

The dental pulp is that loose
delicate connective tissue
occupying the cavity lying in the
center of dentin.
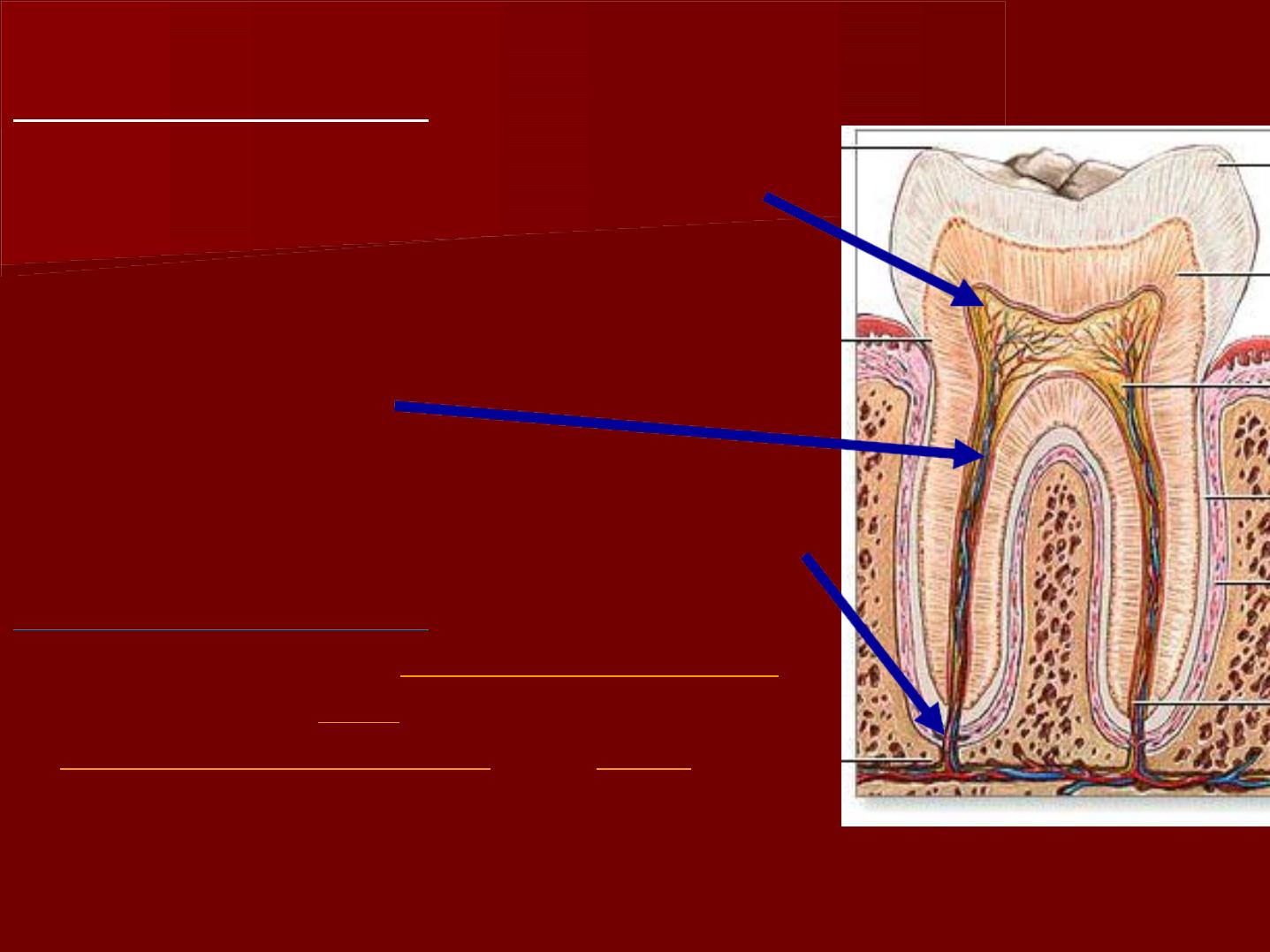
Morphlogy
*The coronal pulp
: it is present in
the pulp chamber.
