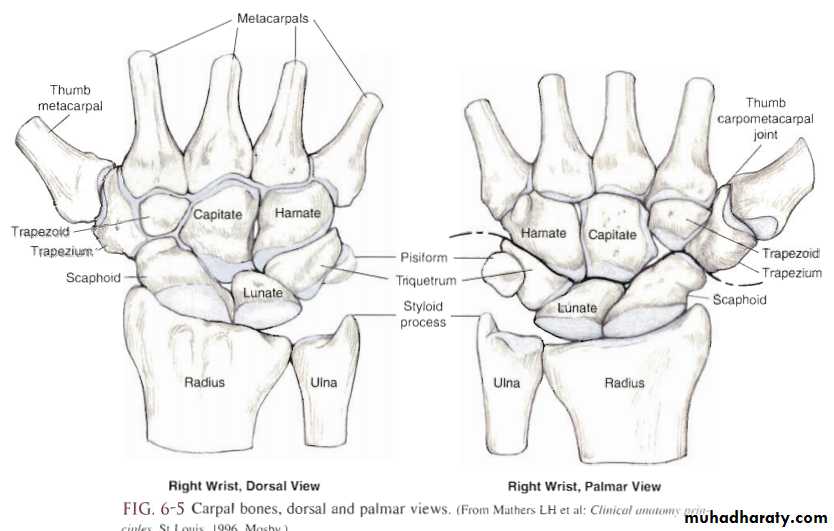
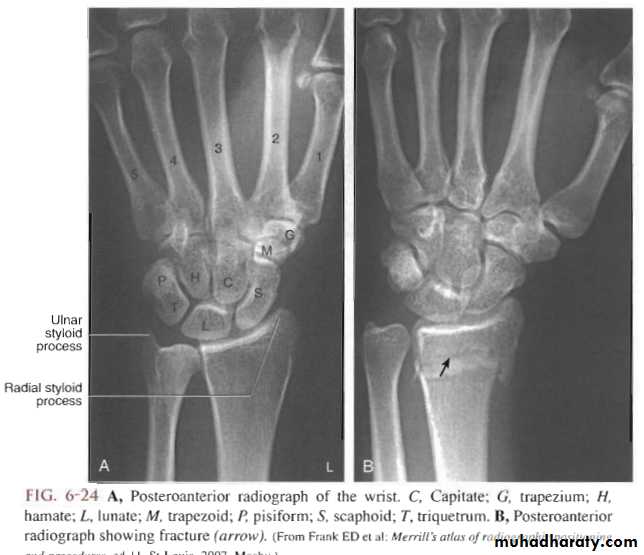
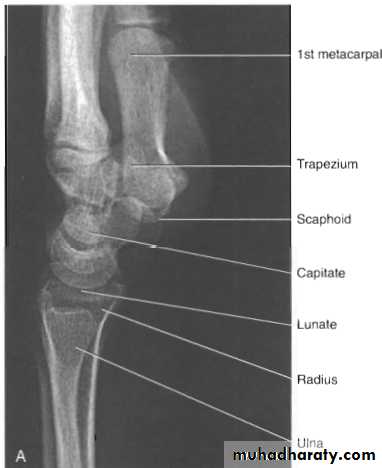
The wrist
symptoms
Pain:eg. Localized to radial side; tenosinovitis of the thumb tendons (De Quervain’s disease).
Localized to ulnar side; inferior radio-ulnar joint disorders.
Swelling:
Of joints; eg rheumatoid arthritis.
Of tendons; tenosynovitis.
Localized; eg ganglion.
Stiffness.
