4th stage
SurgeryLec
د.محمد فوزي
20/12/2015
BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION(B.O.O.)It’s urodynamic concept of low flow rates and high intravesical pressures.
Causes:
BPH.
CAP.
bladder neck stenosis.
urethral stricture.
neuropathic conditions.
Pathophysiology :
Boo over time will result in increase in the intravesical voiding pressure (>80 cm H2O), bladder muscle hypertrophy (trabiculation, sacculation and diverticulum formation).
High pressure may transmit to the upper tract causing hydroureter, hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency.
Boo results in incomplete bladder evacuation (residual urine) which predisposes to UTI and stone formation.
Decrease uro flow rate under 10 ml /sec
Symptomatology (LUTS)
1-Obstructive:
Hesitancy
Straining
Weak stream
Intermittency.
Post voiding dribbling.
Retention of urine.
2-Irritative:
Frequency.,nocturia
Urgency & urge incontinence.
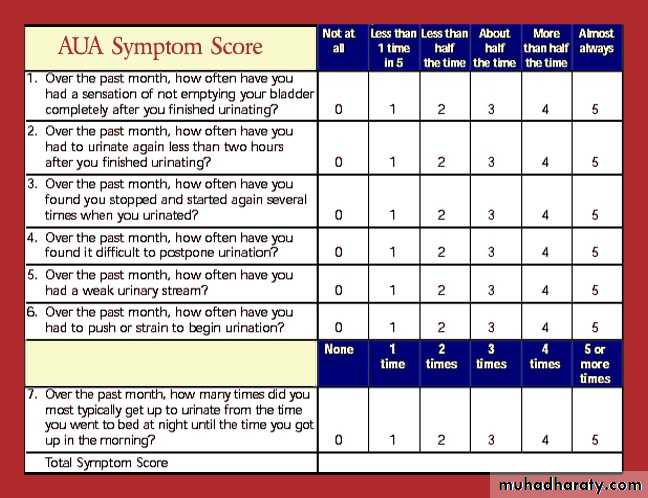
IPSS [international prostatic symptom score]
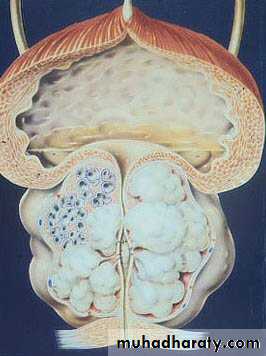
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Third most common urological pathology , Starts at late 30s & appear clinically at 60s.
Theories:
Hormonal: DHT, growth factor.Neoplastic: fibromyoadenoma.
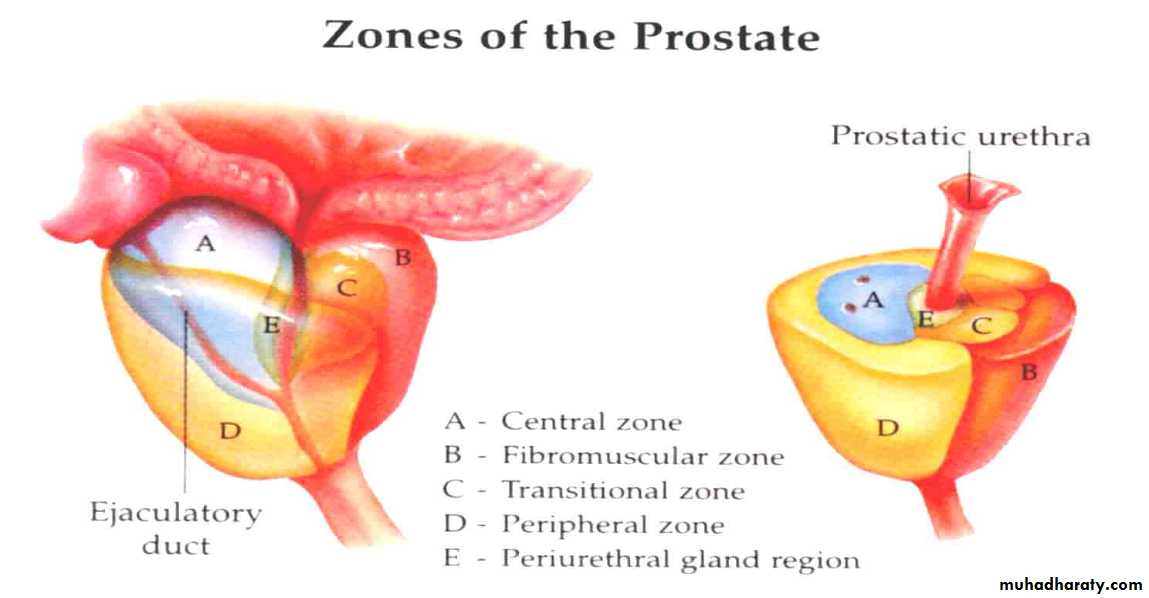
Typically affects submucosal glands at transitional zone.
