Types of Tissues &Epithelial Tissue
2nd lecture October 29, 2015Introduction
As mentioned earlier,cells are the smallest units of life. In complex organisms, cells group together with one another based on similar structure and function to form tissues.
Tissues provide the numerous functions of organs necessary to maintain biological life
Classifications of Tissues
The human body is composed of four basic types of tissues; epithelium, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
These tissues vary in their composition and their function. A basic understanding of the role of each tissue makes understanding the specific functions easier.
1. Epithelium- lines and covers surfaces
2. Connective tissue- protects, support, and bind together
3. Muscular tissue- produces movement
4. Nervous tissue- receives stimuli and conduct impulses
Epithelium:
Epithelium covers the whole surface of the body. It is made up of cells closely packed and ranged in one or more layers. This tissue is specialized to form the covering or lining of all internal and external body surfaces. Epithelial tissue that occurs on surfaces on the interior of the body is known as endothelium.
Epithelium serves many purposes, including protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, filtration, and sensory reception.
Epithelial Tissue 2 categories:
1. Epithelia - covering2. Glands -produce fluid secretions
The main characteristics of tissue epithelium, is as following:
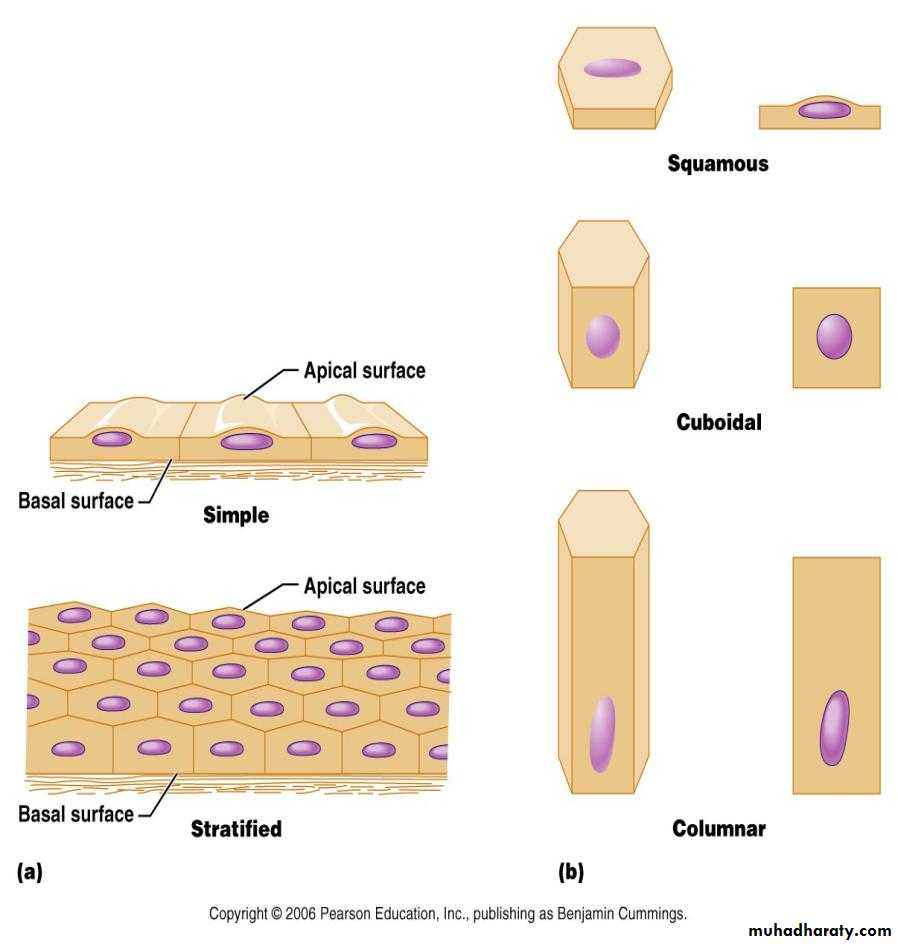
Polarity- Epithelium is arranged so there is one free surface (apical surface) and one attached surface (basal surface).Cellular nature- Cells in epithelium fit closely together side by side and sometimes atop each other to form sheets of cells. These sheets are held together by specialized junctions.
Supported by connective tissue- Attachment to a layer of connective tissue at the basal surface forms layer called the basement membrane, an adhesive layer formed by secretions from the epithelial cells and the connective tissue cells.
Avascular- Epithelium typically lacks its own blood supply.
Regeneration- Epithelium cells can regenerate if proper nourished.Arrangements & Shapes of Epithelial cell
Classification of epithelium is based onthe shape of the cells and the arrangement of the cells within the tissue. Typically, the arrangement of the cells is stated first, then the shape, and is followed by “epithelium” to complete the naming (Ex. Simple Squamous Epithelium).
Arrangements:
Simple- Cells are found in a single layer attached to the basement membrane
Stratified- Cells are found in 2 or more
layers stacked atop each other
Pseudostratified- a single layer of cells that appears to be multiple layers due to variance in height and location of the nuclei in the cells.
Transitional- cells are rounded and can slide across one another to allow stretching
Pseudostratified
TransitionalShapes:
Squamous- (Latin, squama- scale)- flat, thin, scale-like cellsCuboidal- cells that have a basic cube shape. Typically the cell's height and width are about equal.
Columnar- tall, rectangular or column- shaped cells. Typically taller than they are wide.
- Simple Epithelial Tissue 1- Simple Squamous Epithelium:
- Simple Epithelial Tissue 2- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium:
- Simple Epithelial Tissue 3-Simple Columnar Epithelium:
- Simple Epithelial Tissue 4- Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium:
- Stratified Epithelial Tissue 1- Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Non keratinized):
- Stratified Epithelial Tissue 2- Stratified Squamous Epithelium (keratinized):
- Stratified Epithelial Tissue 3- Stratified cuboidal Epithelium
- Stratified Epithelial Tissue 4- Transitional Epithelium
Summary of this lecture
At the end of this lecture, students should be able to answer the following questions:
1- Define the epithelium tissue2- what is the main characteristics of epithelium tissue?
3- how epithelium tissue can be classified and named?
4- what is the main functions of epithelium tissue?
5- student could be able to recognize all the types of epithelium tissue.
6- student could able to recognize the function of each type of epithelium tissue.