

Temporary Restoration
(provisionalrestoration)
Dr. Emad farhan alkhalidi
MSc, phD
Dr. Emad Farhan Alkalidi
MSc, pHD
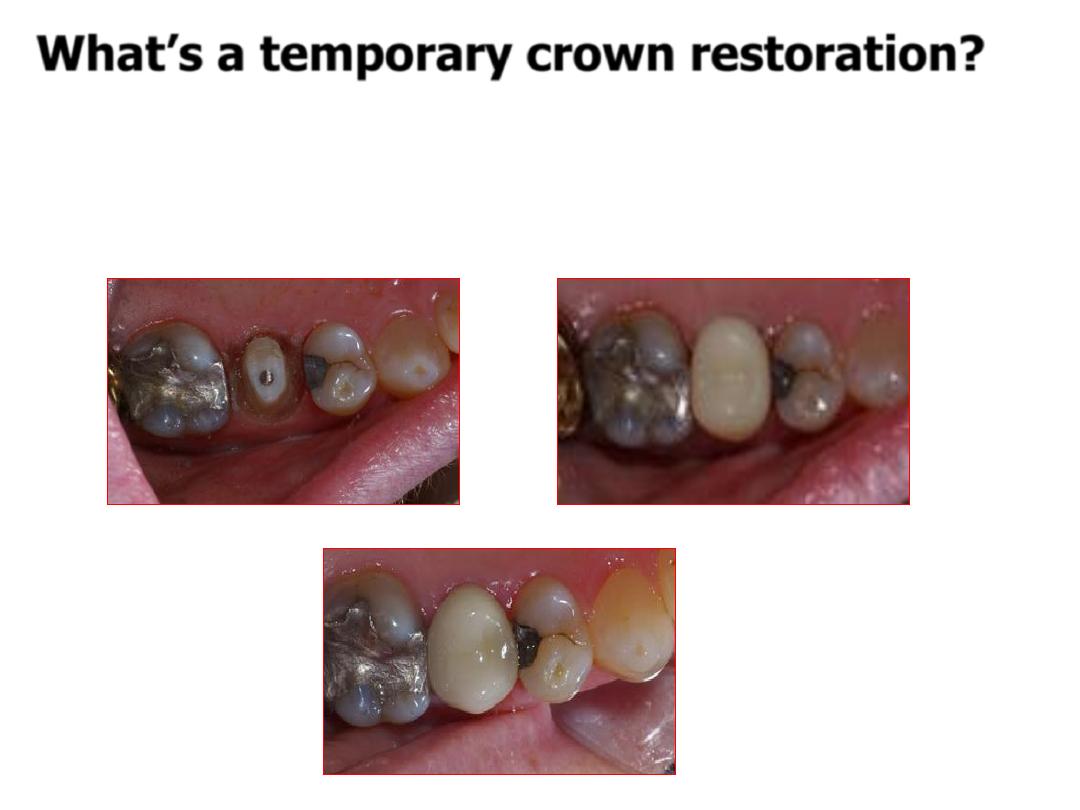
What’s a temporary crown restoration?
A crown restoration that is used in fixed
prosthodontics during the interim between
tooth preparation and final placement of the
definitive crown restoration.

Objectives of provisional restoration:
2.
prevent sensitivity and further irritation to the pulp since a
certain degree of pulp trauma is inevitable during tooth
preparation because of the sectioning of the dentinal tubules.
3.
prevent movement of the prepared, adjacent, and opposing
teeth. i.e., to prevent supraeruption and drifting.
4.
protect the gingival tissue from irritation and food impaction.
5.
provide esthetic, phonetic, and function.
6.
prevent tooth fracture.
1.
protect the tooth from pain stimuli as a result of thermal,
chemical, and osmotic changes in the mouth.
Requirements of an optimum provisional restoration:
I. Biologic.
II. Mechanical.
III. Esthetic.
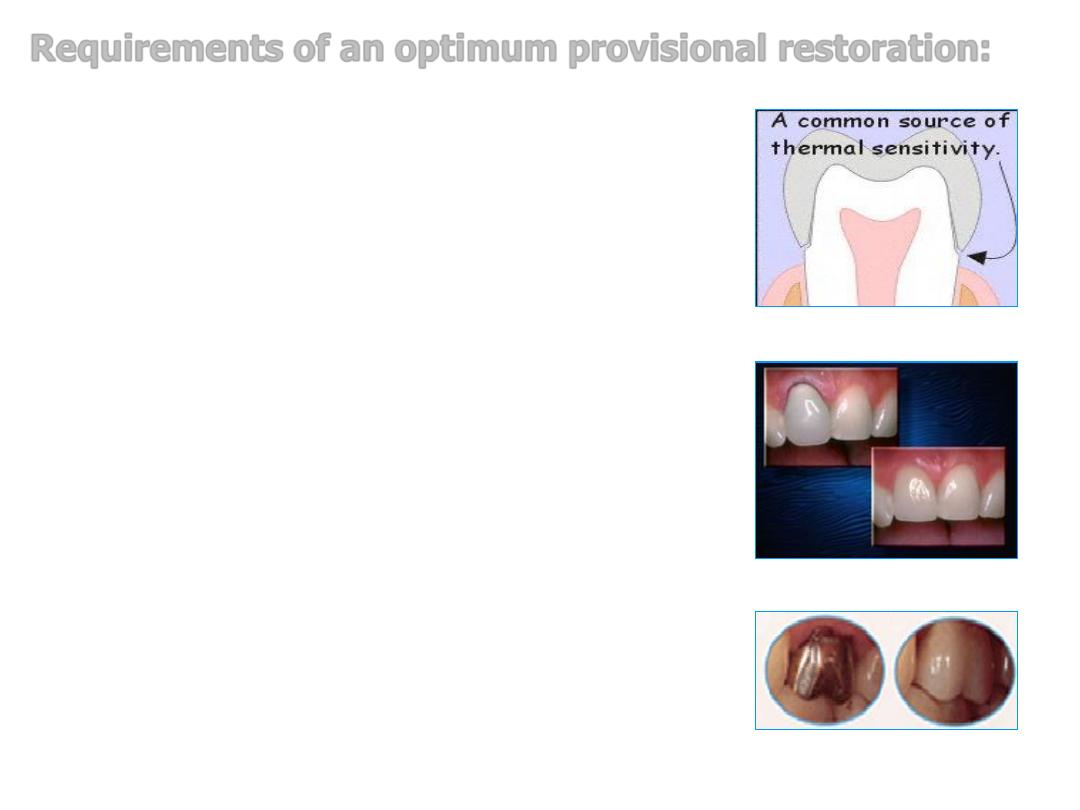
1.
A provisional restoration must seal and
insulate the prepared tooth surface from the
oral environment to prevent sensitivity and
further irritation to the pulp.
2.
A provisional restoration must have good
marginal fit, proper contour, and a smooth
surface to maintain the health of the gingival
tissue and facilitate plaque control by the
patient.
3.
A provisional restoration should maintain
proper contacts with the adjacent and opposing
teeth to prevent supraeruption and horizontal
movement (drifting).
Requirements of an optimum provisional restoration:
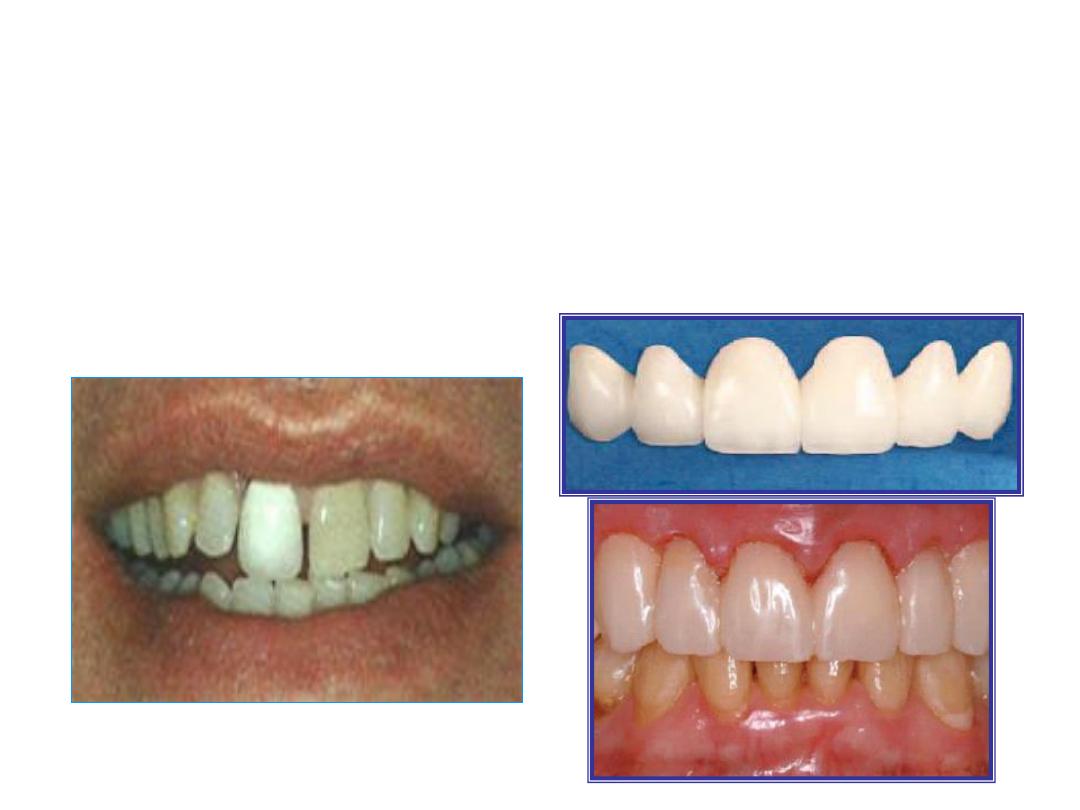
4.
A provisional restoration should have enough strength and retention
to withstand the forces to which it is subjected without fracture or
coming off the tooth. In addition, it should remain intact during its
removal so that it can be reused again-if necessary-.
5.
A provisional restoration should provide esthetic, phonetic, and
function.