*The radicular pulp:
it is that part
of the pulp extending from the
cervical region of the crown to the
root apex.
*Apical foramen:
The pulp organs
are continuous with the periapical
tissue through the apical foramen.
The average size
of the apical
foramen of the
maxillary teeth
in
the adult is
0.4
mm, while in the
mandibular teeth
it is
0.3
mm in
diameter.

Accessory canals:
They are commonly seen to
extend from the radicular
pulp laterally through the
root dentin to the
periodontal ligament.
They are
numerous
in the
apical third of the root.
A
A
c
c
c
c
e
e
s
s
s
s
o
o
r
r
y
y
c
c
a
a
n
n
a
a
l
l
s
s
1- it occurs in areas, where the developing root
encounters a
large blood vessel
, where
dentin will be formed around it, then making
the lateral canal .
2-
Early degeneration
of the epithelial root
sheath of Hertwig before the differentiation of
the odontoblasts.
3-Lack of complete union of the
epithelial
diaphragm
at the floor of the pulp chamber.
M
M
e
e
c
c
h
h
a
a
n
n
i
i
s
s
m
m
o
o
f
f
a
a
c
c
c
c
e
e
s
s
s
s
o
o
r
r
y
y
c
c
a
a
n
n
a
a
l
l
s
s
f
f
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
:
:
The dental pulp is formed of specialize loose
connective tissue:
cells
fibers
intercellular substances
blood vessels, nerves &
lymphatics.
H
H
i
i
s
s
t
t
o
o
l
l
o
o
g
g
i
i
c
c
a
a
l
l
s
s
t
t
r
r
u
u
c
c
t
t
u
u
r
r
e
e
o
o
f
f
t
t
h
h
e
e
p
p
u
u
l
l
p
p
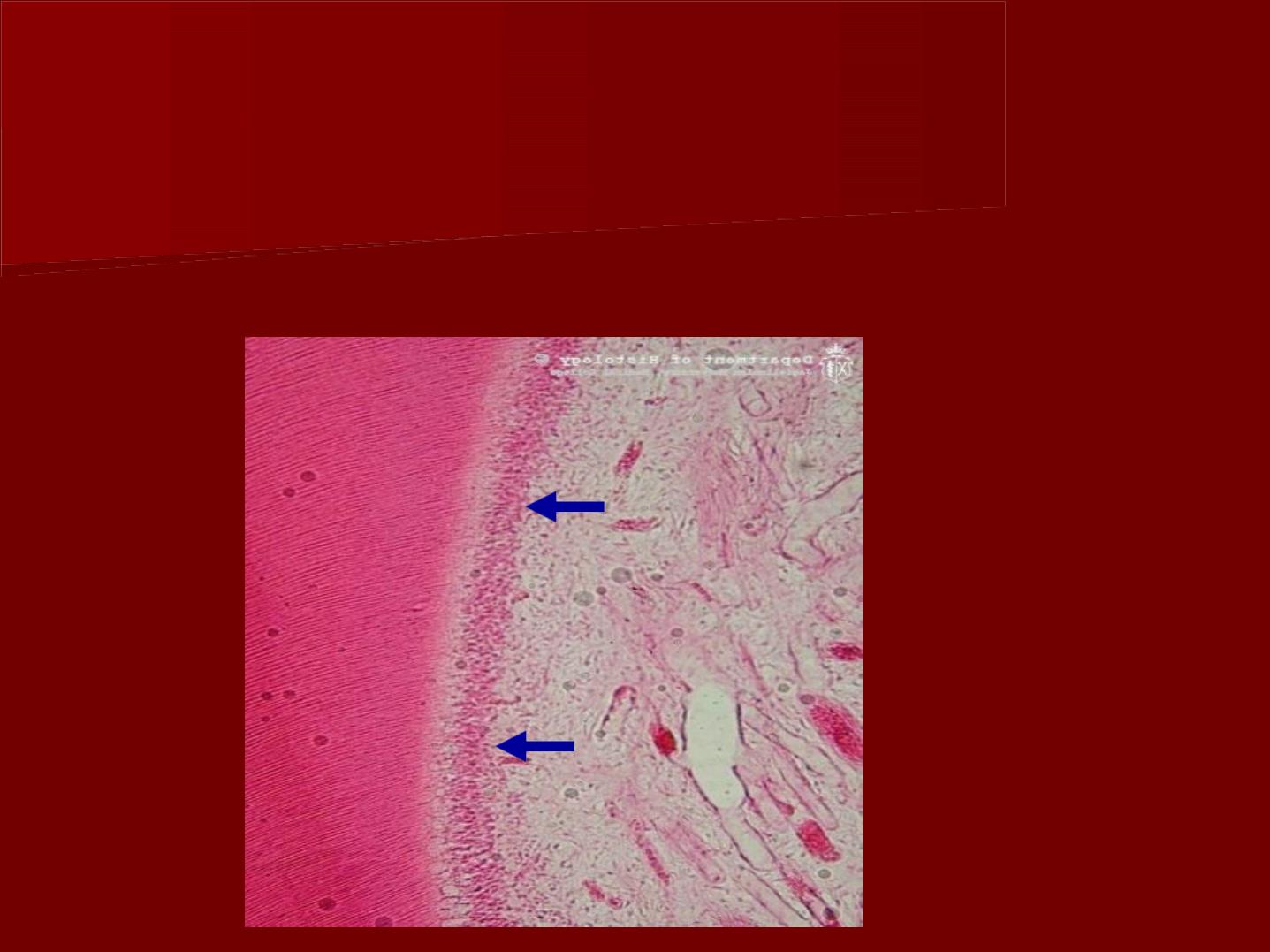
odontogenic zone:
a- odontoblasts:
Location: Adjacent to the predentin with the cell bodies in the
pulp and cell processes in the dentinal tubules.

B- cell free zone:
It is present Immediately beneath the
odontoblastic layer .
The cell free zone is the area of mobilization