Symptomatology :
Boo (irritative and obstructive).Symptoms are slowly progressive over years, worsening at winter time.
Renal failure.
Hematuria.
Pain is not afeature of BPH the presence of which may indicate acute retention,vesical stone,infection,CAprostate
Precipitating causes for retention :
Severe pain. MI, joint pain.
Psychological upset.
Cold exposure.
Constipation.
Drugs
Anticholenergic & diuretic ,decongestant,antihistamin
Ignoring first desire for urination.
Clinically :
Usually normal.
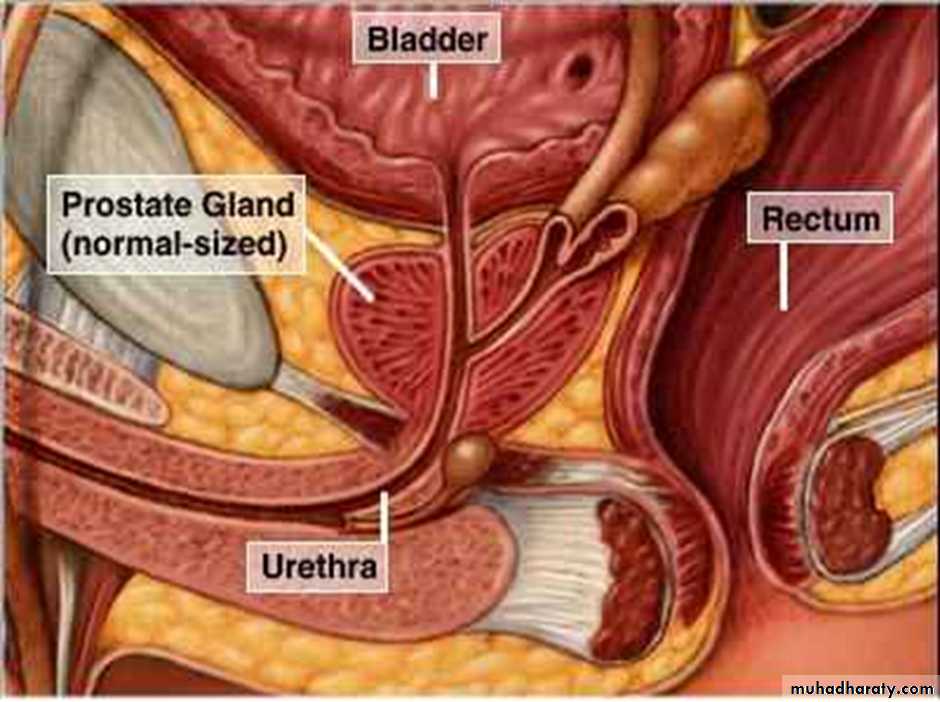
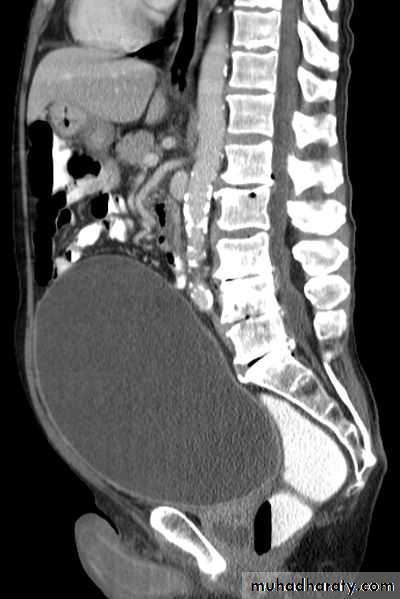
Distended bladder.in acute or chronic retention
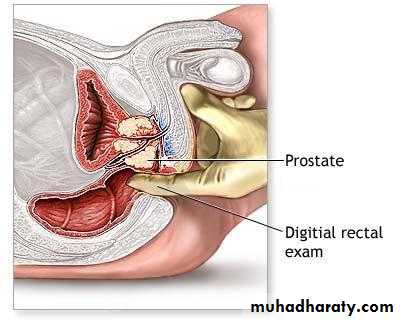
PR ex: enlarged prostate, smooth, regular, firm, maintained median sulcus and mobile rectal mucosa
Normal anal sphencter tone.
