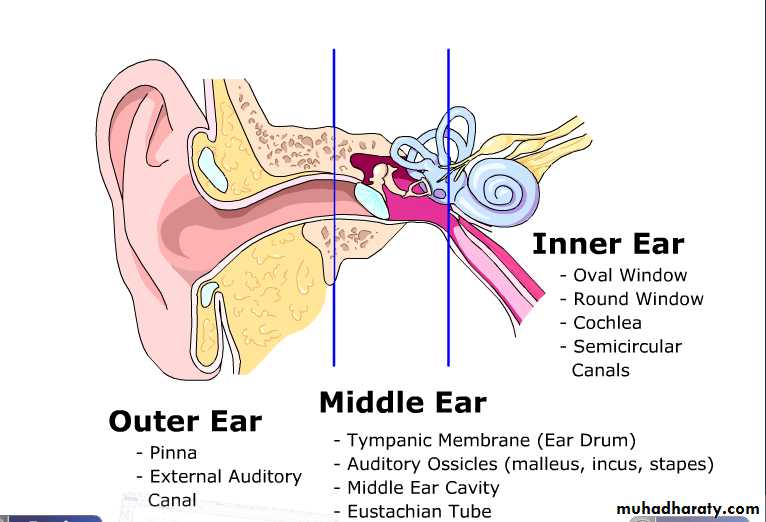
Anatomy of the EarThree Main Sections
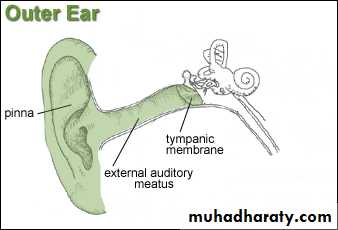
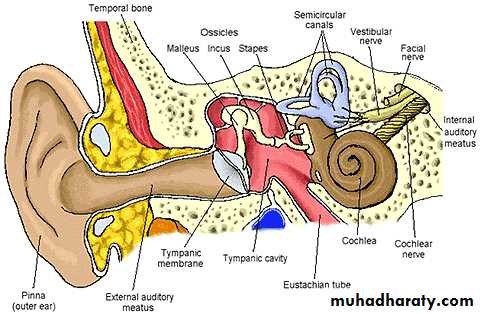
The External EarConsists of:
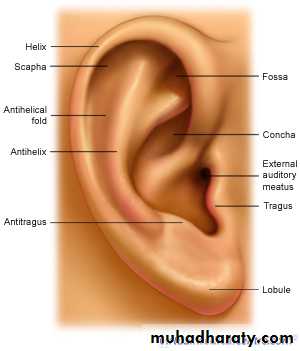
Auricle (pinna)
Made of elastic cartilage
Helix (rim)
Lobule (ear lobe)
External auditory canal
Lies within temporal bone & connects to ear drum (tympanic memb)
Contains ceruminous glands which secrete ear wax
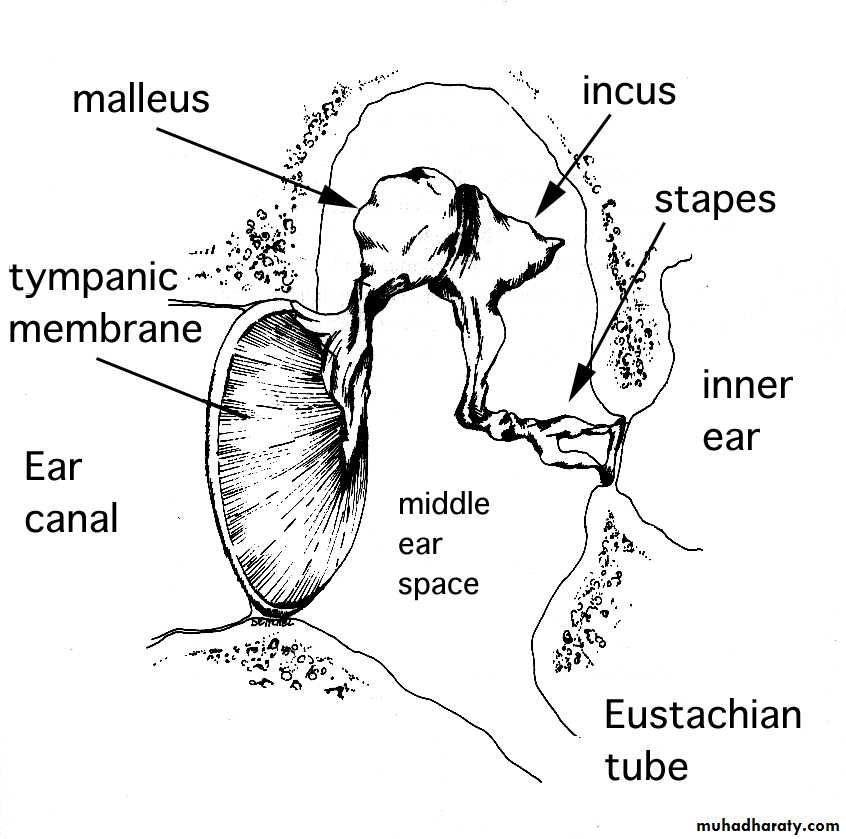
Tympanic membrane
Epithelial & simple cuboidal
Changes acoustic energy into mechanical energy
Perforated eardrum = tear
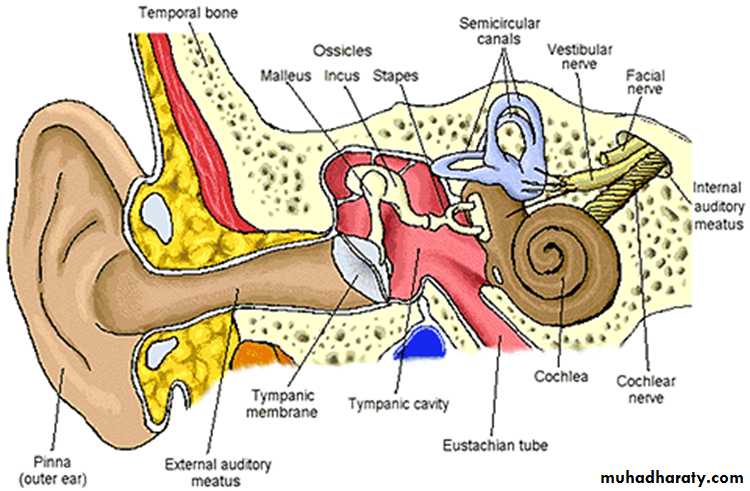
The Middle Ear
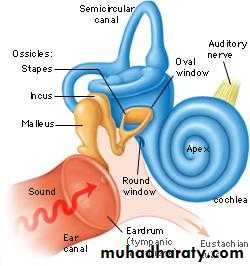
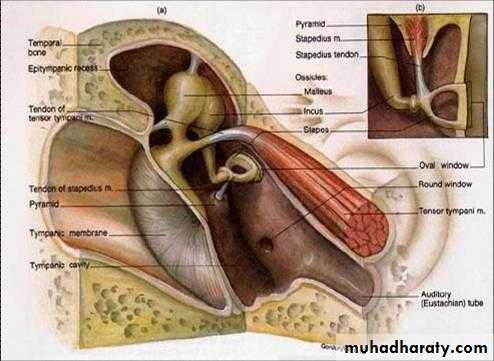
Auditory Ossicles (smallest bones in body)Malleus
Attaches to ear drum
Articulates with incus
Incus
Articulates with stapes
Stapes (stirrup)
Footplate of stapes fits into oval window
Opening to Eustachian tube
