DIAGNOSIS Of CARIES
Dr. Huda Y. K
INTRODUCTION• Diagnosis It is the determination of the nature of the disease, injury or other defect by examination, test and investigation.
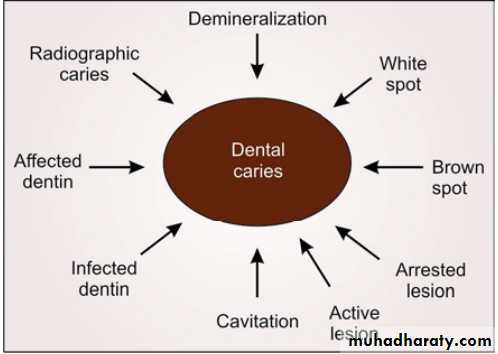
• As we know dental caries is an infectious disease, but there are many terms which describe the signs of the disease, for example, cavitation, white or brown spot, affected or infected dentin, etc
INTRODUCTION
In order to conserve tooth structure and perform minimally invasive dentistry, carious lesions must be detected (DIAGNOSED) at the earliest possible time.By doing so, caries progress can be arrested, thus avoiding a more invasive operative intervention
INTRODUCTION
The accuracy of any diagnostic test or evaluation is typically measured according to its sensitivity and specificity.
• Sensitivity Vs Specificity
• Sensitivity: It is defined by the probability of the test giving a positive finding when disease is present• True Positive……False Positive
• Specificity: It is the probability of a negative finding when disease is absent.
•
• The application of multiple diagnostic tests to the individual patient increases the overall efficacy of caries diagnosis.
True Negative……False Negative
Visual-Tactile Method of Diagnosis
Mirror
Explorer
Light
Conventional Methods - Tactile examination
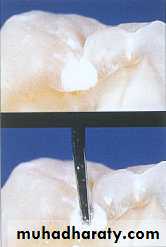
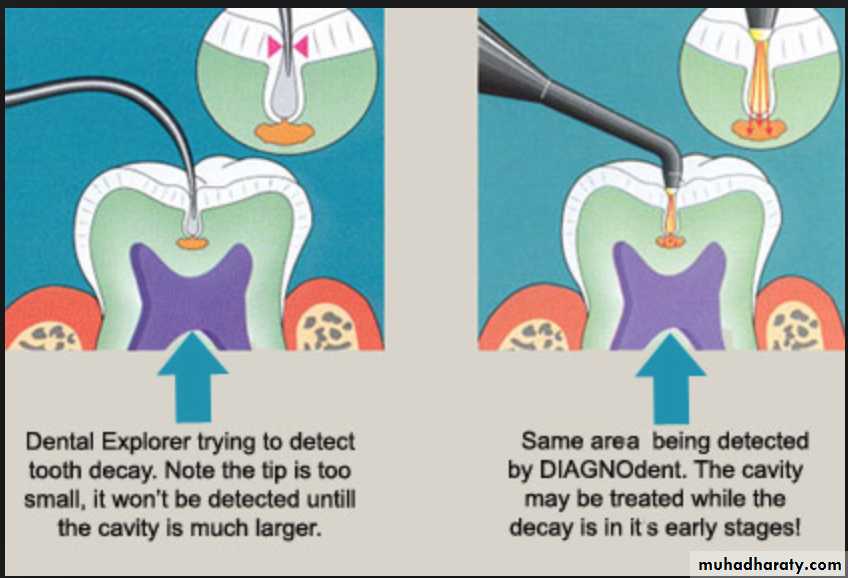
In this method explorer has been used for the tactile examination of the tooth for a long time.The explorer is used to detect softened tooth structure.
Since demineralization is a process that does not always involve sufficient softening of the enamel to be detectable by an explorer.
When an explorer sticks, it’s usually a good indication that there is decay beneath; however, when it does not stick, it does not necessarily mean that decay is not present
Conventional Methods - Tactile examination
Sturdevant said cavitation at the base of a pit or fissure can be detected tactilely as softness, but mechanical binding of an explorer in the pits or fissures may be due to noncarious causes, like shape of the fissure, sharpness of the explorer, or the force of applicationUse of explorer is not advocated because;
DisadvantagesSharp edge of explorer may fracture the demineralized enamel, if left alone, such lesion could have remineralized and reverted back to normal.