Deformity: trauma, nerve injury (eg wrist drop).Loss of function; decreased grip strength.
Signs
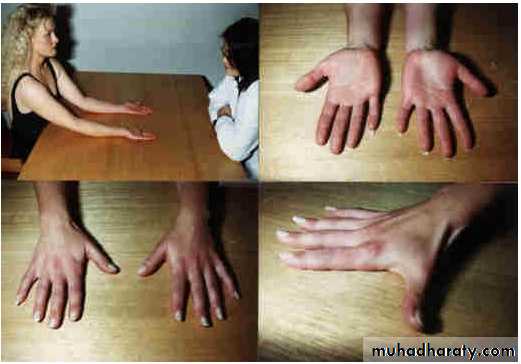
Look:
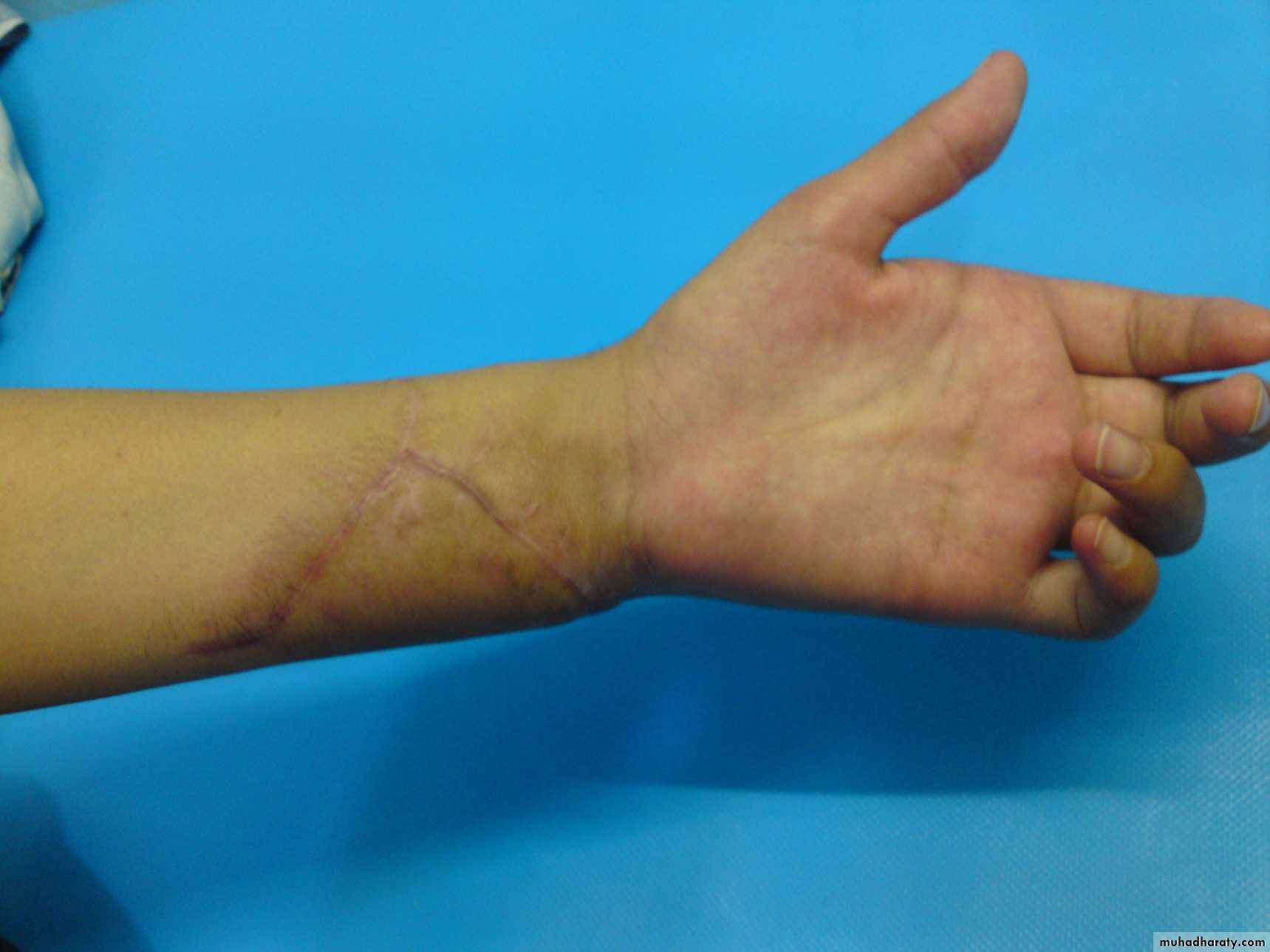
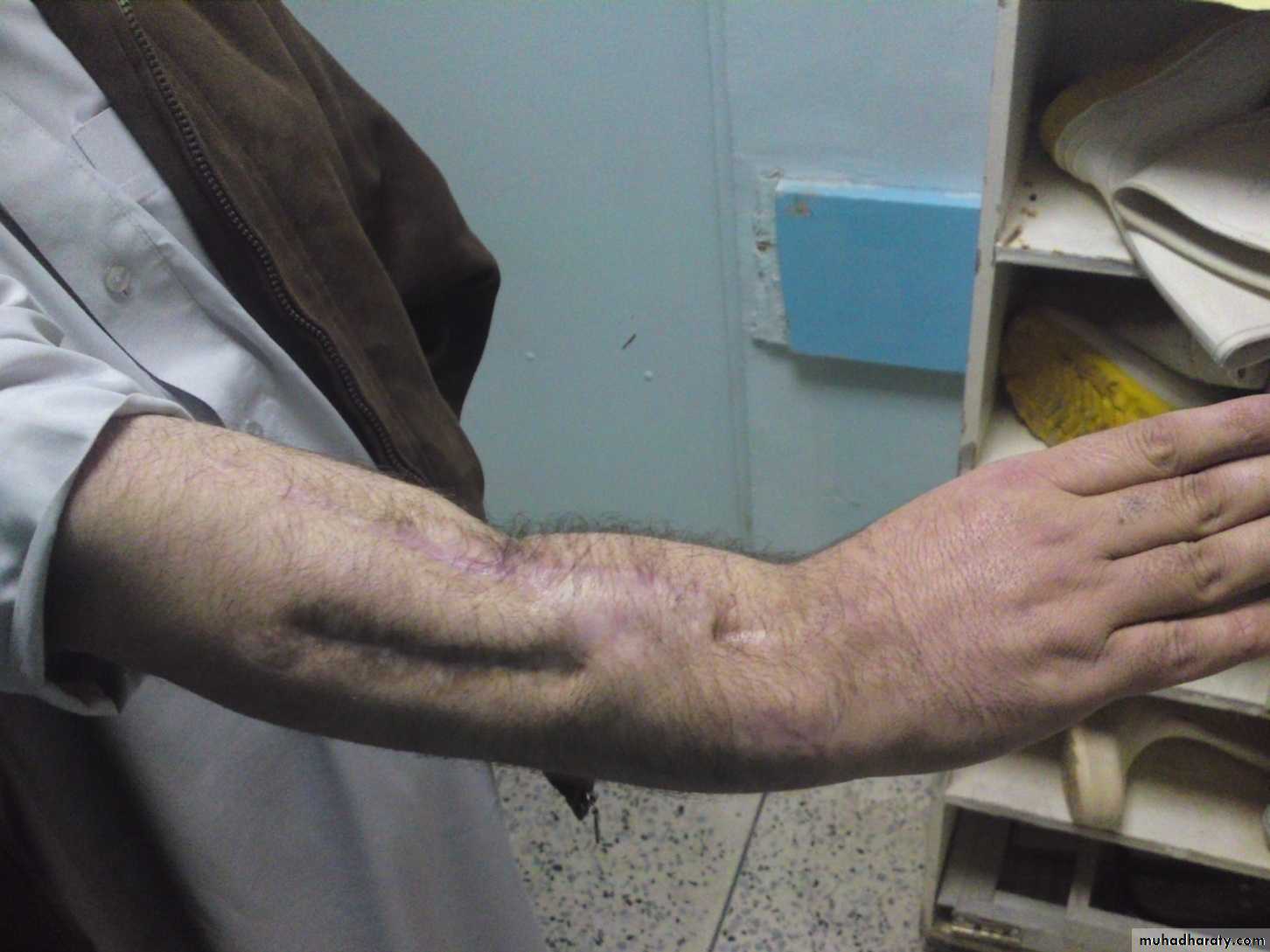
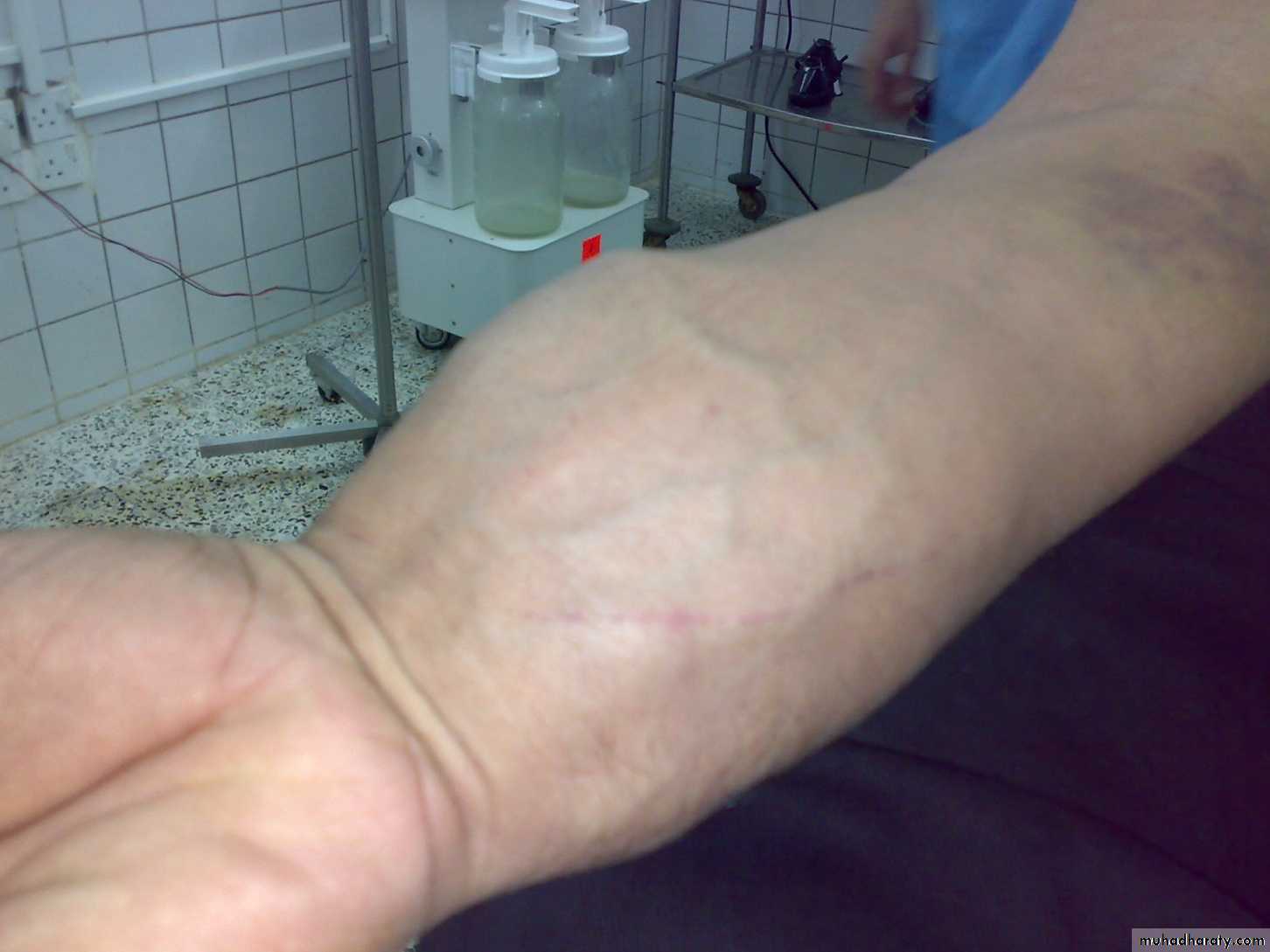
Skin; scars or sinuses.
Deformity, swelling.
Feel:
Warmth.
Tender points: tip of radial styloid in de Quervain’s disease.
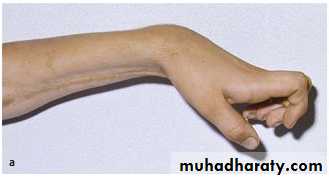
Claw hand of ulnar nerve injury