Protection by Two Tiny Muscles
Tensor TympaniAttaches to Malleus to increase tension on ear drum & prevent damage to inner ear.
Stapedius
Smallest skeletal muscle
Dampens large vibrations of stapes to protect oval window.
stapedius
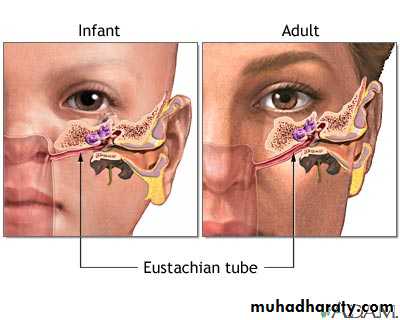
Auditory Tube (Eustachian tube)
Is a route for pathogens to travel from nose and throat to ear causing Otitis MediaDuring swallowing and
• yawning it opens to equal
• pressure in middle ear.
•
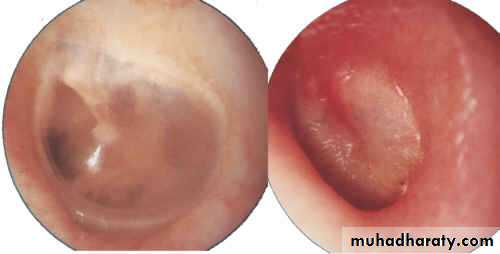
Normal Ear Drum
Inflamed Ear Drum
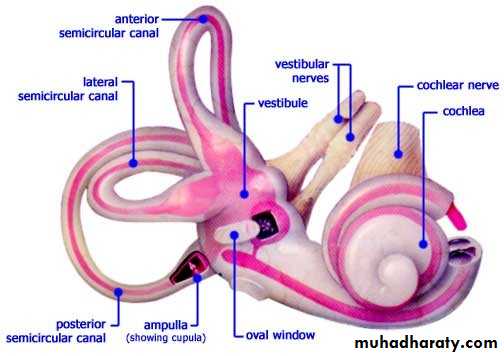
The Inner Ear (Labyrinth)
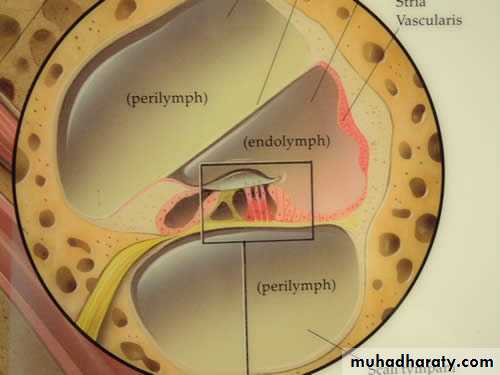
Bony labyrinth
Contains perilymphSemicircular canals
Anterior, posterior, and lateral
Lie right angles to each other
Vestibule
Oval portion
Cochlea
Looks like a snail
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
Membranous labyrinth
Contains endolymph, high in K+ ions