
D
D
r
r
.
.
D
D
u
u
r
r
a
a
n
n
K
K
A
A
L
L
A
A
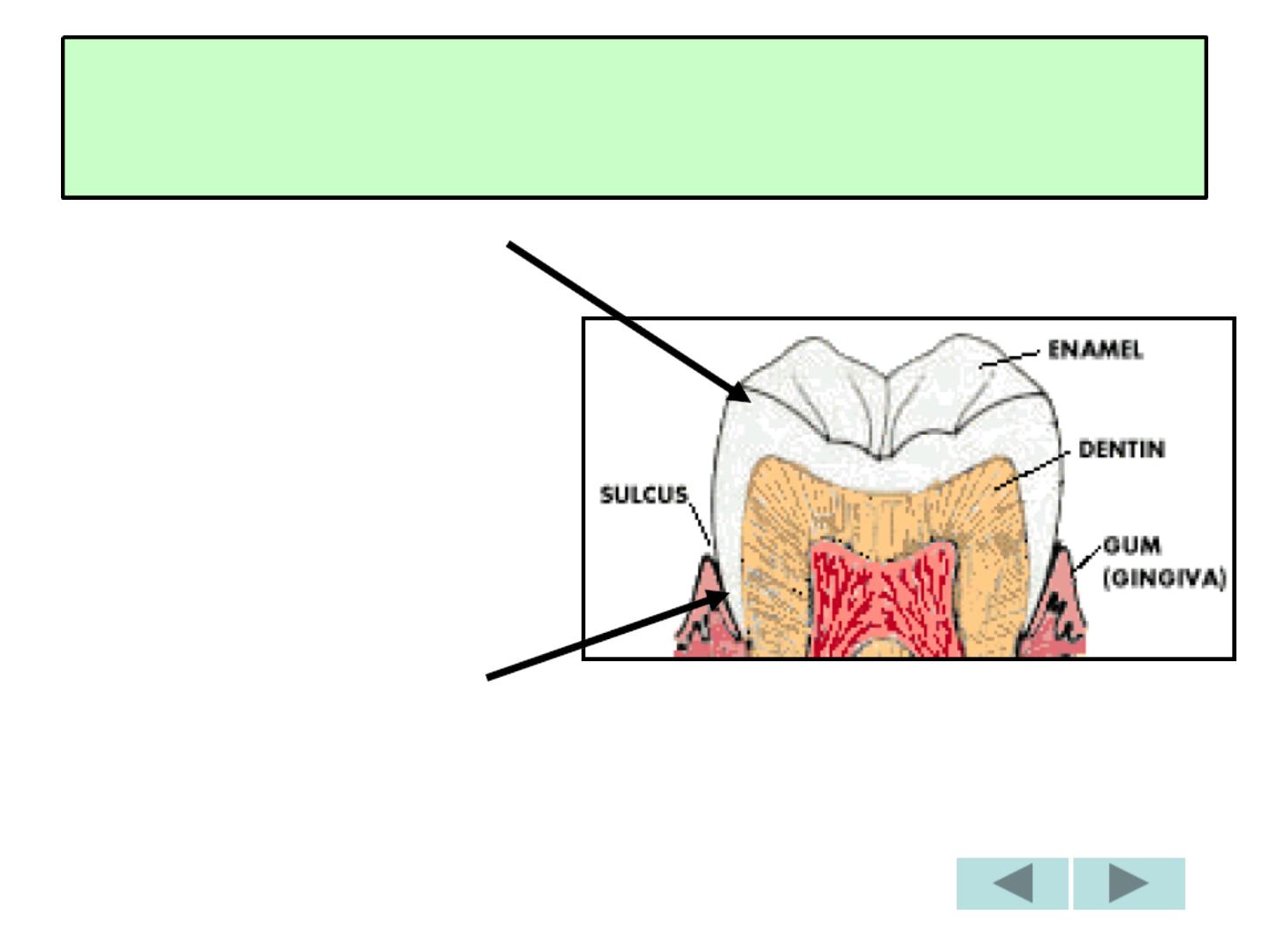
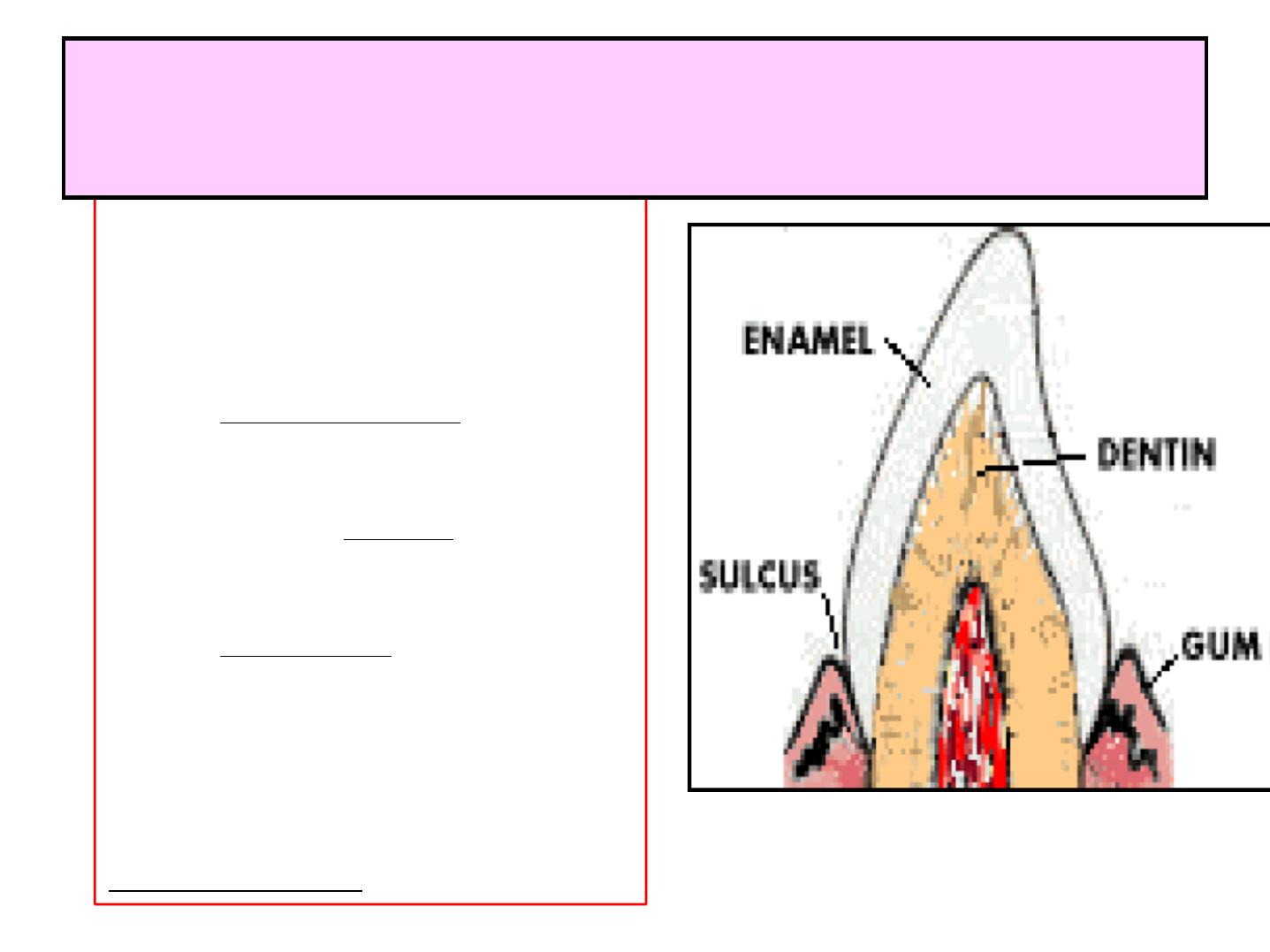
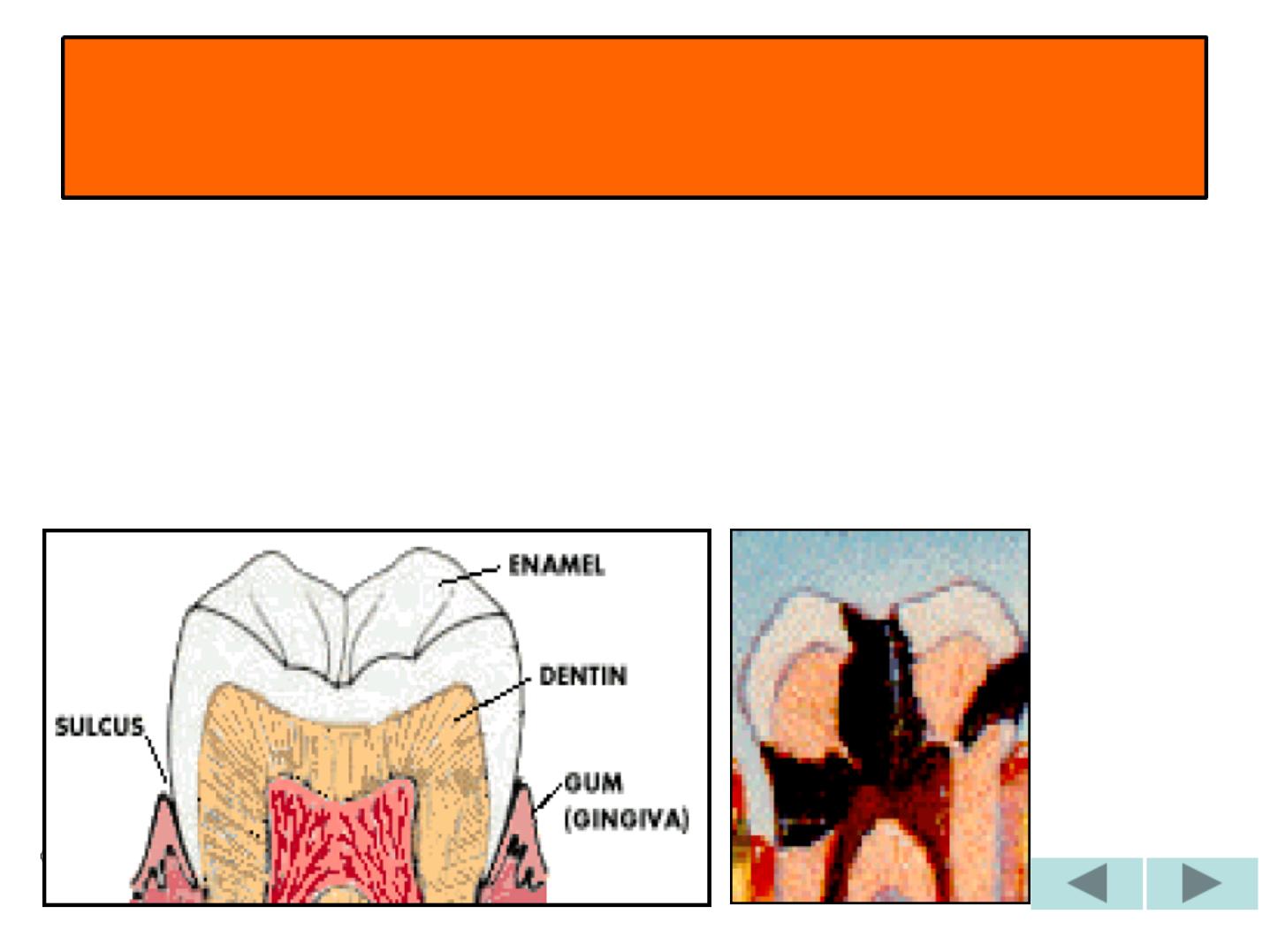
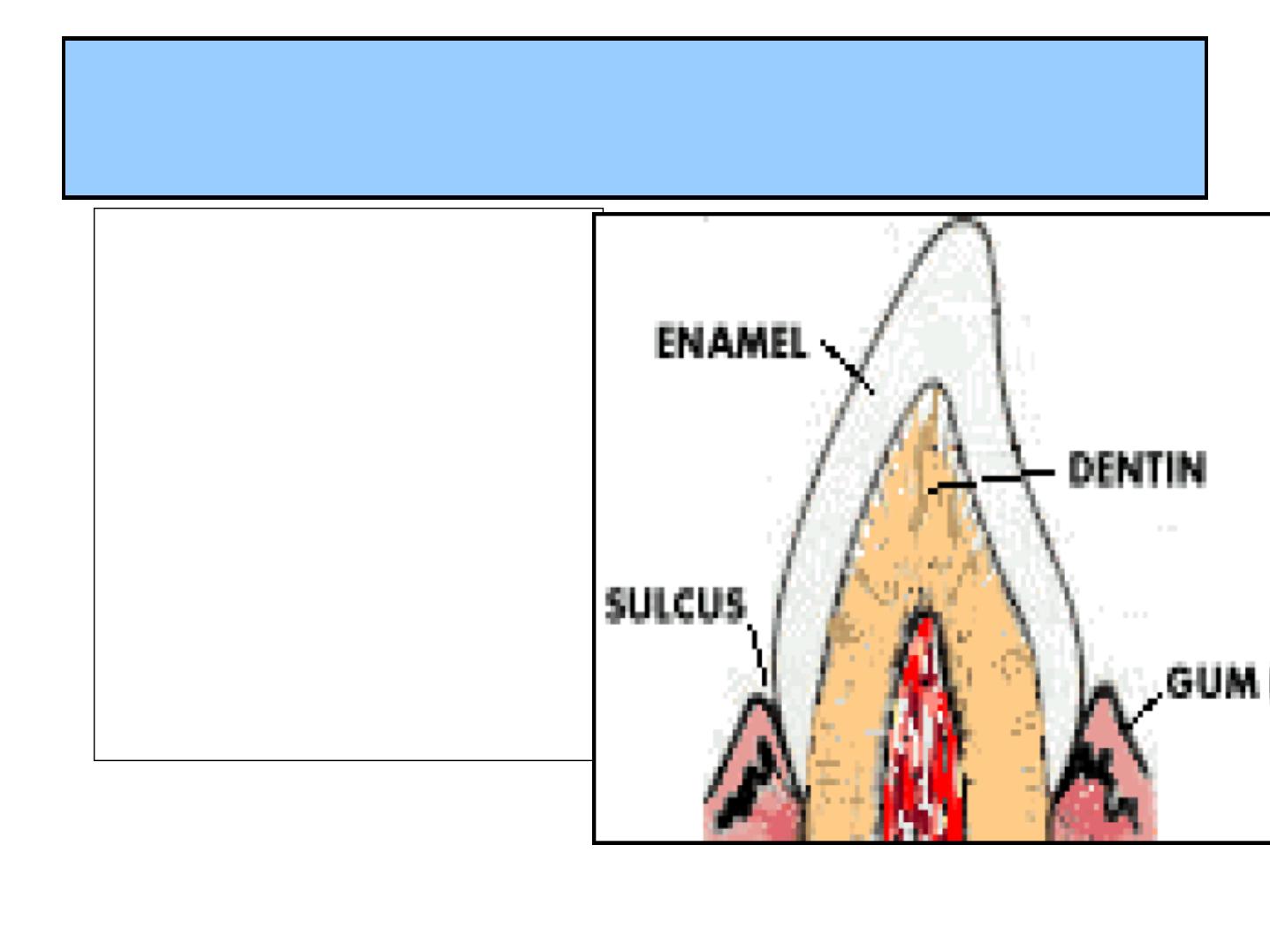
GENERAL CHARACTERS
1-ECTODERMAL TISSUE
COVERING THE
ANATOMICAL CROWN.
2-HIGHLY MINERALIZED
,
RESIST
MASTICATORY(chewing)
FORCES.
3-ACELLULAR,
INERT,
NONVITAL AND
INSENSITIVE.
4-CANNOT
REPALCED OR
REGENERATED.
5-PERMEABLE
TO IONIC
STRUCTURE.
PHYSICAL
PROPERTIES
2-THICKNESS
5-PERMEABILITY
1-COLOUR
4-BRITTLNESS
3-HARDNESS
1 - COLOUR
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
L
L
O
O
W
W
I
I
H
H
W
W
H
H
I
I
T
T
E
E
T
T
O
O
G
G
R
R
A
A
Y
Y
I
I
S
S
H
H
W
W
H
H
I
I
T
T
E
E
DEPENDS ON :
1- DEGREE OF
CALCIFICATION
2- HOMOGENISITY OF
THE ENAMEL
SO:
Y
Y
E
E
L
L
L
L
O
O
W
W
I
I
S
S
H
H
TEETH….
TRANSLUCENT E.
G
GR
RA
A Y
YIIS
SH
H
TEETH ……
OPAQUE E.
2 - THICKNESS
-
2
2
–
–
2
2
.
.
5
5
m
m
m
m
. at
the cusps of the
molars and
premolars.
-
T
T
h
h
i
i
n
n
n
n
i
i
n
n
g
g
d
d
o
o
w
w
n
n
to
Almost knife edge
at the cervical
margin of the
tooth