Types of provisional restoration:
2.
Customized temporary restorations (chair side
temporary restorations).
3.
Laboratory-made temporary restorations.
1.
Preformed temporary crowns.

Generally, preformed temporary crowns consist of a shell of plastic
or metal that could be cemented directly on the prepared tooth
following adjustment, or after its lining with a resin material. They
could be used for single or multiple preparations.
1. Preformed temporary crowns:
Types of preformed temporary crowns:
C. Celluloid crown forms.
B. Plastic temporary crowns.
A. Metal temporary crowns.
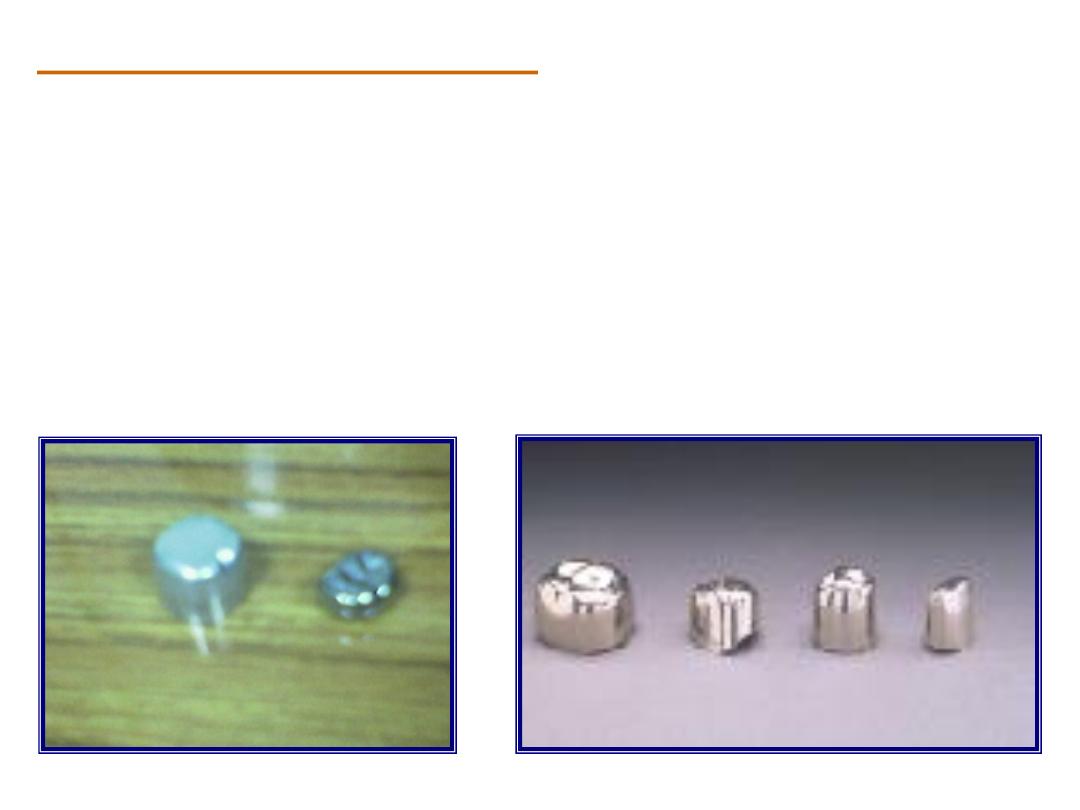

A. Metal temporary crowns:
Metal temporary crowns are mainly indicated for use in the
posterior teeth. They are made of stainless steel, nickel-
chromium, or aluminum. The most commonly used type is
aluminum temporary crowns, which are of two types:
1. Non-anatomical or flat-topped cylindrical temporary crowns.
2. Anatomical or morphological aluminum temporary crowns.