and replacement of odontoblasts,
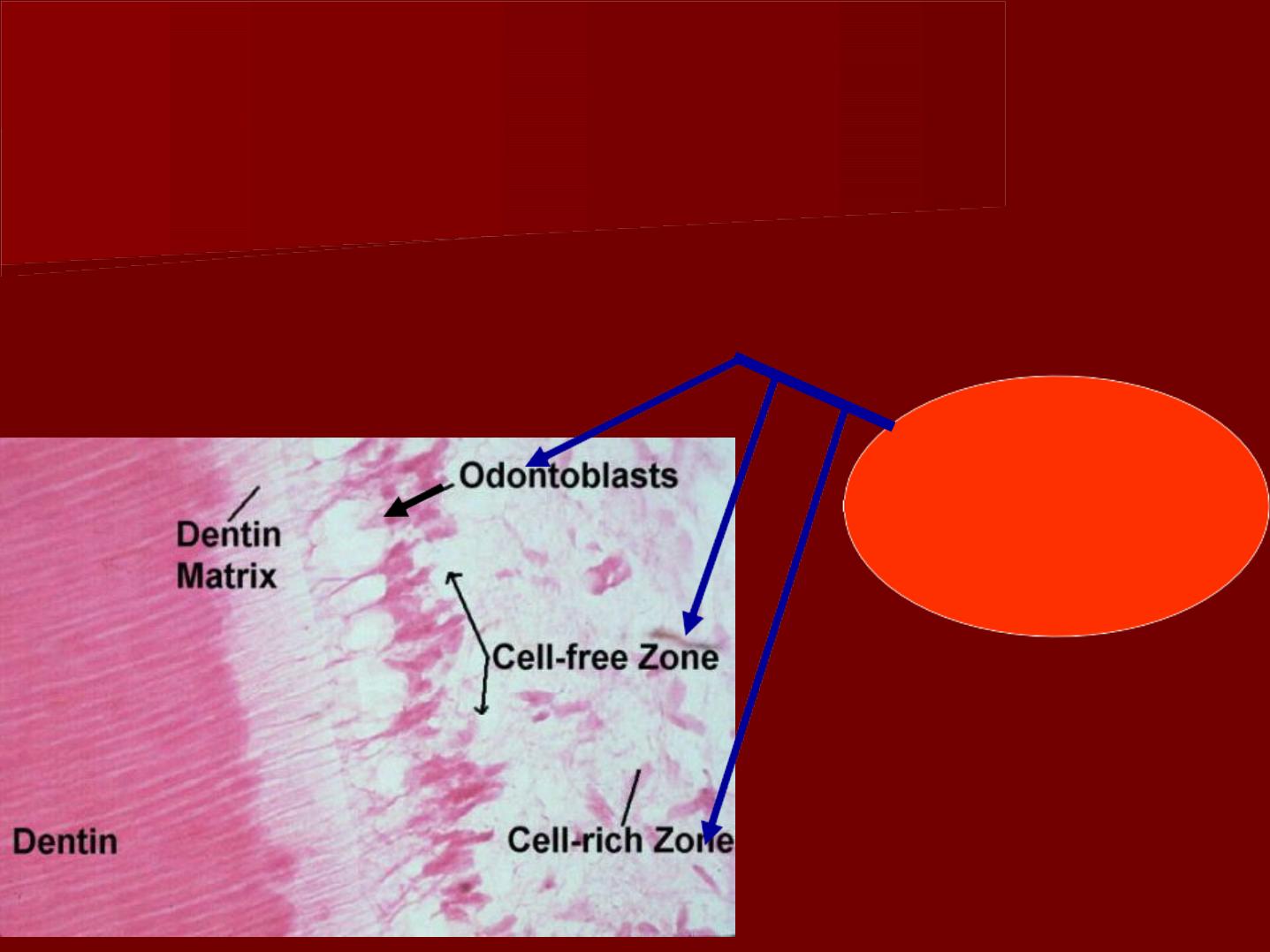
C- cell rich zone
It is present beneath the cell free zone.
It is composed of fibroblasts and undifferentiated
mesenchymal cells.
o
o
d
d
o
o
n
n
t
t
o
o
g
g
e
e
n
n
i
i
c
c
z
z
o
o
n
n
e
e

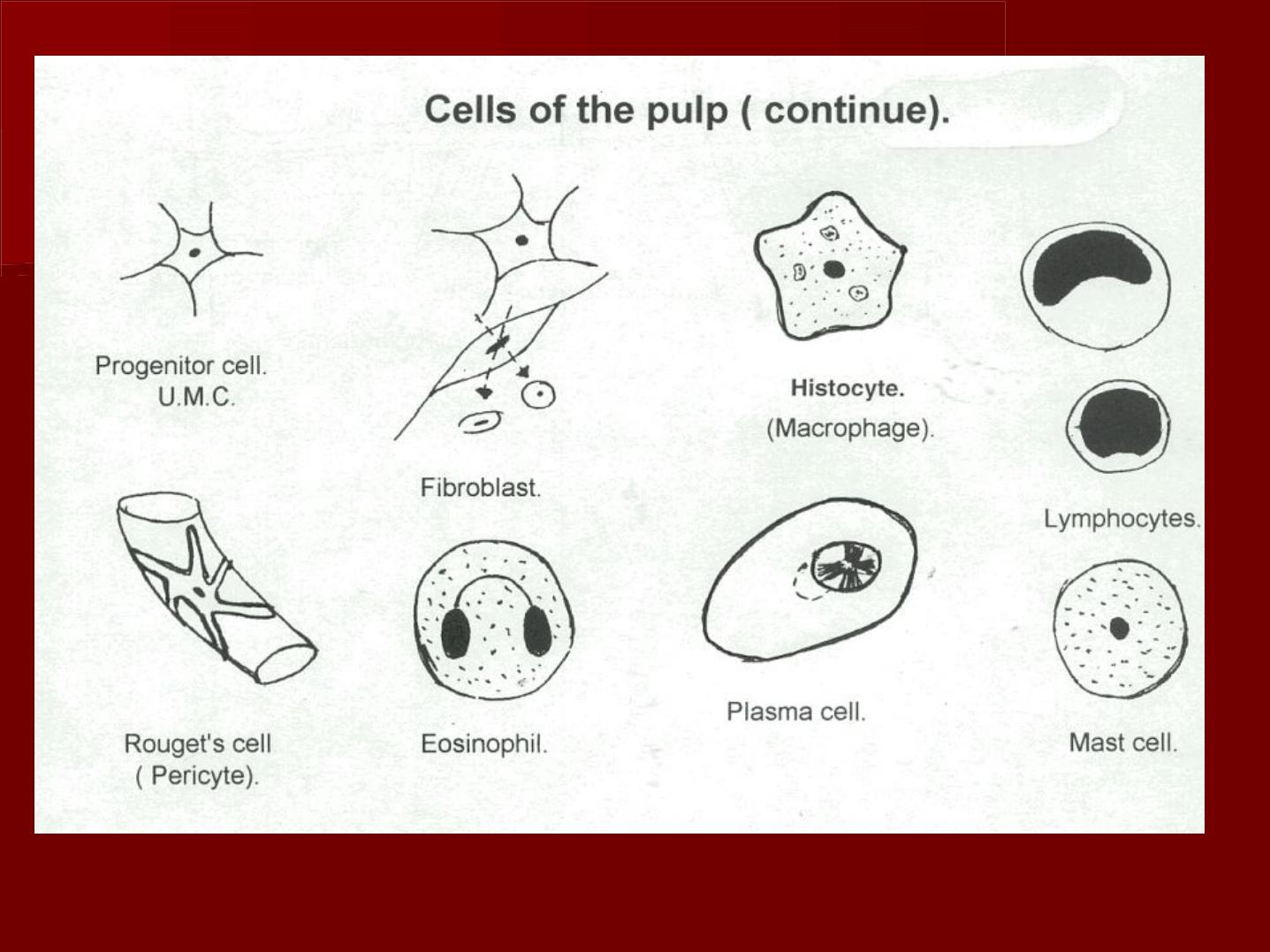
Cells of the pulp
1- Synthetic cells (formative cells):
odontoblasts and fibroblasts.
2- Defensive cells:
Macrophages, small lymphocytes,
eosinophils, mast cells and plasma cells.
3- Progenitor cells:
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells.