3 –HARDNESS
I
I
T
T
I
I
S
S
T
T
H
H
E
E
H
H
A
A
R
R
D
D
E
E
S
S
T
T
C
C
A
A
L
L
C
C
I
I
F
F
I
I
E
E
D
D
T
T
I
I
S
S
S
S
U
U
E
E
I
I
N
N
T
T
H
H
E
E
B
B
O
O
D
D
Y
Y
D
D
U
U
E
E
T
T
O
O
:
1- HIGH CONTENT OF THE
MINERAL SALTS
2- ITS CRYSTALLINE
ARRANGEMENT.
- ENAMEL OF THE
P
P
E
E
R
R
M
M
A
A
N
N
E
E
N
N
T
T
TEETH E. IS
HARDER THAN THAT OF
DECIDUOUS ONES’
-
E
E
N
N
A
A
M
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
I
I
C
C
R
R
O
O
H
H
A
A
R
R
D
D
N
N
E
E
S
S
S
S
1 - IS
GREATEST
AT
THE SURFACE AND
DECREASED
TOWARD DEJ.
2 - IT IS
GREATER
AT
THE CUSPS AND
INCISAL RIDGE AND
DECREASES
TOWARD THE
CERVICAL LINE.
3 –HARDNESS
ASG
4 –BRITTLNESS (fragileness)
ITS STRUCTURE AND HARDNESS
RENDER IT BRITTLE, SPECILY WHEN
IT
LOOSES
ITS ELASTIC FOUNDATION
OF HEALTHY
DENTIN
5- PERMEABILITY
-ENAMEL HAS A
C
C
E
E
R
R
T
T
A
A
I
I
N
N
D
D
E
E
G
G
R
R
E
E
E
E
O
O
F
F
P
P
E
E
R
R
M
M
E
E
A
A
B
B
I
I
L
L
T
T
Y
Y
DEMONSTRATED BY DYES
AND RADIOACTIVE
ISOTOPES.
-
I
I
T
T
A
A
C
C
T
T
S
S
A
A
S
S
A
A
S
S
E
E
M
M
I
I
P
P
E
E
R
R
M
M
E
E
A
A
B
B
L
L
E
E
M
M
E
E
M
M
B
B
R
R
A
A
N
N
E
E
FOR CERTAIN
IONS AND DYESTUFFS OF
SMALL MOLECULAR SIZE
THROUGH PORES
BETWEEN THE CRYSTALS.
-PER. IS
M
M
A
A
I
I
N
N
L
L
Y
Y
FROM SALIVA TO
OUTER LAYER OF
ENAMEL, BUT LESS
FROM THE PULP
TO THE INNER
ENAMEL LAYER
ACROSS THE
DENTIN.
5- PERMEABILITY
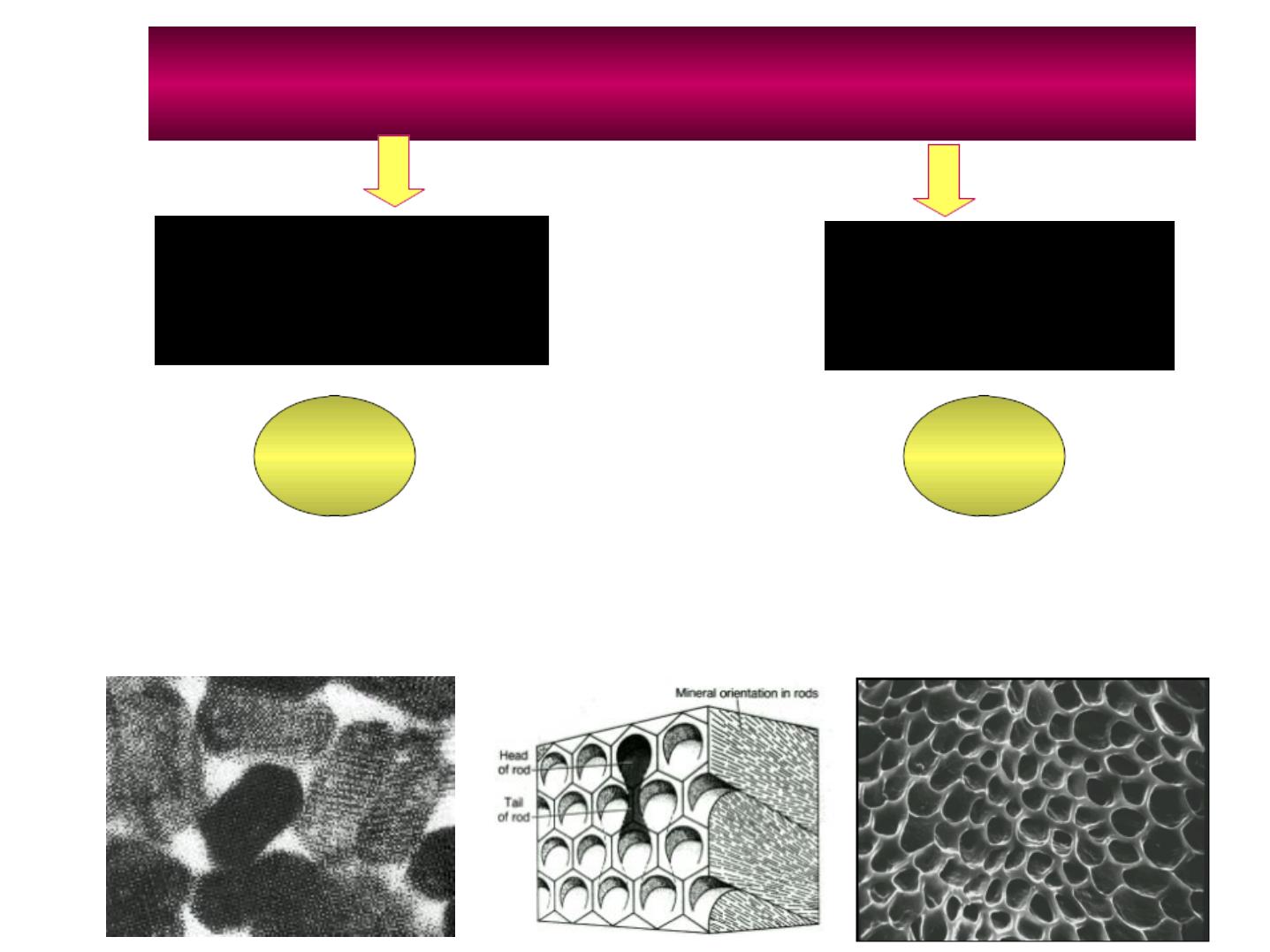
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION:
CRYSTALLINE CALCIUM PHOSPHATE
“
HYDROXYAPATITE”
Ca
10
(PO4)
6
(OH)
2
9
9
6
6
%
%
By w e i gh t
4
4
%
%
AMELOGENINS
ENAMELINS and Water
I
I
N
N
O
O
R
R
G
G
A
A
N
N
I
I
C
C
C
C
O
O
N
N
T
T
E
E
N
N
T
T
O
O
R
R
G
G
A
A
N
N
I
I
C
C
C
C
O
O
N
N
T
T
E
E
N
N
T
T
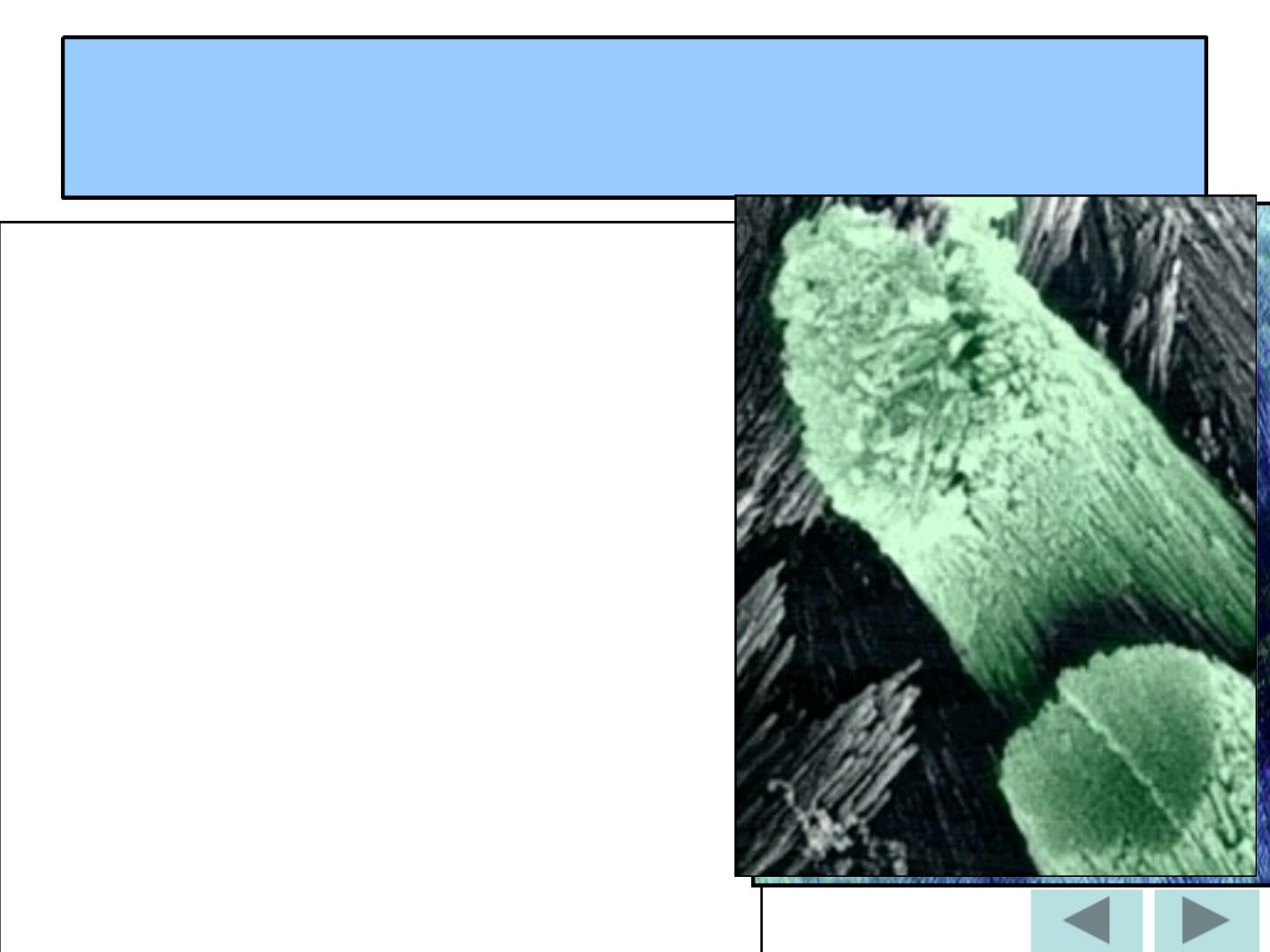
Enamel rods
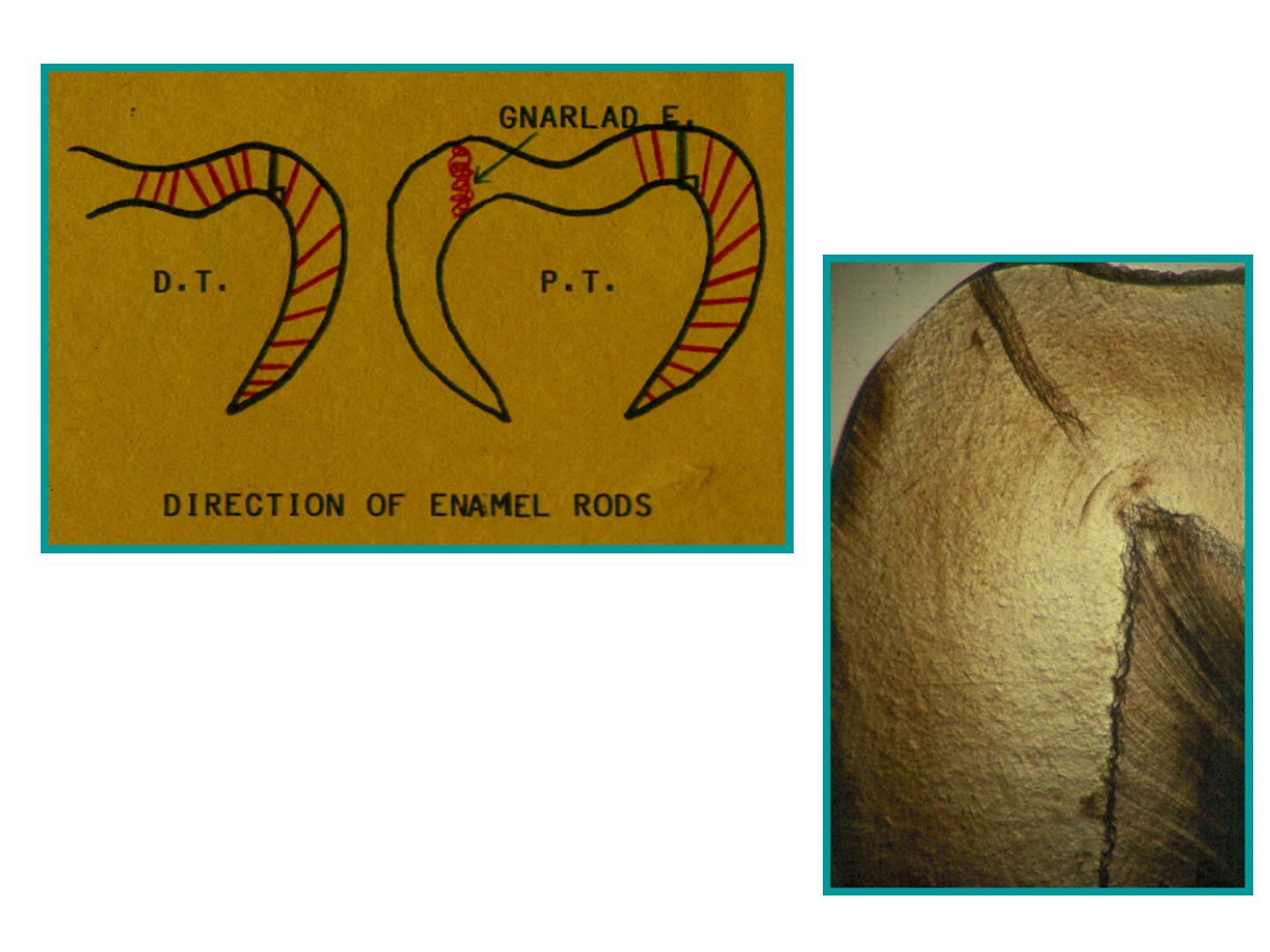
Wavy Course ofEnamel Rods

•
Usually at right angles to the Dentin surface.
•
Follow a wavy course in clockwise and
anticlockwise deviation.
•
At the cusps or incisal edges: gnarled
enamel.
•
At pits and fissures: rods converge in their
outward course.
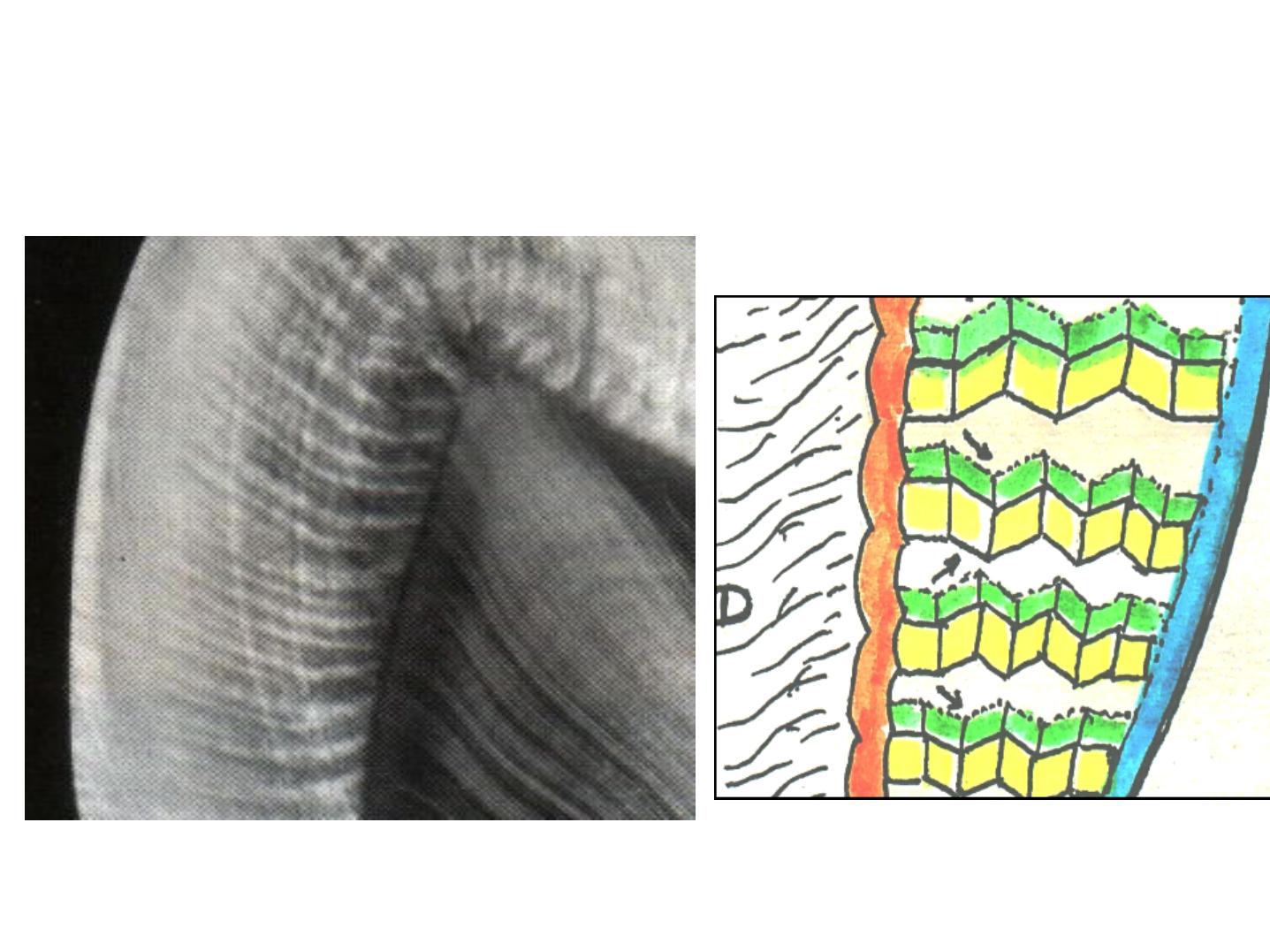
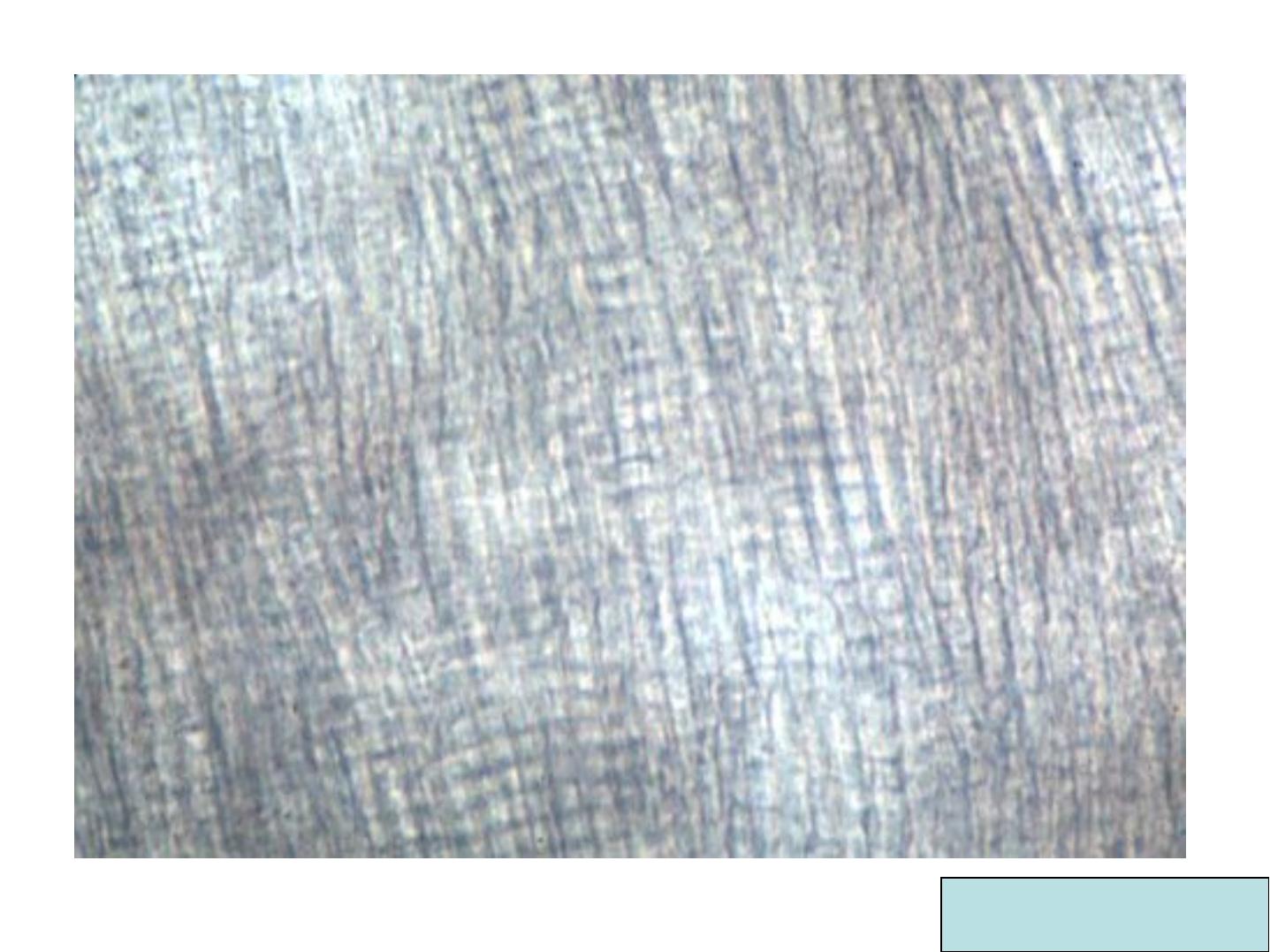
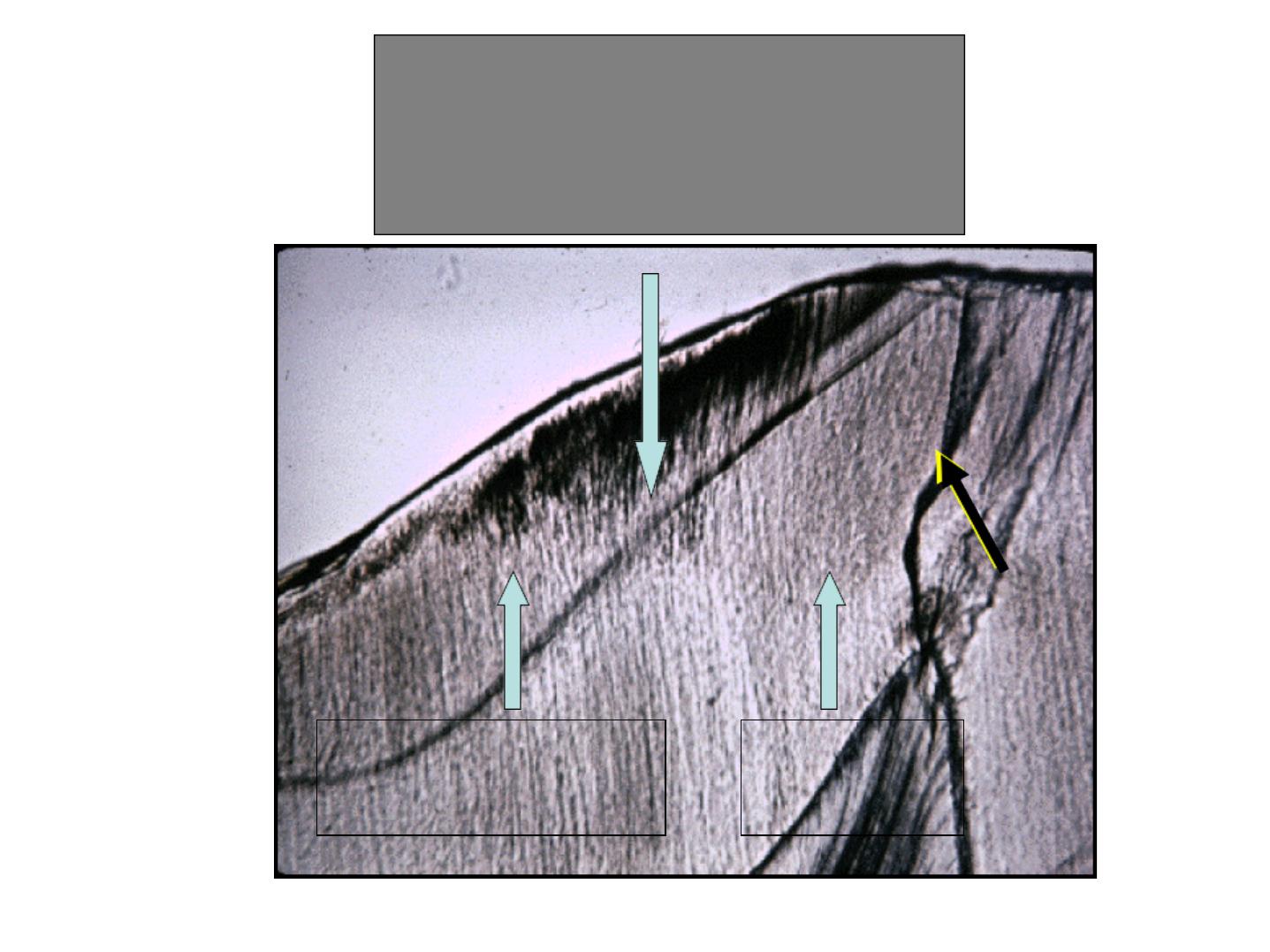
HUNTER-SCHREGER BANDS
(optical phenomenon) dark and lightbands

•
Alternating dark and light strips.
•
Have varying width.
•
Seen in large ground section (oblique
reflected light).
•
Originate from the DEJ.
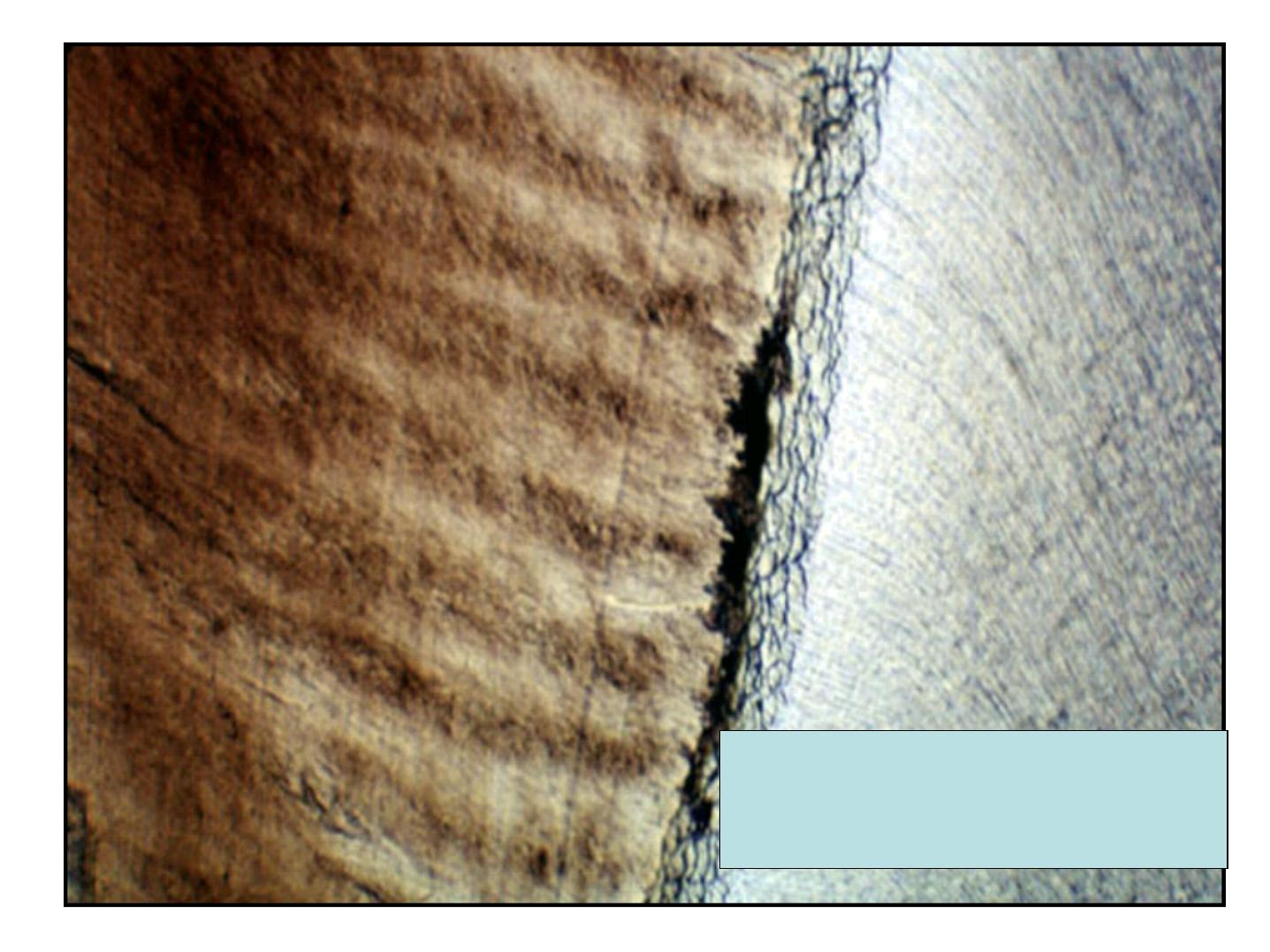
Hunter Schreger bands
Note that Hunter
Schreger bands
Start from the ADJ
and end before
reaching the outer
surface of enamel
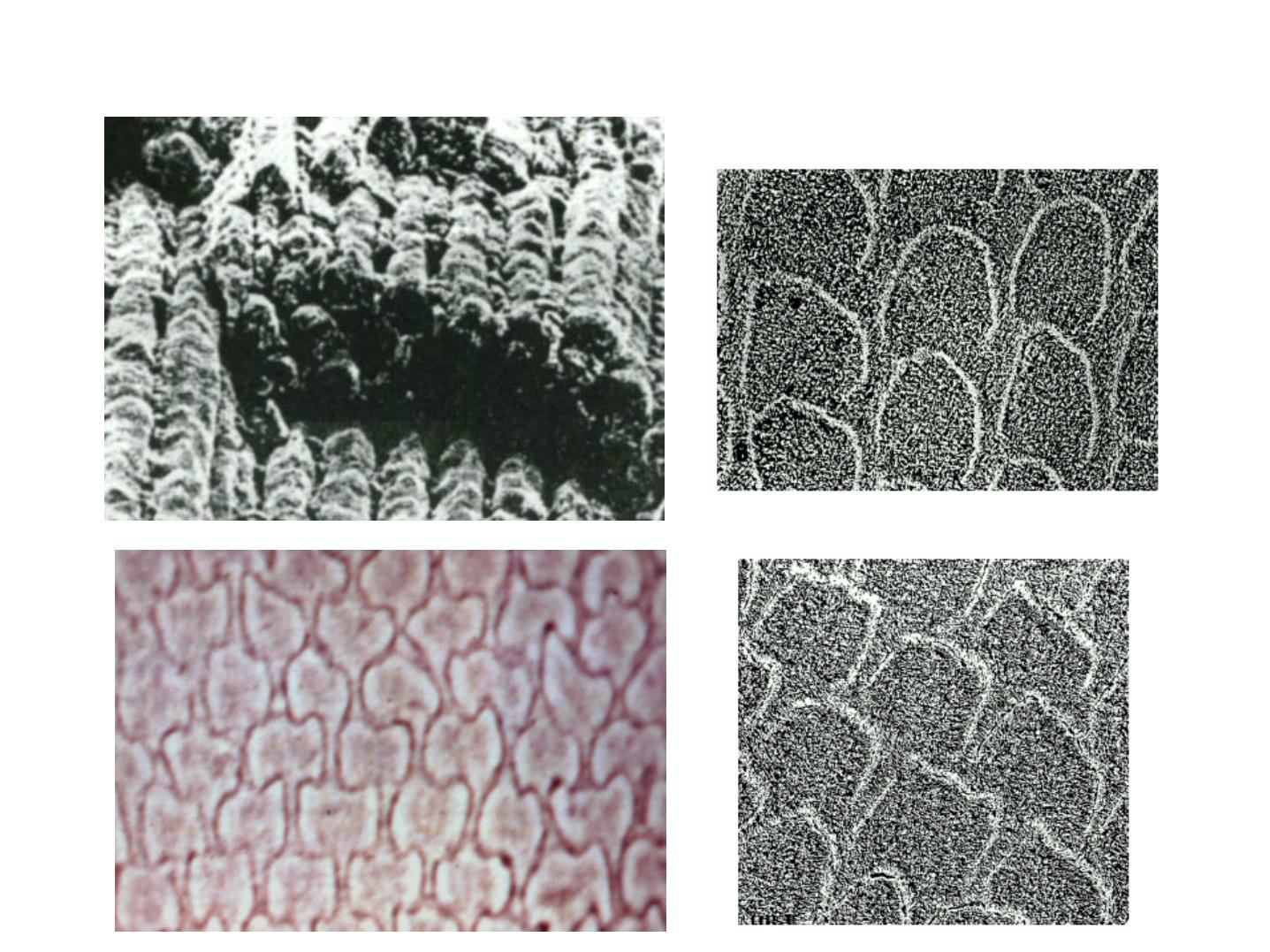
Cross Section
:
Hexagonal, fish scales,
keyhole pattern

HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURESOF
ENAMEL
• Incremental lines
• Enamel lamellae
• Enamel tufts
• Enamel spindle
• Dentino-enamel junction

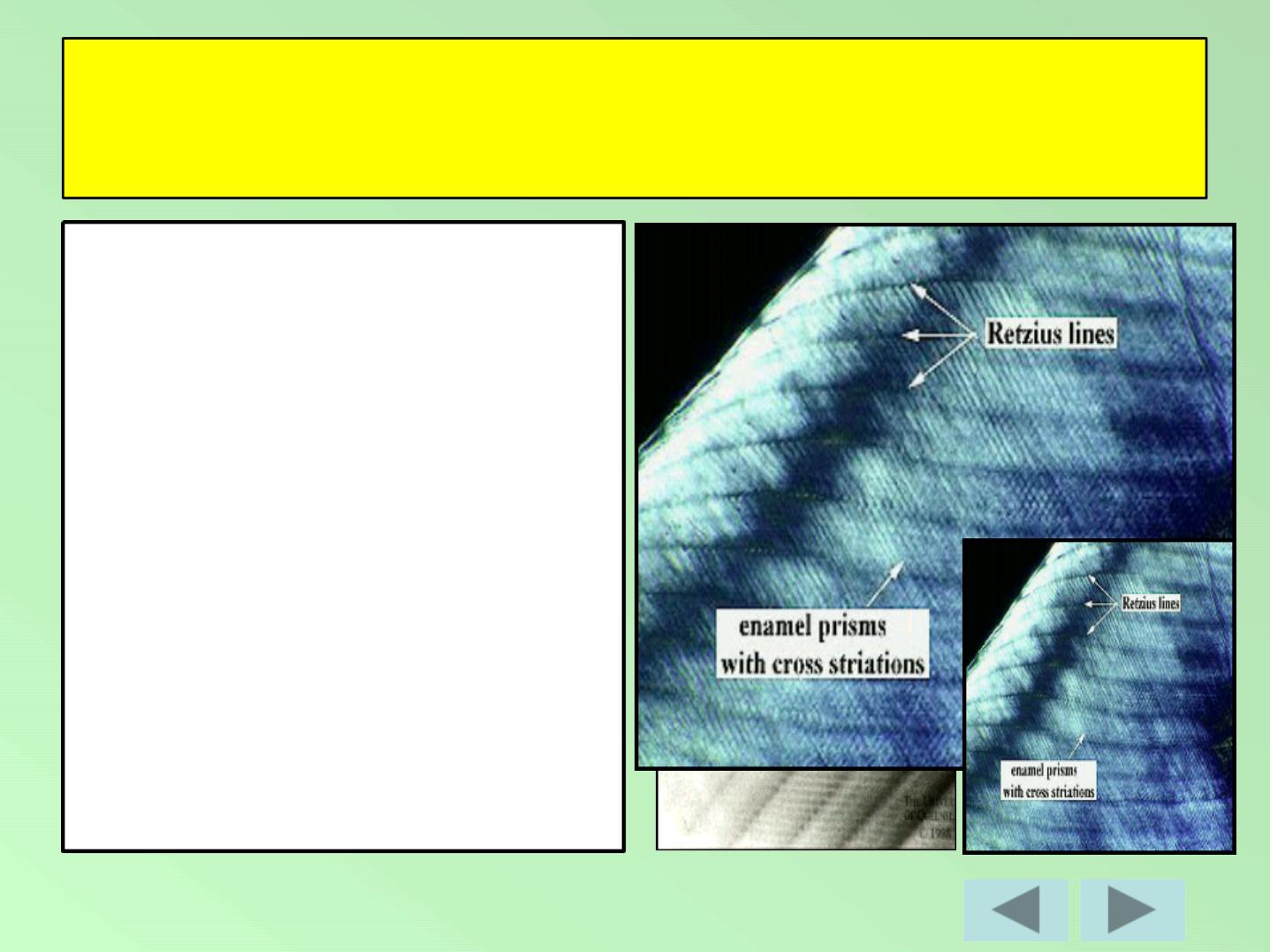
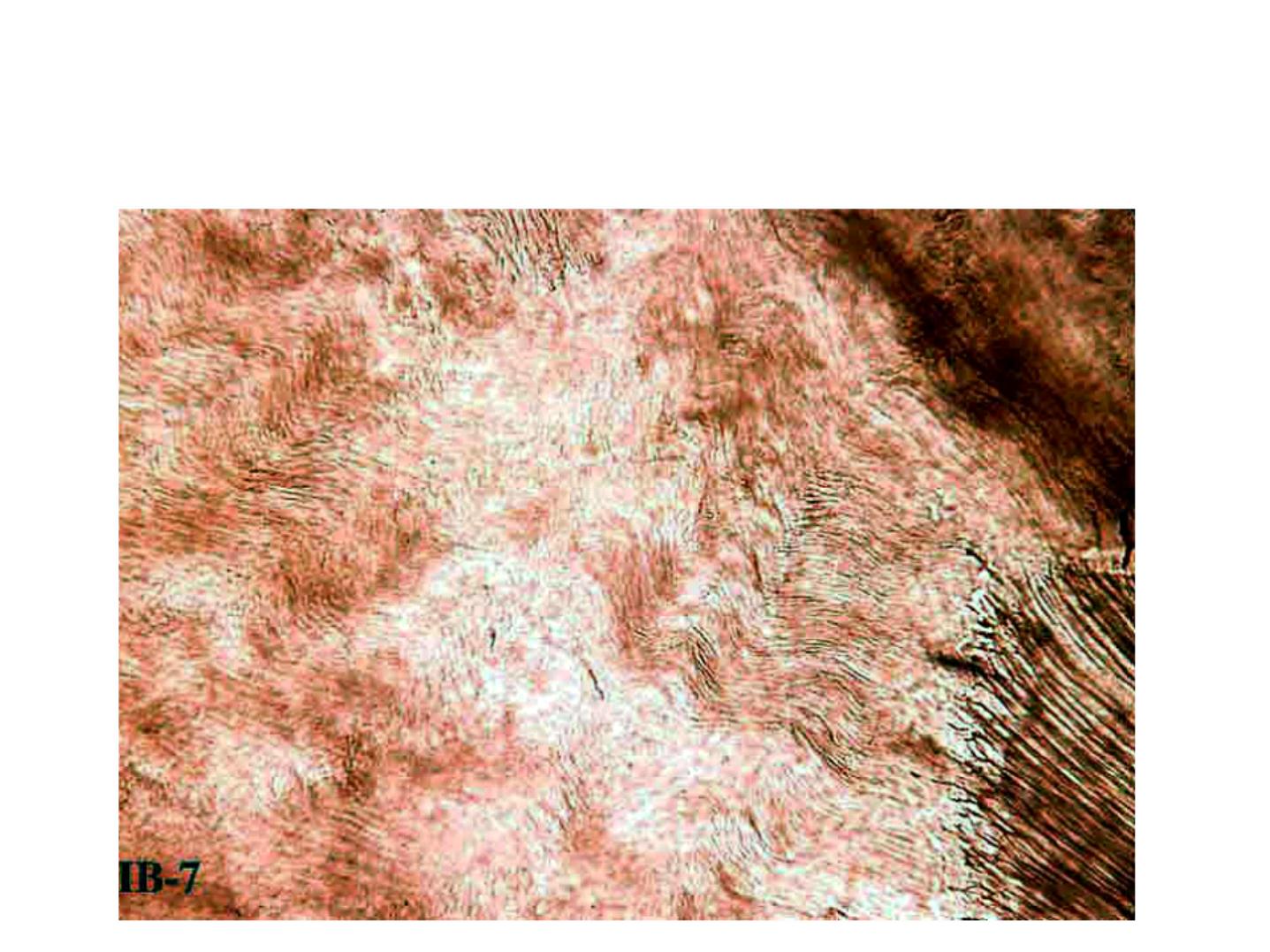
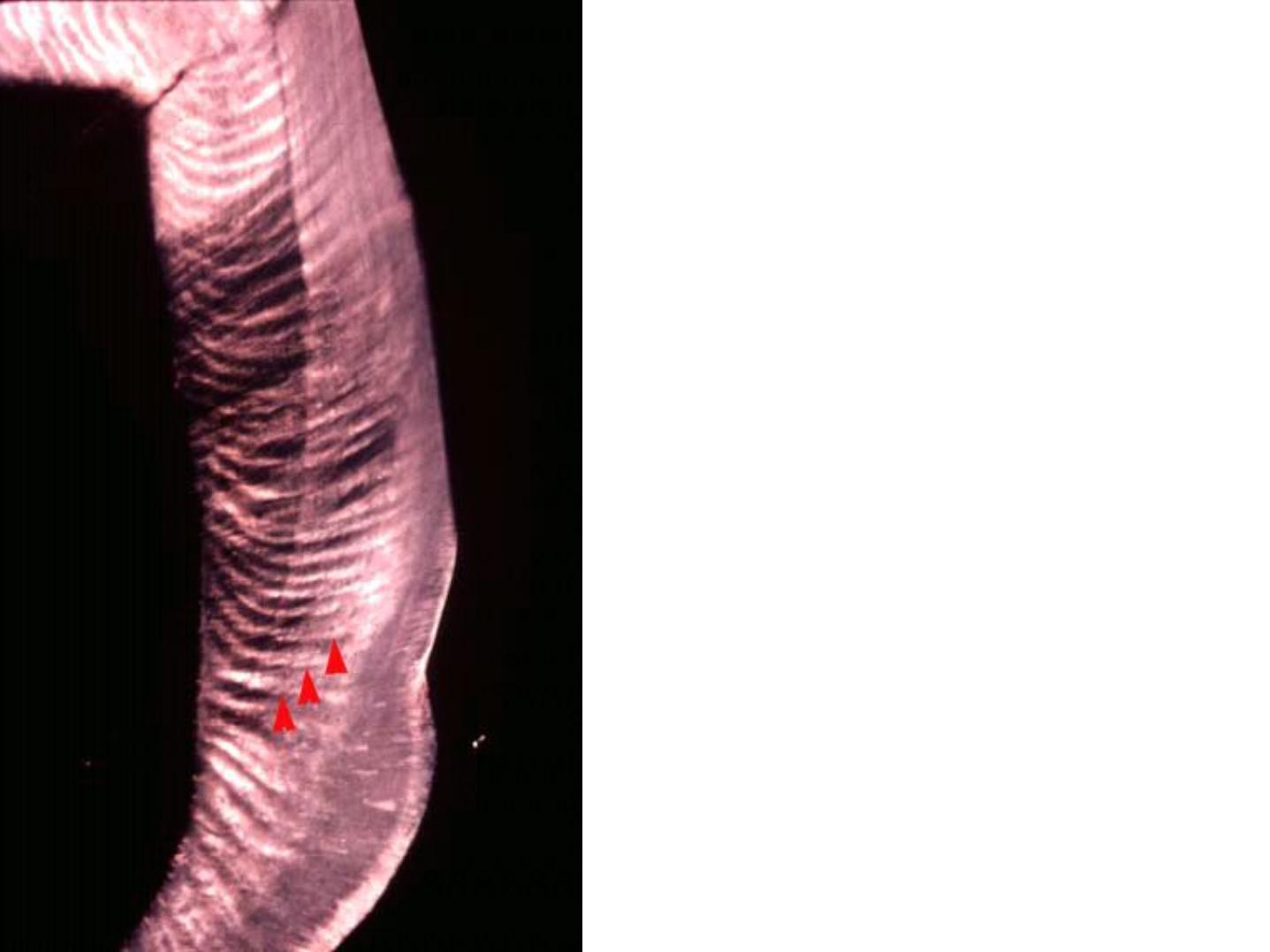
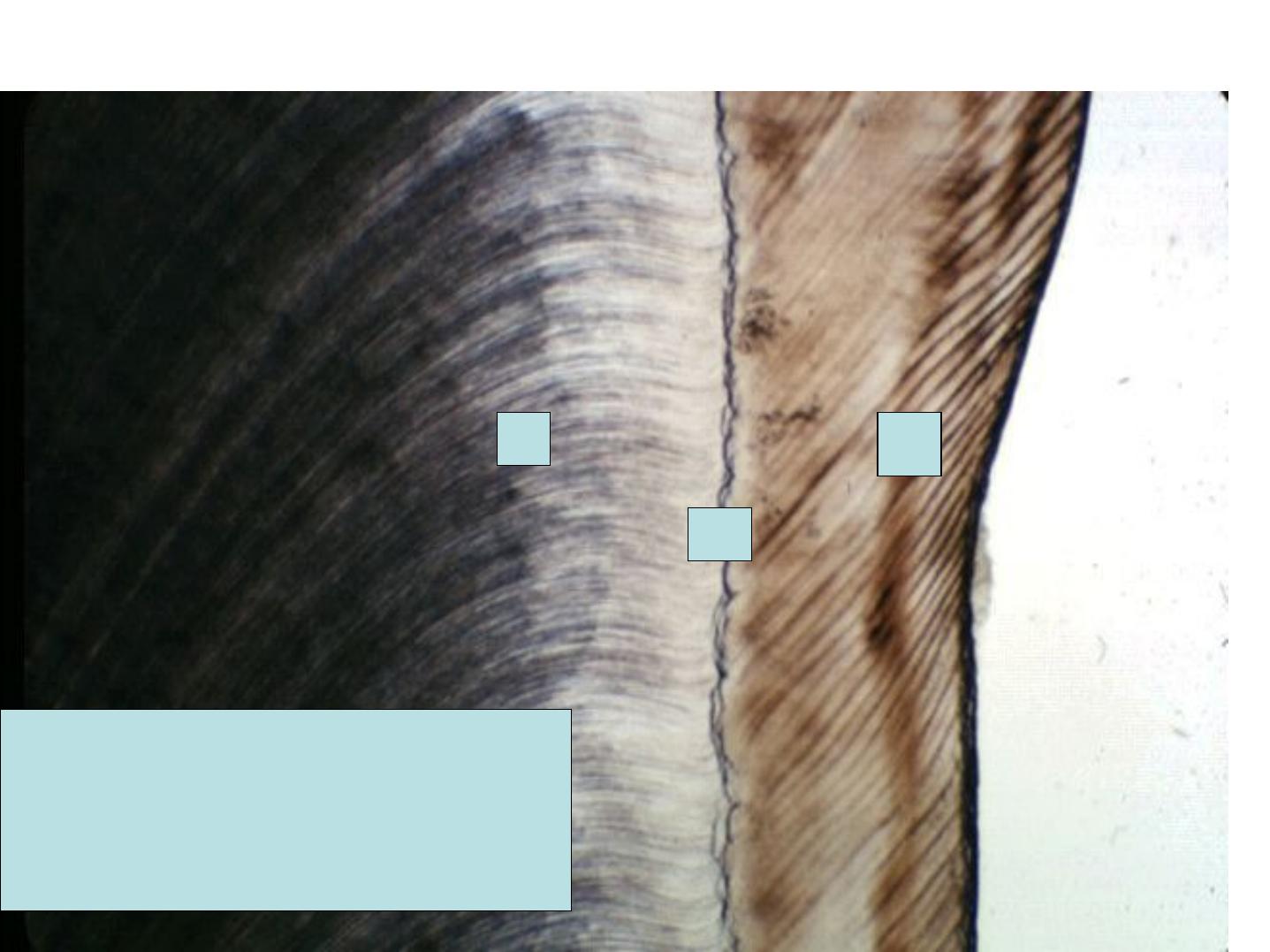
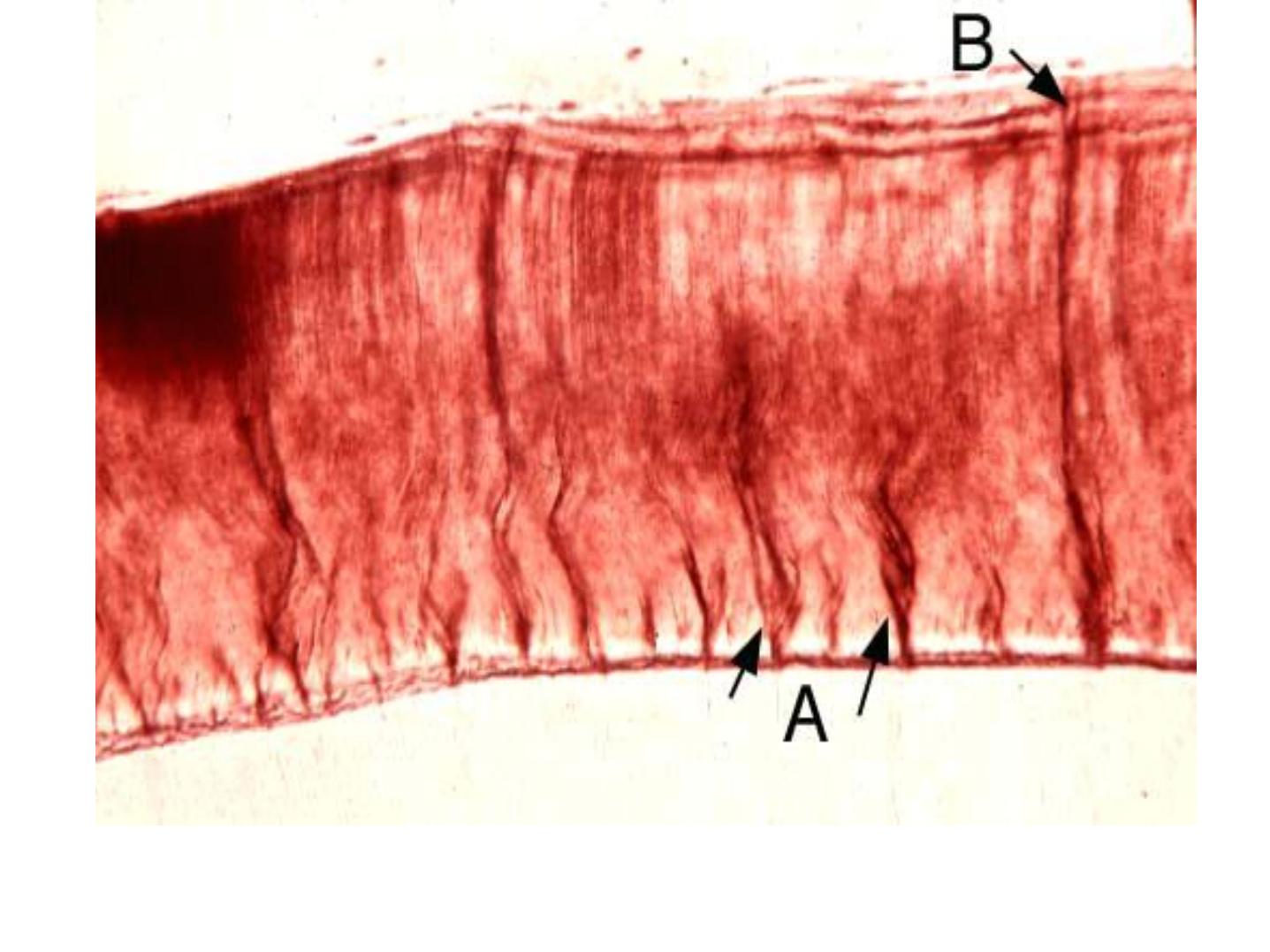
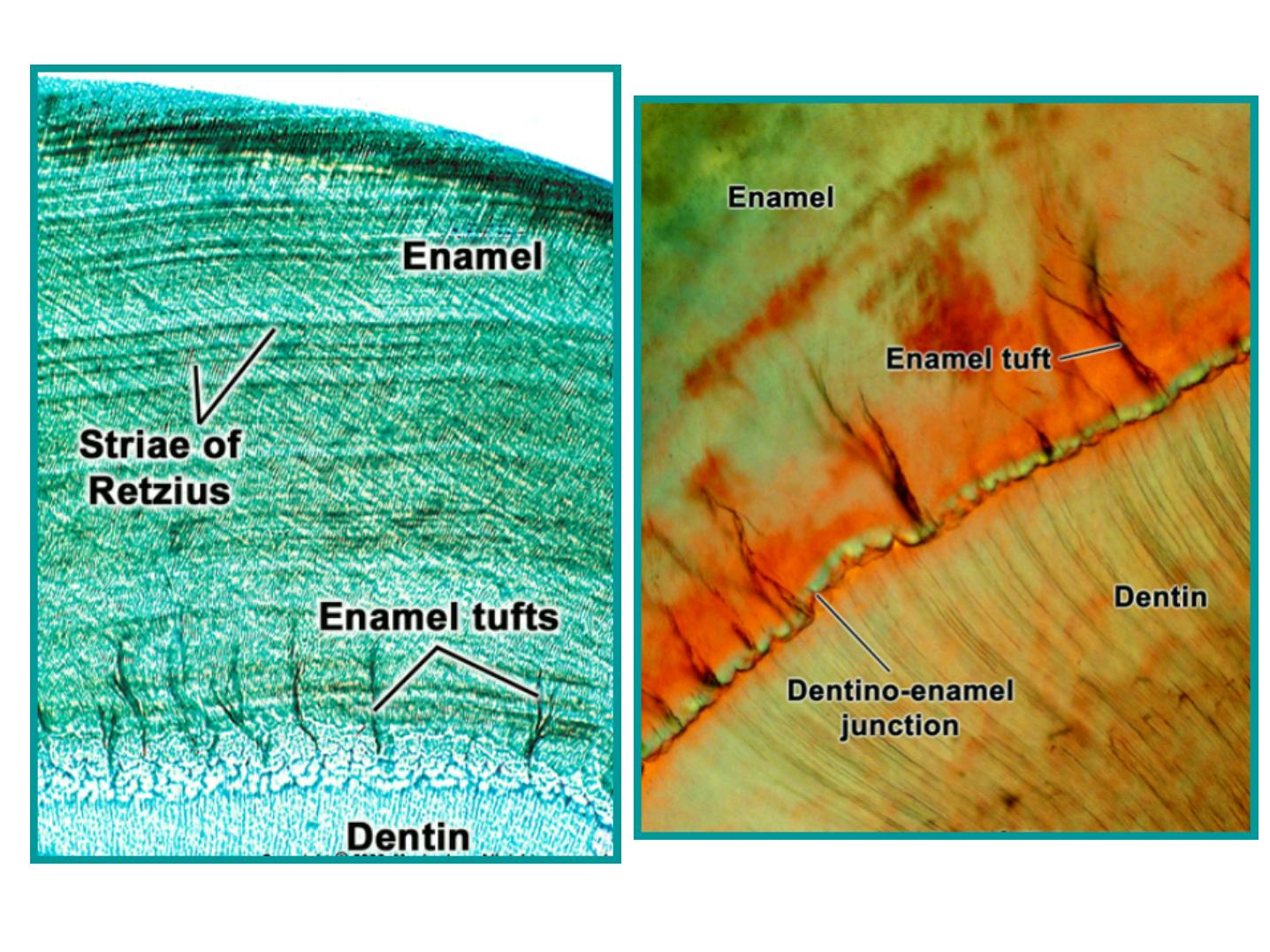
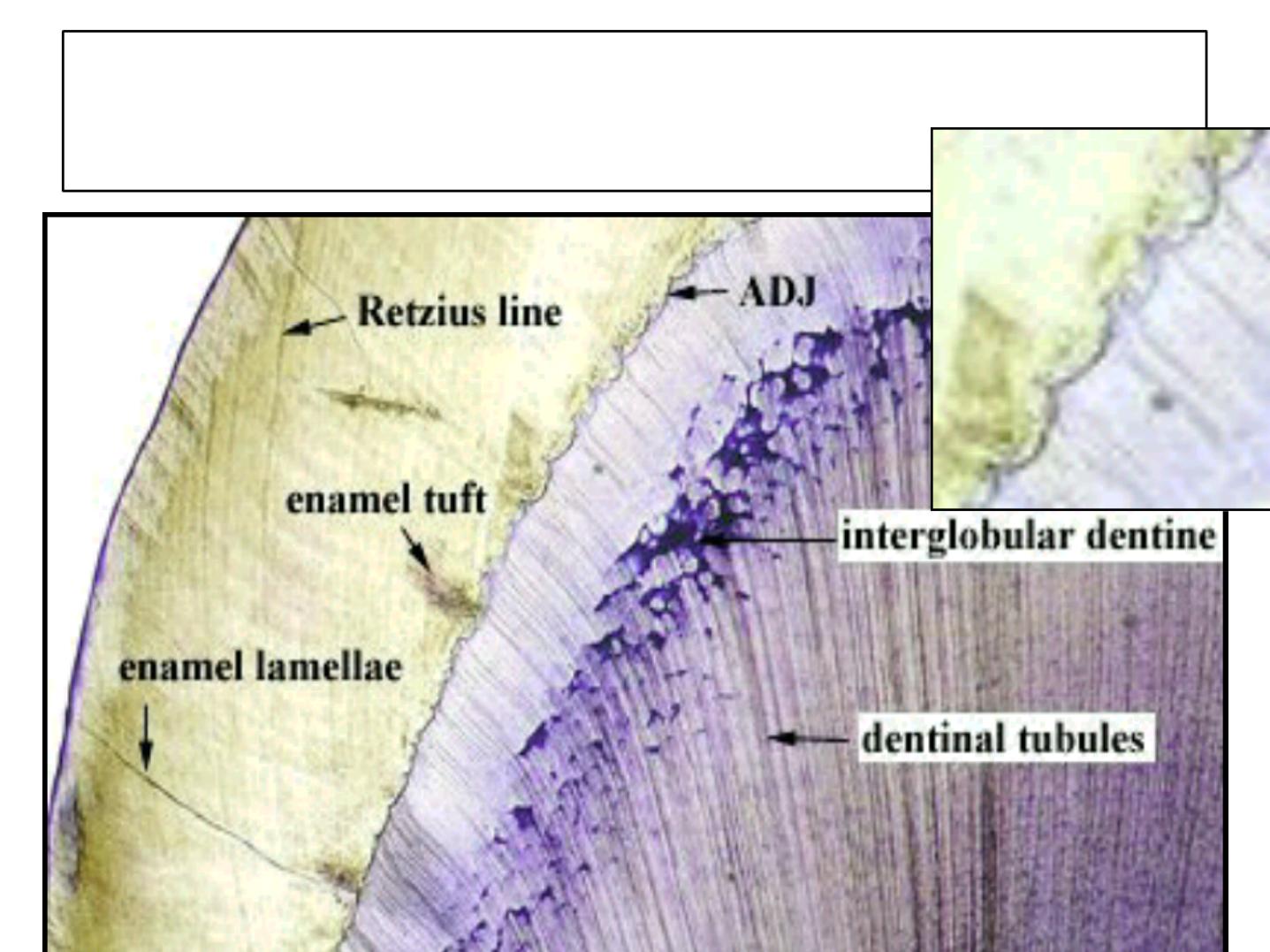
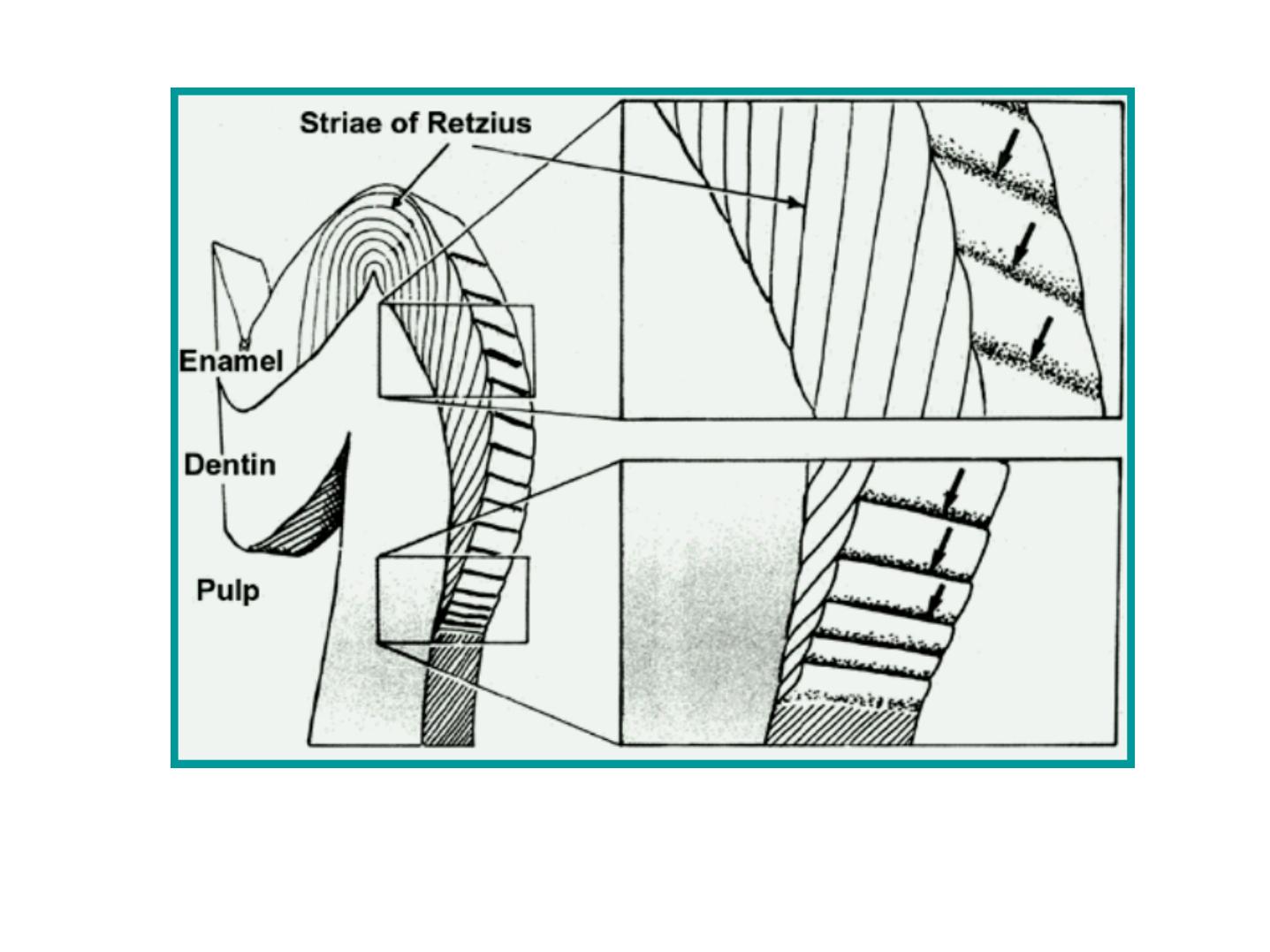
Incremental Lines of Retzius:
•
Brownish bands in ground sections.
•
Reflect variation in structure and
mineralization.
•
Widening of these lines occur in metabolic
disturbances.

STRUCTURAL FEATURESOF ENAMEL
•
CROSS
STRAIATIONS
(short increm ent)
n
INCREMENTAL LINES
OF RETZIUS
( long increm ent)
Incremental lines
:
n
INCREMENTAL LINES OF RETZIUS
( long increm ent)
1
3
1
3
2
1. A.D.J
2. Brown striae of Retzius
3. Dentinal tubule
Brown striae of Retzius
A.D.J
Dentinal tubules

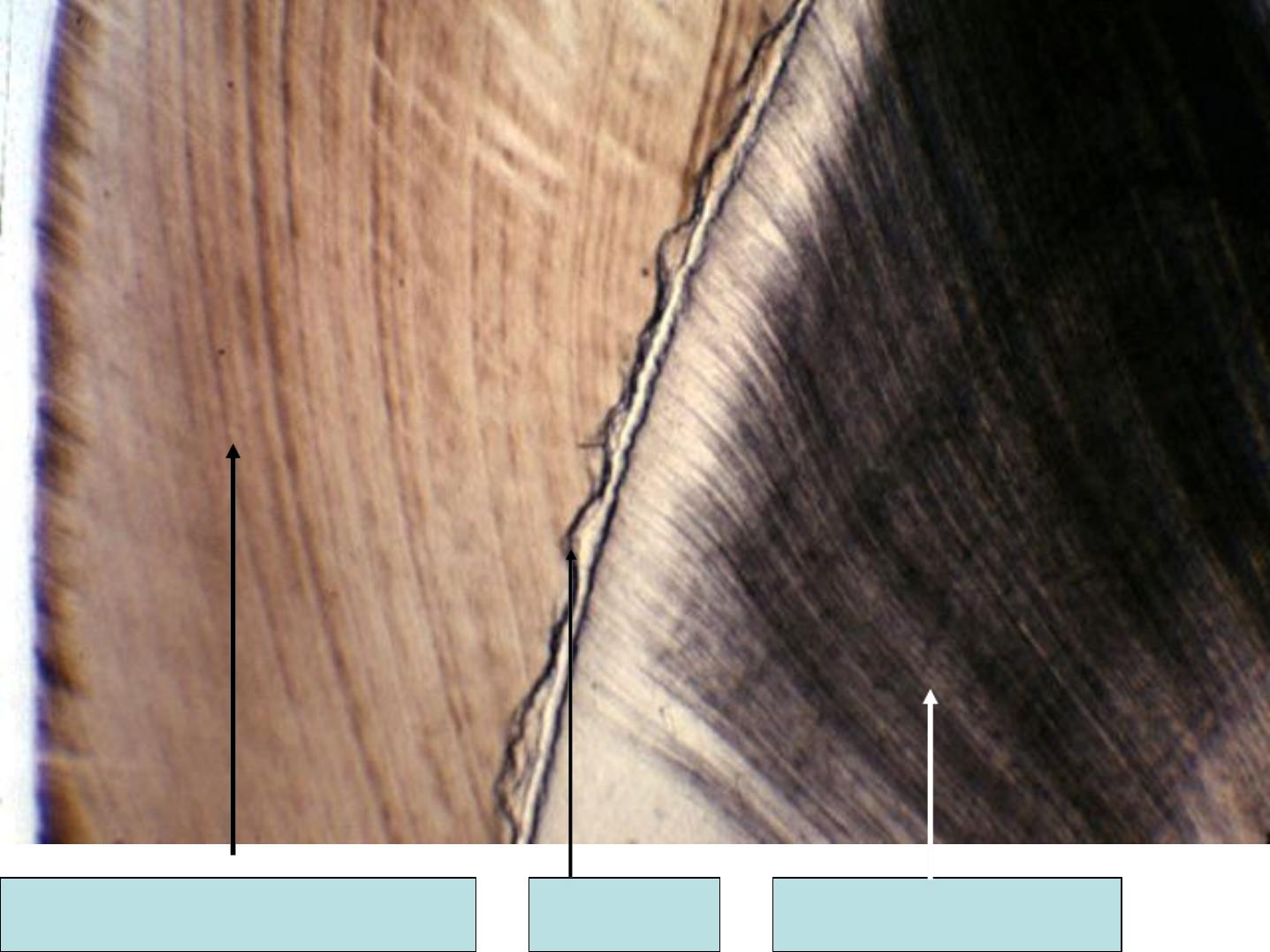
Neonatal Line:
The E. of the deciduous teeth and the 1
s t
permanent molar develop partly before
birth and partly after birth, the
boundary between both is marked by
neonatal line or ring.
NEONATAL LINE
Postnatal
Enamel
Prenatal
Enamel

E
E
n
n
a
a
m
m
e
e
l
l
l
l
a
a
m
m
e
e
l
l
l
l
a
a

Are thin, leaf like structures,
Develop in planes of tension.
Extends from E. surface towards the DEJ.
Confused with cracks caused by grinding
(decalcification).
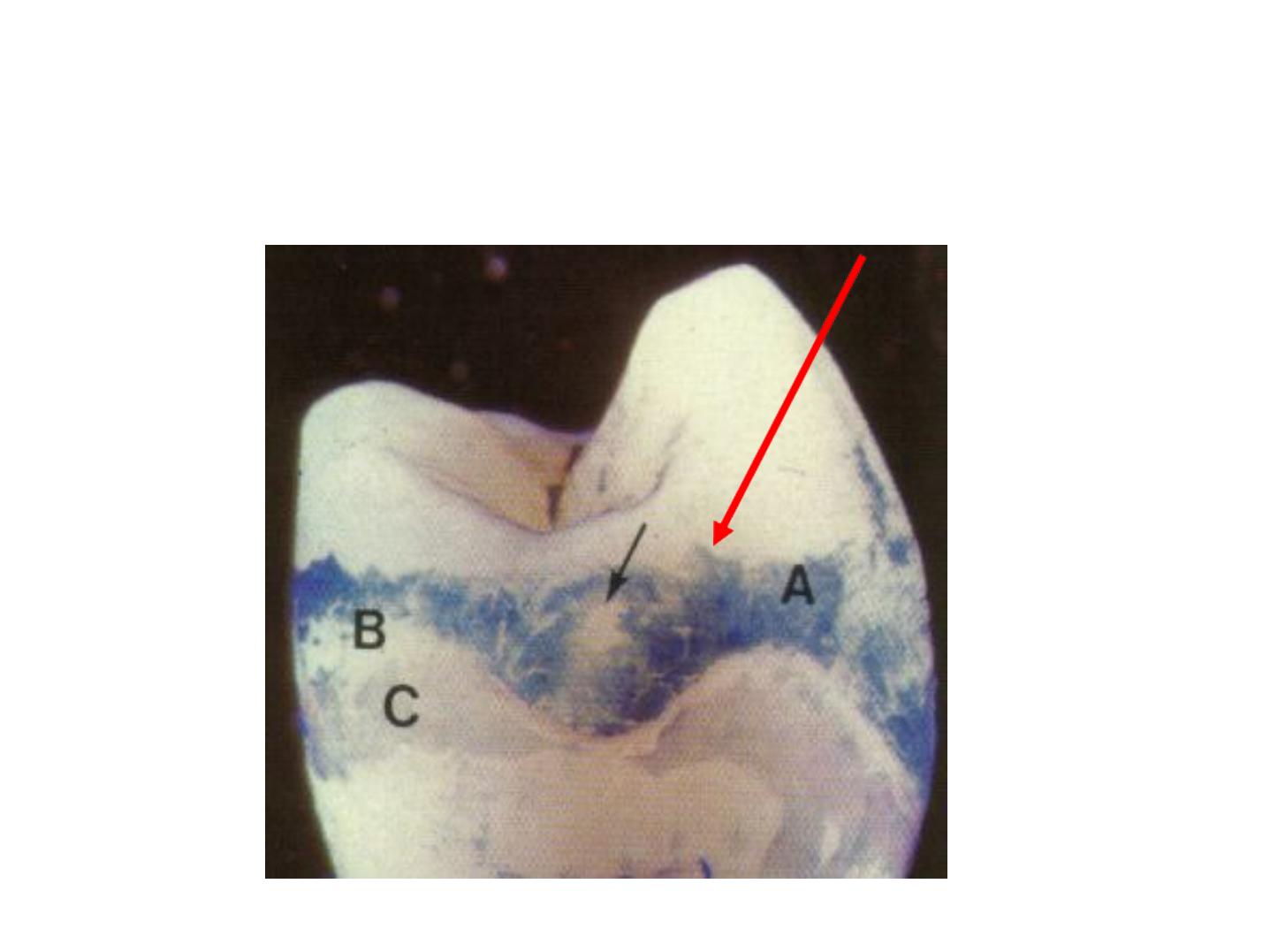
Extend in longitudinal and radial direction.
Represent site of weakness in the tooth and
three types; A, B, and C can be seen.

Enamel Lamellae
Type A
Type B
Type C
Consistency
Poorly calcified rod
seg.
Degenerated cells
Organic matter
from saliva
Tooth
Unerupted
Unerupted
Erupted
Location
Restricted to the E.
Reach into the D.
Reach into the D.
Occurrence
Less common
Less common
More common
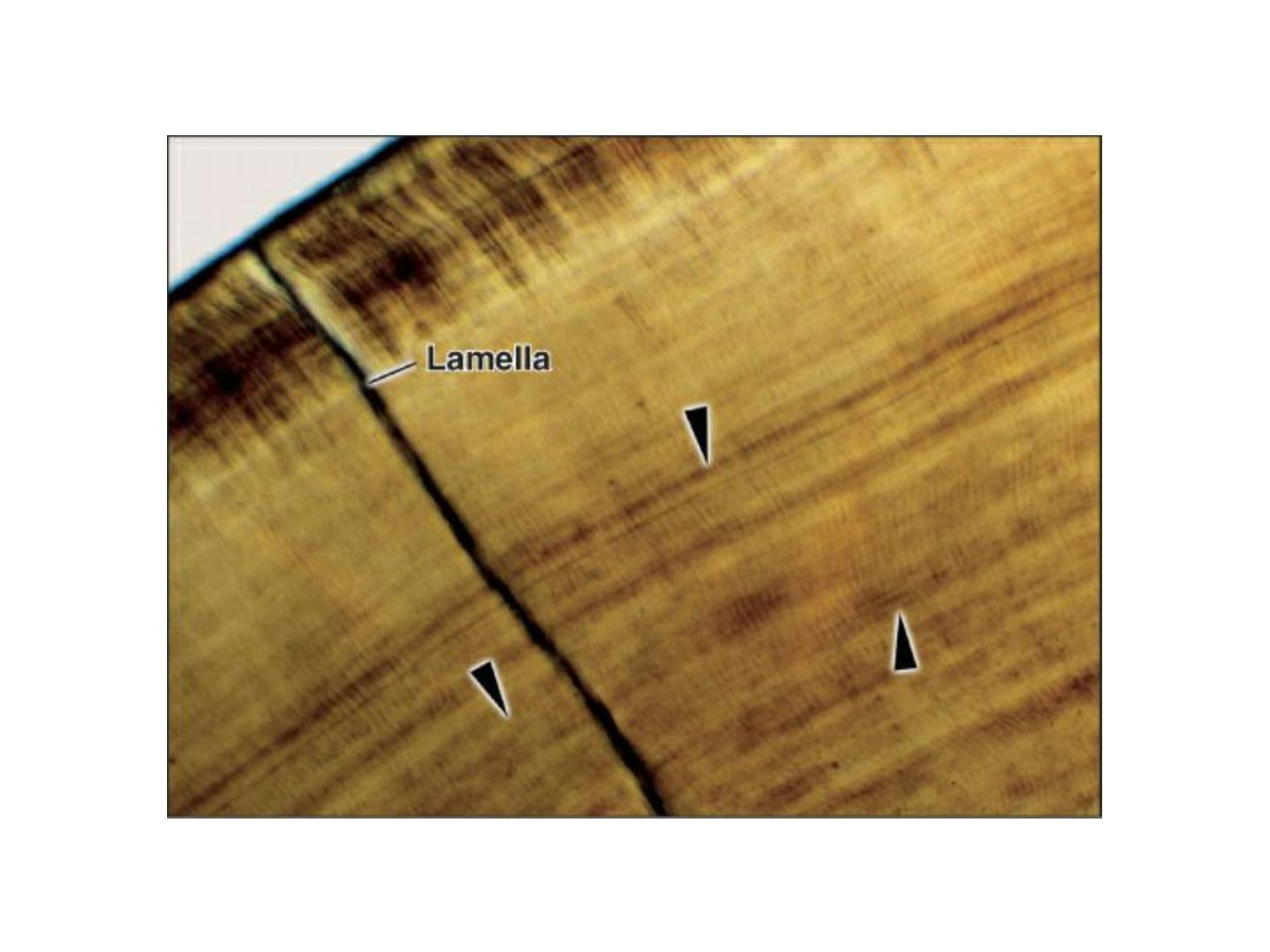
Enamel lamellae
In enamel
only
Extending in enamel and
dentin
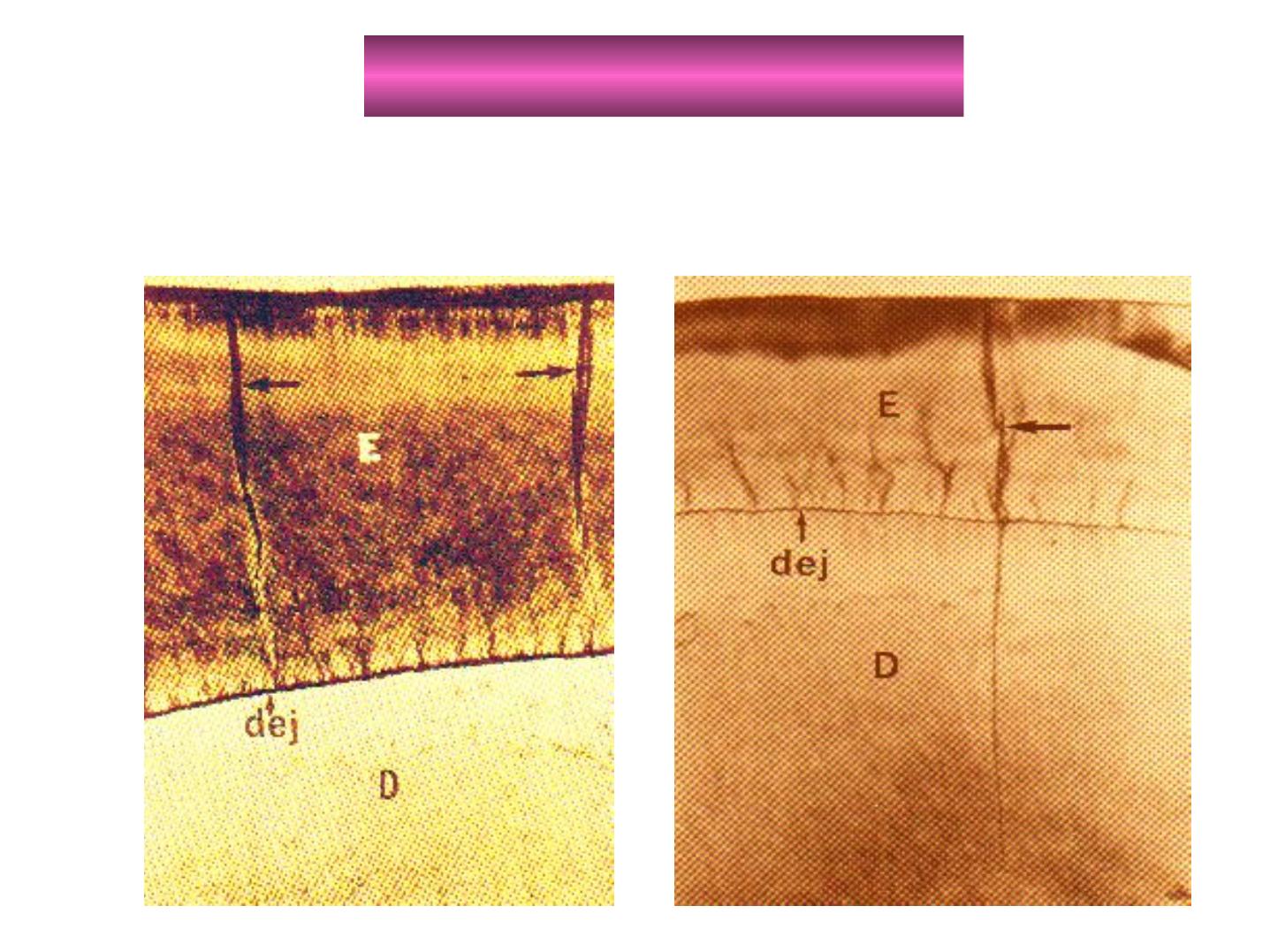
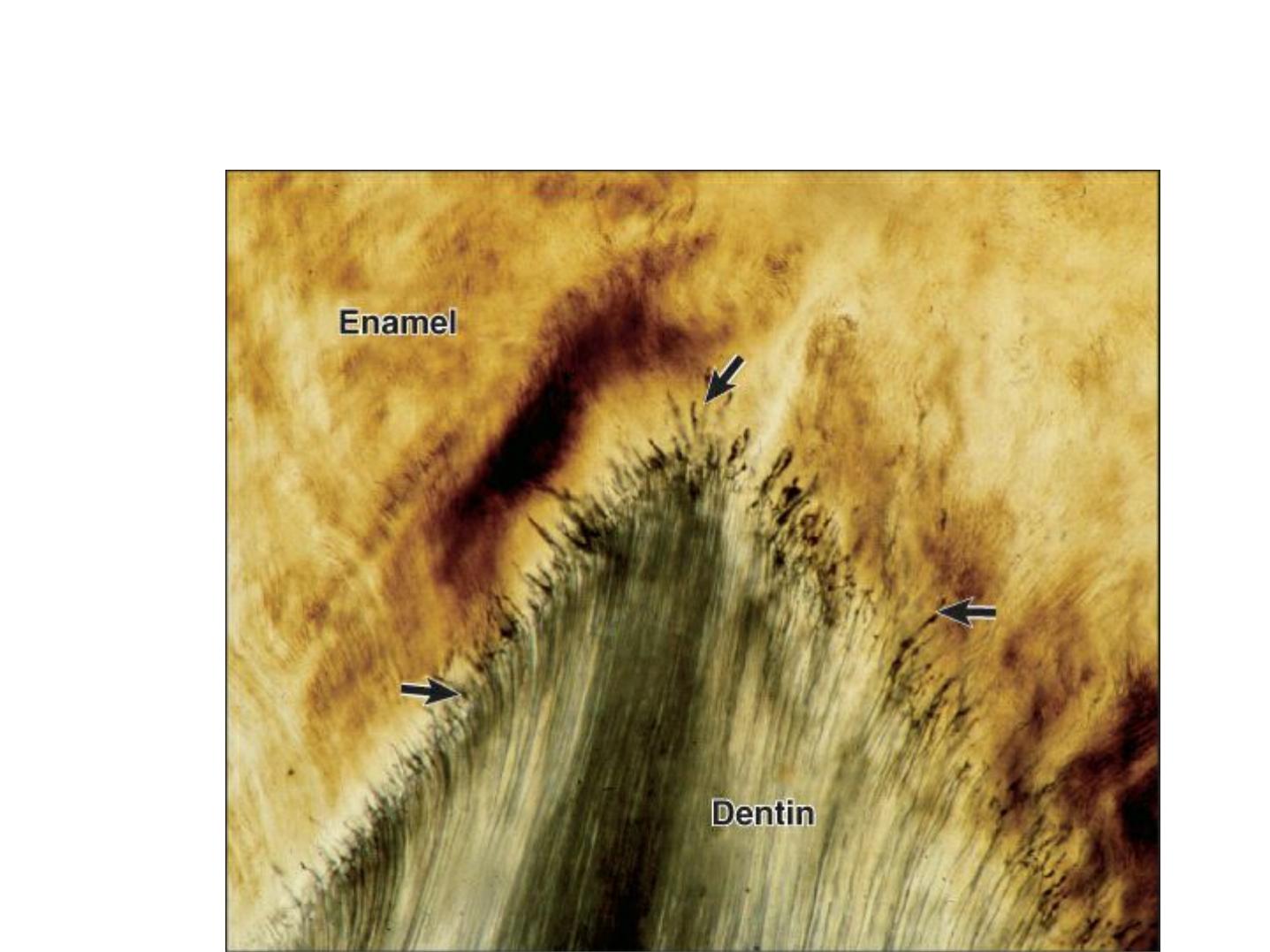
A: enamel tuft (twist)
B: enamel Lamella

-ENAMEL TUFTS
-Arise from DEJ.
-Reach to
1
/
5
–
1
/
3
the thickness of E.
-In ground section: resemble tufts of grass.
-The inner end arises at the dentin.
-Consist of hypocalcified E. rods and
interprismatic substance.
-They extend in the direction of the long axis of
the crown (best seen in horizontal sections).

E
E
n
n
a
a
m
m
e
e
l
l
S
S
p
p
i
i
n
n
d
d
l
l
e
e
s
s
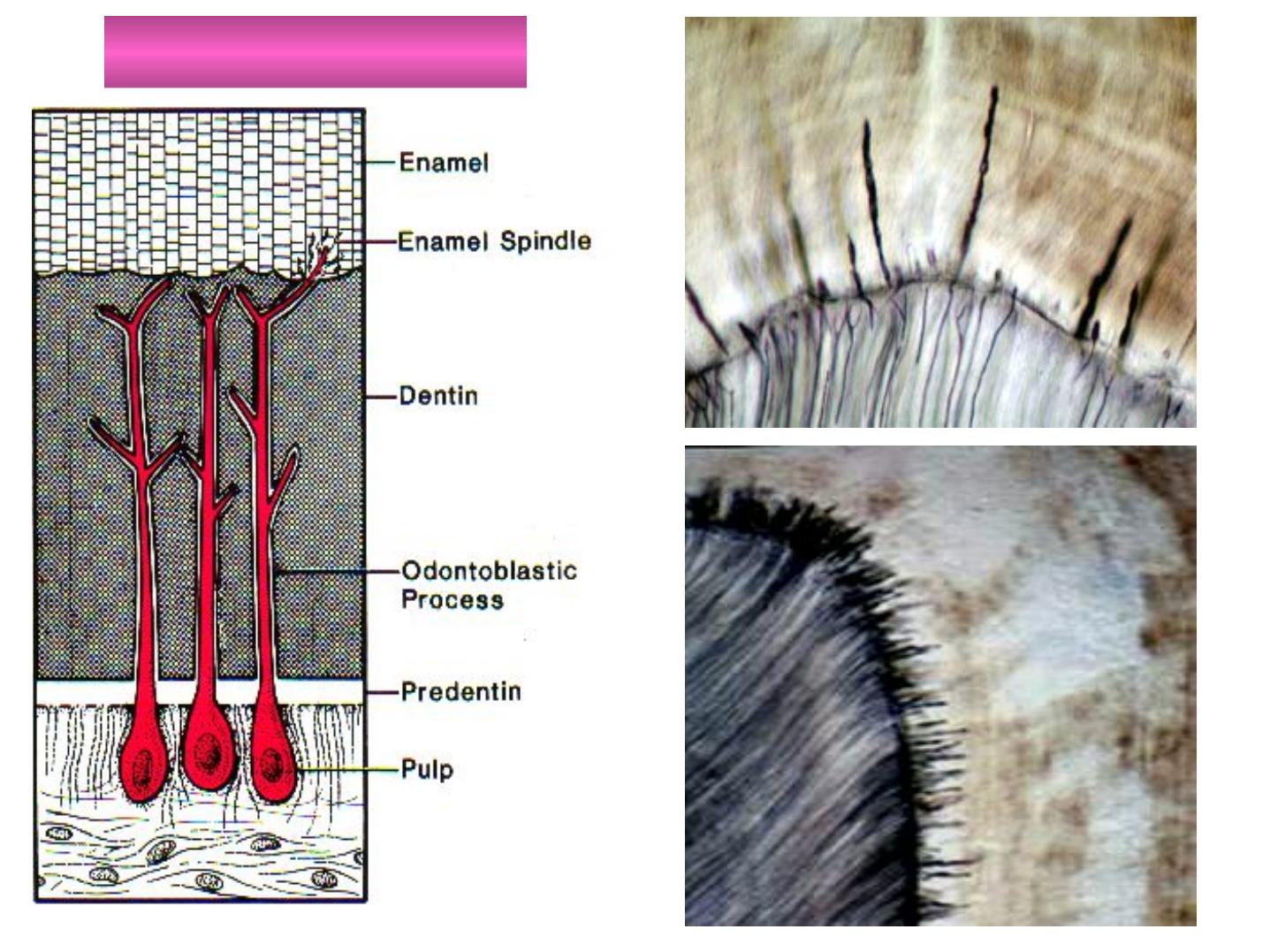
The odontoblasts processes may cross DEJ
(before the hard substance is formed) to the
E. and ends as E. spindles.
They are filled with organic matter.
The processes and spindles are at right angle
to the surface of the dentin.
The direction of spindles and rods is divergent.
Spindles appear dark in ground sections under
transmitted light
E
E
n
n
a
a
m
m
e
e
l
l
S
S
p
p
i
i
n
n
d
d
l
l
e
e
s
s
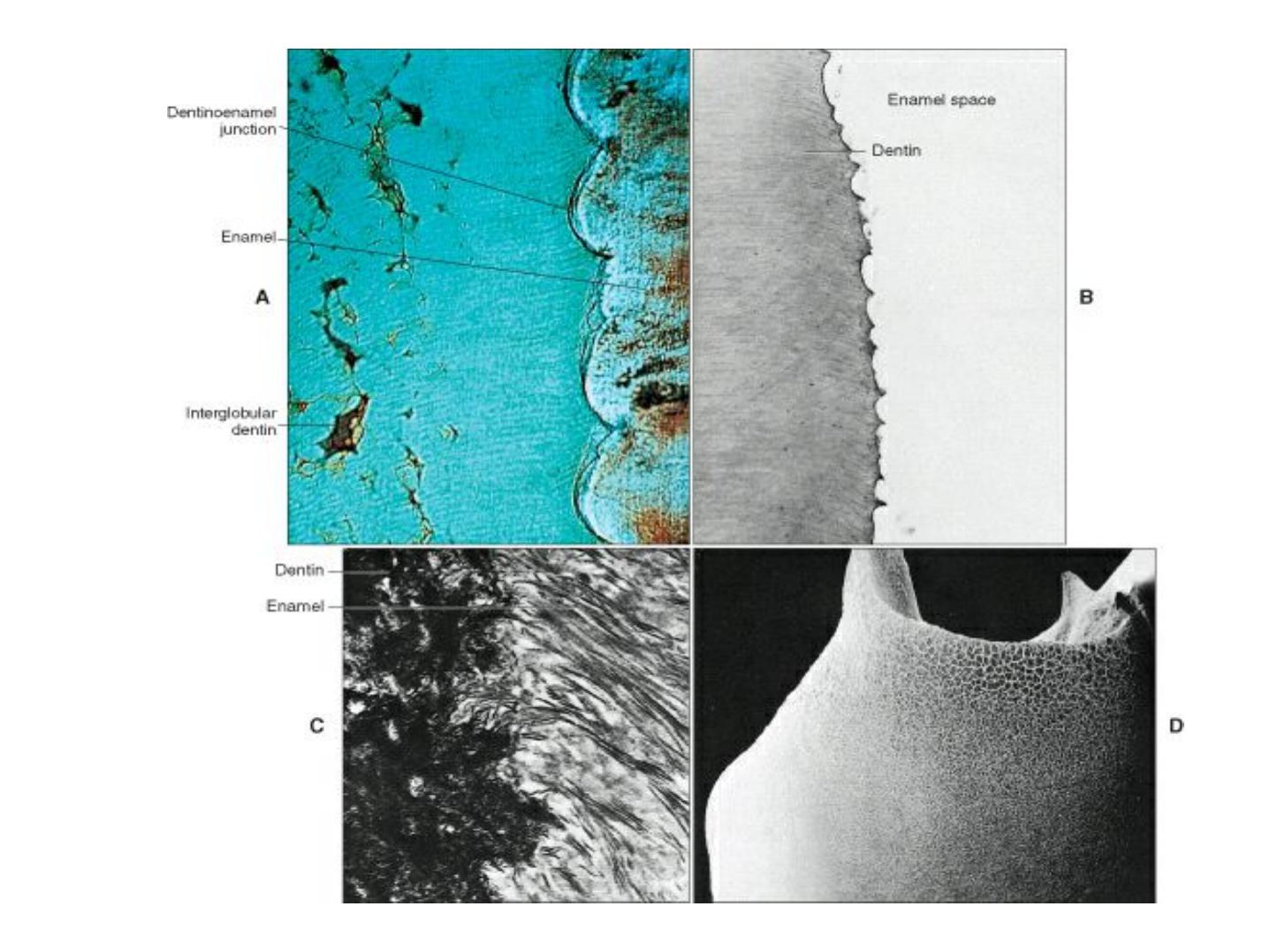
THE AMELODENTINAL
JUNCTION

Scalloped junction –the convexities towards
Dentin.
At this junction, the pitted Dentin surface fit
rounded projections of the enamel.
The outline of the junction is performed by the
arrangement of the ameloblasts and Basal
Membrane.

*
OUTER STRUCTURELESS ENAMEL
(Ename Skin)
*
PERIKYMATA
*ENAMEL ROD ENDS
* CRACKs
*Afibrillar cementum
*
Enam el Cuticle
n
SURFACE STRUCTURES
OF ENAMEL

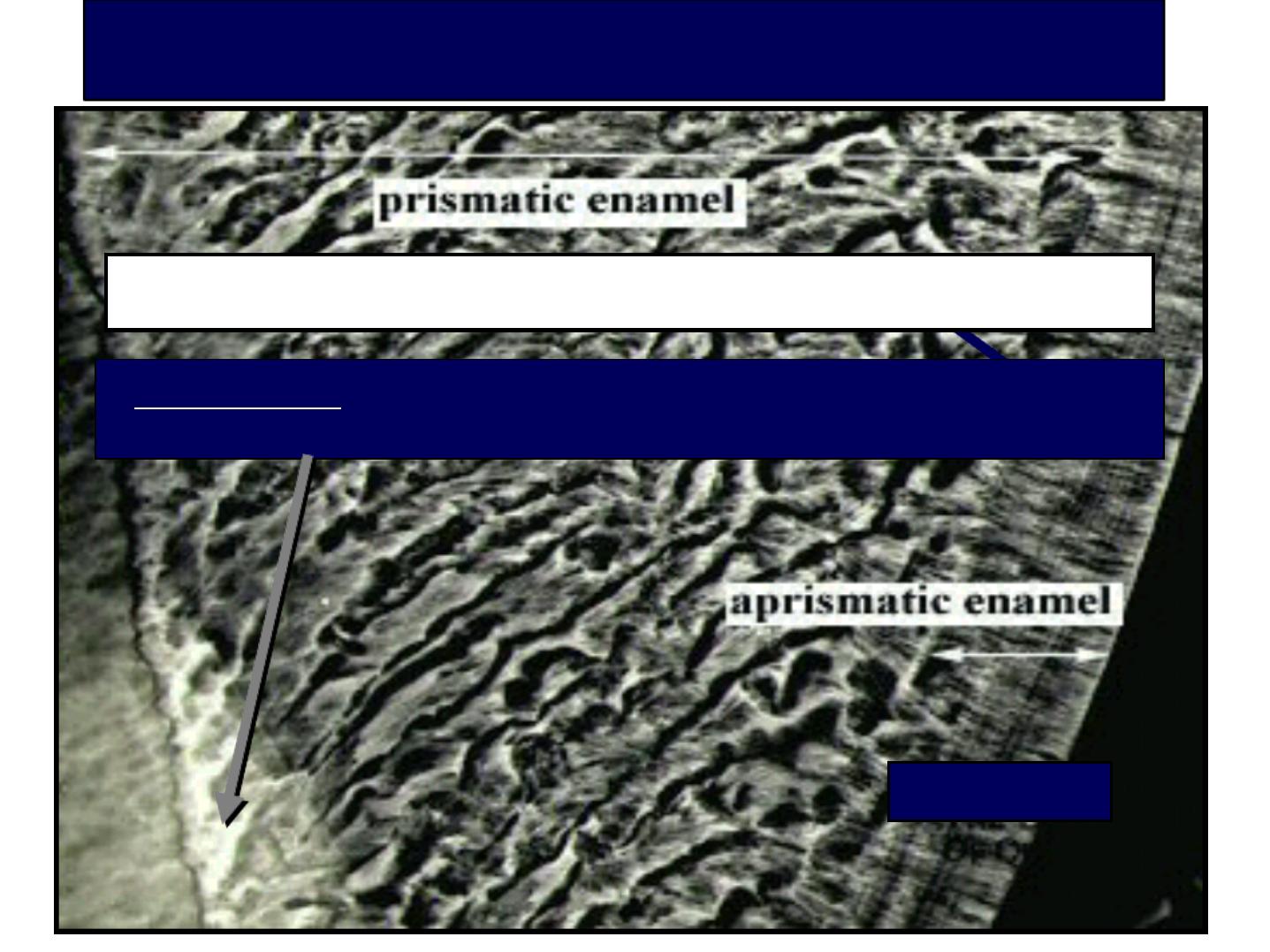
a. Structureless layer
About 30 µm thick.
In 70% permanent teeth and all deciduous teeth.
Found least often over the cusp tips.
Found commonly in the cervical areas.
No Enamel prisms.
All the apatite crystals area parallel to one another and
vertical to the striae of Retzius.
More mineralized than the bulk of Enamel beneath it.
SURFACE STRUCTURES
REMEMBER: THAT THERE IS AN INNER STRUCTURELESS
ENAMEL
1 –OUTER STRUCTURELESS ENAMEL
30 um thick

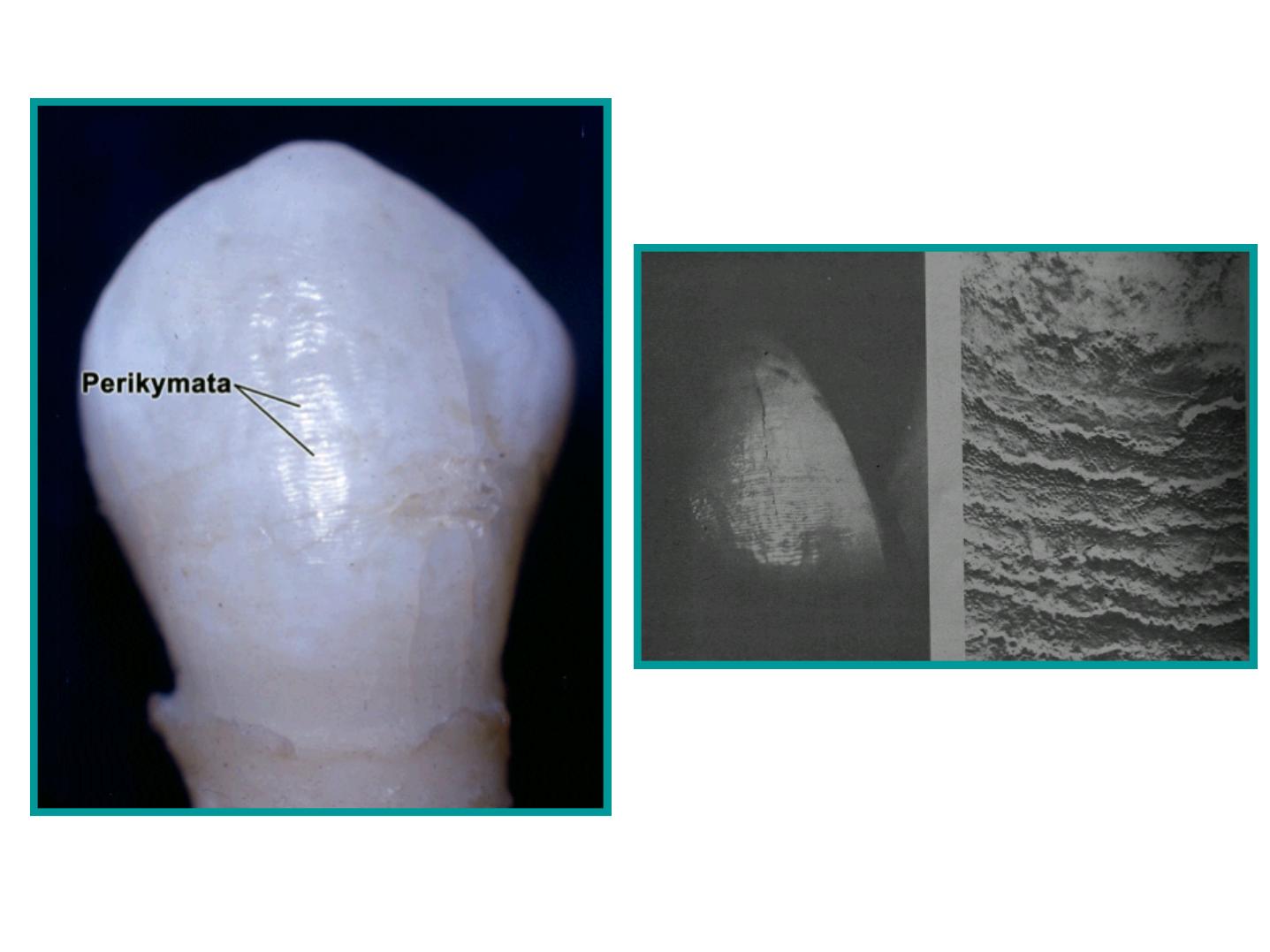
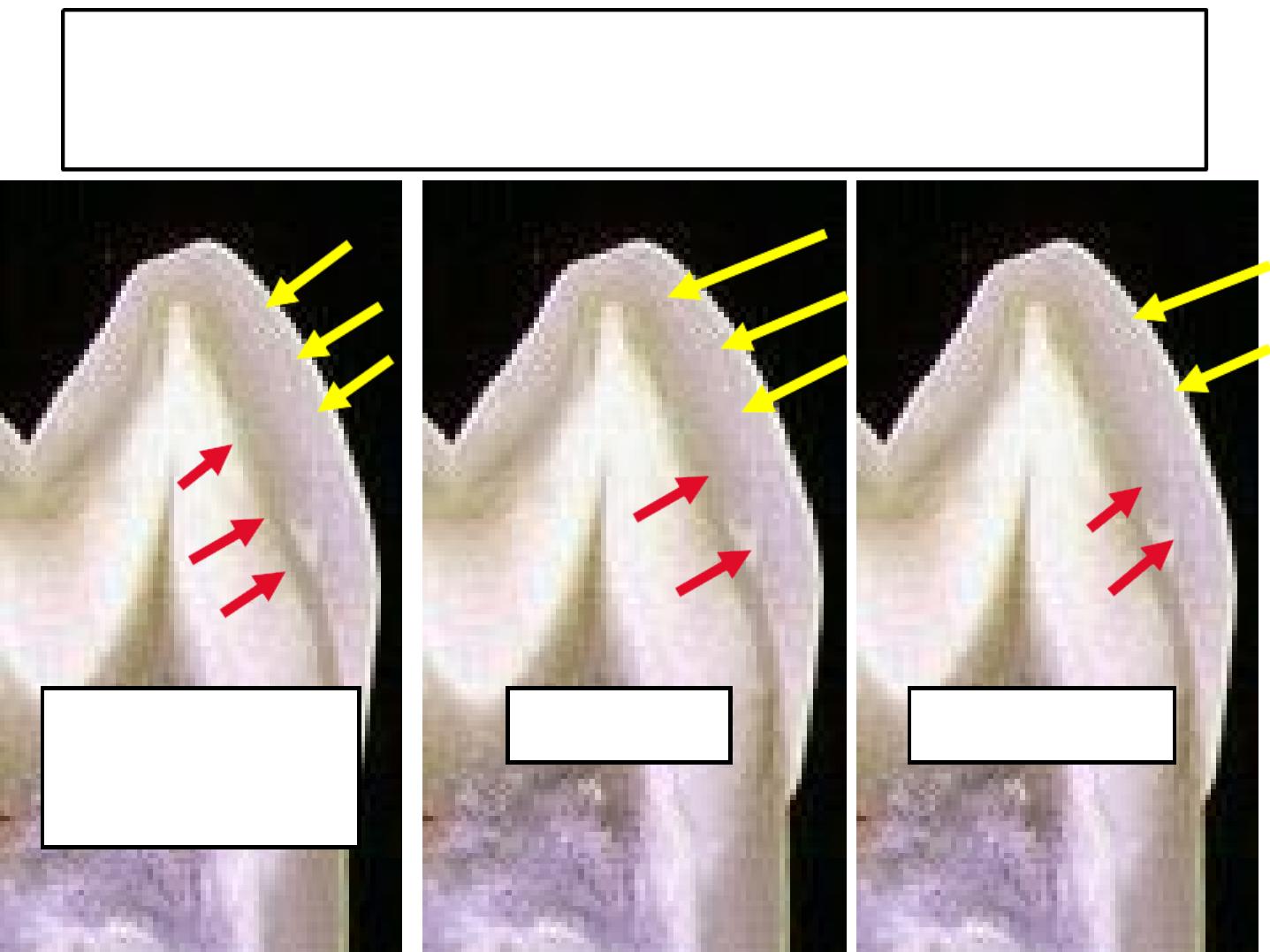
b. Perikymata
Transverse wave like grooves.
Thought to be the external manifestation of the
striae of Retzius.
Lie parallel to each other and to CEJ.
Number:
-About 30 perikymata/mm at the CEJ.
-About 10 perikymata /mm near the incisal
edge.
The relationship between the striae of Retziuz and surface perikymata

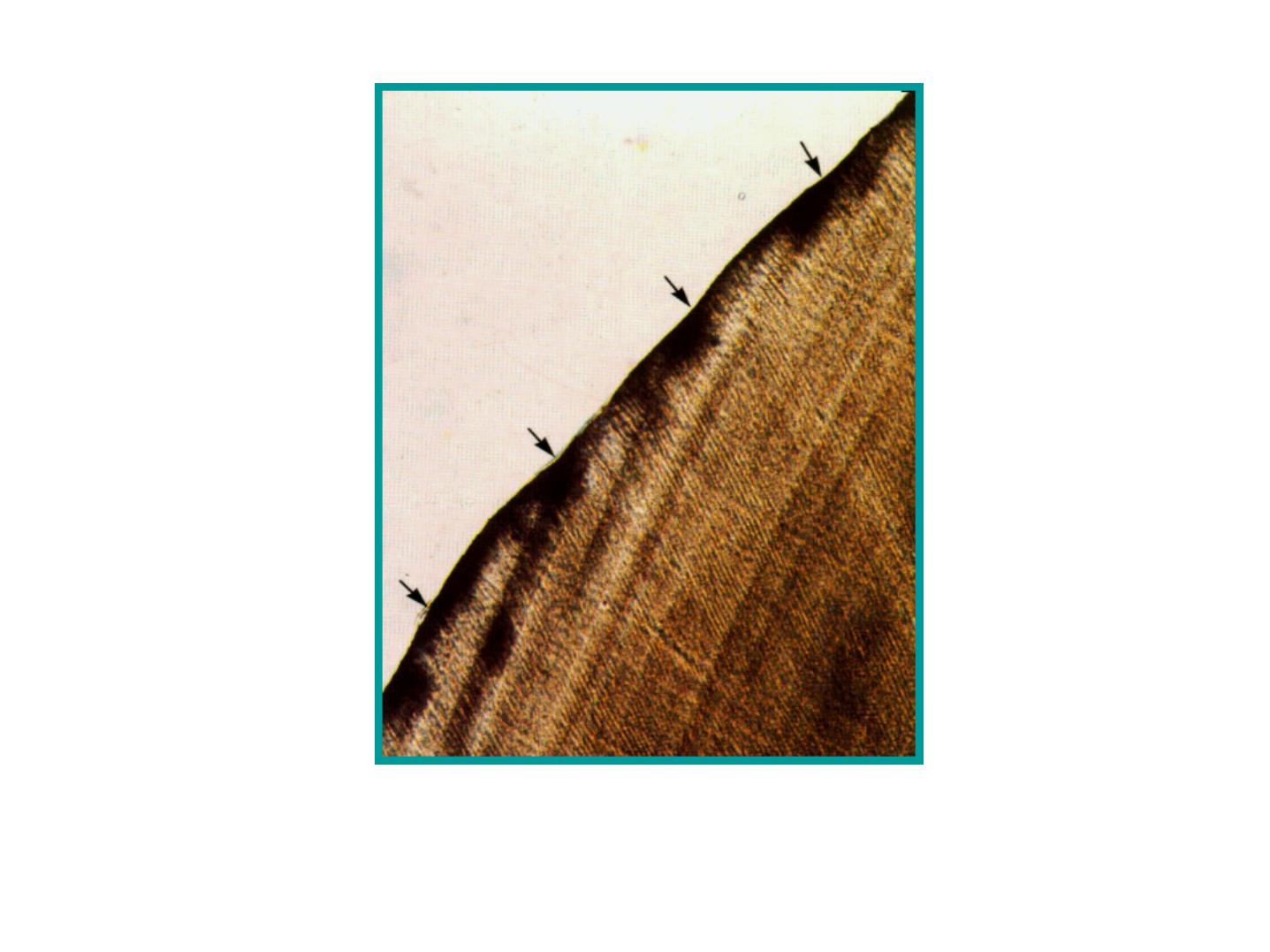
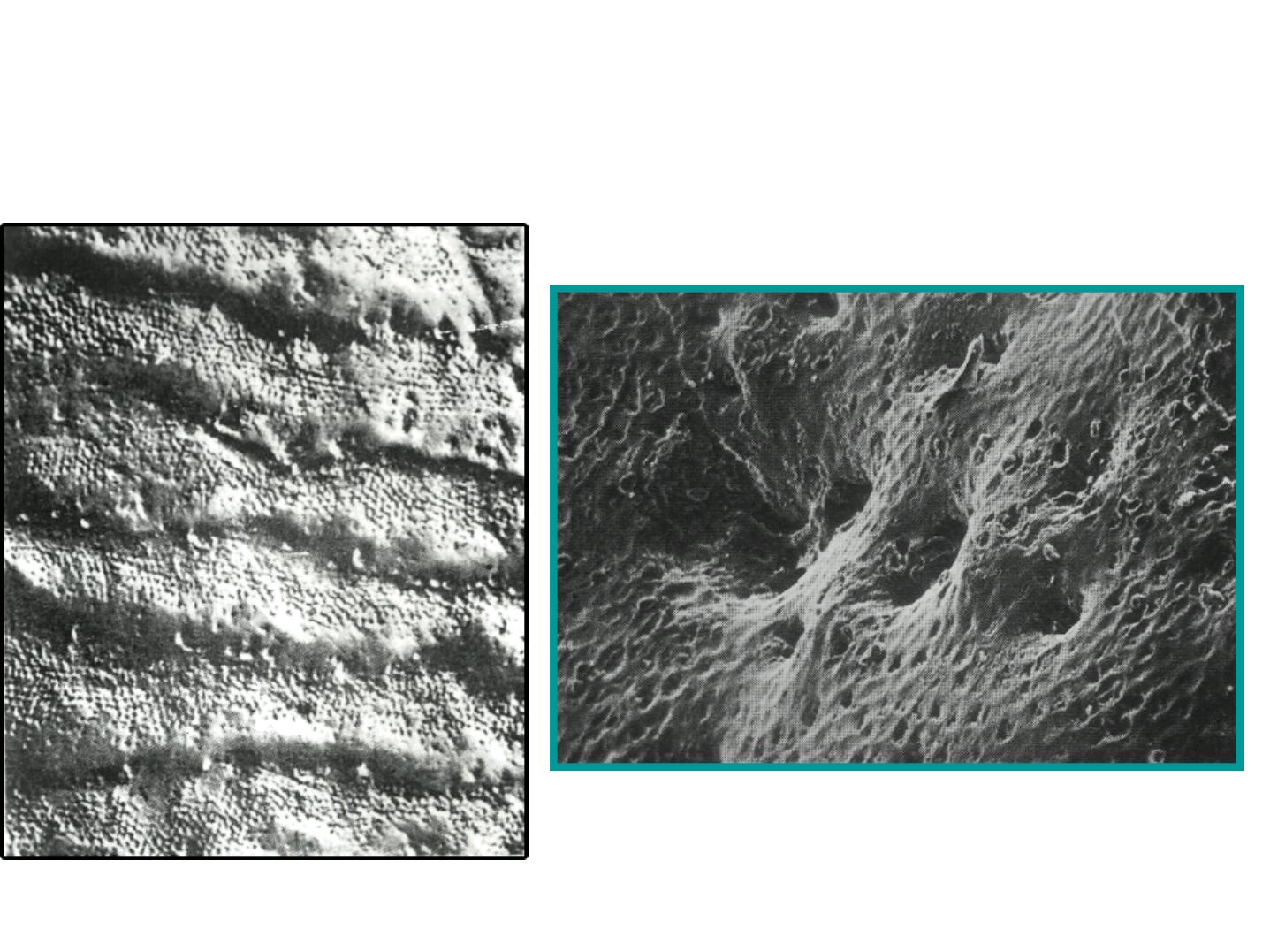
c. Rod ends
-Are concave and vary in depth and shape.
-Are shallow in the cervical regions.
-Deep near the incisal or occlusal edges.

Rod ends
Enamel Rod Ends
S
S
H
H
A
A
L
L
L
L
O
O
W
W
E
E
R
R
CERVICALLY
D
D
E
E
E
E
P
P
E
E
R
R
OCCLUSALLY

d. Cracks
•
Narrow fissure like structure.
•
Seen on almost all surfaces.
•
They are the outer edges of lamellae.
•
Extend for varying distance along the surface.
•
At right angles to CEJ.
•
Long cracks are thicker than the short one.
•
May reach the occlusal or incisal edge.
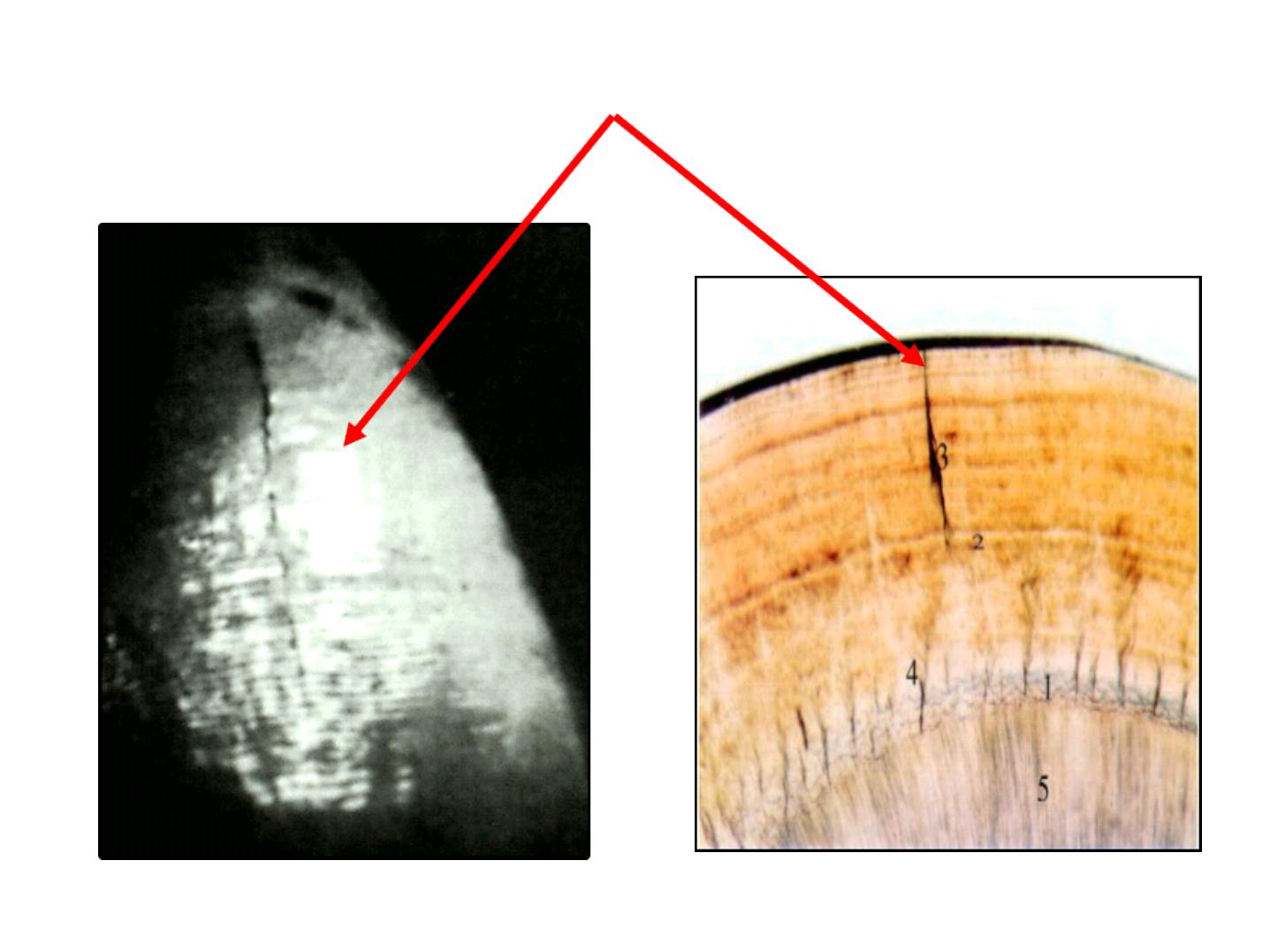
CRACKs

e. Enamel cuticle
1-Primary E. cuticle (Nasmyth’
s
membrane).
2-Secondary E. cutile (afibrilar cementum).
3-Pellicle (a precipitate of salivary
proteins.
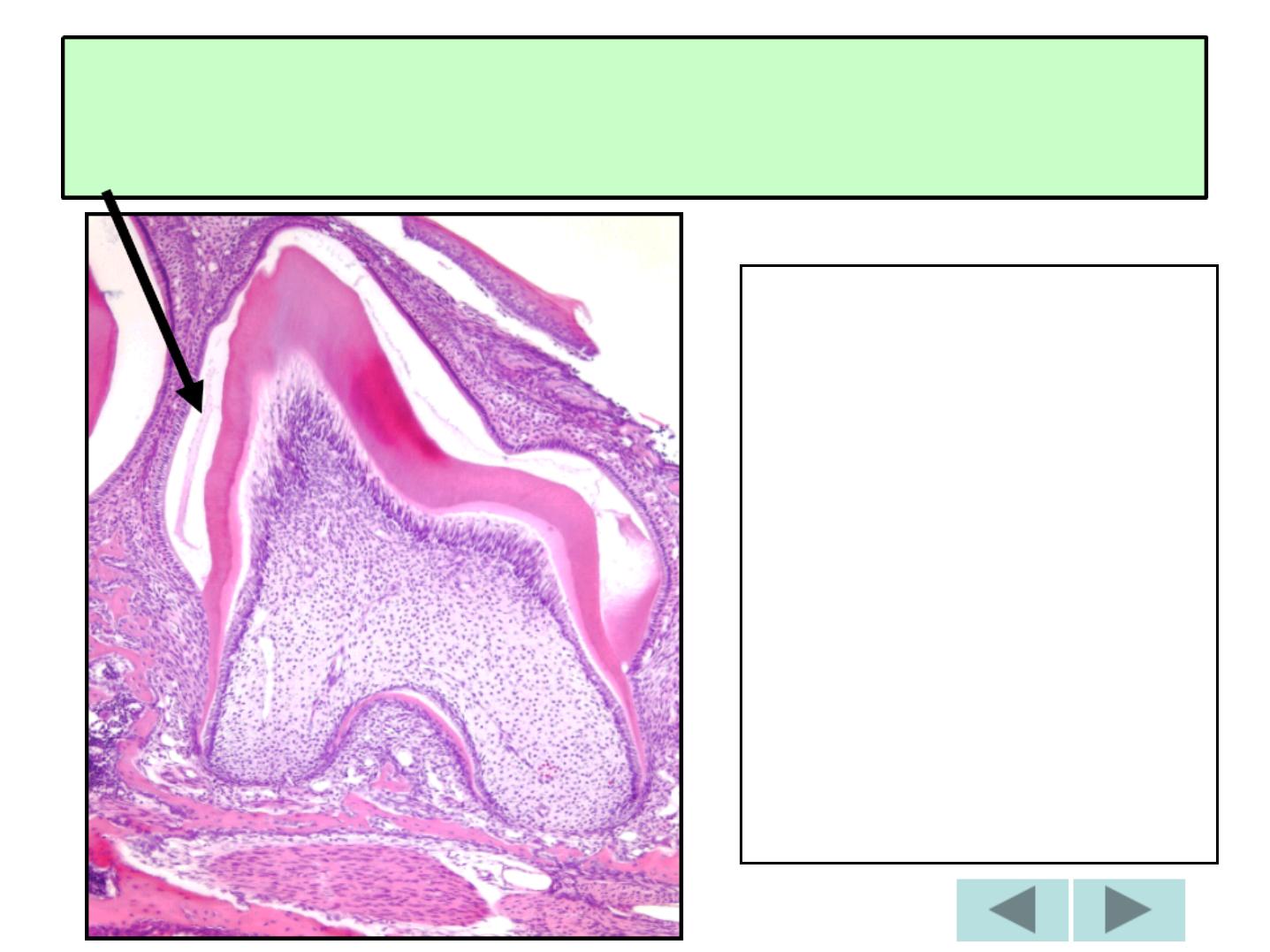
ASG
PRIMARY ENAMEL CUTICLE
(Nasmyth’
s membrane)
-
0
0
.
.
2
2
u
u
m
m
thick.
- Its
s
s
t
t
r
r
u
u
c
c
t
t
u
u
r
r
e
e
is
similar to the basal
lamina of the
epithelium.
- It is
t
t
h
h
e
e
l
l
a
a
s
s
t
t
product
of the ameloblasts.
--Covers the entire
crown of newly
erupted tooth
.

Secondary enamel cuticle
•
Covered the cervical area of the
enamel.
•
Thickness: up to 10 µm.
•
Continuous with the cementum.
•
Probably of mesodermal origin or may
be elaborated by the attachment
epithelium.
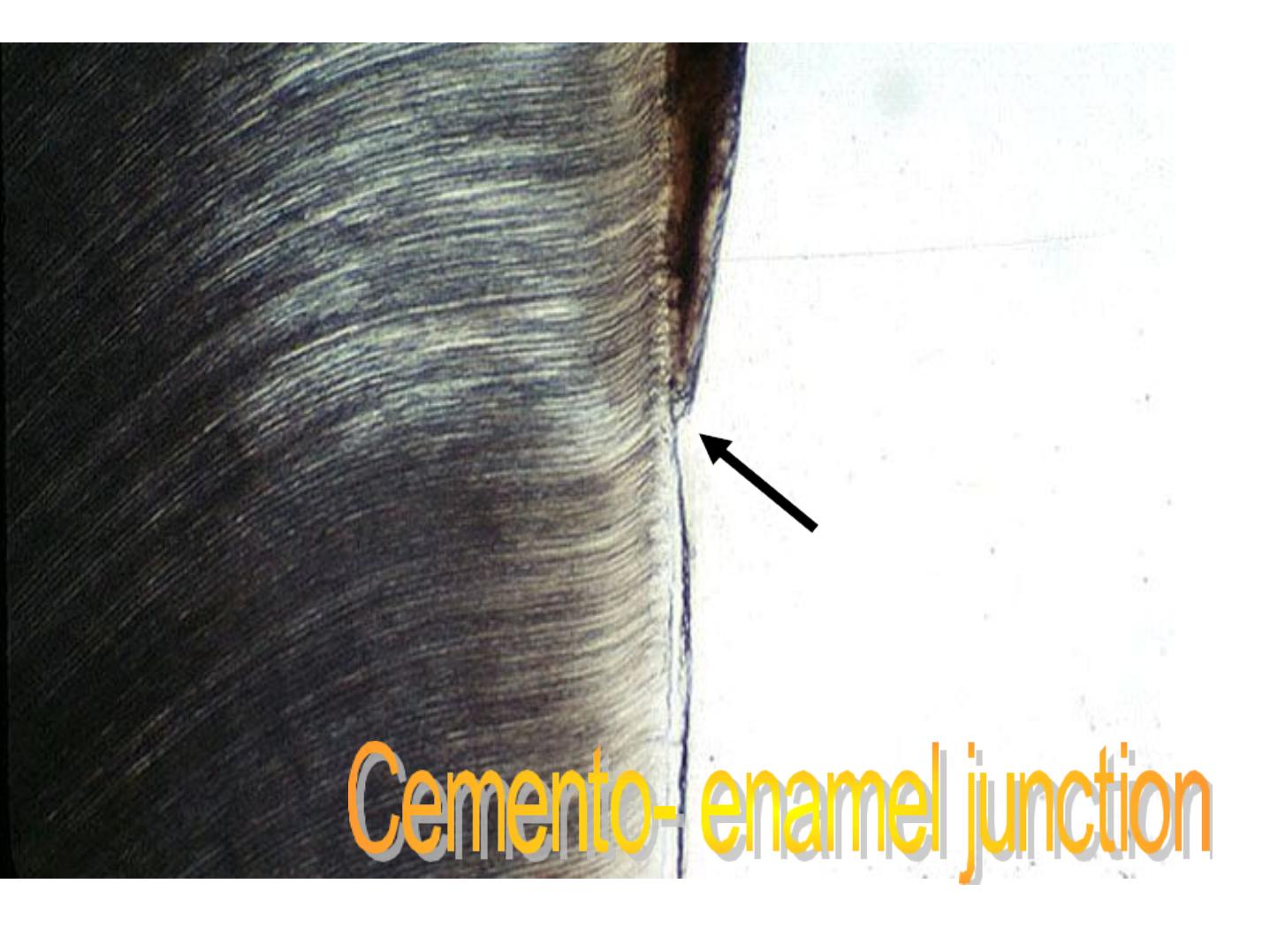
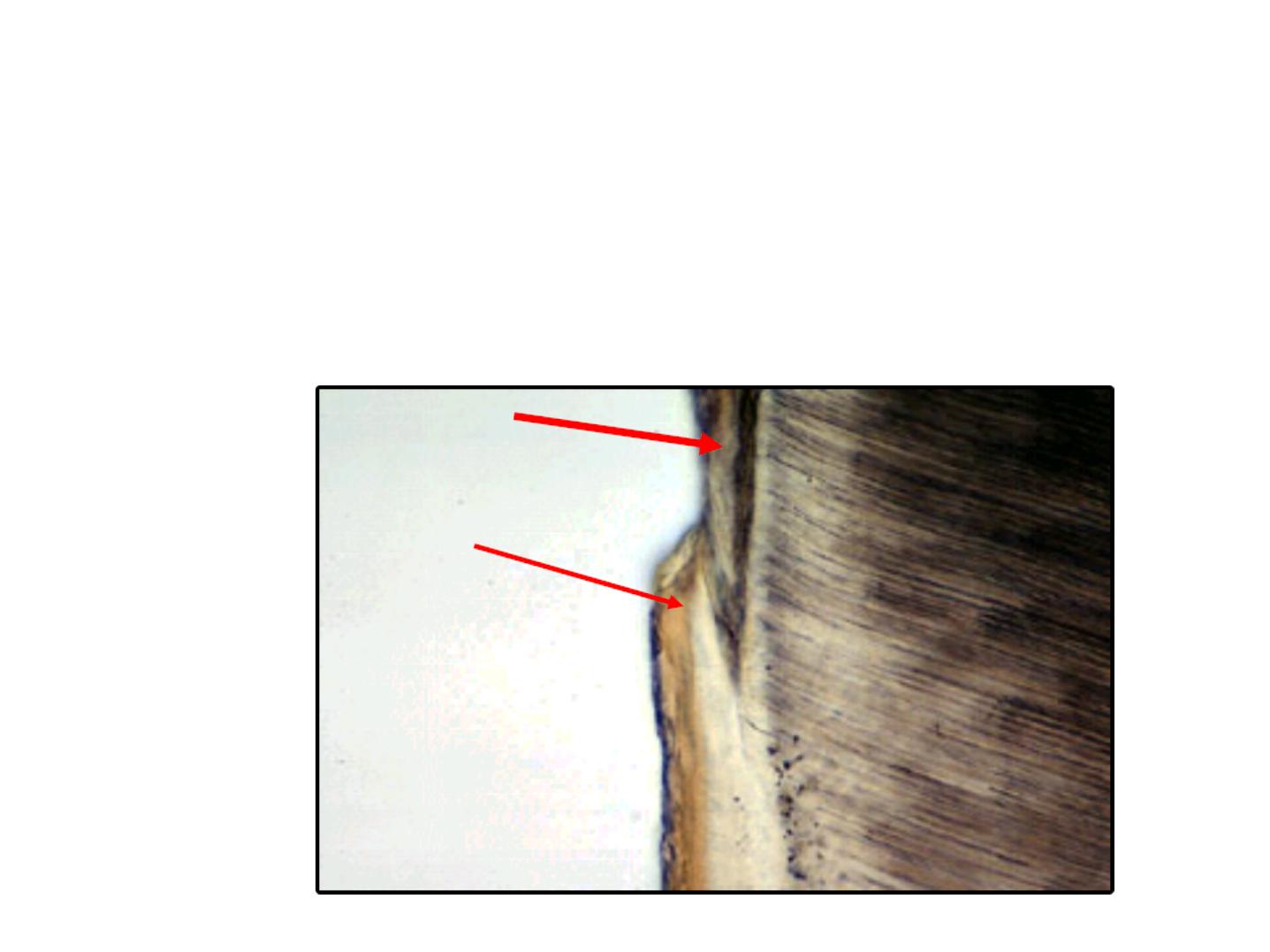
AFIBRILLAR CEMENTUM
E
C

Pellicle
•
Re-form within hours after mechanical
cleaning .
•
May be colonized by microorganisms to form
a bacterial plaque.
•
Plaque may be calcified forming calculus.
SALIVARY PELLICLE

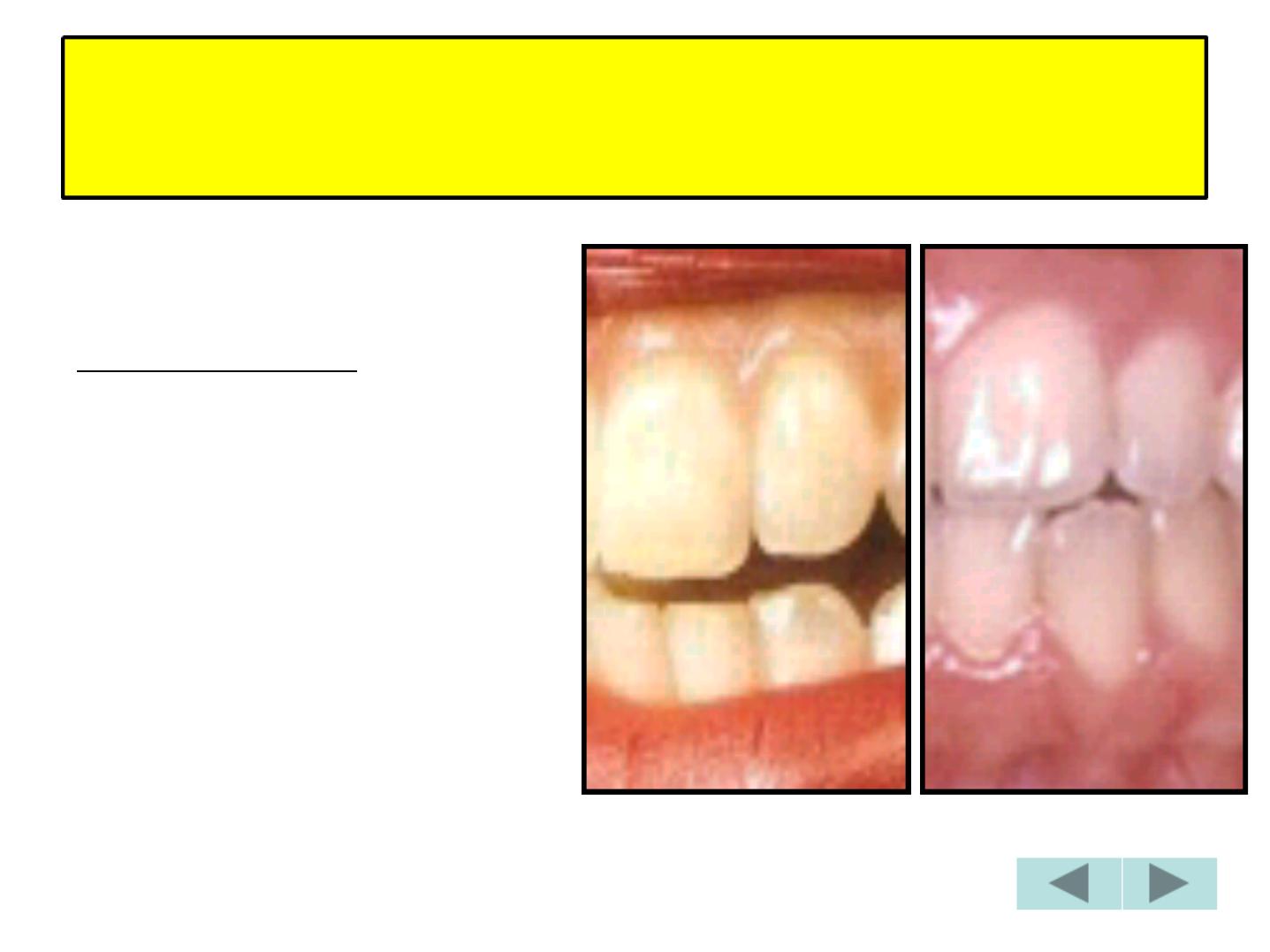
Age changes of Enamel
• Attrition
• Decreased Permeability
• Increased Hardness (ionic exchange)
• Color changes
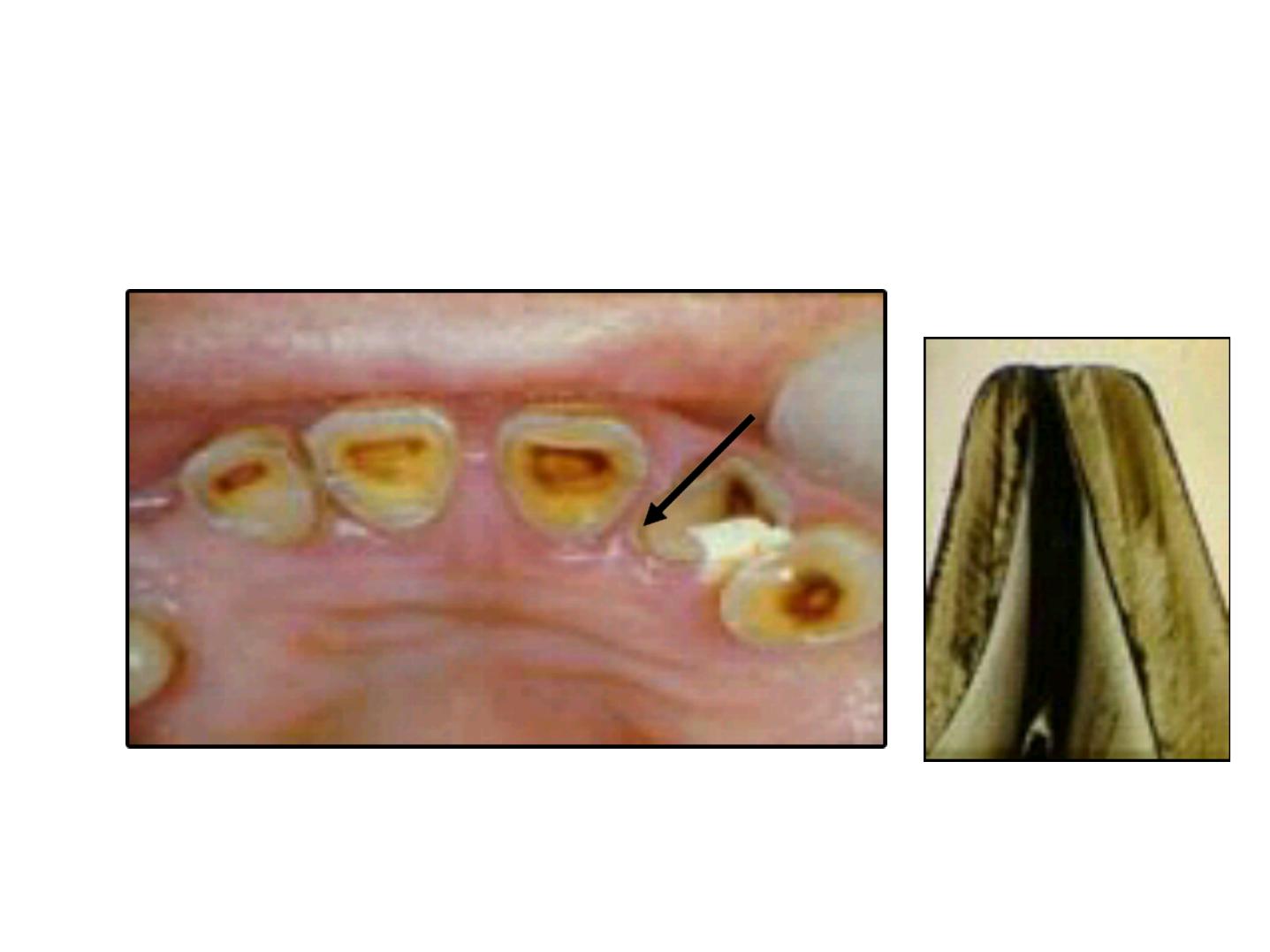
Attrition (Erosion)
Dentin
ASG
2 - PERMEABILITY
Main path
Recently
Erupted teeth
Old enamel
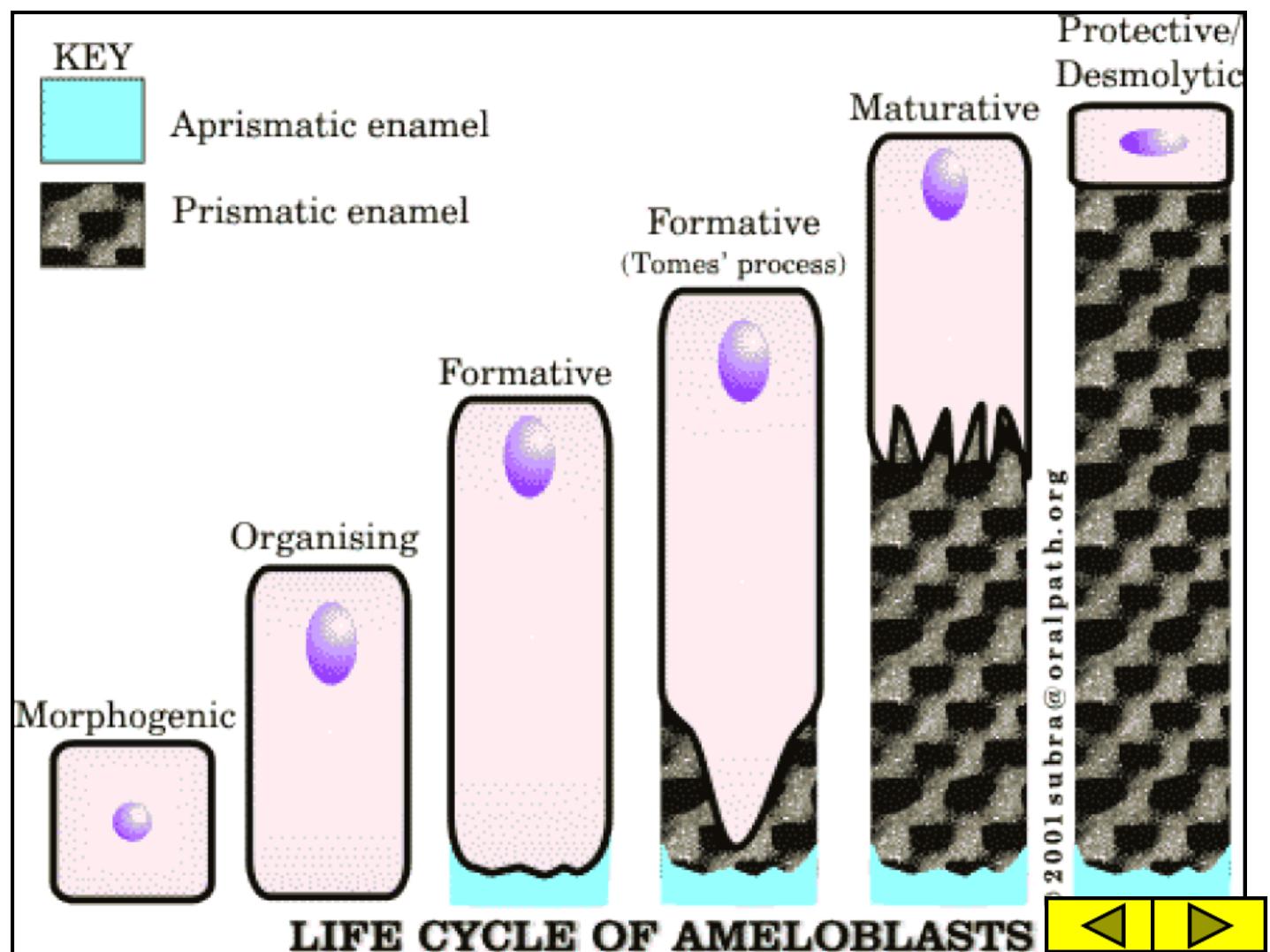
LIFE HISTORY OF THE
AMELOBLASTS
1 - MORPHOGENIC
2 - ORGANIZING
DEAL WITH INNER
DENTAL
EPITHELIUM
7 STAGES
3 –FORMATIVE
4 –TRANSITIONAL
5 - MATURATIVE
FUNCTIONS OF
DIFFERENTIATED
AMELOBLASTS
6 –PROTECTIVE
7 - DESMOLYTIC
FUNCTIONS OF
THE REDUCED
ENAMEL
EPITHELIUM
ASG
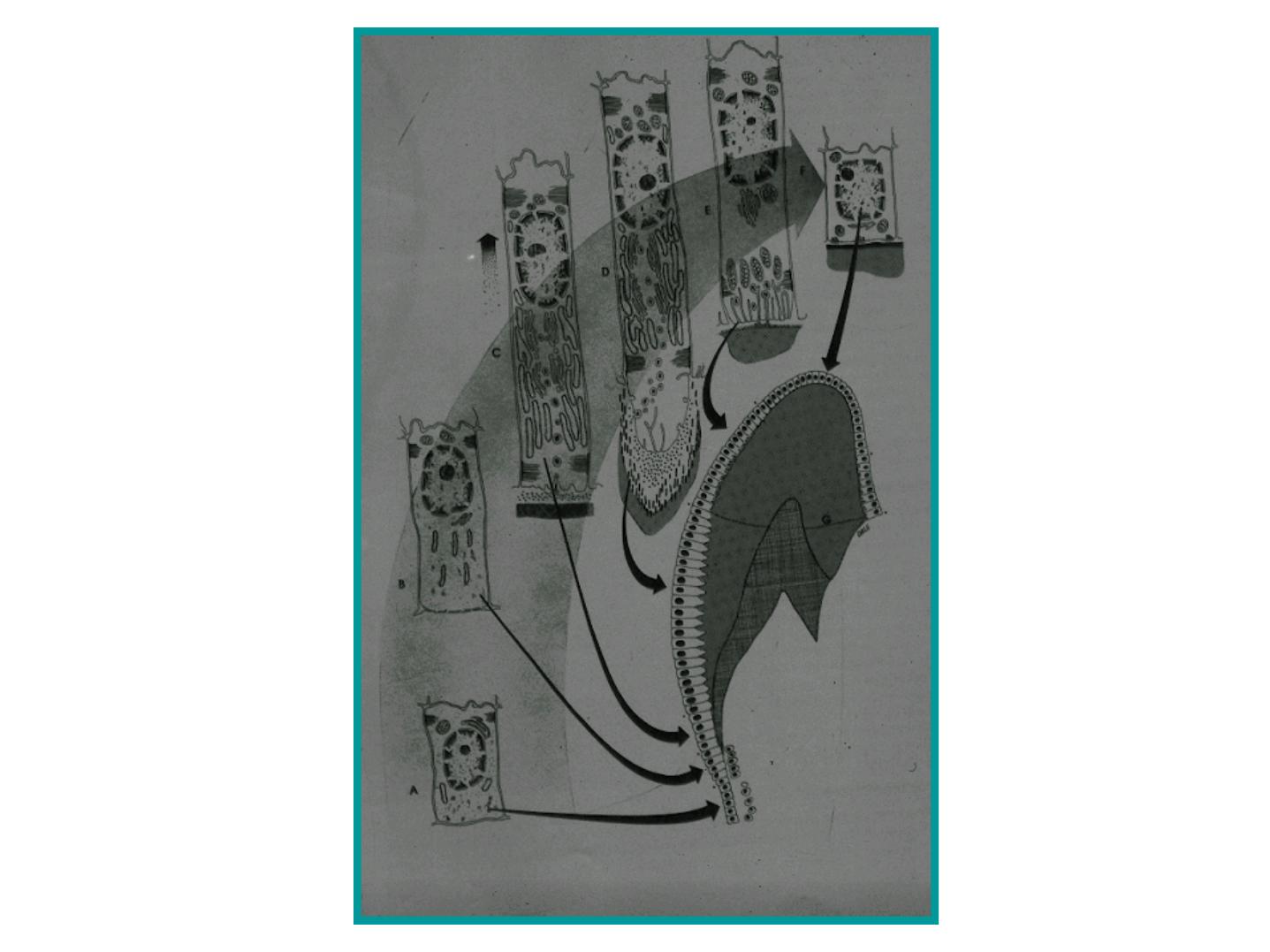

Morphogenic
stage
Organising
stage
Formative
stage
Maturative
stage
Protective
stage
Desmolytic
stage
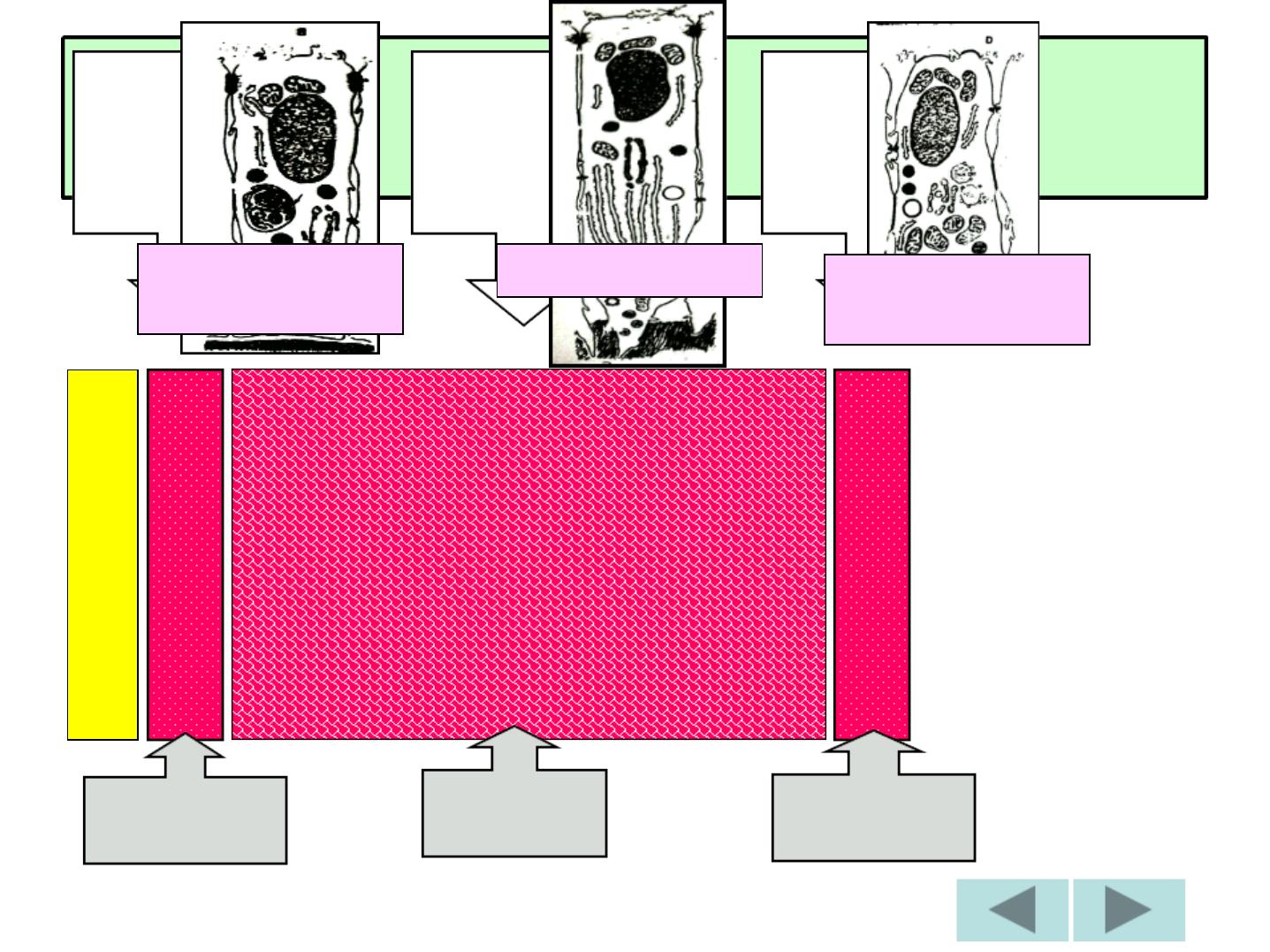
SUMMARY
D
e
n
ti
n
Aprismatic
enamel
Aprismatic
enamel
Prismatic
enamel
Ameloblast
without
Tome’
s
process
Ameloblast
without
Tome’
s
process
Ameloblast
with
Tome’
s
process
Late organizing
stage
Formative stage
Transitional
stage
ASG
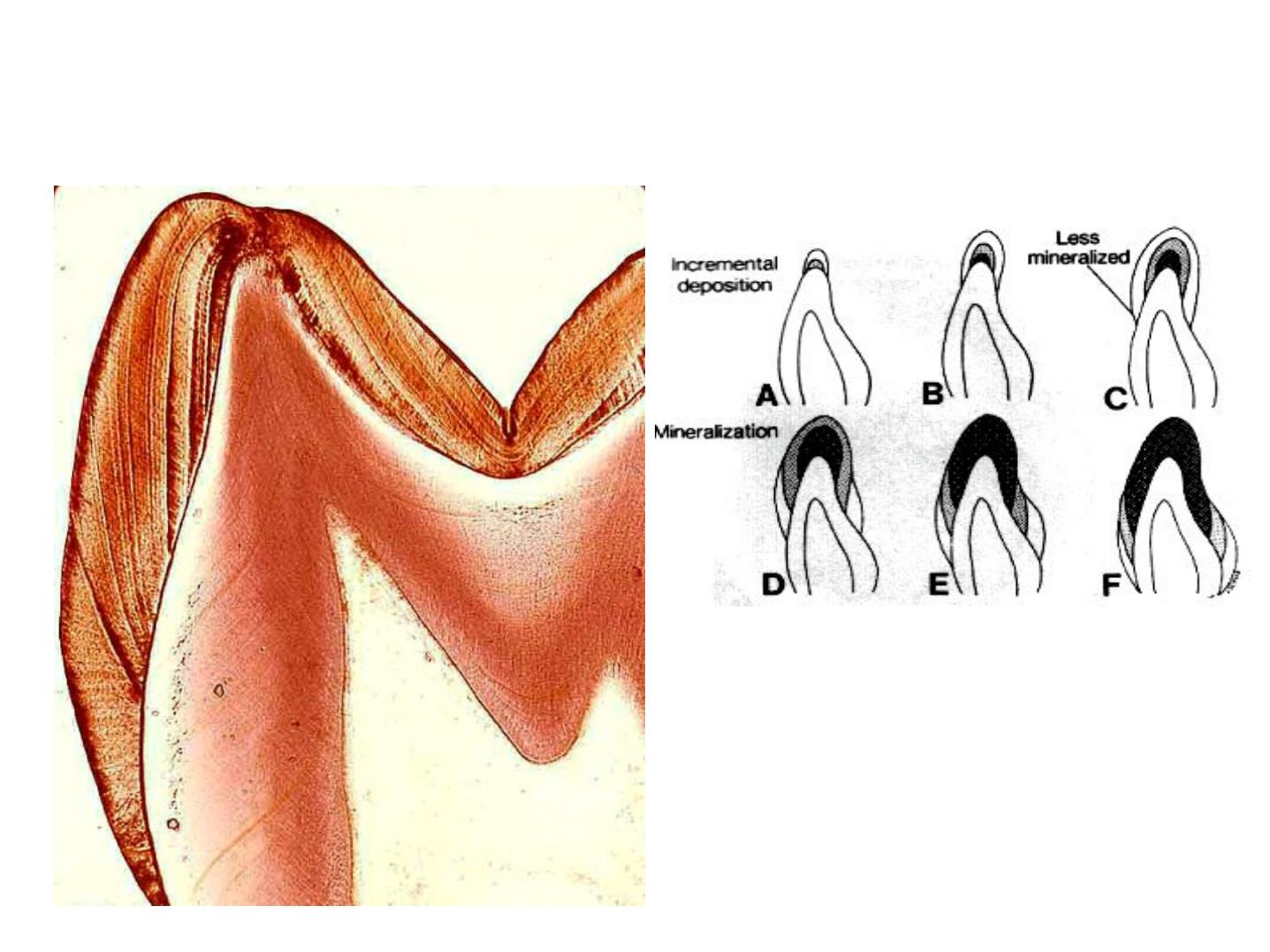
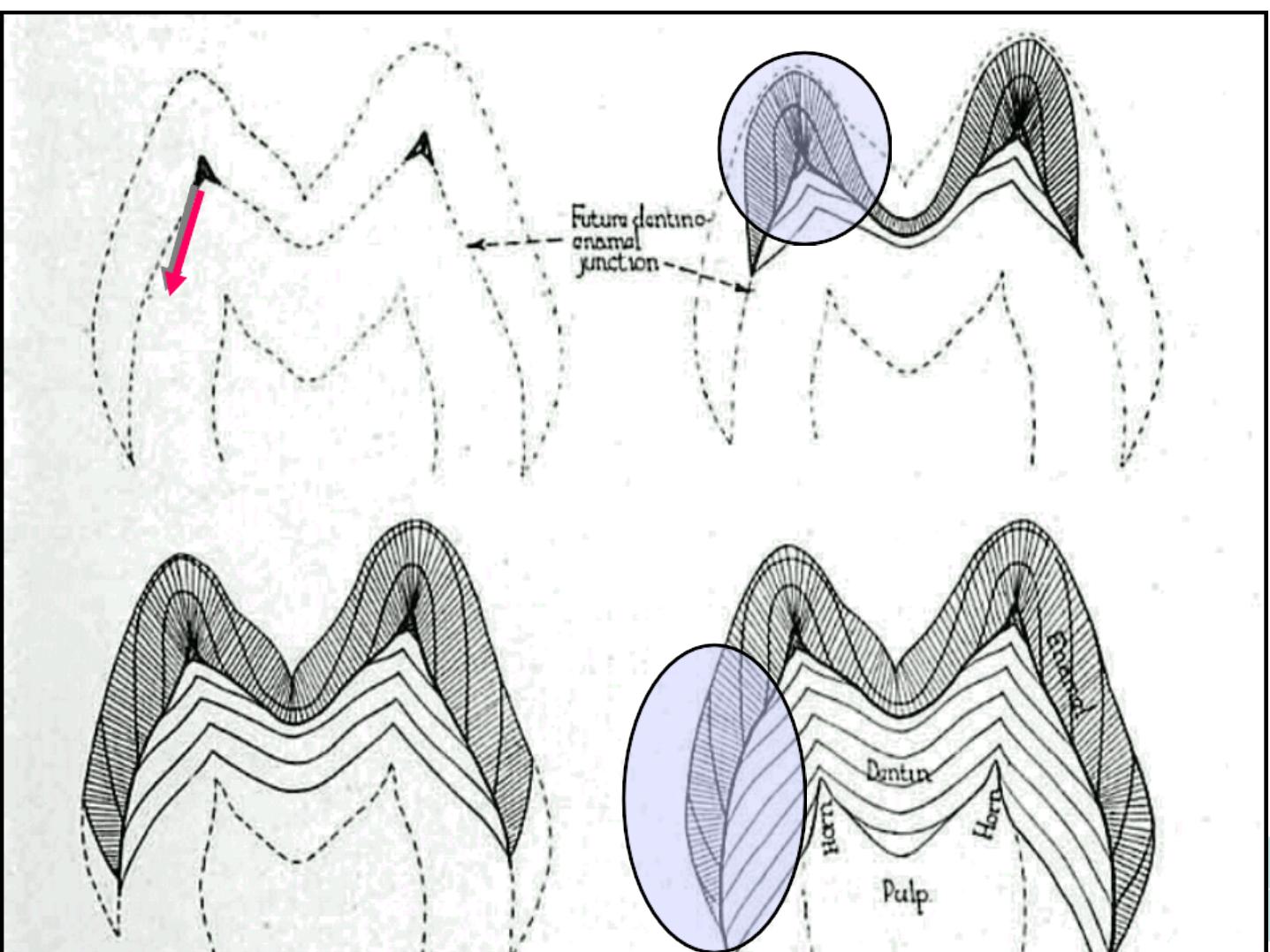
THE BEGINNING OF MINERALIZATION OF THE
ENAMEL MATRIX DOES NOT AWAIT THE
COMPLETION OF ITS FORMATION.
A
A
M
M
E
E
L
L
O
O
G
G
E
E
N
N
E
E
S
S
I
I
S
S
1
1
-
-
F
F
O
O
R
R
M
M
A
A
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
O
O
F
F
E
E
N
N
A
A
M
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
A
A
T
T
R
R
I
I
X
X
2
2
-
-
M
M
A
A
T
T
U
U
R
R
A
A
T
T
I
I
O
O
N
N
O
O
F
F
E
E
N
N
A
A
M
M
E
E
L
L
ASG
ASG
DIRECTIONS OF MATURATION
ENAMEL
DENTIN
PREDENTIN
ENAMEL
DENTIN
PREDENTIN

