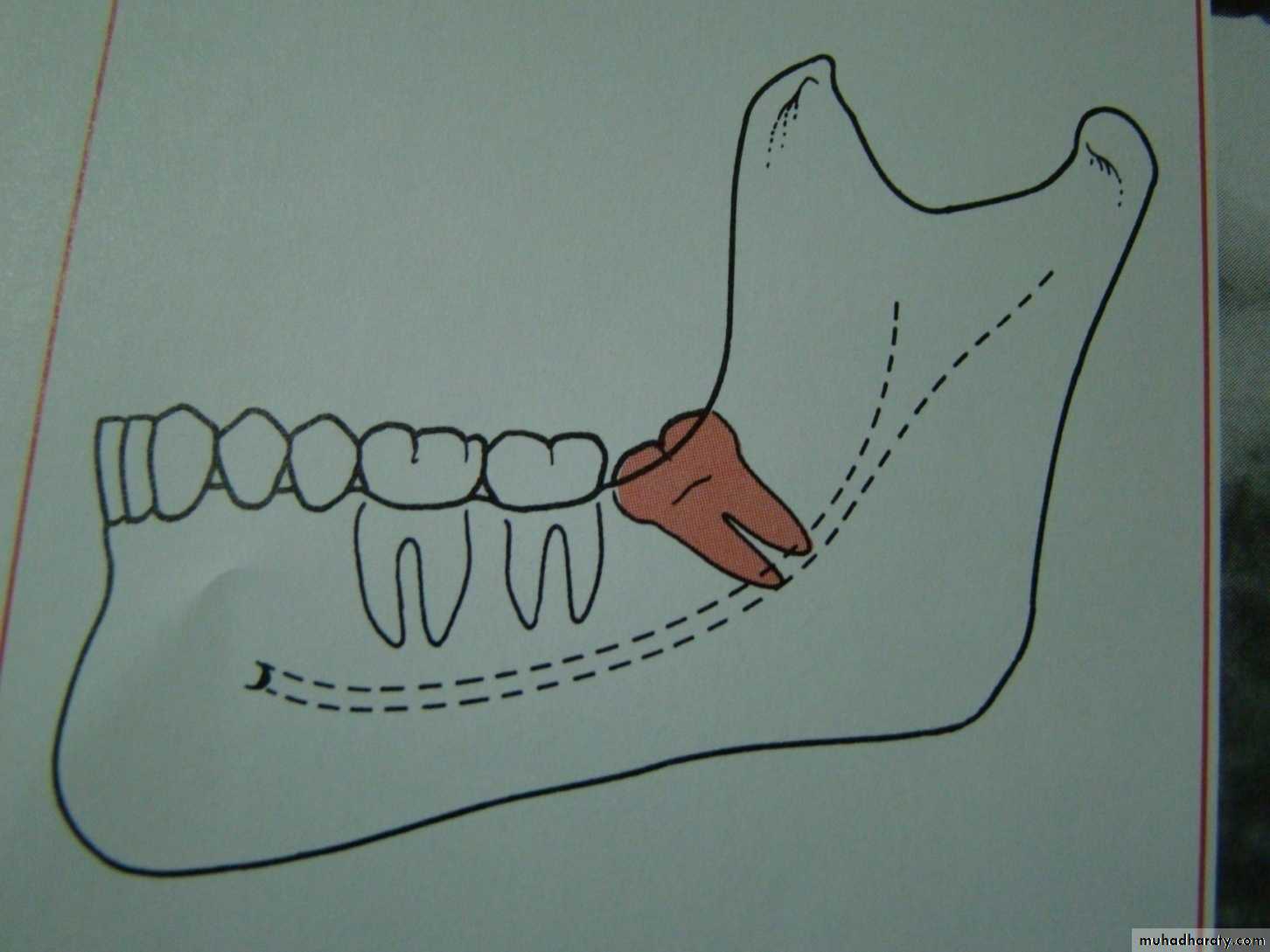
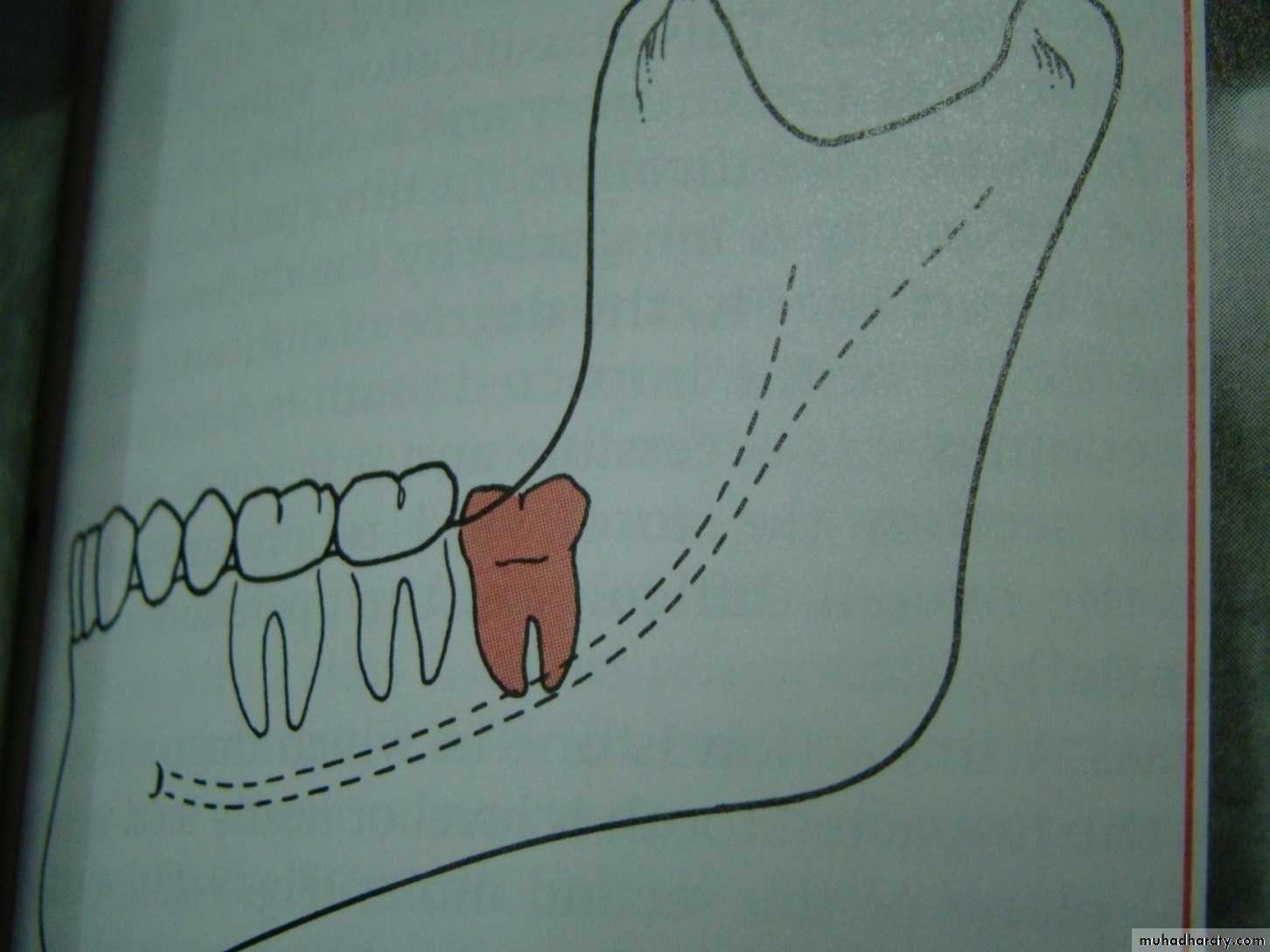
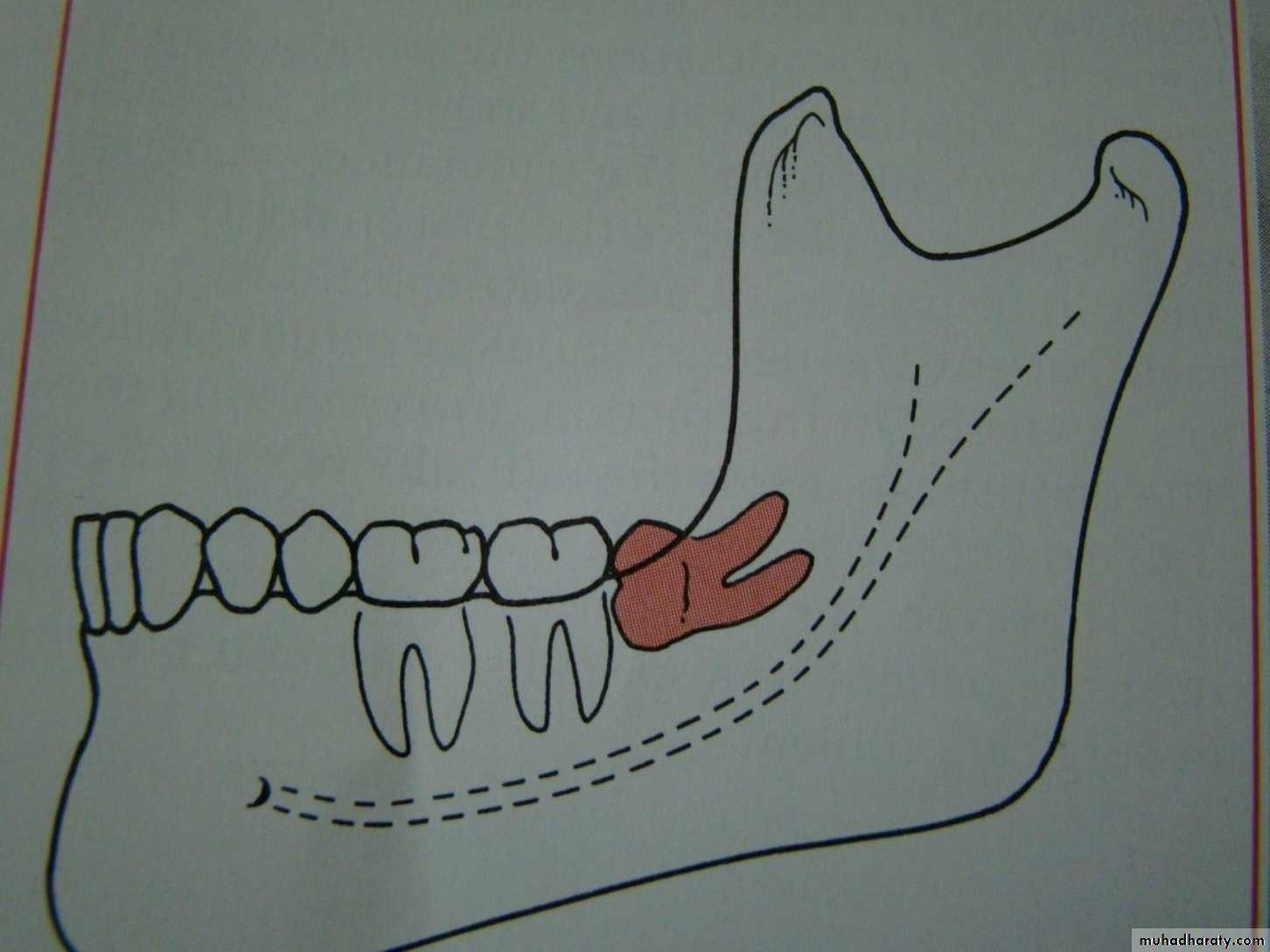
mesioangular
hotizontalvertical
distoangular
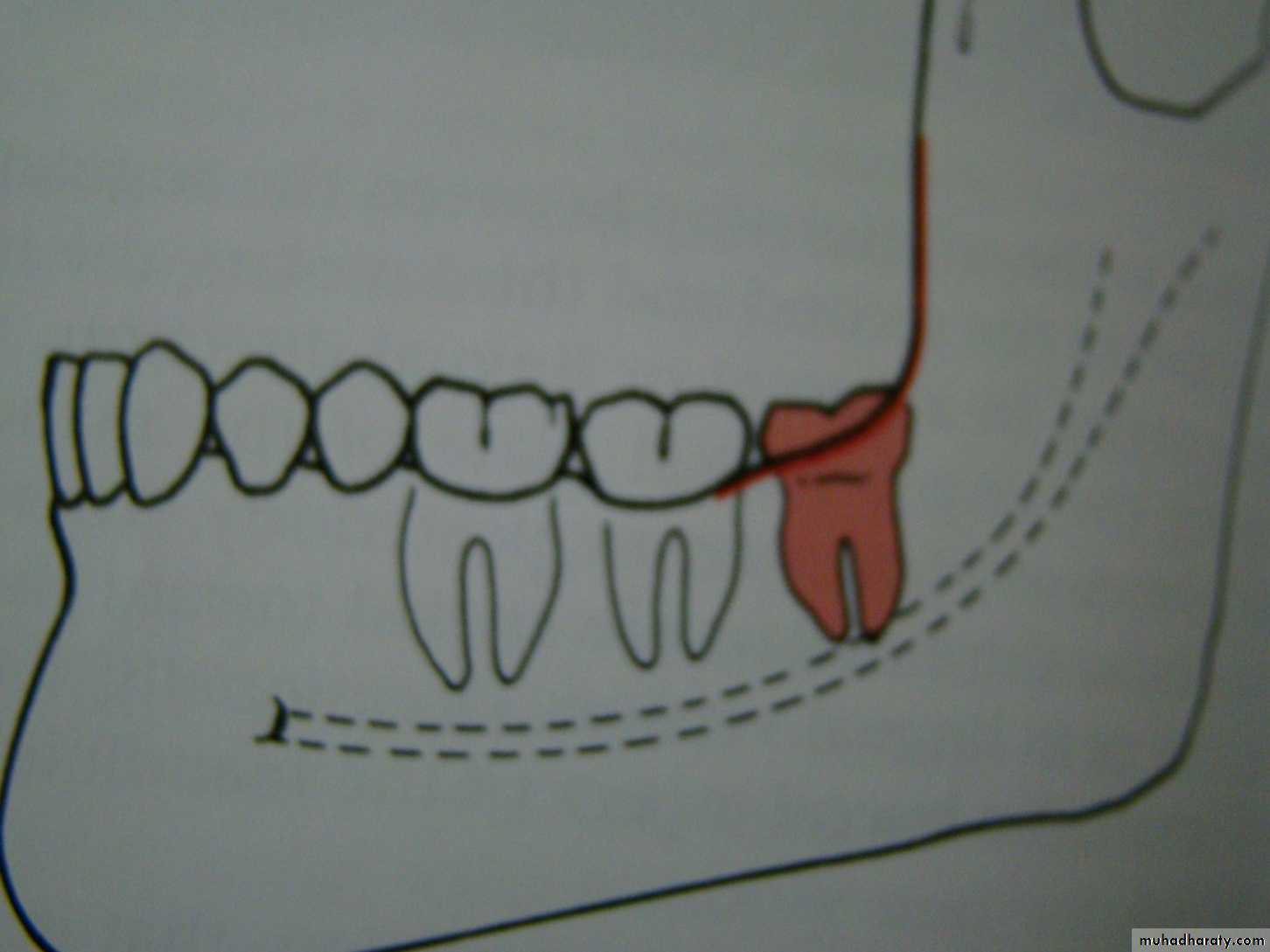
Winter’s lines
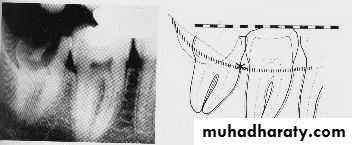
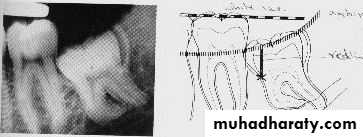
1-White line: it is an imaginary line draw along the occlusal surface of erupted first and second molars extend posteriorly over 3rd molar region . Its benefit is to determine the angulations of an impacted tooth and its relationship with occlusal surface of erupted 2nd molar(depth).2- Amber line: It is a line drawn from the surface of bone laying distally to the 8 and to the crest of interdental septum or alveolar septum between 6 and 7. it determine the amount of bone removal
3-Red line : it is draw perpendicular from amber line to an imaginary point of elevator application located mesially to the CEJ except in Disto angular impaction it is distally located . It is used to measure the depth of the impacted tooth.
