Orthodontic
Dr. Enas Talb4th class
Introduction to Orthodontics
Orthodontics: is the branch of science and art of dentistry which deals with the developmental and positional anomalies of the teeth and the jaw as they effect on oral health and the physical, esthetic, mental wellbeing of the person.Or
Orthodontics: is the branch of dentistry concerned with the treatment and prevention of irregularities of the teeth and jaw.
Branches of Orthodontics:
1-Preventive orthodontic: is the action taken to preserve the integrity of what appears to be normal occlusion at a specific time.2-Interceptive orthodontics: that phase of orthodontics employed to recognize and eliminated potential irregularities and malpositions in the developing dentofacial complex.
3-Corrective orthodontics: employing certain technical procedures to reduce or eliminated the problem and the procedures employed in correction may be mechanical, functional, surgical in nature.
Aims of orthodontic treatments:
1-Functional efficiency:
The teeth along with their surrounding structures are required to perform certain important functions. The orthodontic treatment should increase the efficiency of the functions performed by the stomatognathic system.
Aims of orthodontic treatments:
2-Structural balance:The structures affected by the orthodontic treatment include, not only the teeth but also the surrounding soft tissue envelop and the associated skeletal structures. The treatment should maintain a balance between these structures, and the correction of one should not be detrimental to the health of another
Aims of orthodontic treatments:
3-Esthetic demand:The orthodontic treatment should increase the overall esthetic appeal of the individual. This might just require the alignment of certain teeth or the forward movement of the complete jaw including its basal bone. The aim is to get results which gel with the patient's personality and make him/her to look more esthetic.
Occlusion
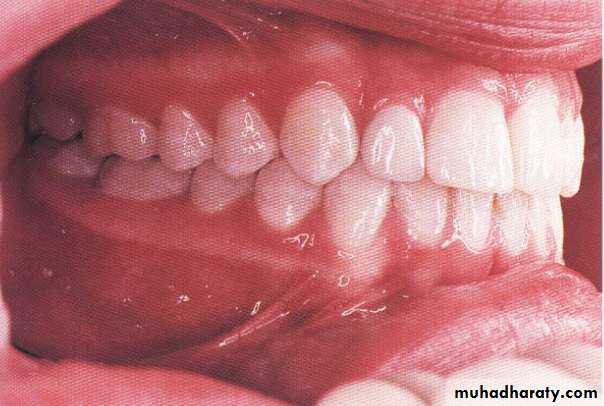
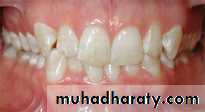
Occlusion: the relation of the maxillary and mandibular teeth when the jaws are closed in centric relation without strain of musculature or displacement of condyles in their fossa.Ideal occlusion
Ideal occlusion: is a hypothetical concept or a standardized goal.It is a theoretical concept based on the ideal teeth position and arches relationships. It is rarely, if ever, found in nature. However, it provides a standard by which all other occlusions may be judged.
Ideal occlusion
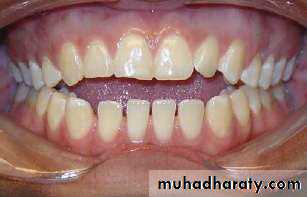
In ideal occlusion:• * A coincident mid-line
• *No(crowding/spacing/rotations……)
• * Over-jet = 2-3mm
• * Correct crown angulation and inclination
• * Class I molar & canine relationship
• * A flat or slightly upwards curve of Spee
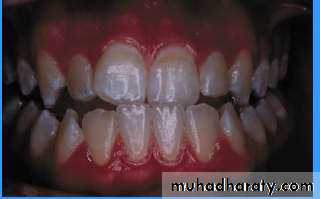
Normal occlusion
Normal occlusion: implies to the variations around an average mean value, in which shows:some deviation from that of the ideal but is aesthetically acceptable and functionally stable for the individual , the upper and lower teeth fit nicely and evenly together with the least amount of destructive interferences.
