Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron Metabolism:IRON INTAKE (Dietary)
- “average” adult diet = 10-20 mg Fe/day
- absorption = 5-10% (0.5-2 mg/day)
- Fe absorption increases with
• increased erythropoiesis e.g. pregnancy
• anemia
• Reducing substances in food
- males have a positive Fe balance
- menstruating females have a negative Fe balance
PHYSIOLOGIC CAUSES OF INCREASED IRON REQUIREMENTS
- infancy-growth spurt 2x basal need
- puberty-growth spurt, menarche 3x basal need
- pregnancy 4x basal need
- blood donation 4x basal need
• 500 mL blood = 250 mg Fe
IRON ABSORPTION
- occurs in duodenum mainly .
IRON TRANSPORT
Majority of non-heme Fe in plasma is bound to a beta-globulin called transferrin
Transferrin
• carries Fe from mucosal cell to RBC precursors in marrow.
• carries Fe from storage pool in hepatocytes and macrophages to RBC
precursors in marrow.
IRON STORAGE
Fe is stored in two forms: ferritin and hemosiderin.
Ferritin in hepatocytes
Hemosiderin in macrophage-monocyte system
IRON METABOLISM
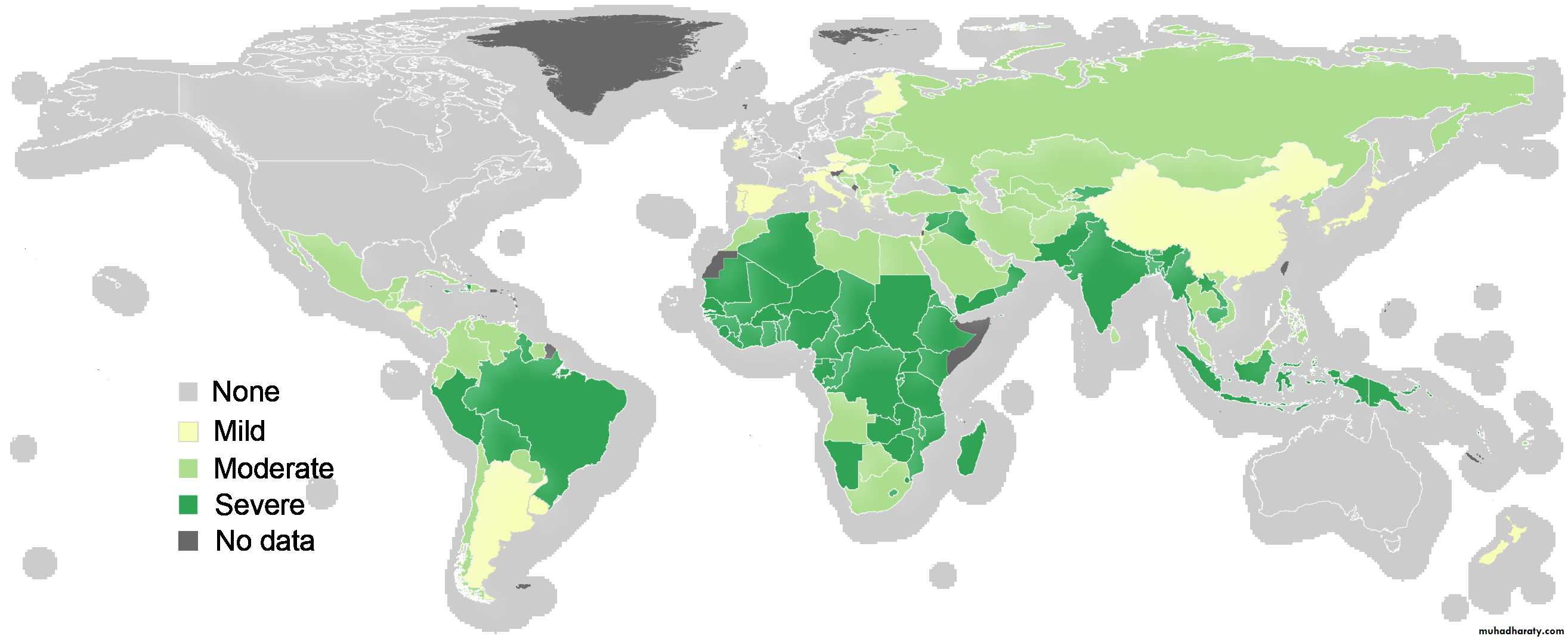
Distribution of Iron DeficiencyCauses of IDA
PHYSIOLOGIC CAUSESIncreased need for iron in the body.
Infancy.
Adolescence, menstruation.
Pregnancy, lactation.
PATHOLOGIC CAUSES
In adult males and post-menopausal females, Fe deficiency is usually related to chronic blood loss mainly from GIT.
Dietary deficiencies (rarely the only etiology)
• cow’s milk (infant diet)
• poor dietary iron intake (elderly)
Absorption imbalances
• post-gastrectomy
• malabsorption
Hemorrhage
• obvious causes - menorrhagia
• occult - peptic ulcer disease, aspirin, GI tract cancer,ankylostoma.
