د.مجاهد OSTEOARTHRITIS lec.6
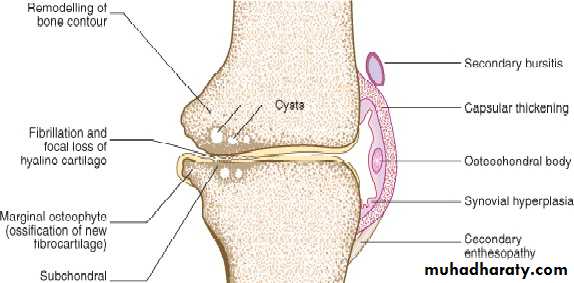
(OA) is the most common form of arthritis. It has a strong relation with ageing as its a major cause of pain and disability in older peopleOsteoarthritis is characterised by focal loss of articular cartilage, subchondral osteosclerosis, osteophyte formation at the joint margin, and emodelling of joint contour with enlargement of affected joints.
Prevalence
• Females are more commonly affected except that hips OA occurs equally in both sexes• By age of 65, 80% of people have radiological OA 25-30% of them aresymptomatic. The knee and hip are the principal large joints involved, affecting 10-25% of those aged over 65 years Even in joints less frequently targeted by OA, such as the elbow, glenohumeral joint.Risk Factors Increasing age “excessive” joint loading & mobility Abnormal mechanical forces (e.g. varus & valgus knee deformities) Race & female sex Genetic predisposition Obesity (for knees & hands O.A.) Muscle weakness Prior joint disease
PathologyStages of cartilage loss• Superficial fissuring (fibrillation) Erosions & deep ulcers Thinning & hypo-cellularity Areas of repair with fibrocartilageBone Changes•Subchondral sclerosis•Osteophytes•Subchondral cysts•Remodeling (shapechanges)
Symptoms Age over 50 Pain insidious severity varies with time Mobility aggravates & rest relieves Brief morning & post rest stiffness less than 15 minutes . No systemic manifestations Functional limitation : specially the loading & mobility related OA Neurological symptoms in spinal OASigns Gait abnormality : OA hip, knee & lumbar spine Deformity e.g. Bow knees (varus) Tenderness, may not be diffuse No or small effusion (sometimes moderate size) Bony swelling (osteophyts & remodeling) Crepitus Periarticular muscle weakness Painful movement restriction Neurological signs in spinal O.A.Clinical PatternsLocalized interphalangeal OA. (usually DIP)Generalized OA.Loading / mobility related OA.
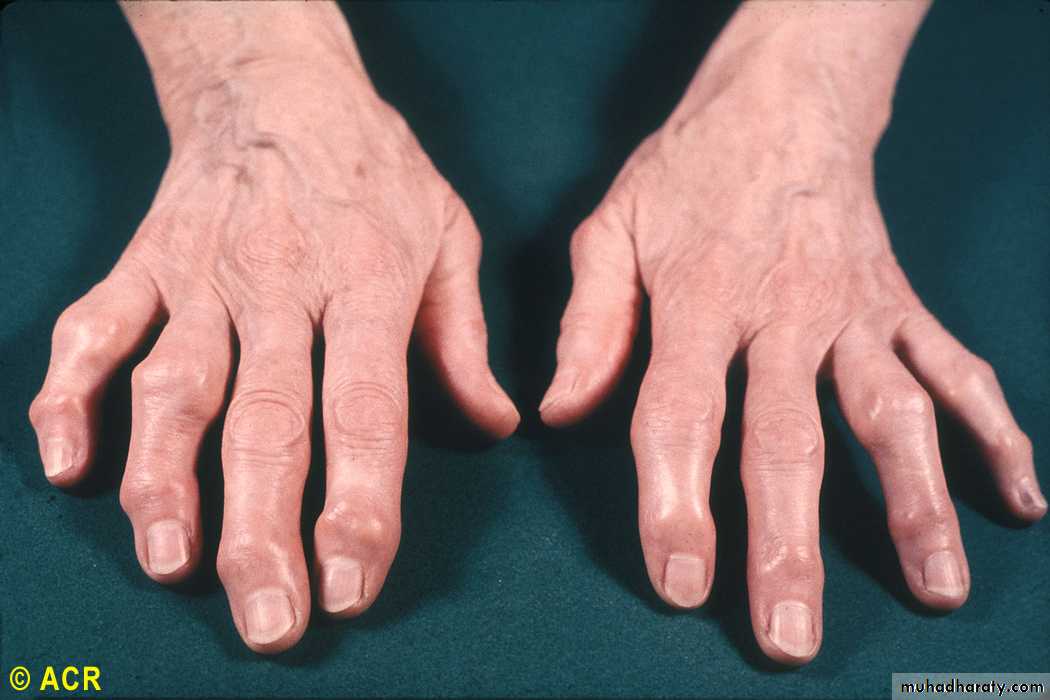
Osteoarthritis: Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes
Localized interphalangeal OA. (usually DIP)• Heberden’s nods appears slowly• Female & male 10/1• Strong genetic factor
Generalized OA• Usually post menopausal women• Affect 3 or more joints or joints group• Usually starts in the interphalangealjoints (DIPs & PIPs)• Tendency to O.A. at other sitesspecially knee
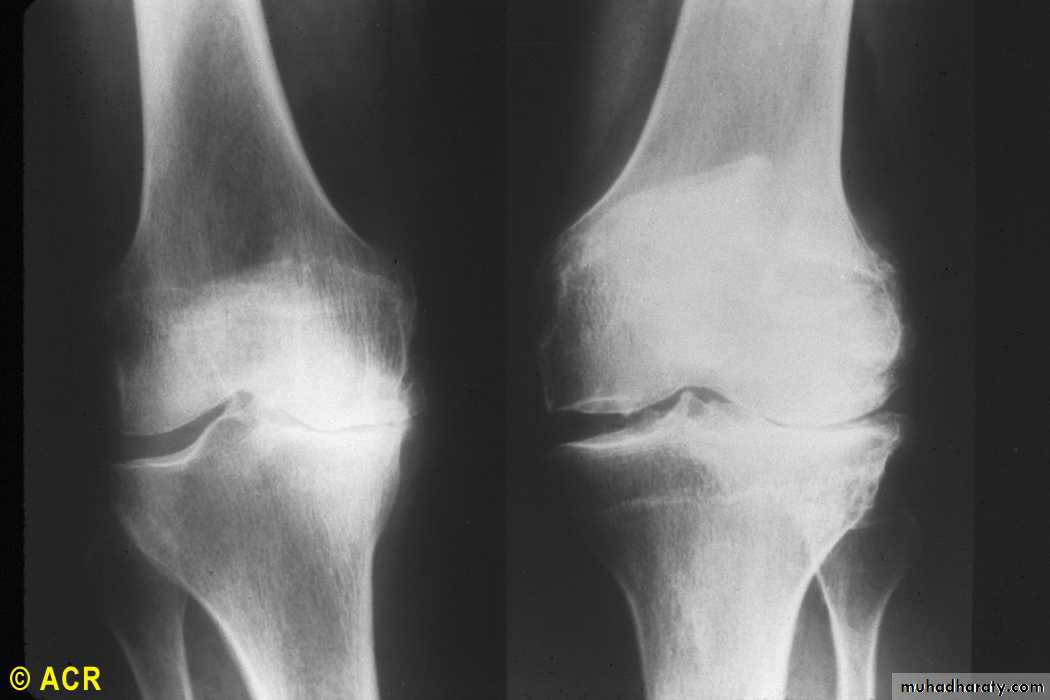
Osteoarthritis: knees, medial (XR1) and lateral (XR2)
cartilage degeneration Medial loss is the usual in
mobility /loading related O.A. knee
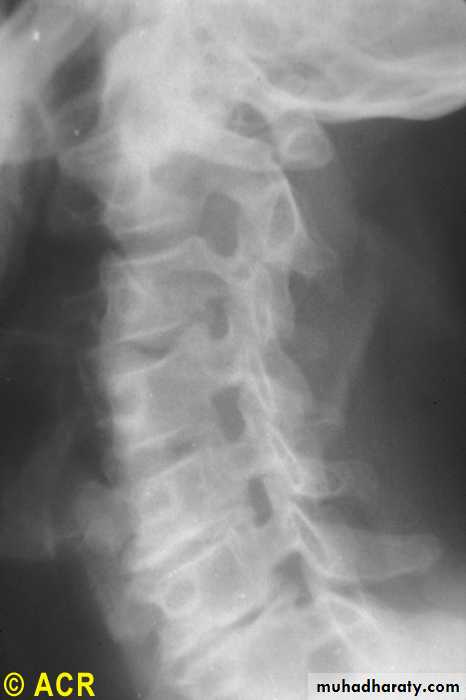
Osteoarthritis:cervicalvertebrae,foraminalencroachment
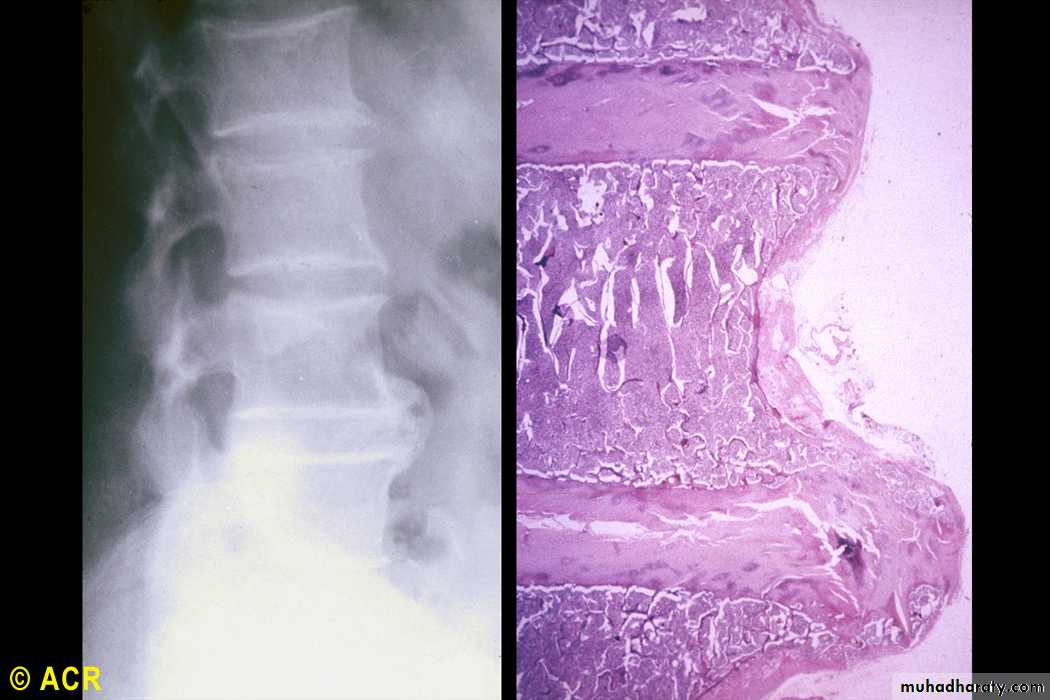
Lumbar vertebrae, osteophytes(radiograph and photomicrograph)
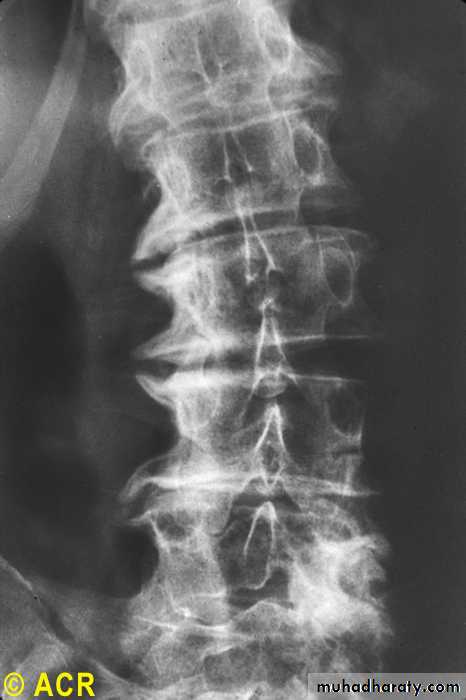
Osteoarthritis:lumbarvertebrae,advancedstages
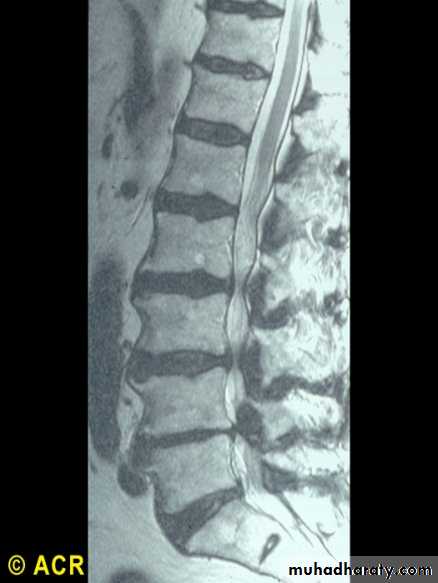
Spinal stenosis:lumbar spine(MRI) due toO.A.
TreatmentTreatment
• Non pharmacologicalReduceobesityAvoid static loading e.g. prolonged squattingPacing of activityExercise specially non weight bearing (bicycle …)Joint rest techniques :Neck collarPharmacologicalOral analgesic : paracetamolTopical : capsacin & NSAIDsSystemic NSAIDsIntra-articular steroids with careful precautionsIntra-articular hyaluronic acid productsGlucosamine & chondroitins sulfateOsteotomyTotal joint replacement (TJR)Cartilage repair surgery (cartilage autograft). Highly specialized centersIndications : uncontrolled pain & functional disability refractory toconservative therapy