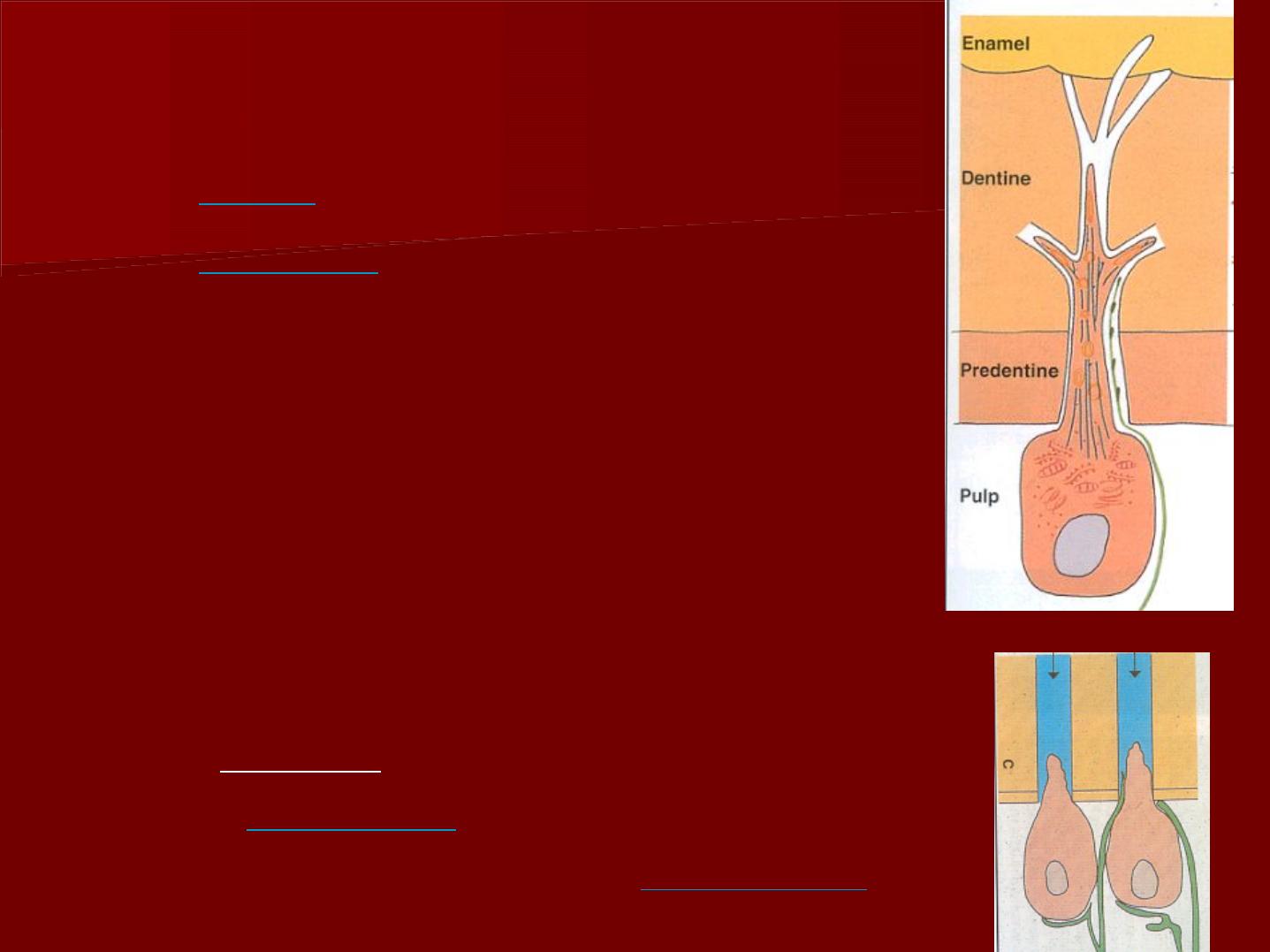
a- odontoblasts:
Length:
5-7u
in the diameter
25-40u
in length.
In the early stage of development
odontoblasts consist of a
single layer of
columnar cells .
In the later stages of development, the
odontoblastic layer appeared
pyriform
(pear like)where the broadest part of
the cell contains the nucleus
They are longer in the crown and then
become
cuboidal
rootwise, at the root
apex, they may be almost
flattened
.