Intravascular hemolysis;iron will be lost in the urine.
Stages of Development of IDA
CLINICAL PRESENTATION Of IDA
Iron deficiency may cause fatigue before clinical anemia developsBrittle hair
Dry skin
Dysphagia (esophageal web, Plummer-Vinson ring)
Nail changes
• brittle
• koilonychia
Glossitis
Angular stomatitis
Pica (appetite for bizarre substances e.g. ice, paint, clay)
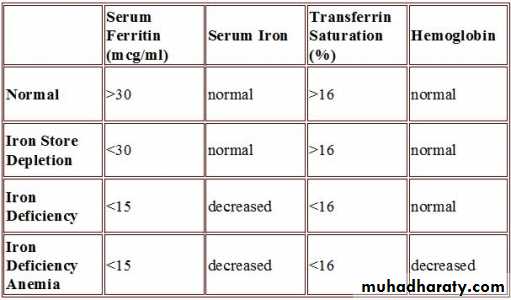
IRON INDICES
* Bone marrow biopsy is the gold standard test for iron stores.Serum ferritin
• Single most important blood test for iron stores.
• Falsely elevated in inflammatory disease, liver disease (from necrotic hepatocytes), neoplasm and hyperthyroidism.
Serum iron.
Total iron binding capacity (TIBC):
• measure of total amount of transferrin present in blood.
• normally, one third of the TIBC is saturated with Fe, the
remainder is unsaturated
Transferrin Saturation:
• serum Fe divided by TIBC, expressed as a proportion
or a percentage.
Diagnosis of IDA
• Laboratory Investigations
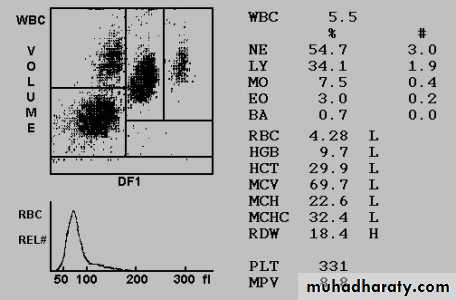
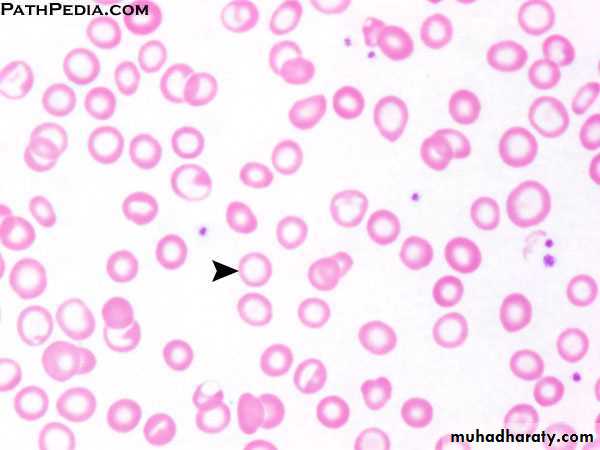
• 1- Peripheral blood film
• • Hypochromic microcytic RBC.
• • Pencil forms.
• • Target cells (thin).
• • Platelet count may be elevated.
• 2- Serum Iron Studies
• • low s.iron, high TIBC, low Fe saturation
• • S. ferritin < 20 ug/l is diagnostic of iron deficiency anemia,
• • Increased plasma level of soluble transferrin receptors.
• 3- Hemoglobin Electrophoresis decreased Hb A2 percentage.
• 4- Bone marrow study (Needed in difficult cases)
• • Micronormoblastic maturation of erythroid precursors.
• • Fe stain (Prussian blue) shows decreased iron in macrophages.
Differential Diagnosis OF IDA
• Hb A2• %Saturation
• TIBC
• Serum iron
• S.Ferritin
• L
• L
• H
• L
• L
• Iron deficiency
• N
• N
• L/N
• L/N
• H/N
• Chronic disease
• N
• H
• N
• H
• H
• Sideroblastic anemia
• H
• -
• L/N
• H/N
• H/N
• β Thalassemia
• minor
Treatment of IDA
1- TREAT THE UNDERLYING CAUSE : to control the site of blood loss, correct malabsorption, improve oral iron intake etc…
2- IRON REPLACEMENT
Different preparations available: tablets, syrup, parenteral
Dose: ferrous sulphate 325 mg PO TID or ferrous gluconate 300 mg PO TID until anemia corrects and then for 3 months after to replenish the stores.
Reticulocytes begin to increase after one week indicating response.
Ensure that the hemoglobin returns completely to normal.
Treatment of IDA
If serum ferritin returns to normal discontinue iron therapy.Common side effects :nausea, dyspepsia, constipation, and diarrhea.
In the rare patient who cannot tolerate or cannot absorb iron from the gastrointestinal tract, parenteral iron is available as an iron-dextran complex and iron sorbitol.
Blood is given for severely symptomatic anemia.