1.
Select the proper size and shape of the temporary
crown according to the prepared tooth.
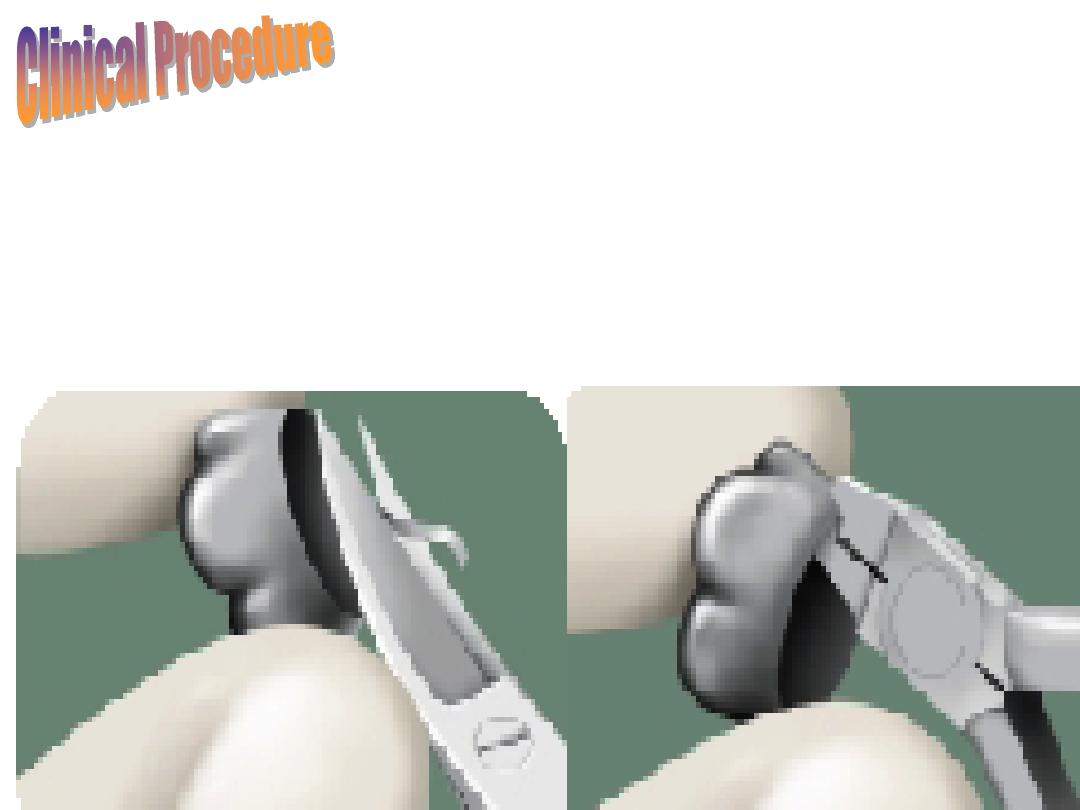
2.
Trim the cervical margin of the temporary crown
using a scissor to conform to the gingival margin of
the preparation (finishing line) and to accommodate
the vertical height of the prepared tooth.
3.
Seat the temporary crown on the prepared tooth
and ask the patient to bite on it. Check the margins
and the occlusion (centric and eccentric).
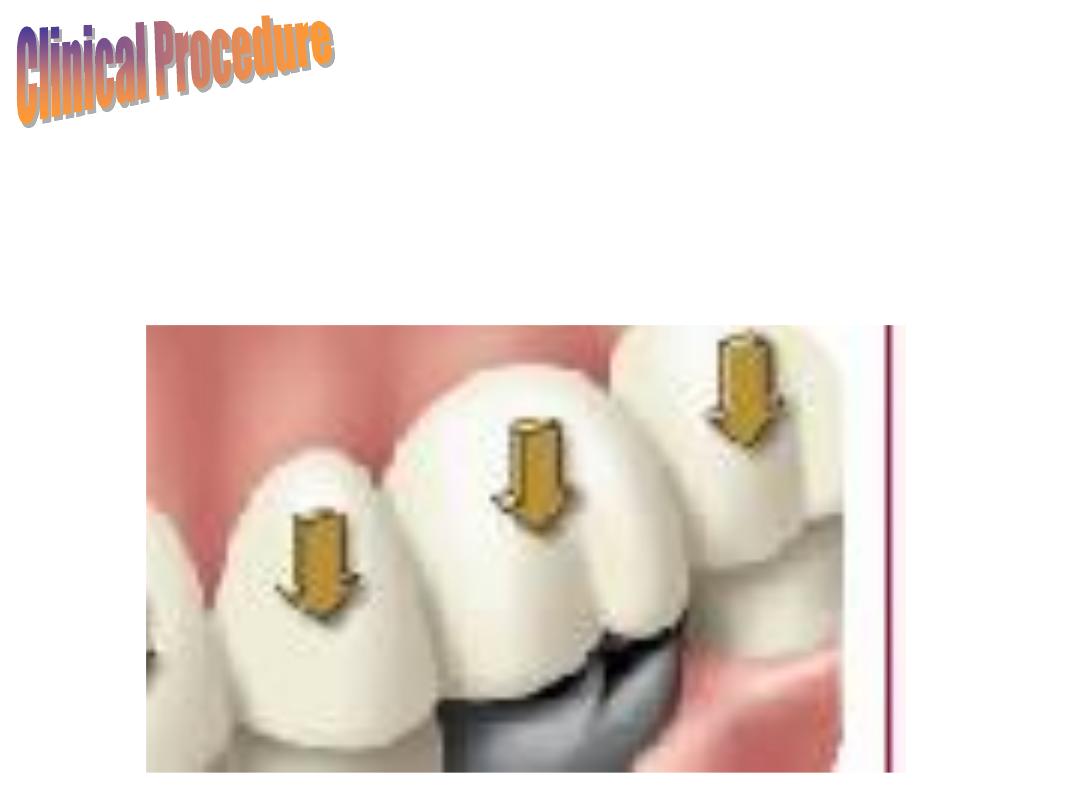
4.
Smooth the margins with a stone bur.
5.
Cement the temporary crown on the prepared
tooth using zinc oxide-eugenol cement.
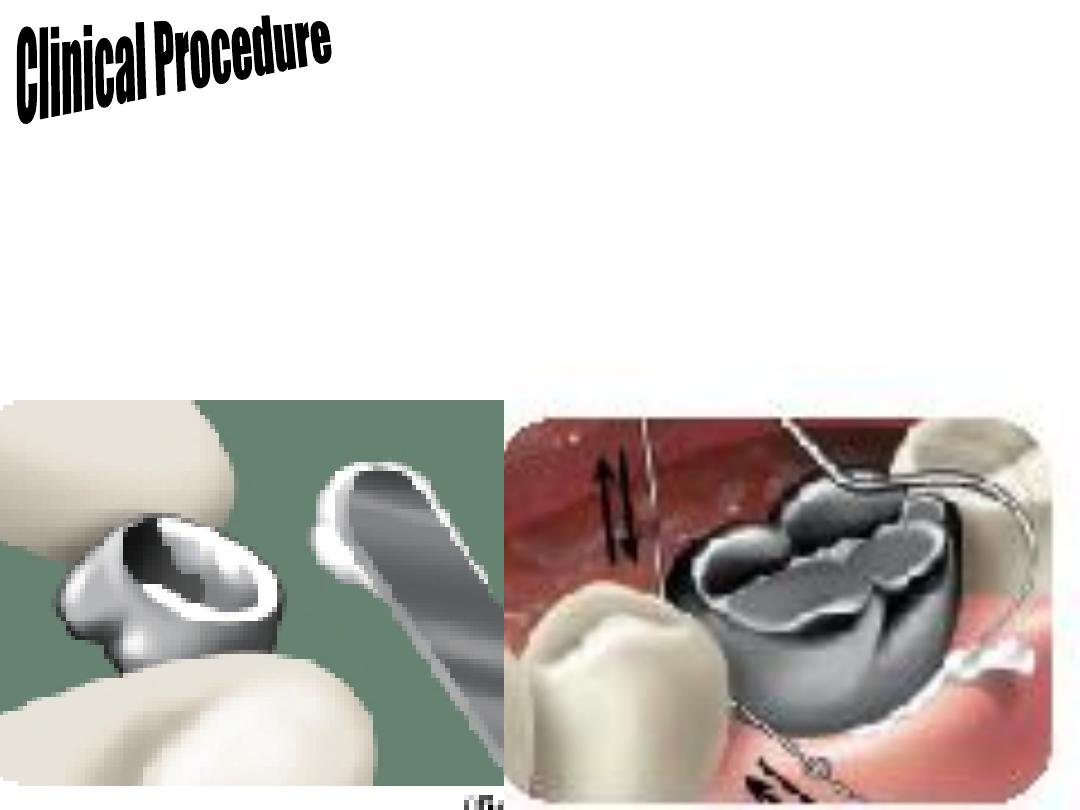