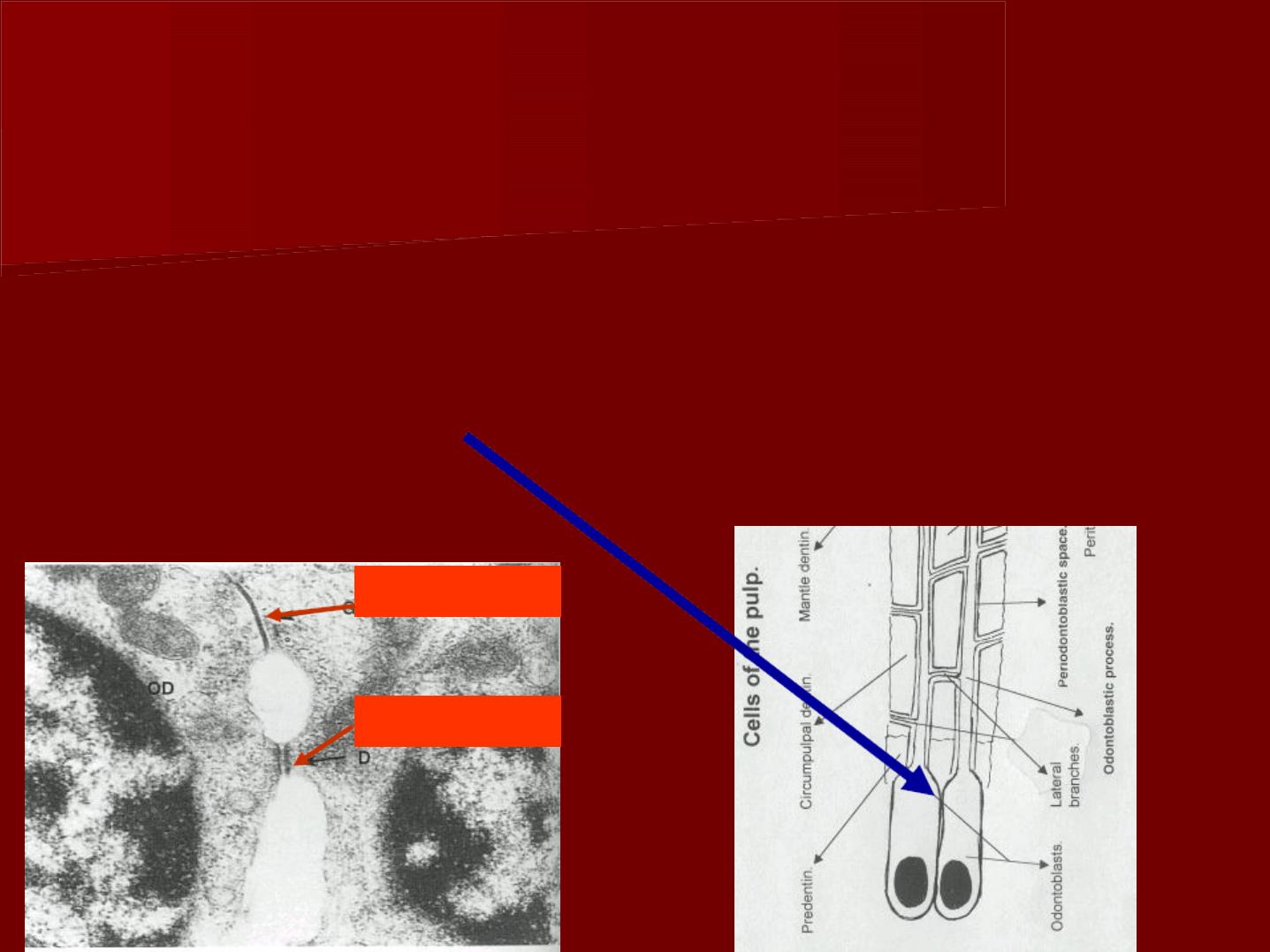
The cell membranes of adjacent odontoblasts
exhibit junctional complexes.
The clear terminal part of the cell body and the
adjacent intercellular junction is known as
terminal bars.