Use of explorer is not advocated because;
Interproximal caries account for more than 40 percent of caries in adults. The dental explorer is not an effective tool for interproximal caries detection.For pit and fissure caries, the explorer is incapable of determining the presence of most occlusal caries
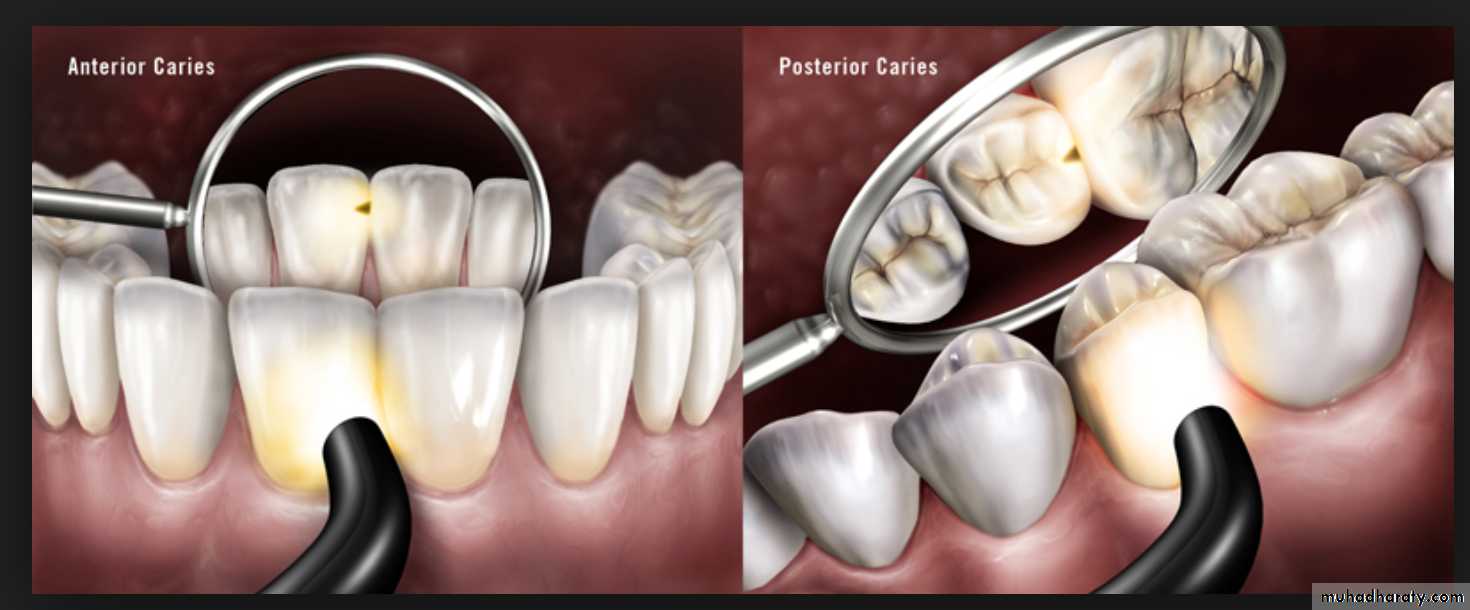
Conventional Methods –Visual examination
Use of visual examination only, is known as the European method, while use of sharp or blunt probe in visual tactile system is popularly known