B. Plastic temporary crowns:
Plastic temporary crowns are used mostly for the anterior teeth. The
clinical procedure for the use of plastic temporary crown is nearly the
same as that for metal temporary crown.
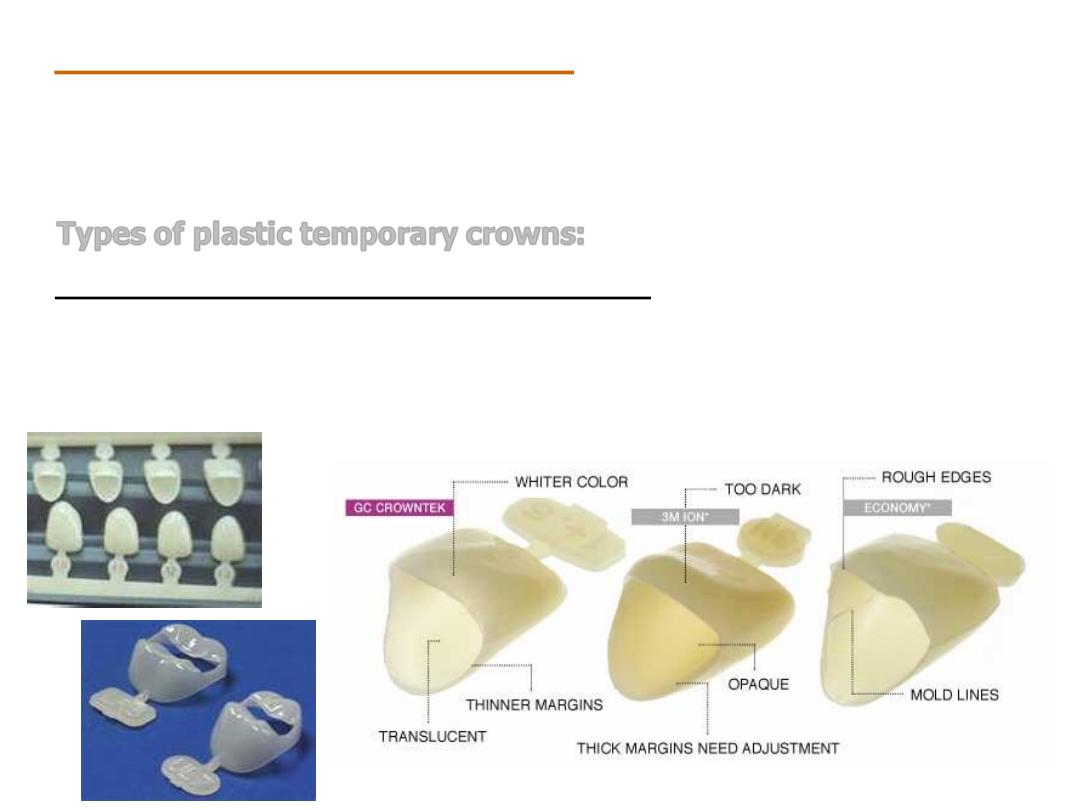
Types of plastic temporary crowns:
1. Polycarbonate temporary crowns: these are made from
polycarbonate plastic combined with micro glass fibers. Preformed
polycarbonate temporary crowns are available for the anterior and
posterior teeth.
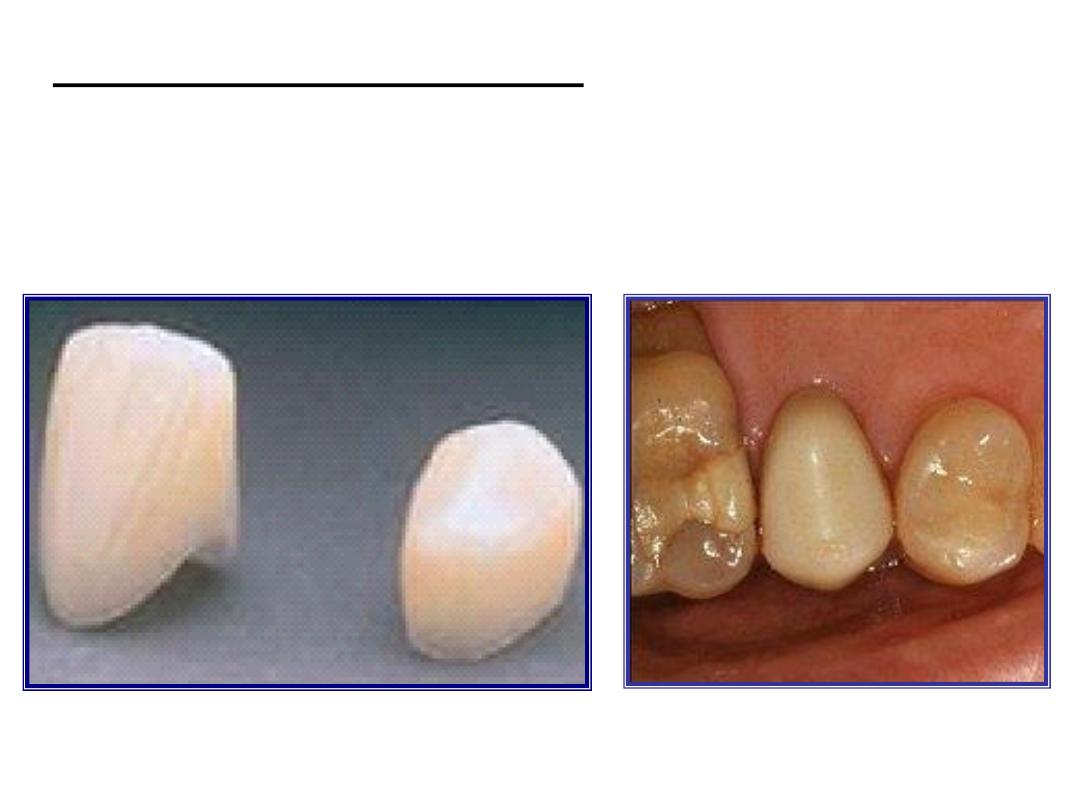
2. Acrylic temporary crowns: these are made from acrylic
resin and are available fin different sizes and colors. Preformed
acrylic temporary crowns are used for the anterior teeth.