Note: Any tooth with red line length more than (5 mm) it is better to remove it under G.A.
White Line
Amber LineVertical Impaction with caries
Point of application
Horizontal Impaction
Red LineMesio-angular Impaction
Disto-angular Impaction
5- Inverted
6- TransverseBased on the Nature of the Overlying Tissue
Soft Tissue Impaction. When the height of the tooth’s contour is above the level of the surrounding alveolar bone and the superficial portion of the tooth is covered only by soft tissue. Soft tissue impaction is usuall the easiest of type of impacted tooth to remove.Hard Tissue ('Bony') Impaction. This is where the wisdom tooth fails to erupt due to being obstructed by the overlying bone. This can be sub-divided into Partial and Complete Bony Impactions.
Partial Bony. The superficial portion of the tooth is covered only by soft tissue but the height of the tooth's contour is below the level of the surrounding alveolar bone. Apart from cutting the gingiva (gum) & possible bone removal from behind the tooth, the tooth's roots may need to be divided.
Complete Bony. The tooth is completely encased in bone so that when the gingiva is cut and reflected back, the tooth is not seen. Bone removal (large amounts) together with root sectioning will be needed to remove the tooth. These are often the most difficult tooth to remove.
Classification of impacted upper third molar
1- pell and Gregory according to the relation of the impacted tooth to the occlusal plane of the upper second molar2- the relation of the impacted upper third molar to the maxillary sinus
According to the depth
Level A the lowest point of the occlusal surface o the impacted upper third molar lie with or below the occlusal plane of the upper second molar.
Level B the lowest point of the impacted tooth lie between the occlusal and cervical line of the second molar
Level C the impacted tooth above the cervical line of the maxillary second molar
Relation of the impacted maxillary third molar to the maxillary sinus
Class A sinus approximation ( less than 2 mm bone between the antrum and the impacted tooth )Class B non sinus approximation ( more than 2 mm of bone exist between the impacted tooth and the sinus )
One simple method of determining the type of impaction involve comparing the distance between the roots of the third and second molar
• with the distance between the roots of the second and first molar(b) :
if (a) is greater than (b) it is a mesioangular impaction ,where (a) is less than (b) it is a distoangular impaction ,where (a) is equal to (b)it is a vertical impaction
If the first molar is missing the impaction can be determined by comparing a line drawn down the long axis of both the second and third molars ; if parallel , it is vertical ; if lower 8 leans toward lower 7 it is mesioangular , if the lower 8 long axis diverges from that of the 7 , then it is a distoangular impaction .
The change in orientation of the occlusal surface from mesial inclination to a vertical inclination occurs primarily during root formation .during this time the tooth rotates from horizontal to mesioangular to vertical . most third molars do not follow this typical eruption sequence and instead become impacted tooth
There may be differential root growth between the mesial and distal root ,which causes the tooth to either remain horizontally inclined or rotates to a vertical position depending on the amount of root formation.
Under development of the mesial root result in mesioangular impaction.
Over development of the mesial root result in over rotation of the third molar into a distoangular impaction
Overdevelopment of the distal root lead to mesioangular or horizontal impaction
Difficulty index of impacted lower third molar
the difficulty index value or score :Angulations Mesioangular 1 , horizontal or transverse 2, Vertical 3, Disto angular 4.
Depth : level A value 1 ,level B value 2 ,level C value 3
Ramus relation ship cl 1 value 1, cl 2 value 2 , cl 3 value 3.
summation of the three categories give the difficulty index value
Difficulty index
minimally difficult 3-4 , moderately difficult 5-6 , Very difficult 7-10 ,Example a tooth which is mesioangular B class 2
mesioangular =1
Level B =2
Class 2 = 2
Difficulty score =5
This impaction can be expected to be moderately difficult to remove .
Classification of pericoronitis
1 – acute pericoronitis2- sub acute pericoronitis
3- chronic pericoronitisAcute pericoronitis
It is characterized by a severe throbbing pain which is exacerbated by chewing , interferes with sleep, with limited mouth opening (trismus) . The patient may complain of extra oral swelling and discomfort during swallowing , submandibular adenopathy can be palpated ,and bad odor may be noted.In this state tooth extraction is absolutely contraindicated.