Malocclusion
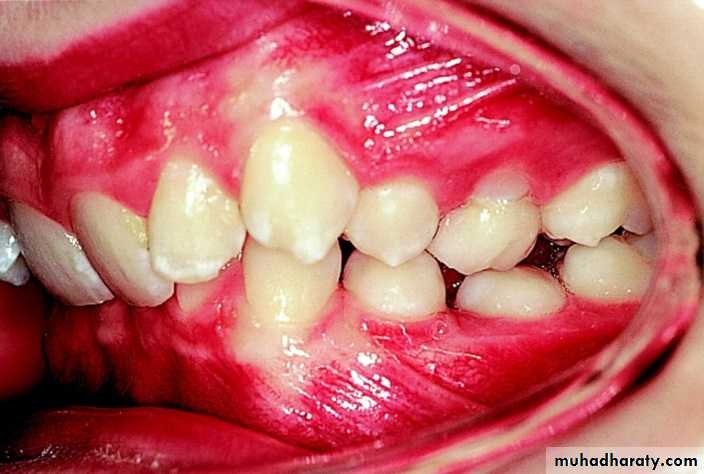
Malocclusion: is an abnormal or malposition relationship of the maxillary teeth to the mandibular teeth when they are in occlusion in which there is a deflection from the normal relation of the teeth to other teeth in the same arch and/or to teeth in the opposing arch.Types of malocclusion:
1-intra arch: Includes variation in individual tooth position or a group of teeth within an arch such asAbnormal inclination
Abnormal Displacements
Spacing and crowding within the same arch
Types of malocclusion:
2-inter arch: Abnormal relationship between two teeth or group of teeth of one arch to the other eg. Abnormal overjet, anterior cross bite, open bite, deep bite, posterior cross bite…Types of malocclusion:
3-skeletal: Malrelation of the upper and lower apical bases is due to:a. Abnormal size;
b. Abnormal shape;
c. Abnormal relation to the skull;
d. Abnormal relation to each other.
Classification of malocclusion:
Angle’s classification of malocclusion:In 1899 Edward H. Angle published the first classification of malocclusion. Maxillary first molar is taken as the key of occlusion.
Angle’s classification of malocclusion:
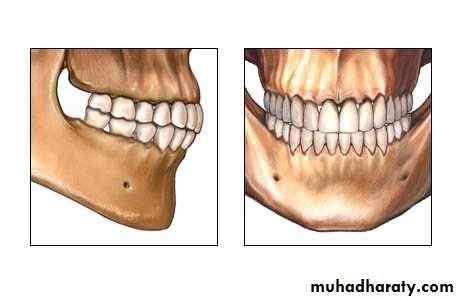
The classifications are based on the relationship of the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and the buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. There are three classes:
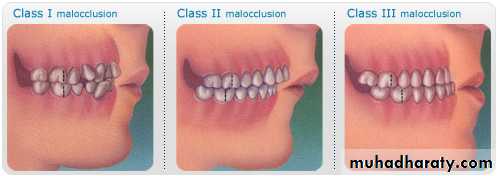
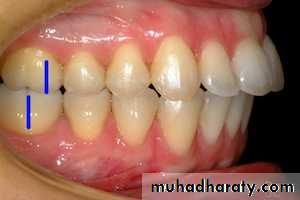
1-class I malocclusion''Neutroclusion":
The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first permanent molar occludes with the mesiobuccal groove of the lower first molar, but line of occlusion is Ln altered in the max. & mand. arches:• individual tooth irregularities (crowding/spacing/ rotations ….)
• Inter-arch problems (deep bite/open bite/ increased overjet………)other
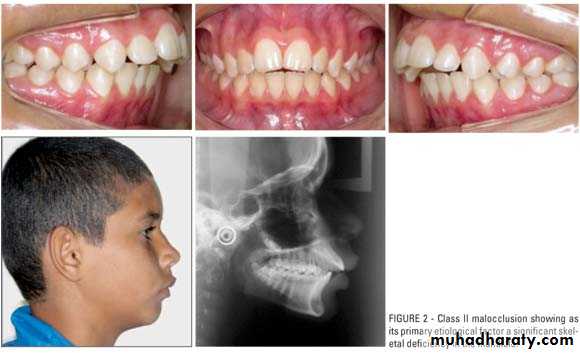
2- Class II malocclusion" Distoclusion":
The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first permanent molar occludes mesially to the mesiobuccal groove of the lower first molar.The Canine relationship:
The distal incline of upper canine anterior to the mesial incline of lower first premolar.