The procedure of relining could be done either directly on the
prepared tooth in a manner similar to that of celluloid temporary
crown (will be discussed later) or could be done indirectly on a
study cast of the prepared tooth.
In case we need to improve the fitness of the temporary crown
or if there is no size which approximately fits the prepared tooth,
we can reline the temporary crown with a resin material to
improve its fitness after the selection of the most suitable size and
shade (color) of the temporary crown and cutting its margin
according to the finishing line of the prepared tooth.

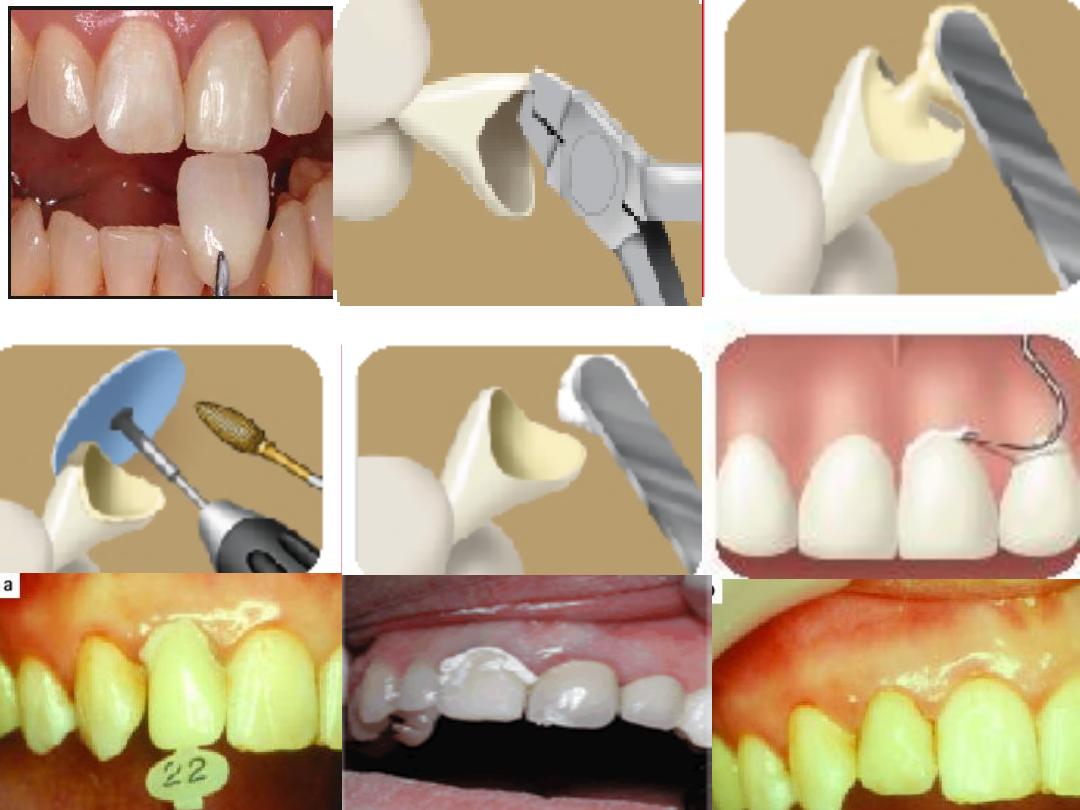

C. Celluloid crown forms:
They are mainly used for the anterior teeth, but can be used
for the posterior teeth also. They are made from a very thin
translucent layer of cellulose acetate. They act as a mold for the
construction of the temporary crown. They come in different
sizes.

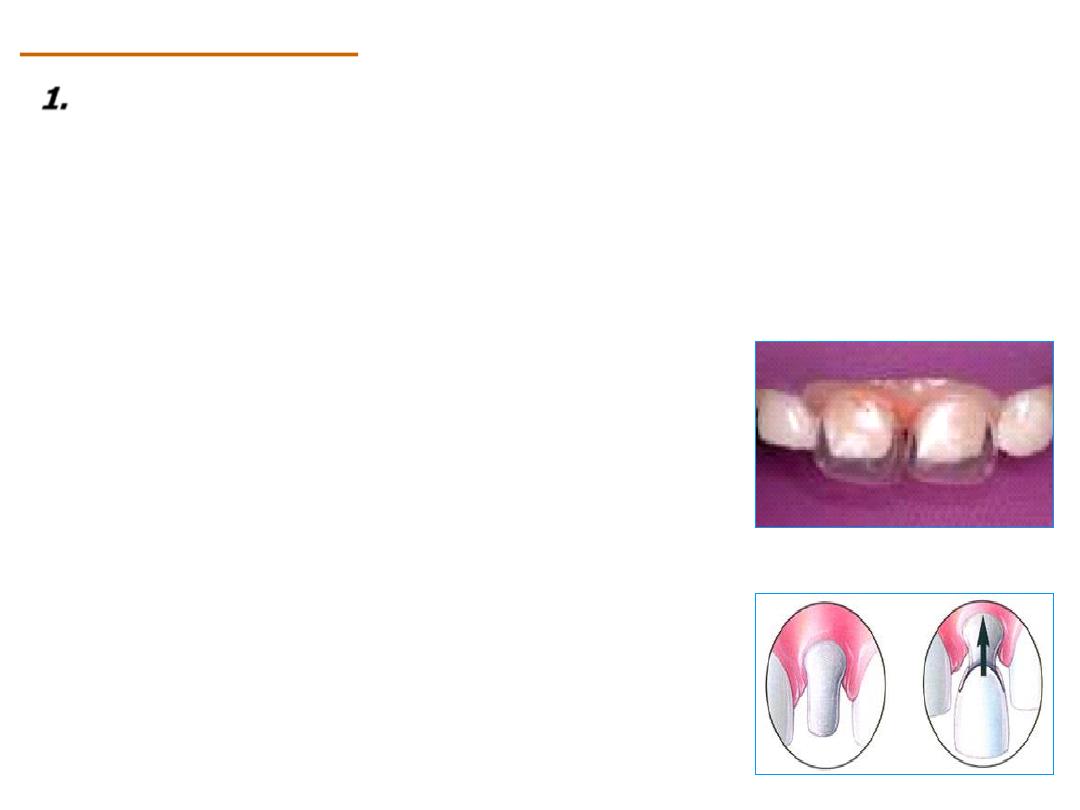
Clinical procedure:
2.
Select the proper size and shape of the celluloid crown.
1.
Coat the prepared tooth with vaseline to facilitate removal of
the temporary crown.
3.
Make two holes in the corners of the temporary crown to
provide an escape way for the excess material.
4.
Cut the gingival margin of the crown to
accommodate that of the prepared tooth.
5.
Fill the celluloid crown with a provisional
crown material (acrylic resin or composite
resin) of the same shade of the tooth and
seat it over the prepared tooth until
setting.