Volkman’s ischemic contracture
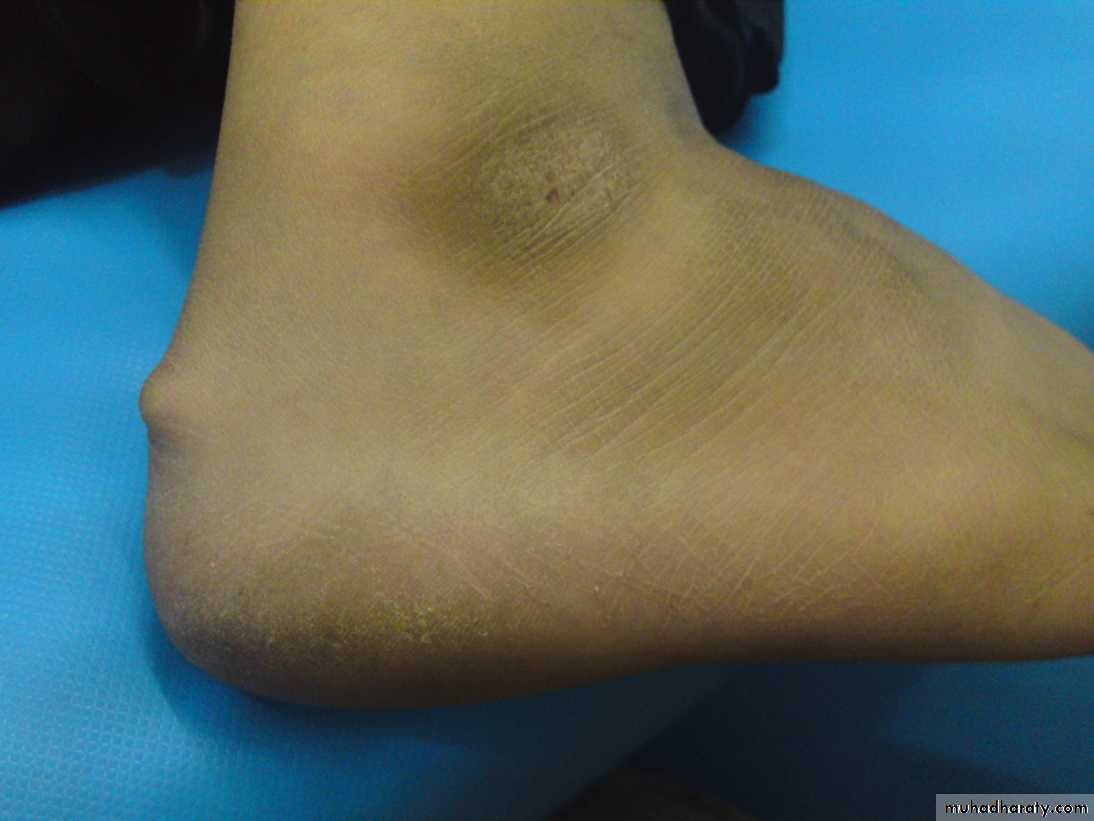
Swelling: tumor of the wrist
Wrist drop
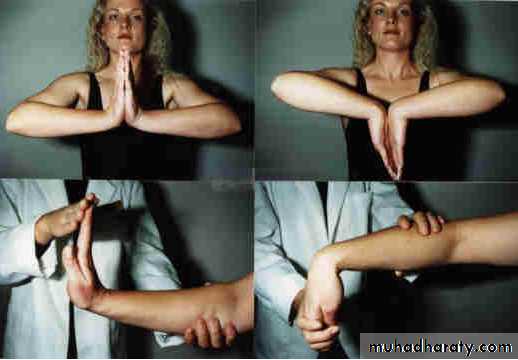
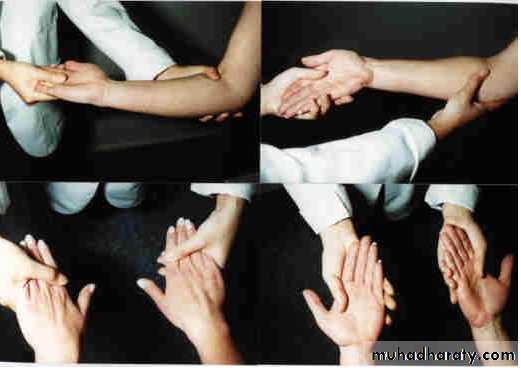
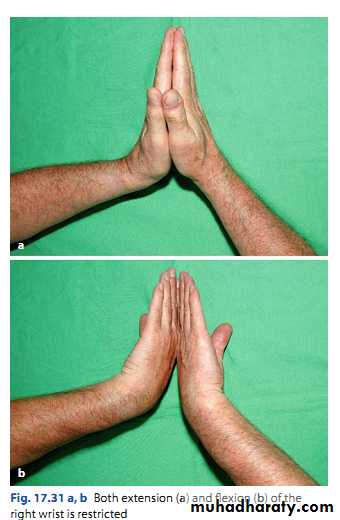
Move: look for limitation of ROM
Passive: dorsi- and plantarflexion; press wrists against each other.Radial and ulnar deviation.
Pronation and supination.