as the American system for diagnosis of dental caries.Visual examination for diagnosing dental caries is a very popular method. It is based on the criteria such as:
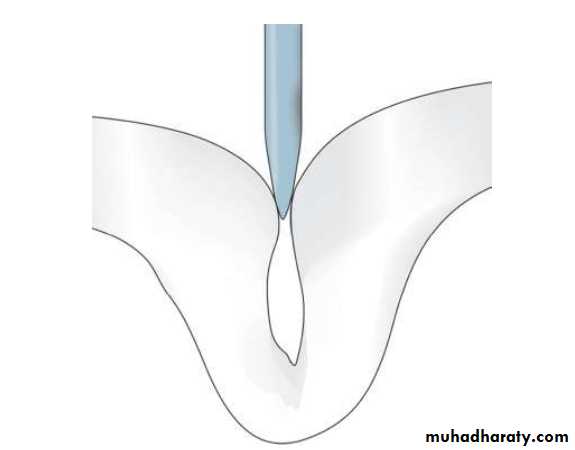
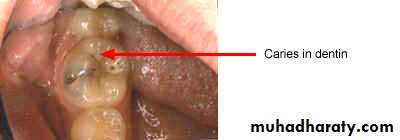
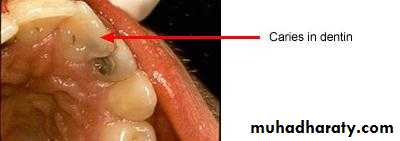
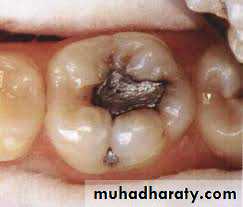
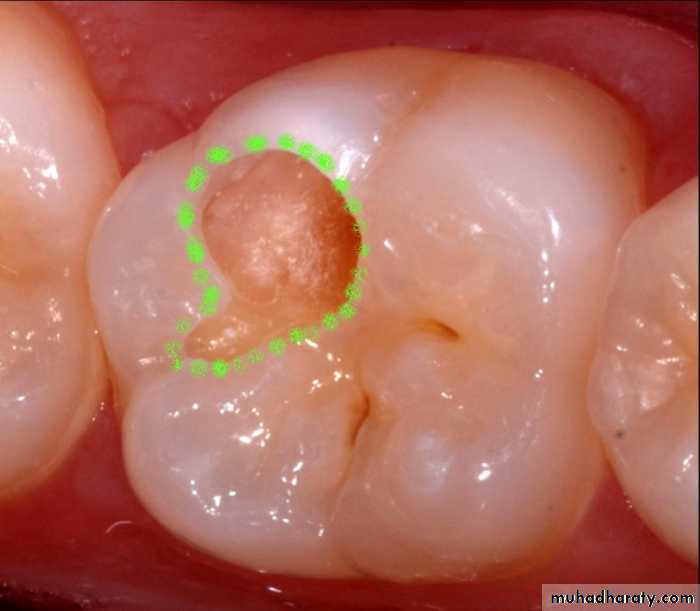
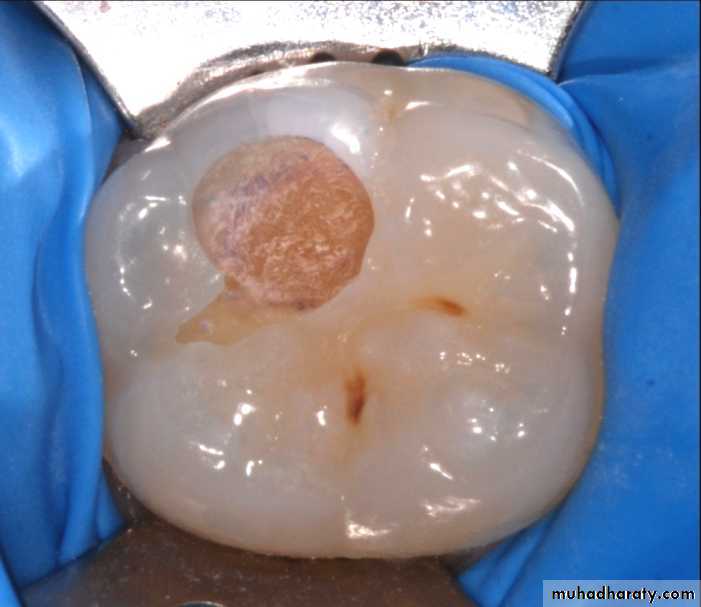
Cavitation, surface roughness, opacification and discoloration of clean and dried teeth under adequate light source.
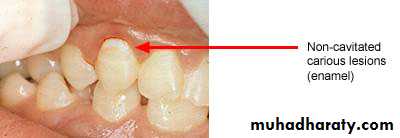
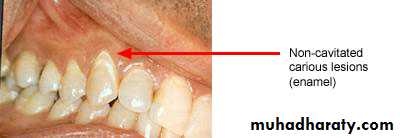
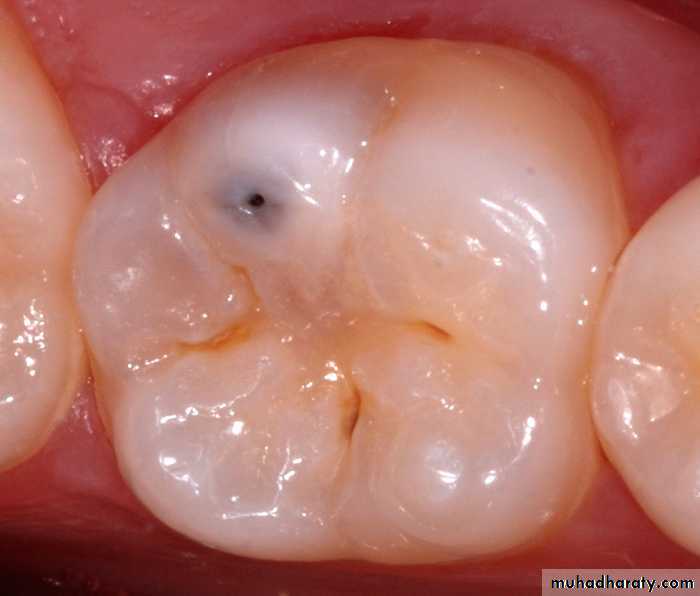
Non-cavitated carious lesion
ENAMELDENTIN
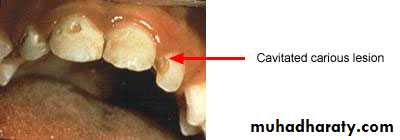
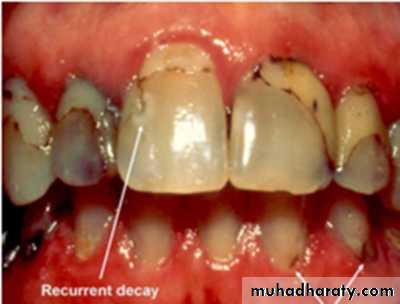
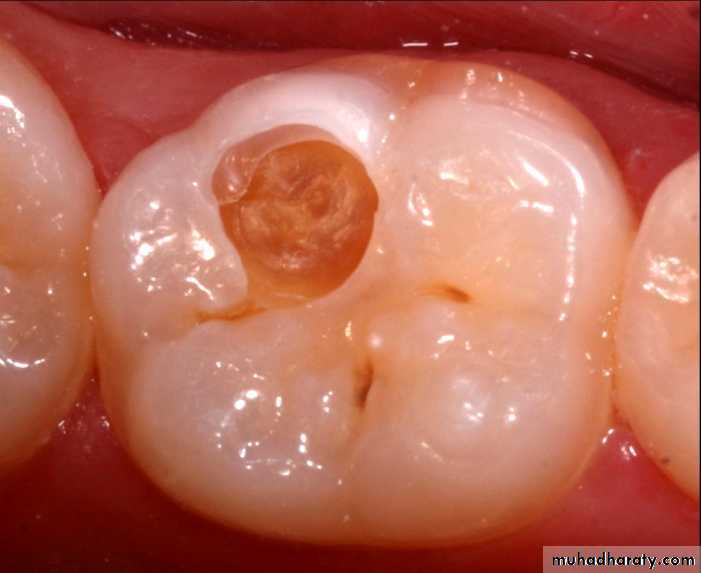
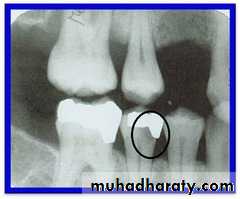
Cavitated Lesions
Where there is visual breakdown of a tooth surface, it is classified as cavitated carious lesion. An active cavity on a smooth surface has soft walls or floors as shown below:Secondary caries
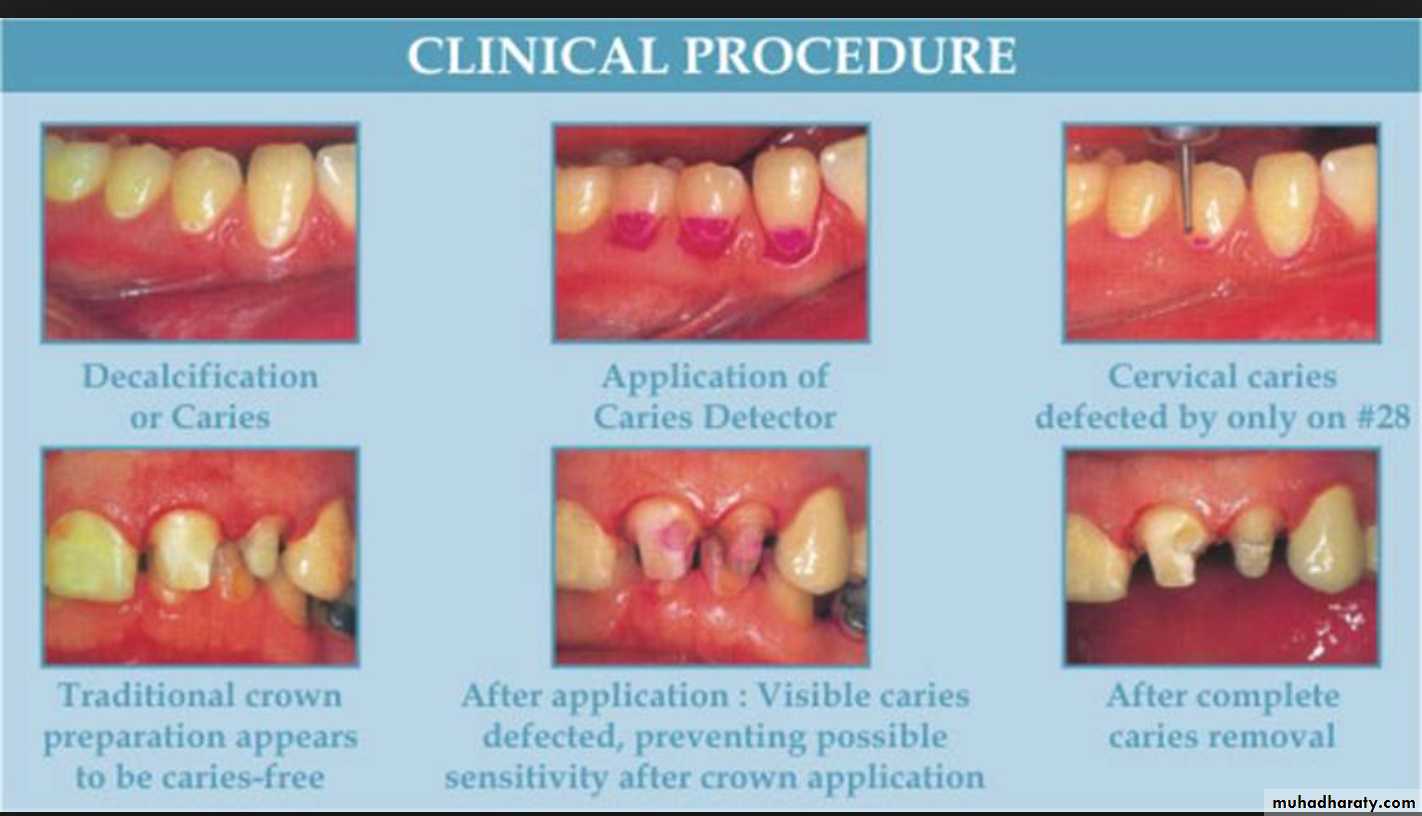
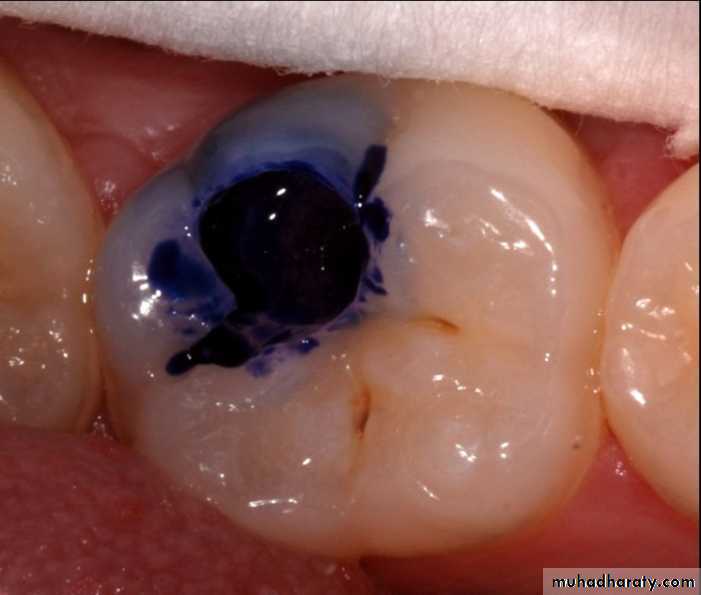
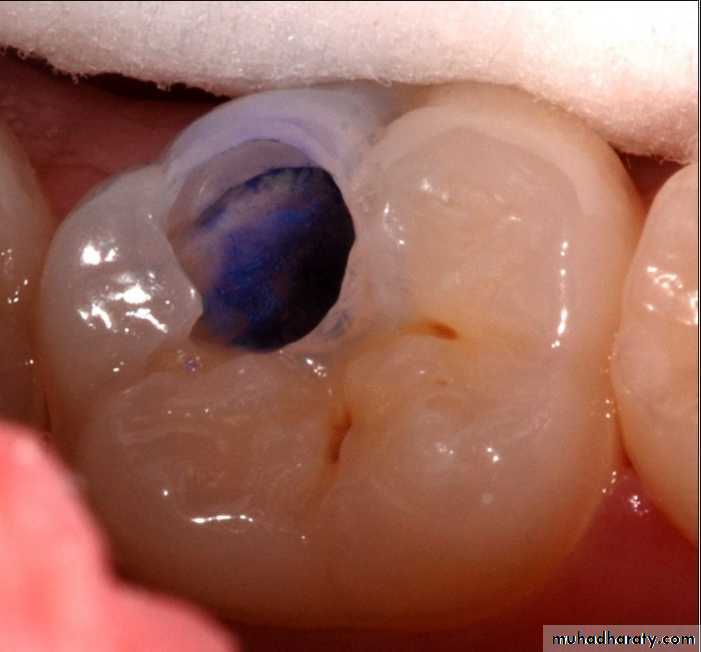
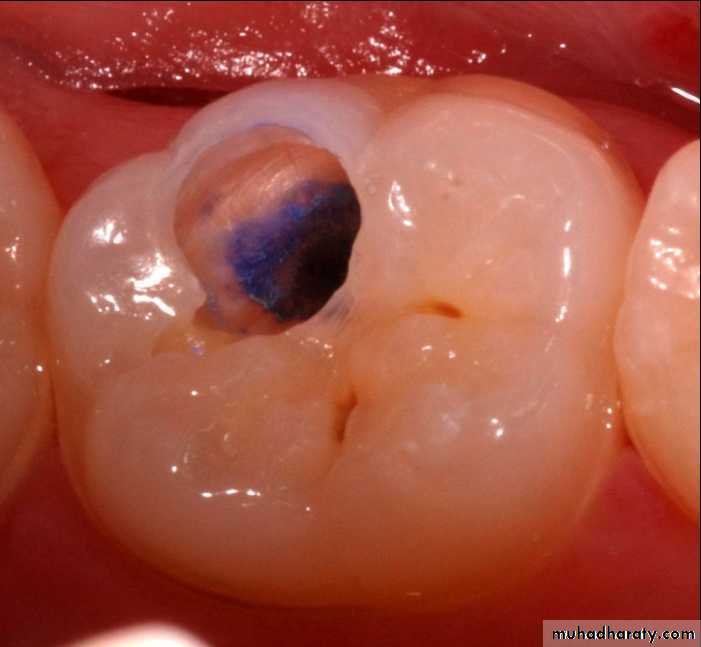
Advanced visual-Dye penetration method
In carious dentin, two layers of decalcification can be identified:One layer which is soft and cannot be remineralized
A second layer, which is hard with intermediate calcification and can be remineralized.
It is now clearly established that these dyes do not stain bacteria but instead stain the organic matrix of less mineralized dentin.
This make them less specific because dyes do not stain bacteria nor delineate (trace an outline) the bacterial front but stain collagen associated with less mineralized organic matrix.
Dye penetration method
Use of basic fuschin in propylene glycol for the diagnosis and treatment of carious dentin has been given by Fusayama, 1980. The dye was found to be carcinogenic.To overcome this disadvantage, acid red or methylene blue were used, but methylene blue is slightly toxic.