If acrylic resin is used as a provisional material, the celluloid
crown should be removed at its semi-plastic stage so that the
polymerization reaction of the acrylic resin will occur outside
the mouth to prevent pulpal irritation since the polymerization
reaction of the acrylic resin is exothermic.
6.
Take the crown out and remove the excess material. Then
place it again on the prepared tooth and check the occlusion,
contact with the adjacent teeth, fitness, and extension.
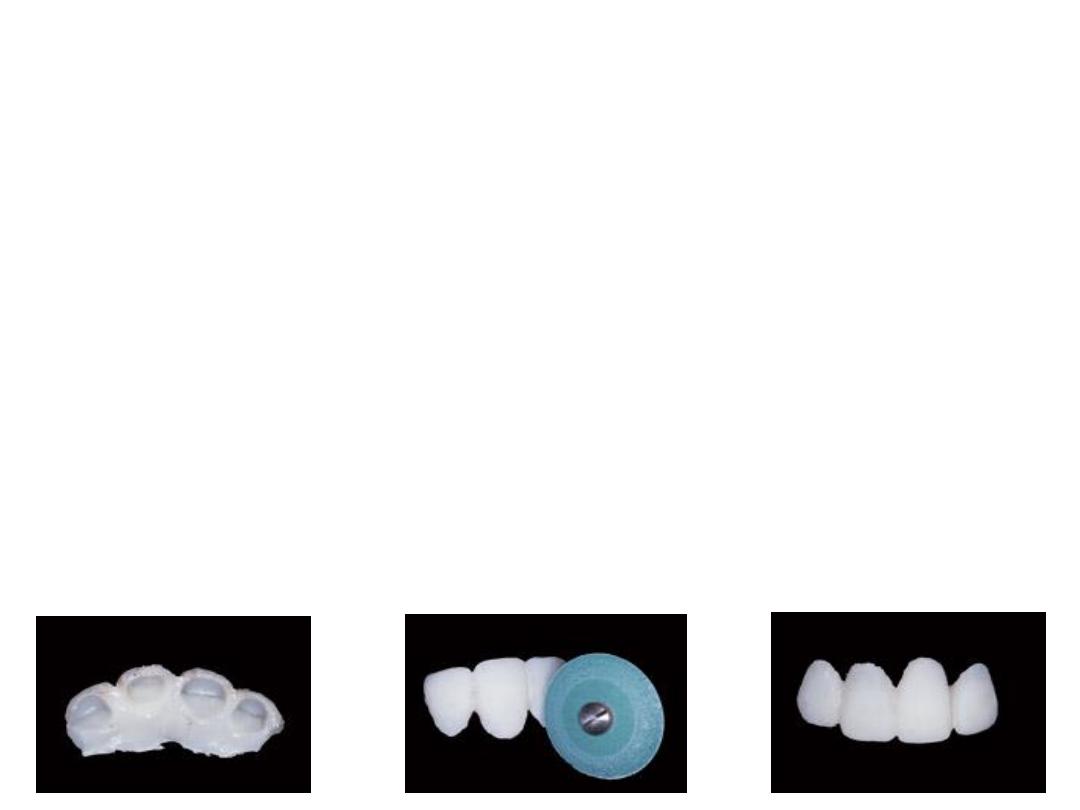
2. Customized temporary crown and bridge :
The fabrication of customized temporary crowns requires the
construction of a mold of the patient’s teeth before their
preparation. This may be obtained from any type of elastic
impression material, into which resin polymer material (acrylic
or composite) is placed and the mold is held either directly on
the prepared tooth (or teeth) or indirectly agaist a cast of the
patient’s teeth.
Indications of customized temporary restoration:
1.
Coverage of multiple individual crown preparations.
2.
Coverage of a single tooth preparation which is usually large
or of a special design. i.e., when a preformed temporary crown
is not fit to the tooth.
3.
Abutment preparations for fixed partial denture to construct
a temporary bridge.

Methods of construction of customized temporary
restorations:
1.
Impression method (the most commonly used method).
2.
Template method.
3.
Polycarbonate matrix method.
4.
Acrylic shell method.