Active: decreased in tendon rupture, nerve injury, painful conditions.
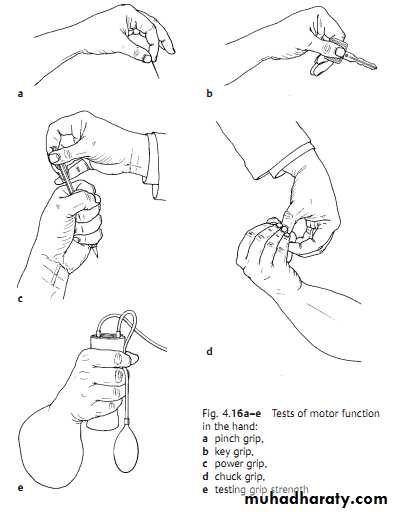
Power grip- squeeze examiner’s hand.
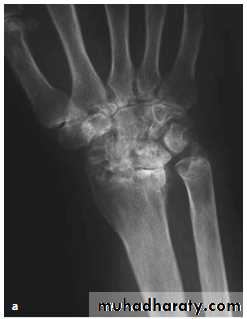
Radiological evaluation
Lateral radiograph
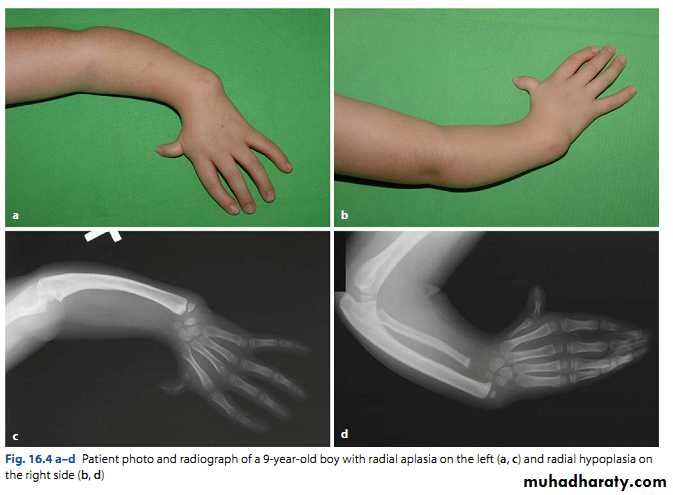
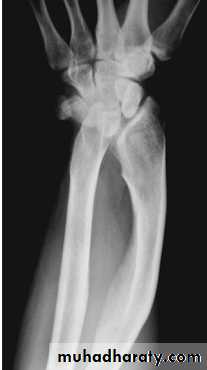
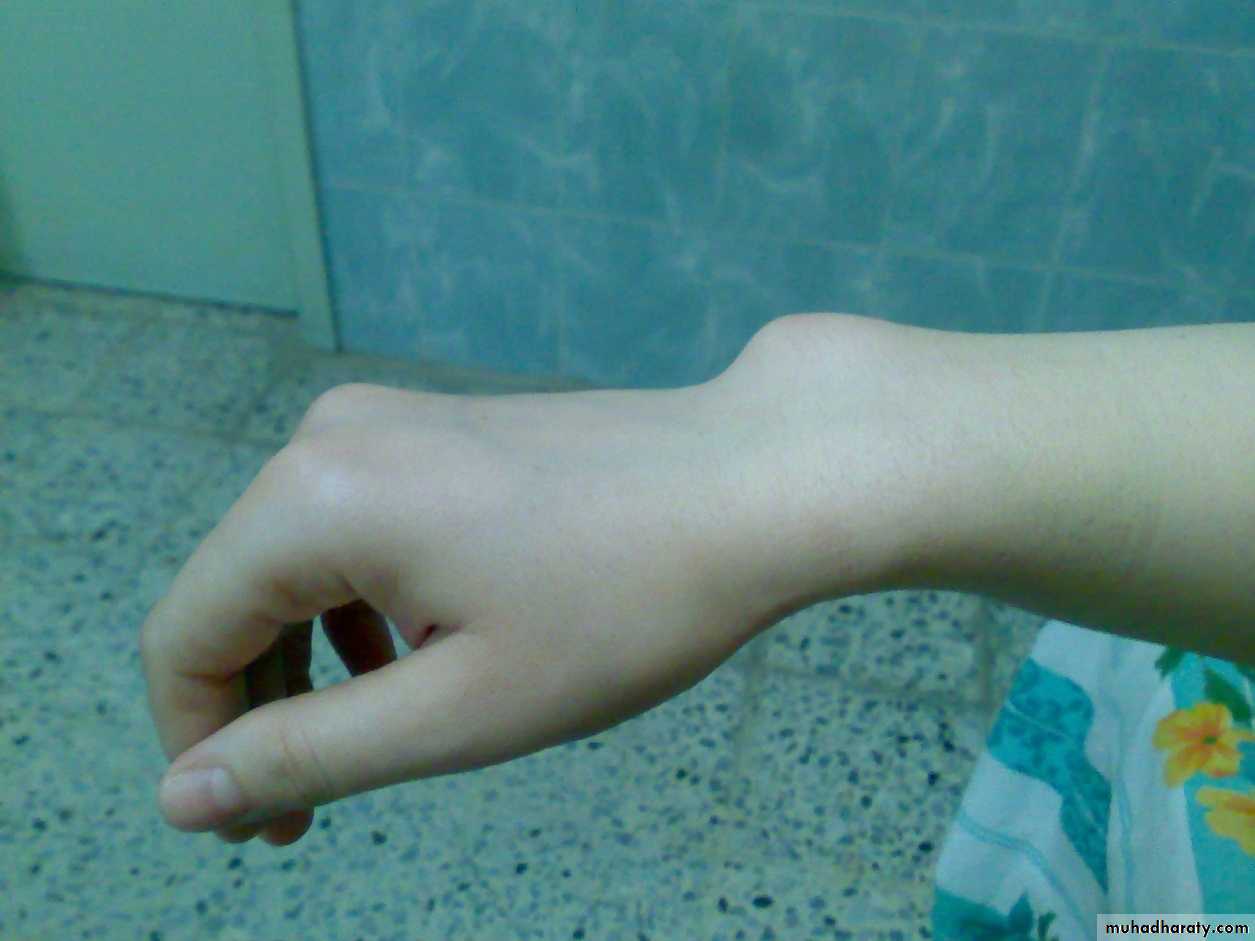
Radial club hand
Partial or complete absence of the radius with radial deviation of the hand.
May be associated with other congenital anomalies or blood dyscrasias (eg thrombocytopenia).
Treated by serial manipulation and casting then surgical correction.
Radial club hand
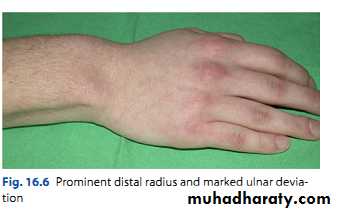
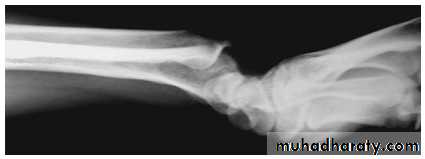
Madelung deformity
Forward curvature of the lower radius and backward subluxation of the lower ulna.Cause: congenital or post-traumatic.
If symptomatic treated by radial osteotomy.
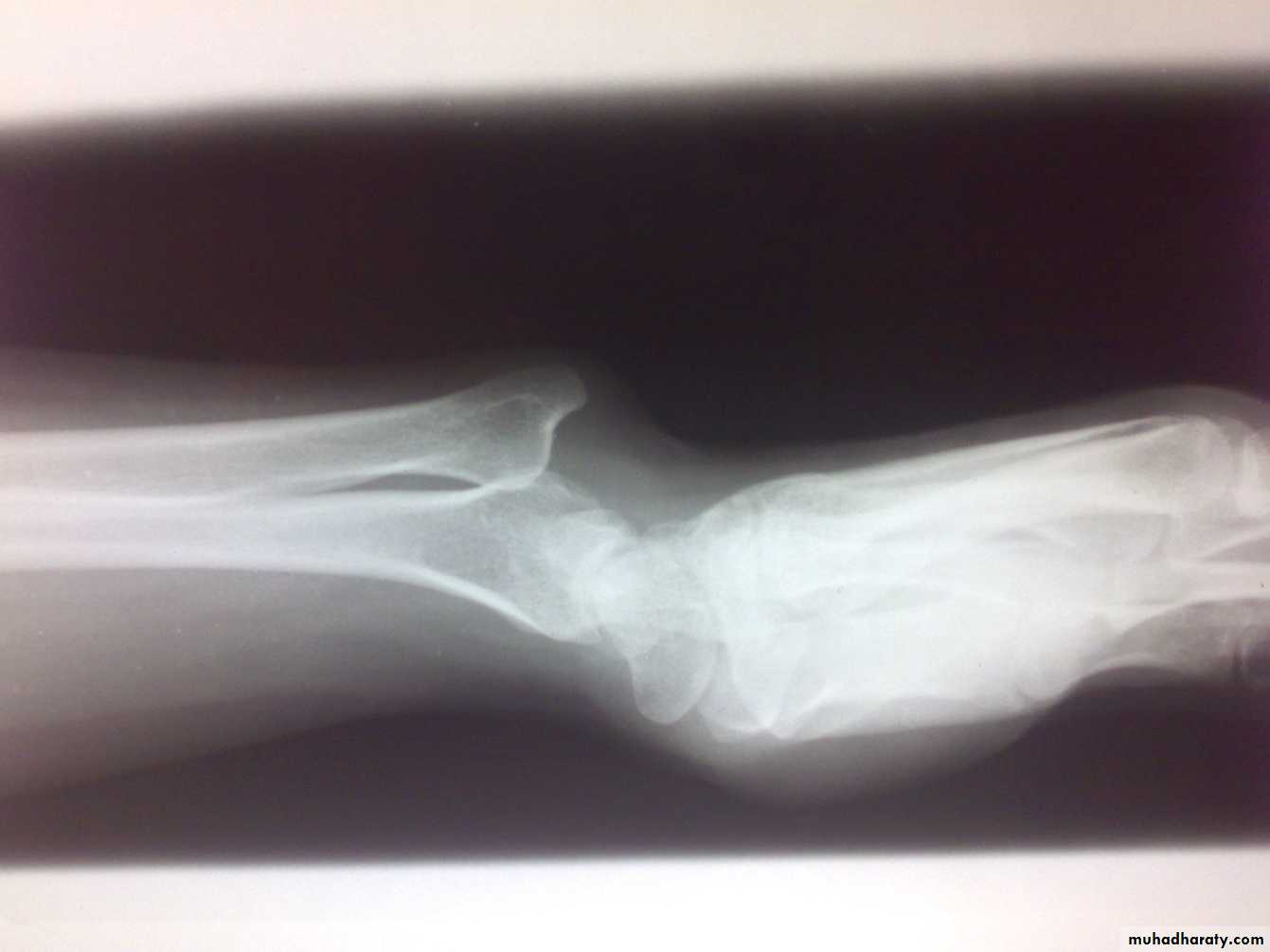
Instability of distal radioulnar joint
Post-traumatic; after fracture of lower radius (Galeazzi fracture dislocation).Associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Painful restriction of pronation and supination.
Backward prominence of the lower ulna.
Piano key sign; balloting the lower ulna.
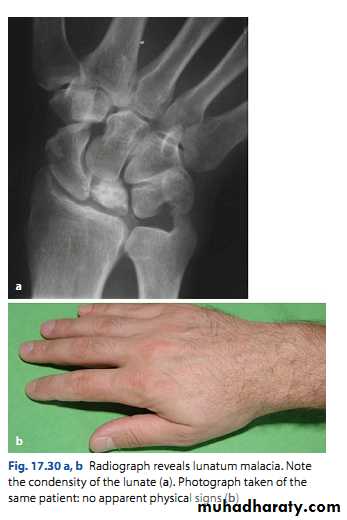
Kienbӧck’s disease
Ischemic necrosis of the lunate bone.Associated with excessive loading of the lunate.
Clinical features:
Pain and stiffness of the wrist.
Tenderness over the lunate bone.
Limitation of movement.
Kienbӧck’s disease
4 stages:• Ischemia without changes, normal x-ray, MRI changes.
• Trabecular necrosis, new bone formation, x-ray show increased density.
• Bone collapse; x-ray show small irregular lunate bone.
• Secondary OA of the wrist.
Kienbӧck’s disease
Early: splintage for 6-12 weaks.Late: surgical treatment eg, wrist arthrodesis.
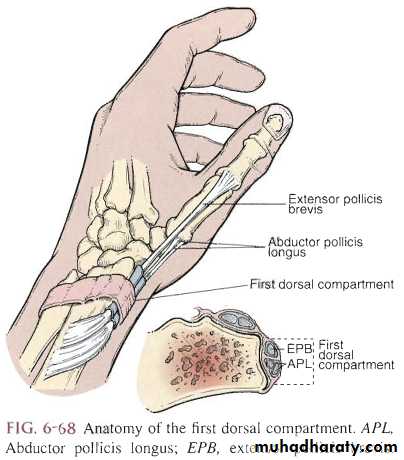
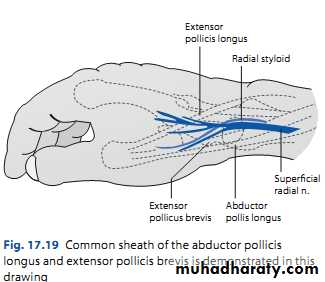
De Quervain’s disease
Thickening of synovial sheath around extensor polices brevis and abductor polices longus in the first extensor compartment due to overuse.DE Quervain’s disease
De Quervain’s disease
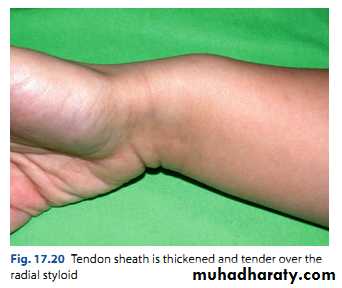
Clinical features:Middle aged, women > men.
Pain on radial side of the wrist.
Tenderness over the radial styloid.
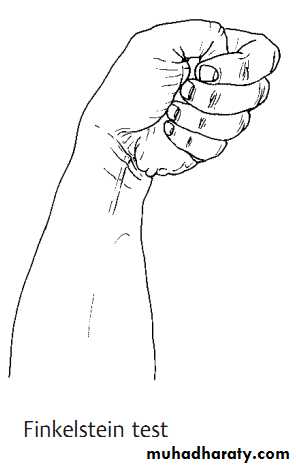
Fenkelstein’s test; pain over the radial styloid induced by flexing the thumb in the palm and abduction of the wrist.
Tratment:
Splintage and corticosteroid injection locally.
Surgical slitting of the thickened synovium.
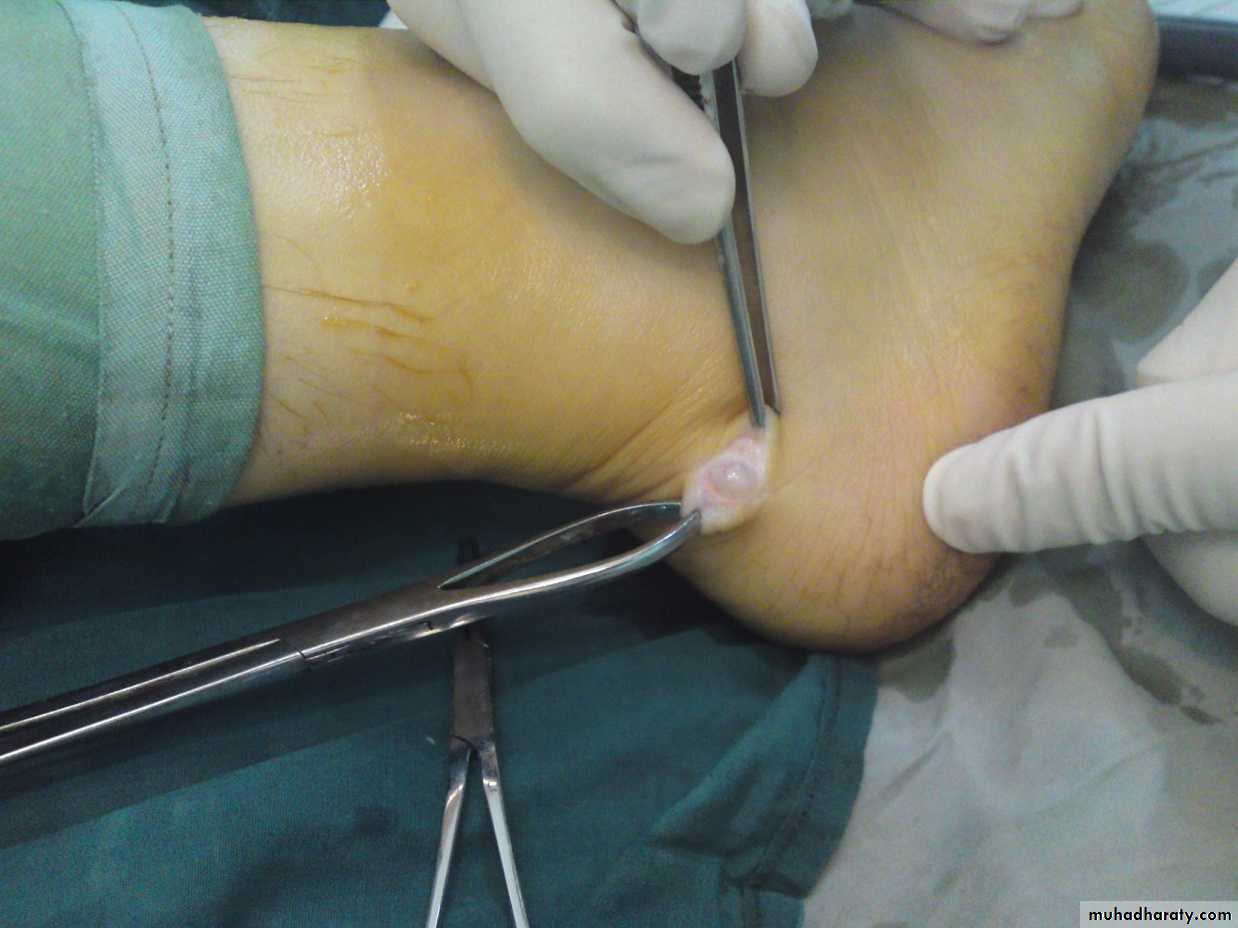
Swellings around the wrist:Ganglion
Most common swelling around the wrist.
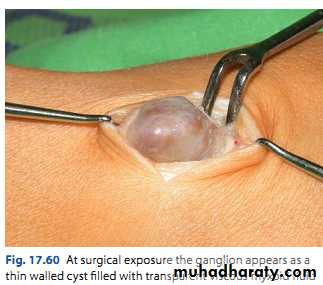
Leakage of synovium from joint or tendon sheath.
Cyst containing glairy viscous fluid.
Usually on dorsum of the scapholunate ligament.
Ganglion
Ganglion
Clinical features:Swelling usually on the dorsum of the wrist.
Does not move with tendons.
Sometimes alongside radial artery.
Treatment:
Usually unnecessary.
If troublesome; surgical excision but recurrence is possible.