Normal bulbocovernosus reflex
Investigations :
GUE: normal or UTIRFT: normal unless there is renal failure
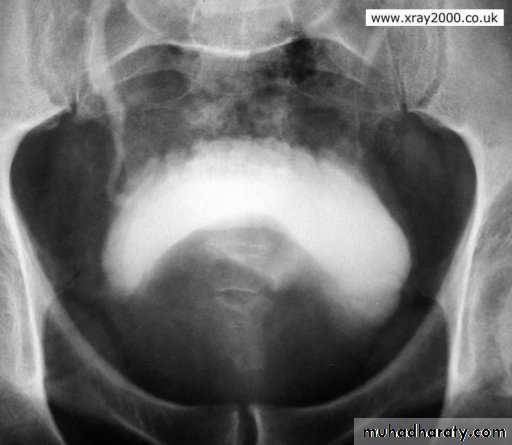
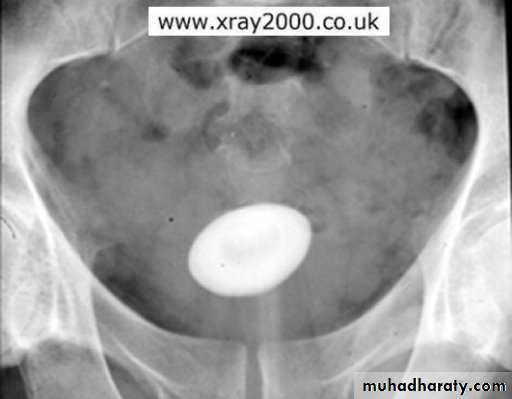
U/S:TRUS: BPH, vesical stone, residual urine and hydronephrosis.
IVU
Vesical stone BPH
PSA: (prostate specific Ag)<10 ng/ml.
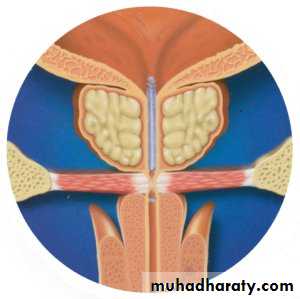
Cystoscopy: enlarged prostate, trabiculation & stones.Size of the prostate has no relation with the severity of the symptom but the degree of urethral compression.
Treatment :
Conservative:
Avoid ppt factors.
Treat pains.
Treat UTI.
Αlfa blocker: prazocin 1 mg, terrazocin 2mg, doxazocin 2mg.tamsulusin,alfuzosin At night ,
S/E hypotension, 1st dose syncope.
5 α reductase inhibitors: fenasteride, prosteride 5 mg/day > 6 months.
S/E impotence.
Usually used in large gland
Semi surgical:
TUMT (trans urethral microwave thermotherapy)HIFU ( high intensity focused u/s)
TUIP (Trans urethral incision of prostate)
TUNA (Trans urethral needle ablation)