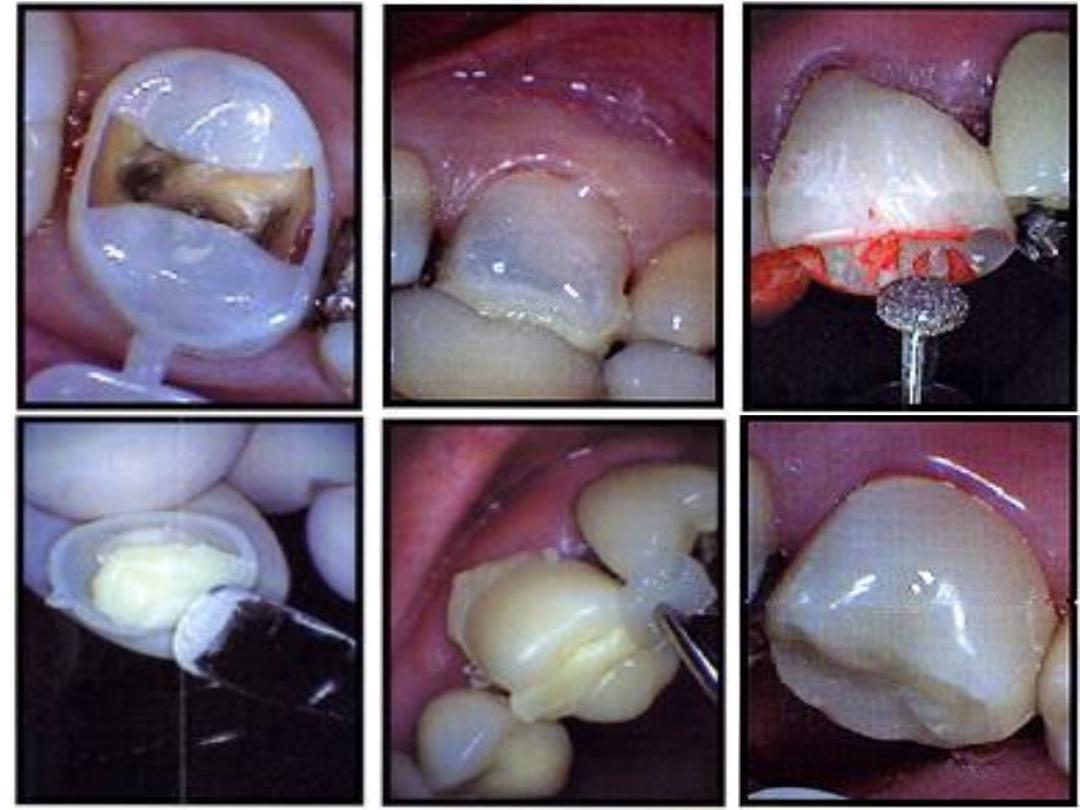
Impression method:
-Indirect impression method.
-Direct impression method.
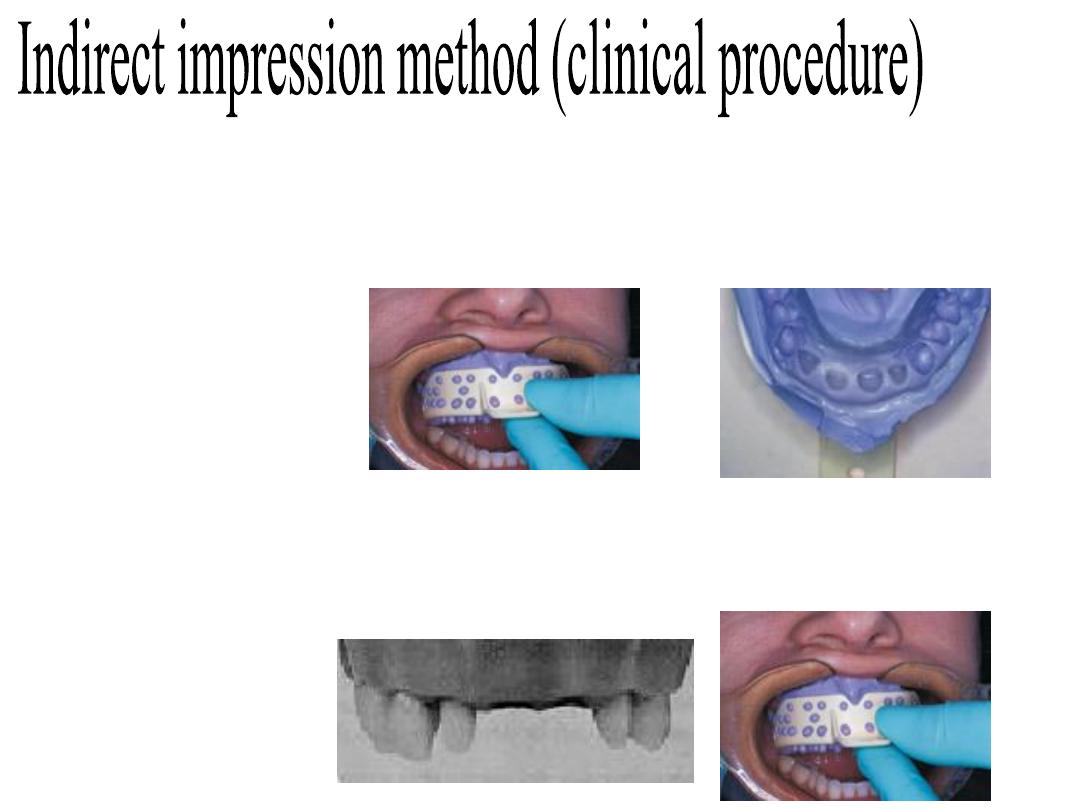
1.
A preoperative over impression with alginate or silicone
impression material is made from the patient’s teeth or from a
study model and carefully stored until completing tooth
preparation (over impression).
2.
After completing the preparation of teeth, another alginate
impression was then taken and poured with fast-setting plaster or
stone. After setting of the plaster or stone, the cast is separated
from the impression.
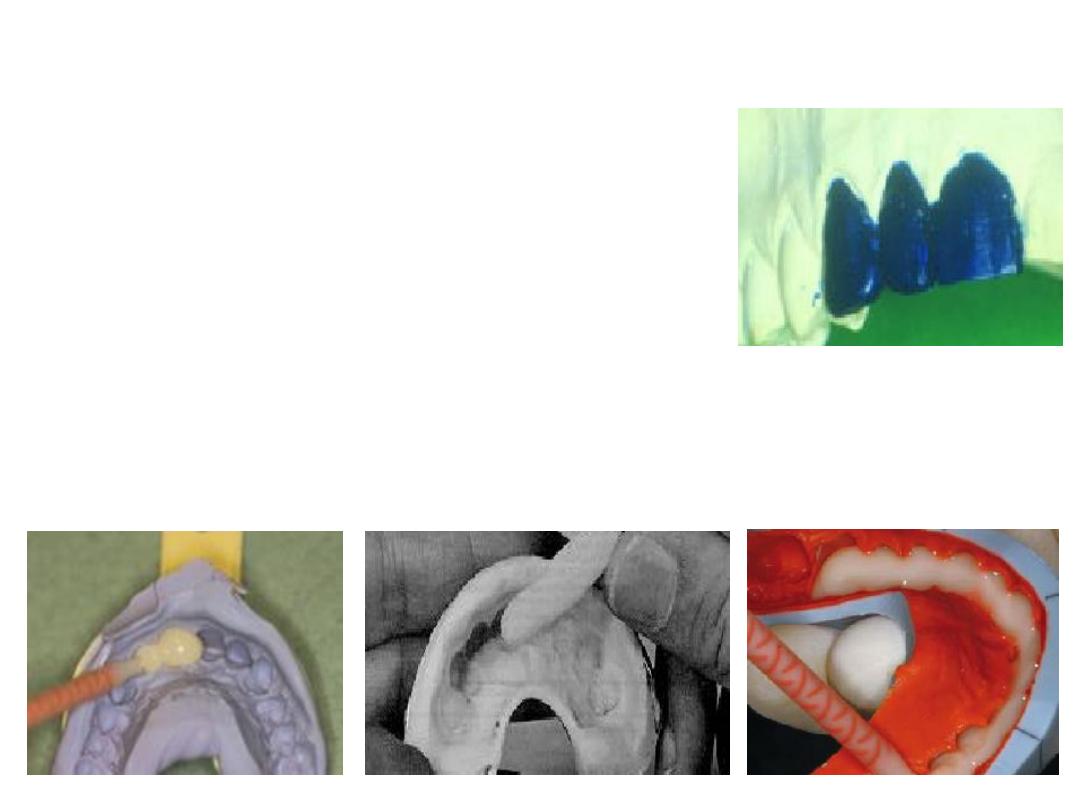
4.
Mix tooth colored acrylic resin according to the manufacturer’s
instructions and place the mixed acrylic in the over impression at
the area of tooth preparation only.
3.
Coat the prepared tooth (or teeth) on the cast with a separating
medium (such as petroleum jelly).
7.
Trim any excess material from the formed crown (or bridge).
Then the crown (or bridge) is seated on the prepared tooth (or
teeth) inside the patient’s mouth. Check the occlusion and remove
any premature contact in centric and eccentric occlusion.
6.
After complete polymerization of the acrylic
resin, separate the cast from the over
impression. The formed crown (or bridge) is then
removed from the prepared tooth (or teeth) in
the cast.
5.
Seat the cast into the over impression in an upright position and
maintain constant pressure until the acrylic resin sets completely. It
is important to note that the cast is correctly seated in the over
impression.
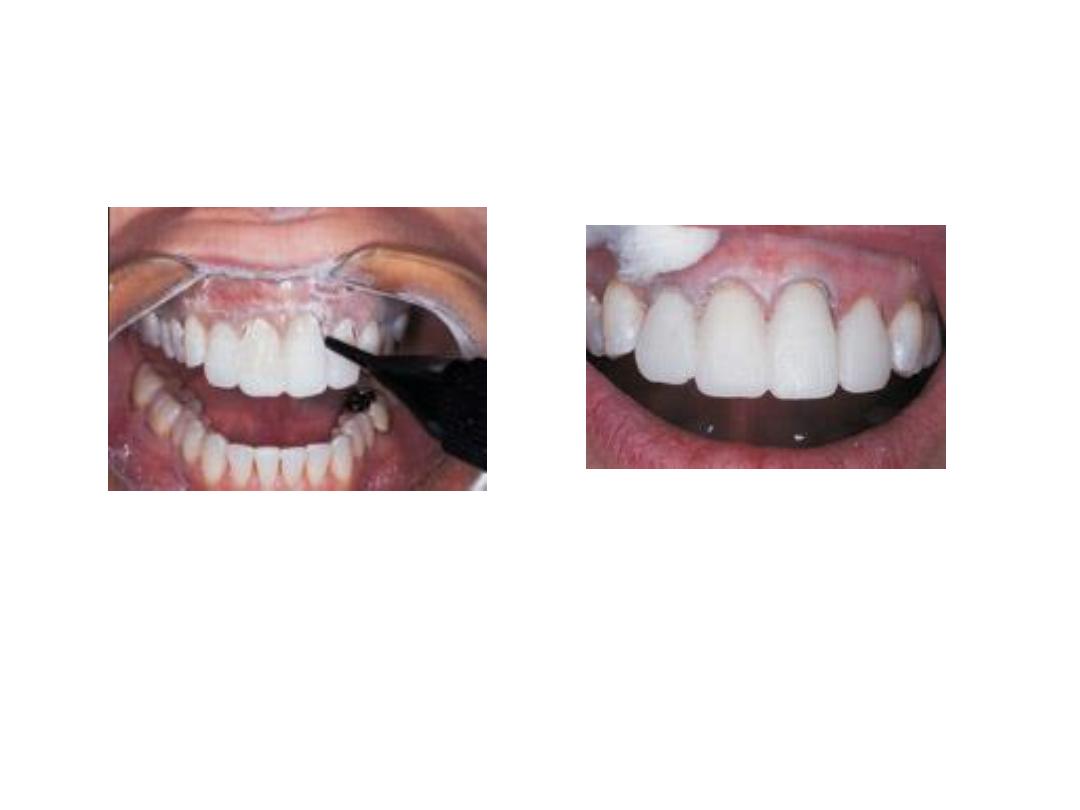
8.
Cement the temporary crown on the prepared tooth using zinc
oxide-eugenol cement.