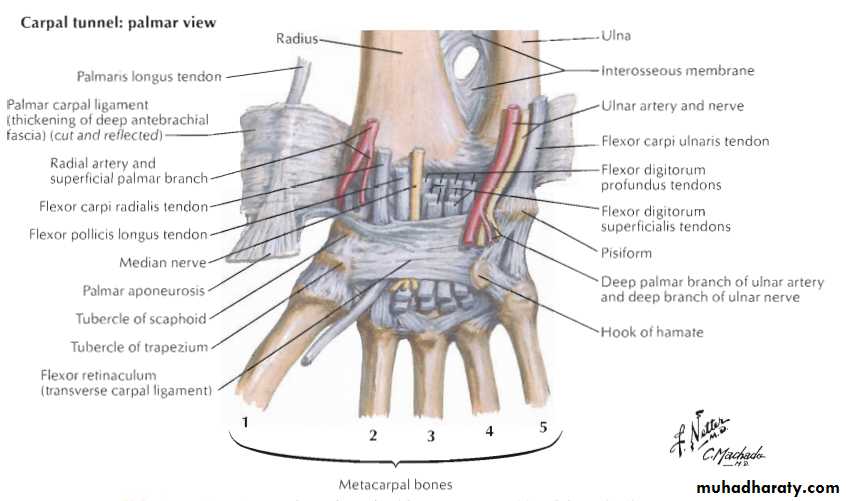
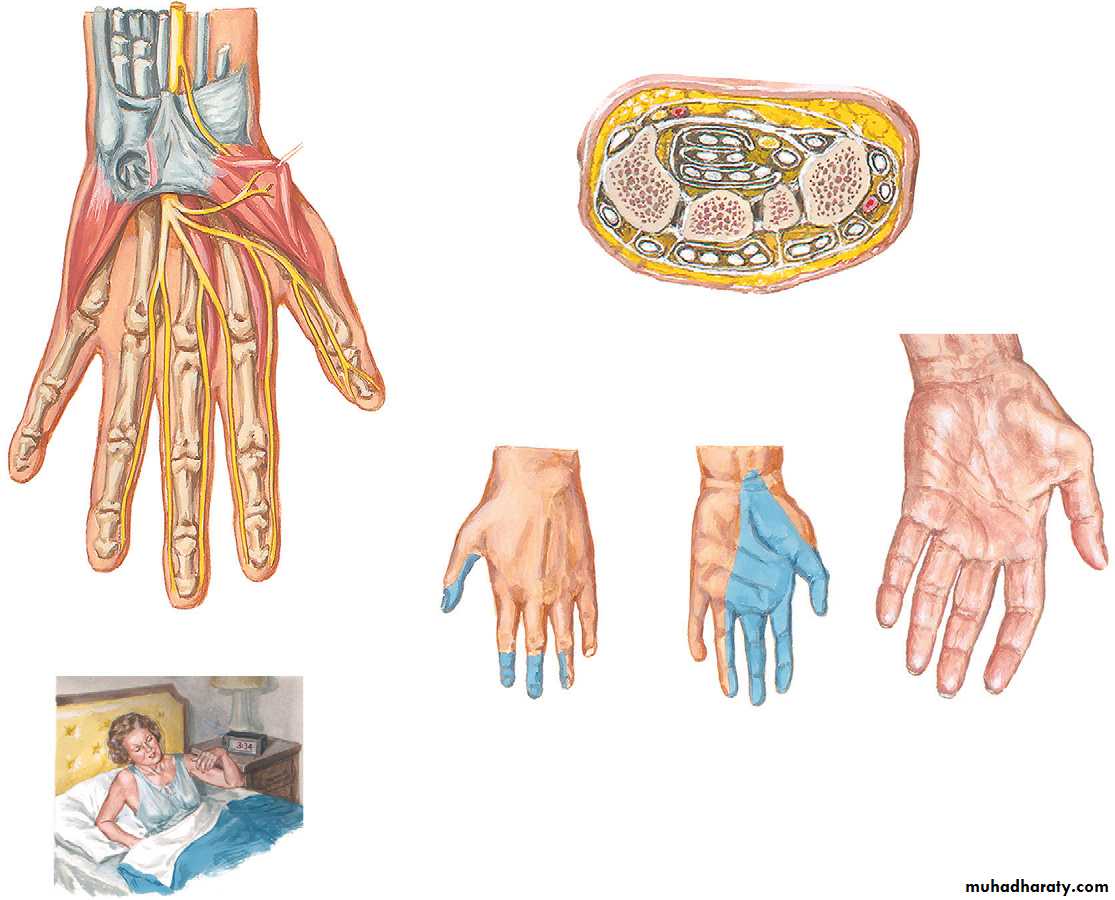
Carpal tunnel syndrome
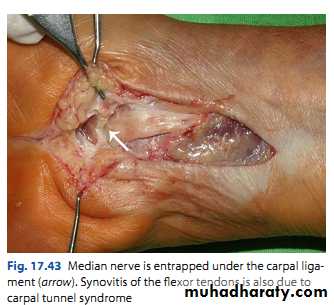
Entrapment neuropathy of the median nerve under the transverse carpal ligament.
Compression and ischemia of the nerve.
Cause;
Idiopathic in most of cases.
Associated with: pregnancy, menopause, rheumatoid arthritis, myxedema, chronic renal failure, gout…
Carpal tunnel syndrome
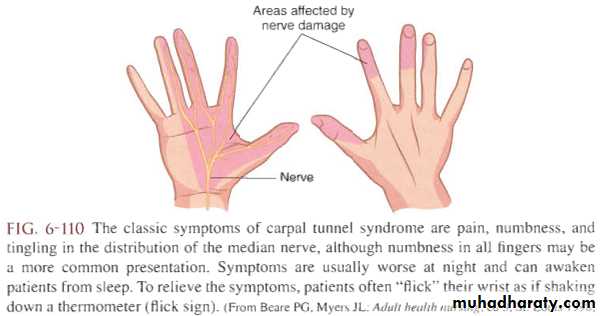
Clinical features:Age 40-50 years.
Female: male ratio 8:1
Pain and paresthesia in 3 and ½ radial fingers.
Burning, tingling and numpness.
Wake up the patient at nigtht.
Releived by shaking.
Weakness and clumpsiness in doing fine movements (eg fastening bottoms).
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome
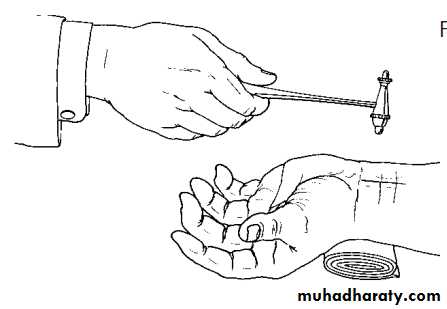
Examination:Tinel sign: symptoms reproduced by tapping over the median nerve.
Phalen’s test: holding the wrist fully flexed for a minute.
Wasting of thenar muscles.
Weakness in thumb abduction.
Paresthesia in median nerve territory.
Tinnel sign
Phalen test
Wasting of thenar muscles
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Electrodiagnosis for difficult cases.Cervical spondylosis and radiculopathy is a differential diagnosis.
Treatment
Light splint at night relieve night pain.Corticosteroid injection in the carpal tunnel.
Surgical division of the transverse carpal ligament.