Prostatic stents
TU baloon dilatation
TUMT TUNA Stent
Surgical treatment
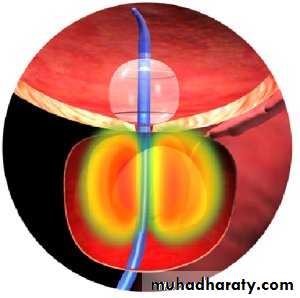
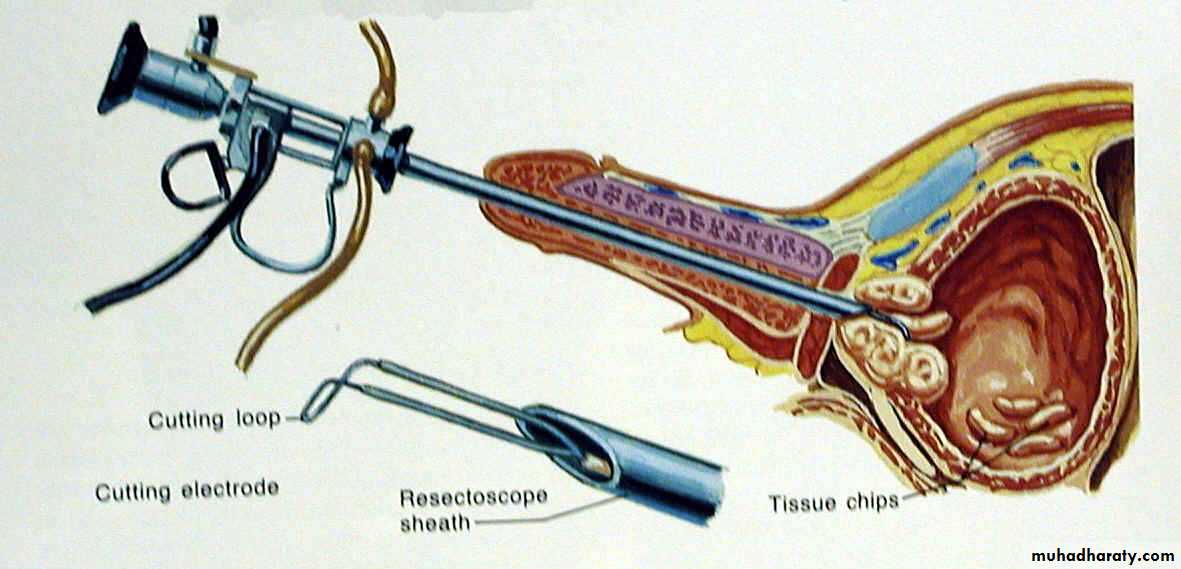
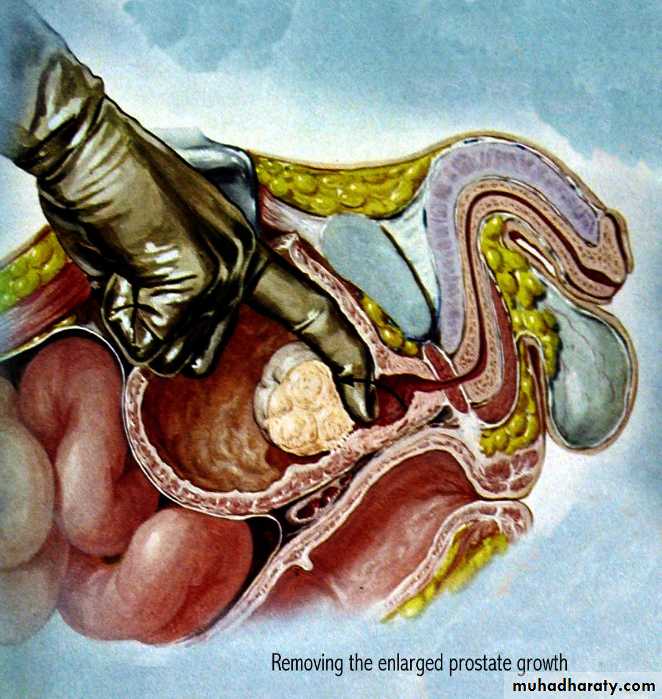
Endoscopic:TURP
Laser
Open surgery:
Trans vesical prostatectomy.
Rertopubic prostatectomy
Indication of surgery in BPH
1-severe symptoms2-failure of medical treatment
3- complications like :
-acute urinary retention
-chronic retention
-repeated hematuria
-repeated UTI
-vesical stone
-renal impairment due to chronic retention
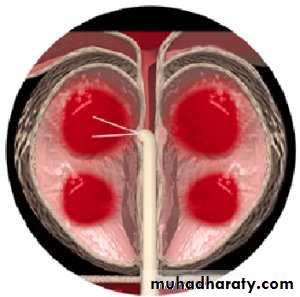
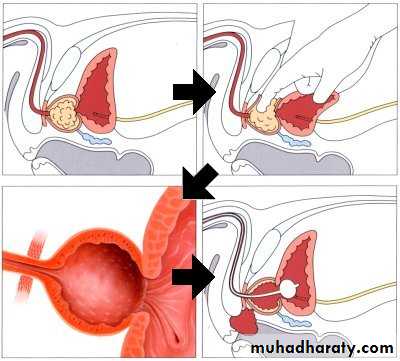
TURP
Transvesical retropubic
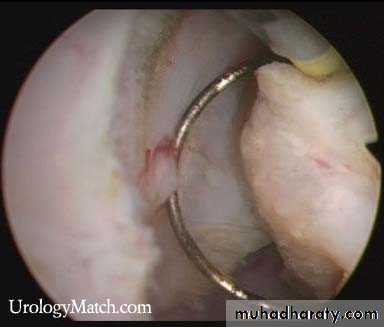
Before TURP After TURP
Complications :
Early:Bleeding and clot retention.
TUR syndrom (water intoxication) due to. dilutional hyponatremia.
Infection.
Wond infection[in open prostatectomy]
Late:
Urethral stricture
Bladder neck contracture
Retrograde ejaculation.
Incontinence.
Impotence.
Recurrence of BPH. After 5-10 years.
SH.J