Clinical procedure of the direct impression method:
1.
There is no direct contact of the free monomer of the acrylic
with the prepared tooth or gingival tissue which might cause
tissue irritation or aalergic reaction.
The clinical procedure of the direct impression method is the
same as that of the indirect method except that it is done
directly inside the patient’s mouth. In this method, we need a
preoperative over impression; there is no need to have a study
cast. Prepare the tooth (or teeth), mix the acrylic resin, place it
in the over impression in the area of tooth preparation, and seat
the over impression inside the patient’s mouth. Then follow the
same steps that are used in the indirect method.
Advantages of the indirect method over the direct method:
2.
The indirect method avoids subjecting the prepared tooth to
the heat of polymerization of the acrylic resin since the
polymerization reaction of the acrylic resin is exothermic.
3.
The indirect method saves the clinician’s chair time.

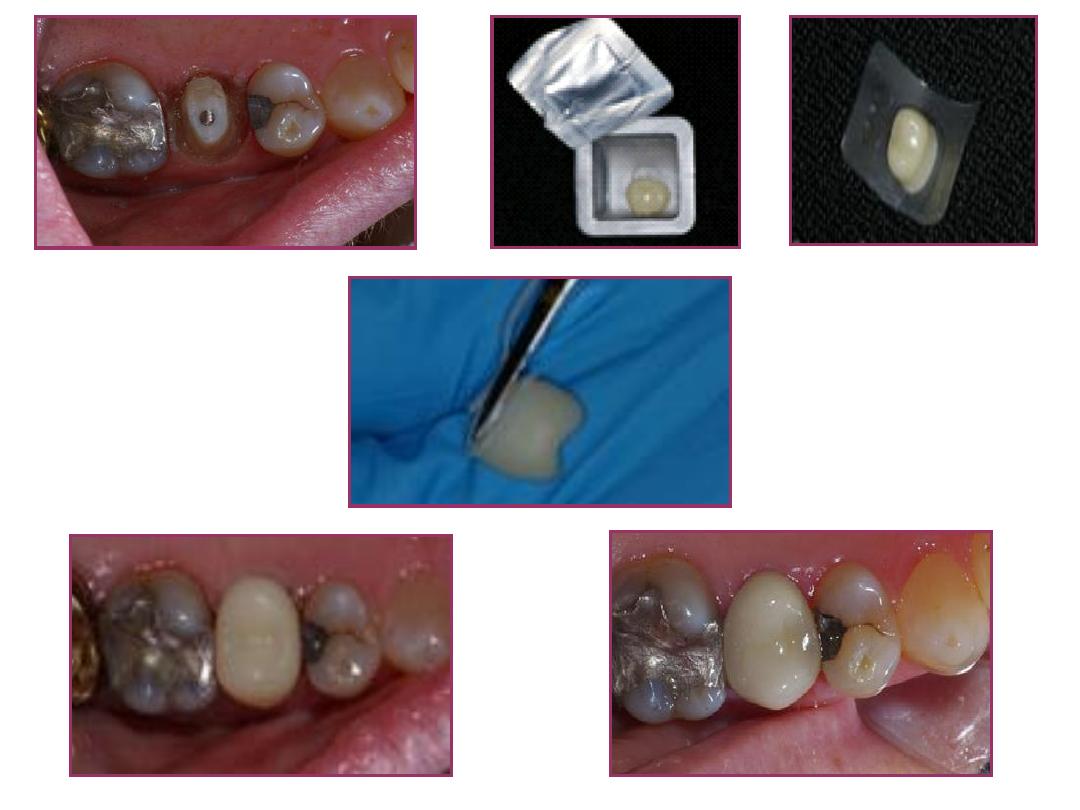
3. Laboratory-made temporary restorations.
A preoperative impression is made, and we prepare the
tooth on the cast, and temporary crown or bridge is done.
Relining by resin or composite material was done if the
restoration has poor fitness. This technique also known as
indirect direct technique.

It is often difficult to fabricate a temporary crown for a tooth
that has been prepared to receive a post crown because there is
so little tooth structure supragingivally that can not give support
to the temporary crown, so in such a case we need intracanal
retentive means to give retention to the temporary crown.
A piece of stainless steel wire could be used as an intracanal
retentive means. The wire should be adapted to the prepared
root canal and should extend coronally at least 4 mm. i.e., 4 mm
of the wire should extend supragingivally outside the canal prior
to the construction of the temporary crown. After that, a
temporary crown could be constructed and the stainless steel
wire will be part of the temporary crown.
Temporary restoration for a tooth prepared to
receive a post crown:

Zinc oxide-eugenol cement is the most commonly used cement
for temporary crowns and bridges. This cement promote healing
and allows easy removal of the temporary restoration.
Cementation of the temporary restoration:

