1
Fifth stage
Dermatology
Lec-1
.د
عمر
10/11/2015
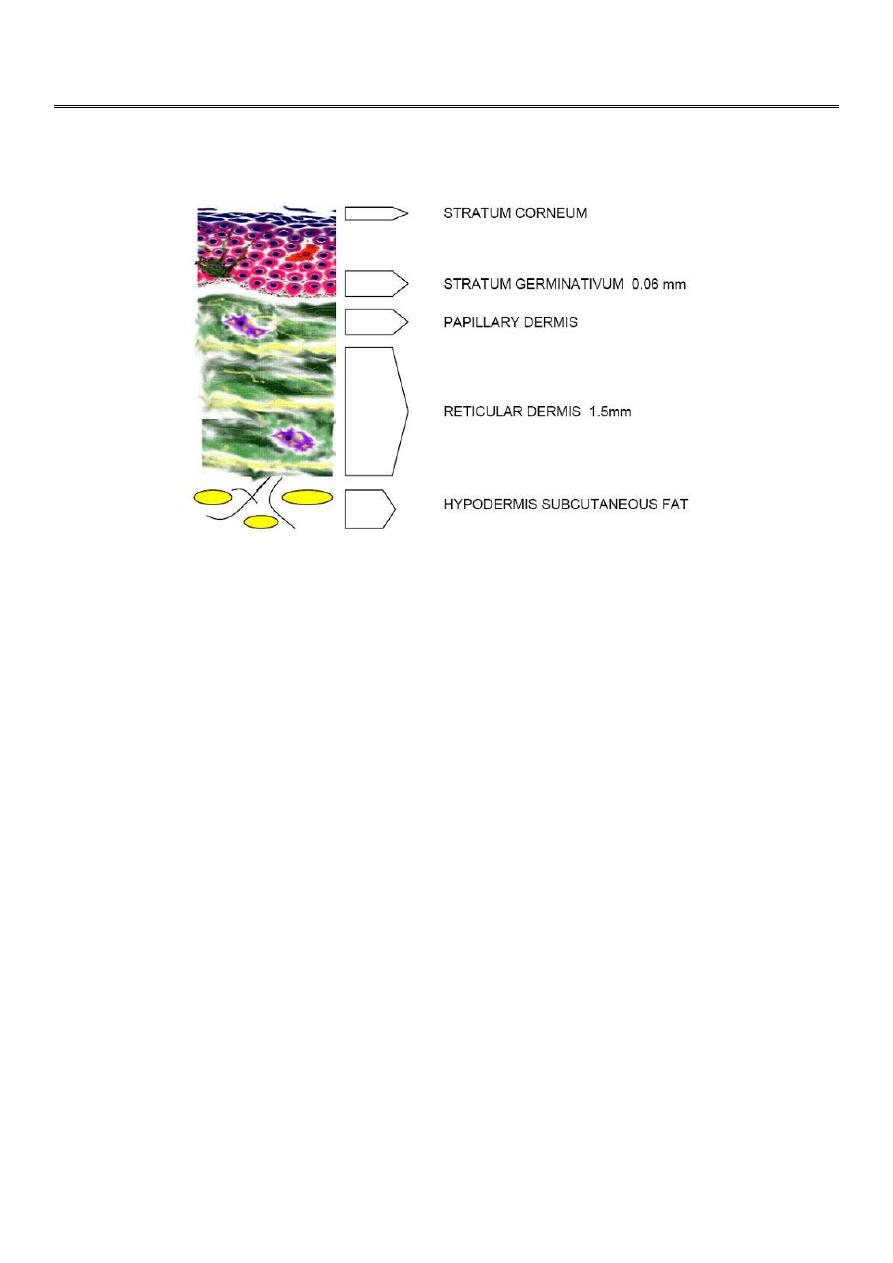
MORPHOLOGY OF SKIN LESIONS
Primary lesions
The original lesions are known as primary lesion which are as follows:
Macule, patch
Papule, plaque, nodule, tumor
Wheals
Vesicle
Bullae
Pustule
B. Secondary Lesions
The primary lesions continue to full development or may be modified by regression, trauma
of other extraneous factors, producing secondary lesion which are as follows:
Scales
Crusts
Excoriations and abrasions
Fissures
Erosions
Ulcers
Scars-hypertrophic scars
Keloid
Atrophy
Cyst
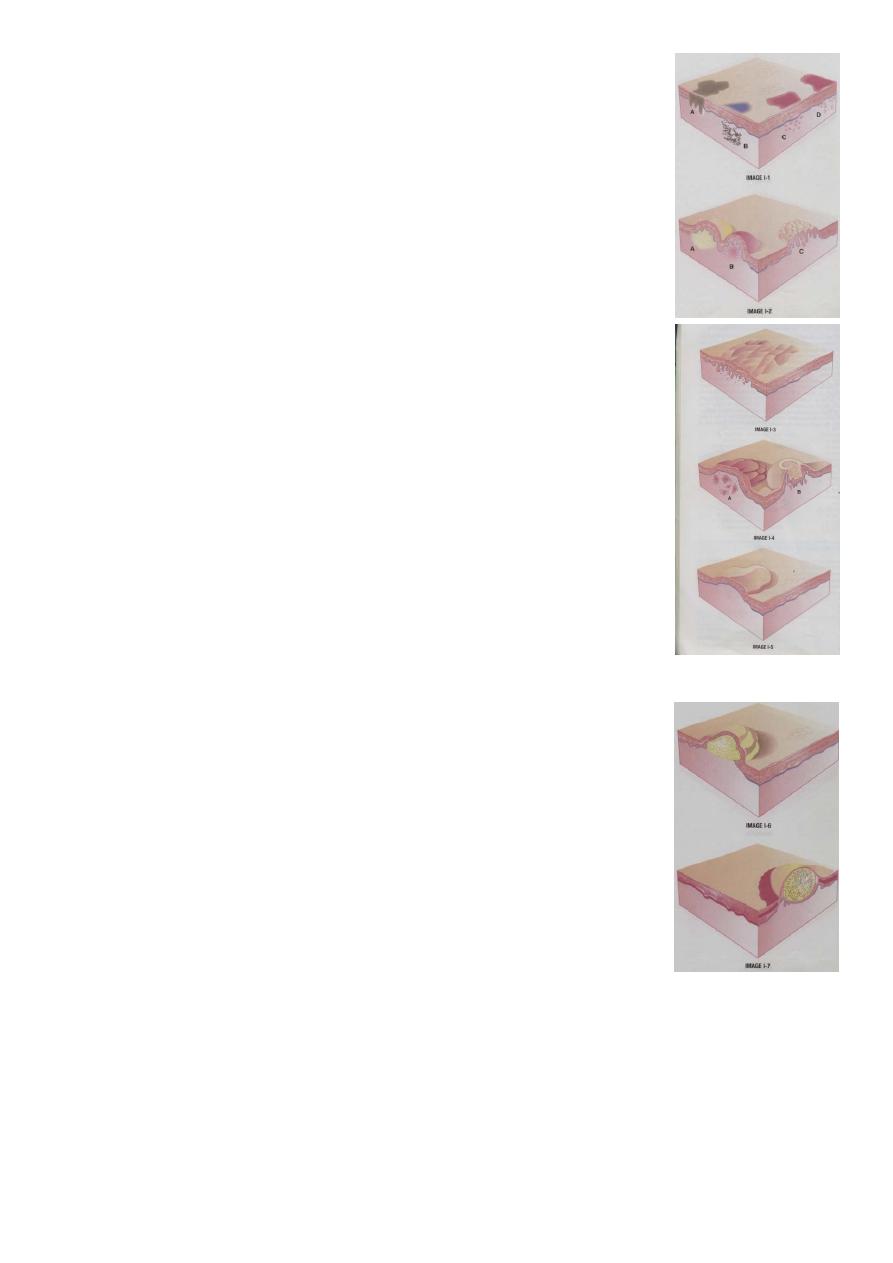

2
Mucule- Latin: macula, “spot”
Macules are variously sized, circumscribed changes in skin color,
without elevation or depression and less than 1 cm in diameter.
Patch
A patch is a circumscribed changes in skin color without elevation or
depression and 1 cm or greater in diameter.
Papule- (Latin Paula, “Pimple”)
Papules are circumscribed, solid elevations of skin having diameter less
than 1 cm.
Plaques: (French- Plaque- “Plate”)
A plaque is a broad papule (or confluences of papules), 1 cm or more in
diameter.
Nodules (Latins: nodulus- “small knot”)
Nodules are form of papules but largest (>1 cm) and invade deeply.
Wheals (Hives) wheals
Are evanescent, oedematous, flat elevations of various sizes.
Vesicles (Latin “Little bladder”)
Vesicles are circumscribed epidermal elevations 1-10 mm in size and
usually containing clear fluid.
Bulloe (Latin-”Bubble”) Bulloe
Are circumscribed or irregularly shaped cavity more than 10 mm in
diameter containing serous or seropurulent fluid.
Pustule (Latin- Pustula-Pus)
Pustules are small elevations of the skin containing pus
Tumors
are soft or firm and freely movable or fixed masses of various sizes and shape. “A
tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue, the growth of which exceeds and un-coordinated with
normal tissue and persists in the same excessive manner after cessation of stimulus which
evoked the change”.

3
Secondary Lesions
Scales: (Latin Squama-scales)
Scales are dry or greasy laminated masses of keratin.
Excoriations (Latin Abrasio)
An excoriation is a punctate or linear abrasion produced by mechanical means usually
involving only the epidermis and rarely reaching the papillary layer of the dermis.
Fissures (Latin- Cracks)
A fissure is a linear cleft through the epidermis or rarely into the dermis caused by disease or
injury
Erosions –
Loss of all or portion of epidermis alone
Ulcers (Latin- Ulcus- “Sore”)
Ulcers are rounded or irregularly shaped excavations that result from loss of epidermis and
dermis.
Crusts (Latin- crusta-bark)
Crusts are dried serum, pus or blood, usually mixed with epithalial and bacterial debris.
Scars
Scars are new formations in the dermis or deeper parts as a result of injury or disease, as a
part of the normal reparative and healing process scar may be hypertrophic.
Keloid (Latin- Cheloid-clawlike)
A keloid is a firm, irregularly shaped, thickened, hypertrophic, fibrous, pink or red
excrescence.
Atrophy
This refers to a diminuation of some or all layers of kin
Cyst
A cyst is a cavity containing
liquid or solid or semi-solid
material may be superficial or
deep.