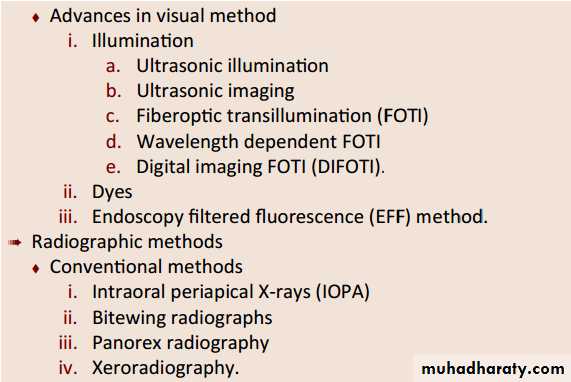
Advanced visual-Fiberoptic transillumination (FOTI)
Transillumination takes advantage of the opacity of a demineralized tooth structure over more translucent healthy structures.The decalcified area will not let light pass through as much as it does in a healthy area, generating a shadow corresponding to decay.
Fiberoptic transillumination (FOTI)
Illumination is delivered by means of fiberoptics from the light source to the tooth surface using a fiberoptic handpiece• Electrical Resistance Measurement
Sound tooth enamel is a good electrical insulator due to its high inorganic content.Caries results in increased porosity. Saliva fills the pores and forms conductive path-ways for electrical current.
• The electrical conductivity is hence directly proportional to the amount of demineralization that has occurred. Electrical resistance refers to measuring the electrical conductivity through these pores
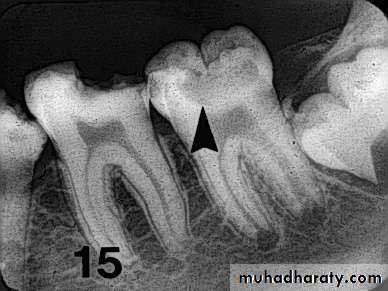
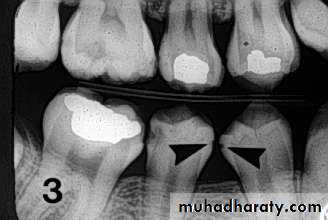
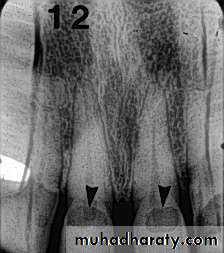
• Radiography
Carious lesions are detectable radiographically when there has been enough demineralization to allow it to be differentiate from normalThey are valuable in detecting proximal caries which may go undetected during clinical examination.
On average they have around 50% to 70% sensitivity in detecting carious lesions.
40% demineralization is required for definitive decision on caries
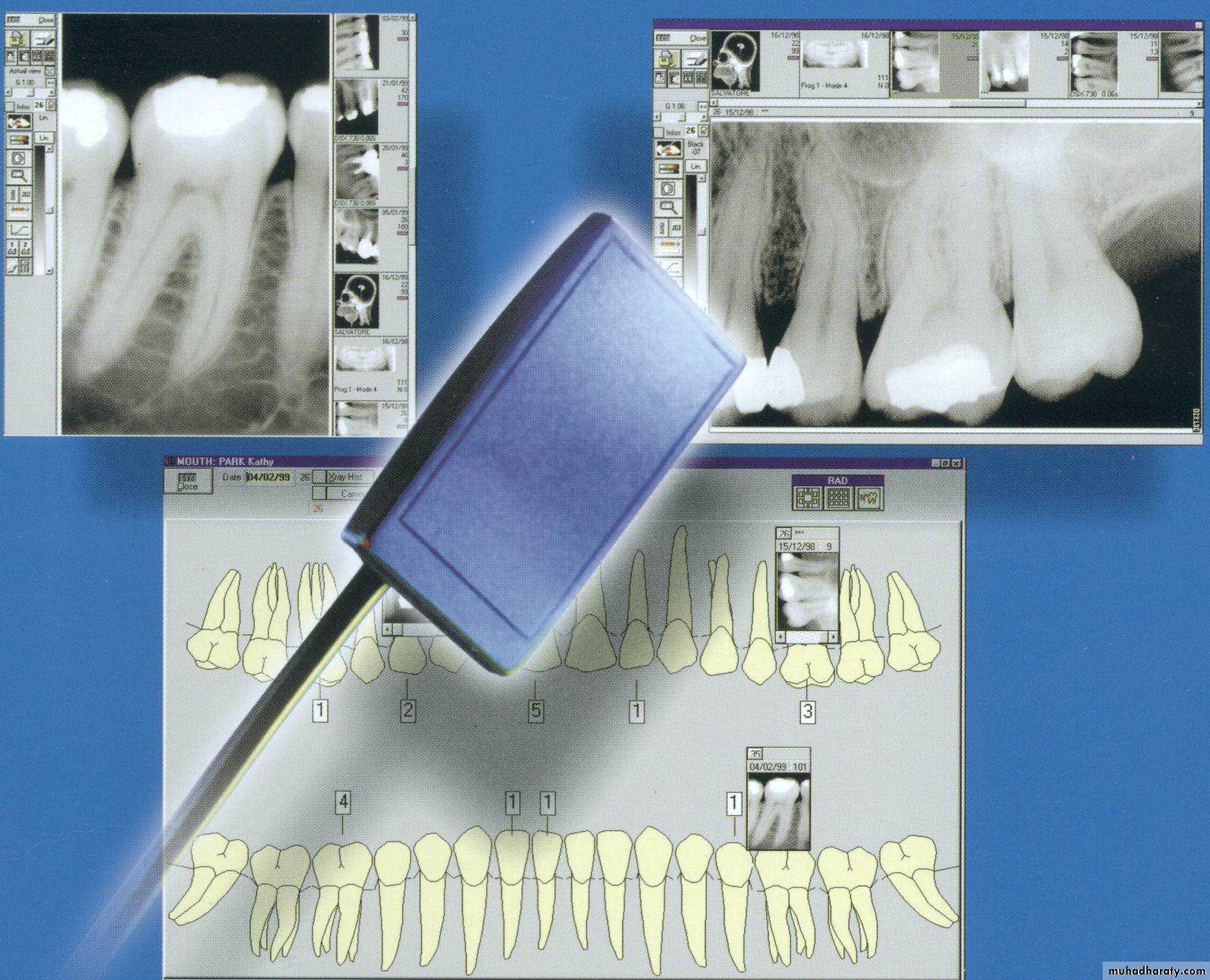
Advanced Radio.-Digital radiography
-Image recorded with non film receptor
The film replaced by flat electronic pad or sensor
-Images sent to computer displayed on monitor screen
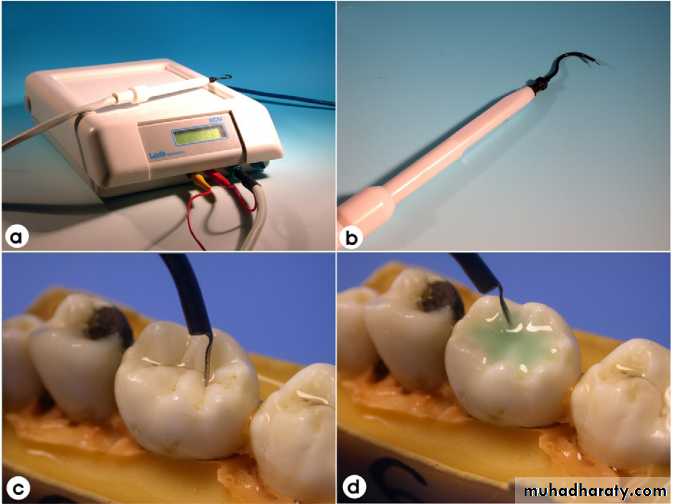
Laser fluorescence—DIAGNODent
Based on principle of fluorescence.It uses a diode laser light source and a fiber optic cable that transmits light to a hand held probe. Light is absorbed induces infrared fluorescence by organic and inorganic materials. Emitted fluorescence is collected at probe tip, processed and presented on display as an integer between 0 and 99
Laser fluorescence—DIAGNODent
The numeric readout on the device (00-99) indicates the amount of fluorescence.Place the tip on the area to be evaluated. Use a rocking motion with the tip. Note and record the peak value.