Class II malocclusion" Distoclusion":
There are two types of class II malocclusion:A-Class II division 1:
Conditions when class II molar relationship is present with proclined upper central incisors that is to say an increase in overjet.
Class II malocclusion" Distoclusion":
B- Class II division 2:Condition when class II molar relationship is present with retroclined upper central incisors, upper lateral incisors may be proclined or normally inclined.
Overjet is usually minimal or may be increased.
3- Class III malocclusion" Mesiocclusion":
The mesiobuccal cusp of the upper first permanent molar occludes distally to the mesiobuccal groove of the lower first molar.The Canine relationship:
The distal incline of upper canine posterior to the mesial incline of lower first premolar.
Class ІІІ malocclusion: 2 types
3-Class III malocclusion“ Mesiocclusion":
A-True class ІІІ malocclusion (Skeletal):Excessively large mandible
Small maxilla than normal range
Retropositioned maxilla
B- Pseudo class ІІІ (False or postural):
Forward movement of mandible during jaw closure due to :Occlusal prematurity
Premature loss of deciduous posteriors
Enlarged adenoids
Pseudo class ІІІ
Advantages of Angle's classification:
1-First comprehensive classification- most widely accepted2-simple
3- easy to use
4- most popular
5- easy to communicate
Disadvantages of Angle's classification:
• Considers malocclusion only in anteroposterior plane not in transverse and vertical planes.
• Considered 1st molar as fixed point for classification so this classification not employ if deciduous dentition present or 1st molar extracted .
• Doesn't distinguish between skeletal and dental malocclusion
• Doesn’t highlight etiology
• Individual tooth positions
Important definitions in orthodontic
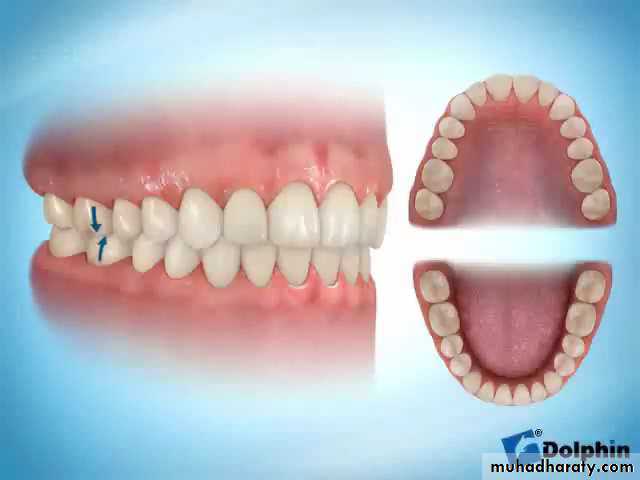
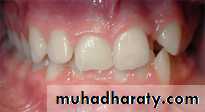
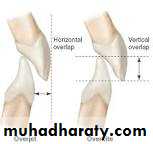
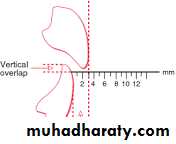
Overbite: amount of vertical overlap between the maxillary and mandibular incisors Normally, the lower incisal edges contact the lingual surface of the upper incisors at or above the cingulum (i.e., normally there is a 1 to 2 mm overbite).Important definitions in orthodontic
Overjet: is defined as horizontal overlap of the incisors. Normally, the upper incisors ahead of the lower by 2 to 3 mm .Important definitions in orthodontic
Open bite : there is no vertical overlap between teeth and open space exists between upper and lower teeth when jaws are closed.
Important definitions in orthodontic
Deep bite: The upper front teeth cover too much (more than 30%) of the lower front teeth.Important definitions in orthodontic
Anterior crossbite: malocclusion in which the labial surfaces of maxillary incisors occlude posterior to the lingual surfaces of mandibular incisors; may involve one or two or all anterior teeth.Important definitions in orthodontic
Posterior crossbite: exists when the maxillary posterior teeth are lingually positioned relative to the mandibular teeth, Posterior crossbite most often reflects a narrow maxillary dental arch but can arise from other causes.Important definitions in orthodontic
Scissors bite: Malocclusion in the posterior teeth occurring when upper posterior teeth are positioned totally buccal to the lower teeth in centric occlusion.
Important definitions in orthodontic
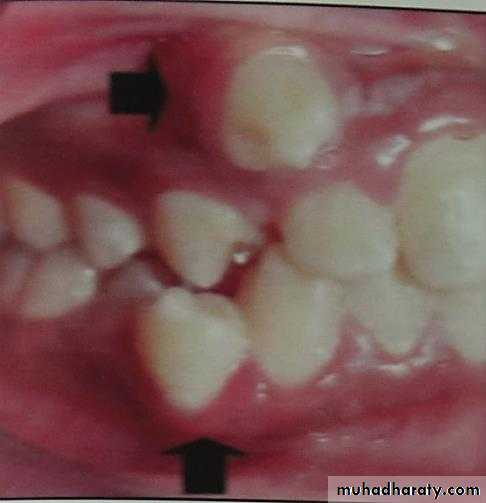
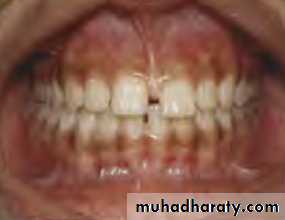
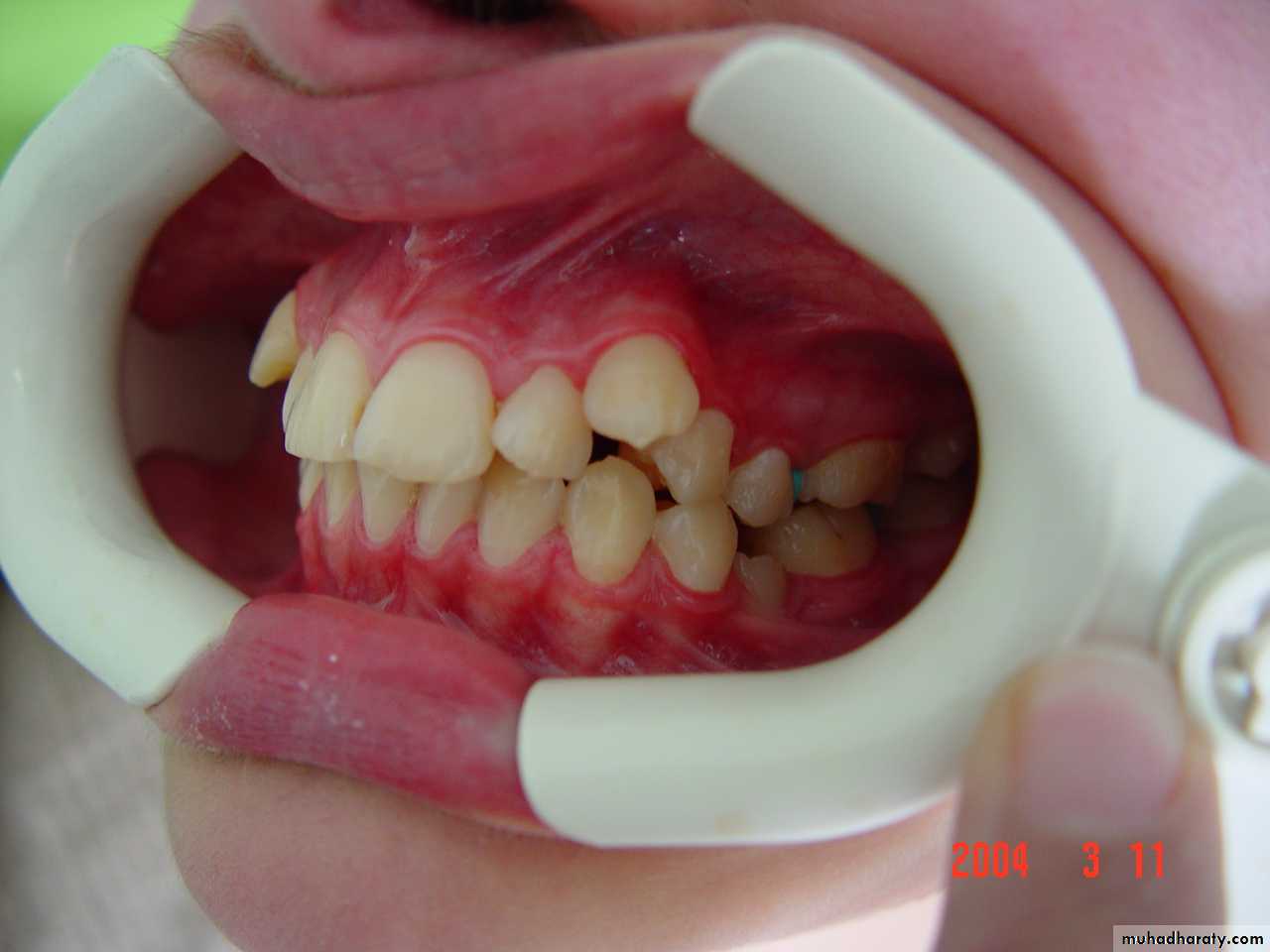
Crowding: Malalignment of teeth caused by inadequate space.Spacing: Imperfections in teeth alignment and distance between teeth.
Important definitions in orthodontic
Diastema: Space between any two neighboring teeth.Midline shift: The center of the upper front teeth is not aligned with the center of the lower front teeth.
Important definitions in orthodontic
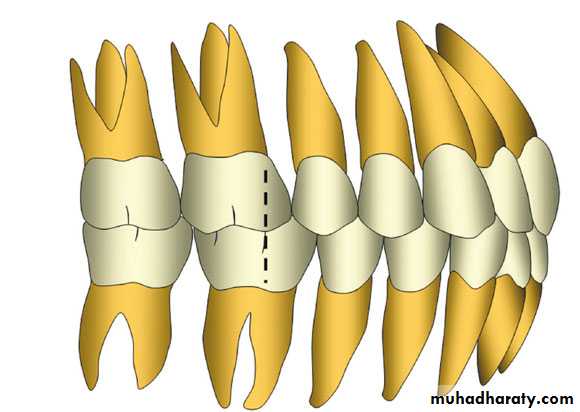
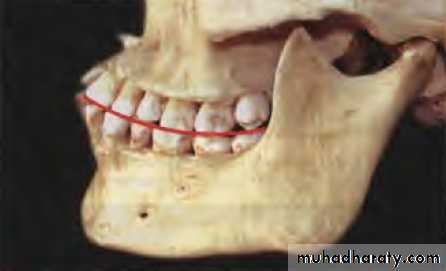
Curve of Spee: Curvature of the incisor edges and occlusal surfaces of teeth beginning at the tips of the lower incisors and canine, following the buccal cusps of the premolars and molars, and continuing to the anterior border of the ramus.
Important definitions in orthodontic
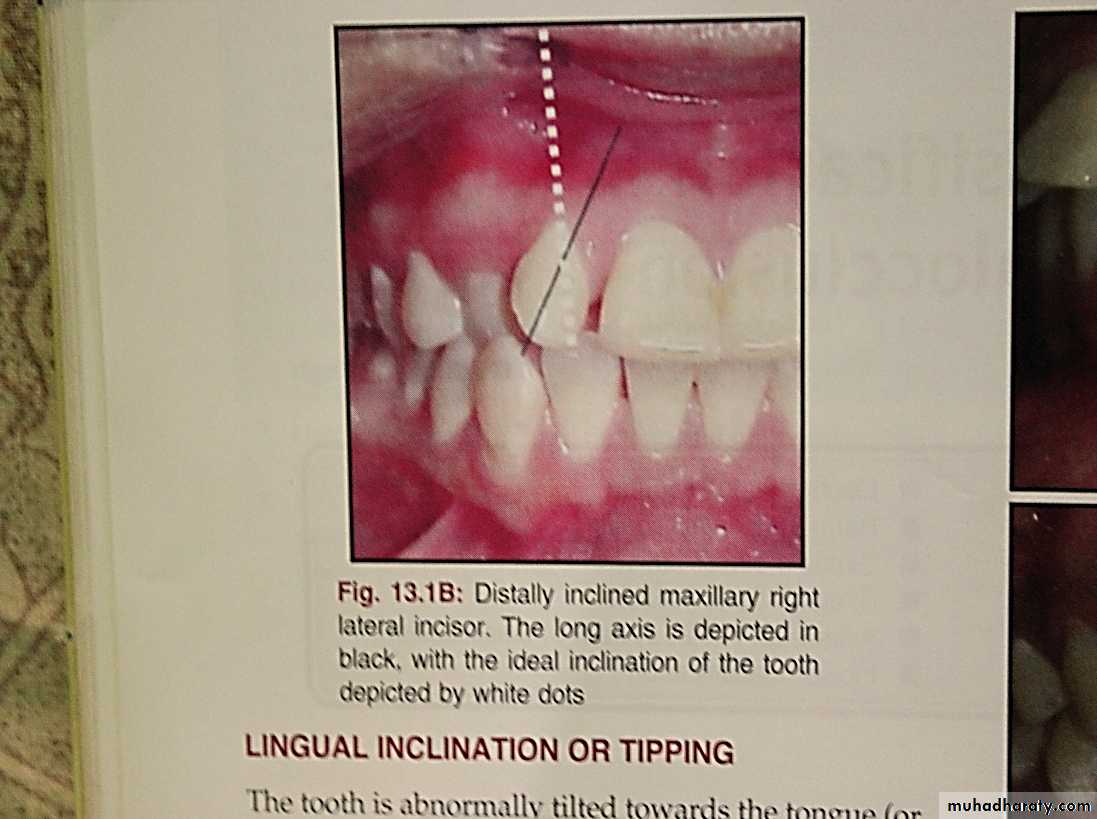
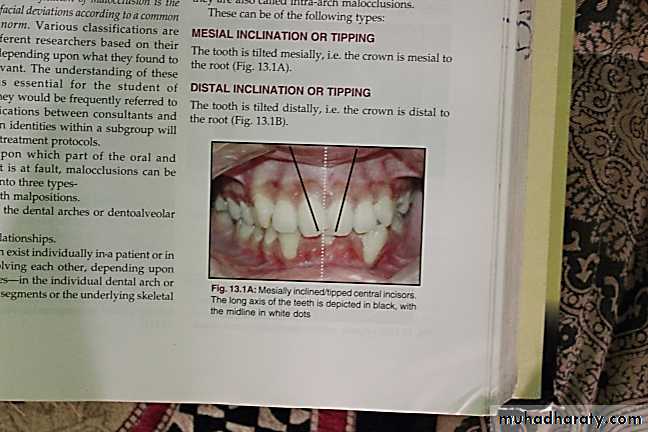
Crown angulation: in which the crowns are angulated mesially or distally ( mesial or distal tip) to different degrees.Crown inclination : Labiolingual or buccolingual inclination of the crowns of the teeth.
Important definitions in orthodontic
Buccocclusion: Buccal displacement of a tooth or a group of teeth.Linguocclusion : lingual displacement of a tooth or a group of teeth.
Important definitions in orthodontic
Supraocclusion : when a tooth or group of teeth have beyond normal level.Infraocclsion : when a tooth or group of teeth have not erupted to normal level.
Important definitions in orthodontic
Mesioversion : mesial to the normal position.Distoversion: distal to the normal position.
Important definitions in orthodonticTransversion : transposition of two teeth.