Gap junction
desmosome
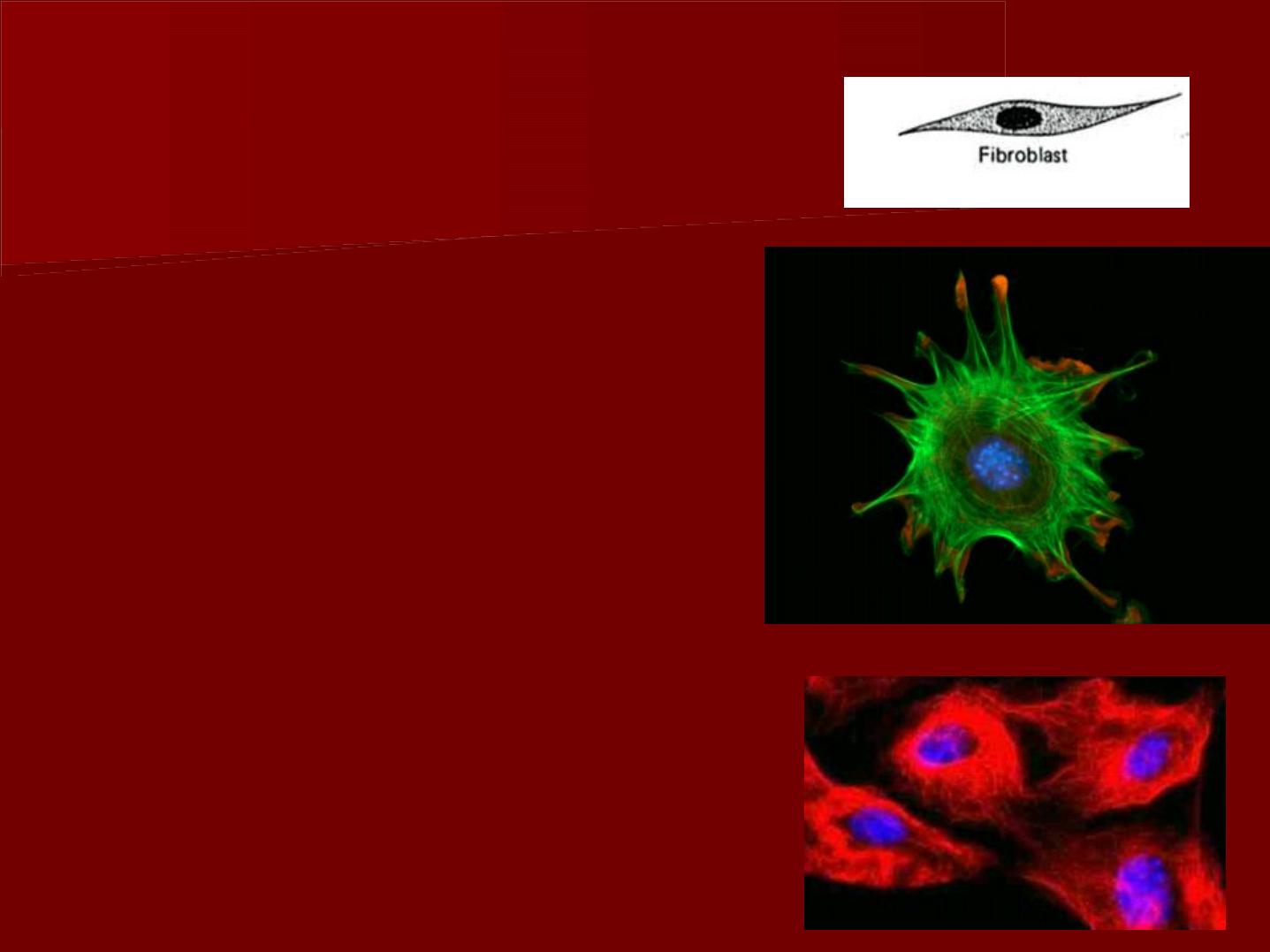
b- Fibroblasts
These are the most numerous
type of cells.
They are
spindle
in shape.
They have
elongated processes
which are widely separated
and link up with those of
other pulpal fibroblasts
(
stellate appearance
).
The nucleus stains deep with
basic dye and the cytoplasm
is highly stained and
homogenous.
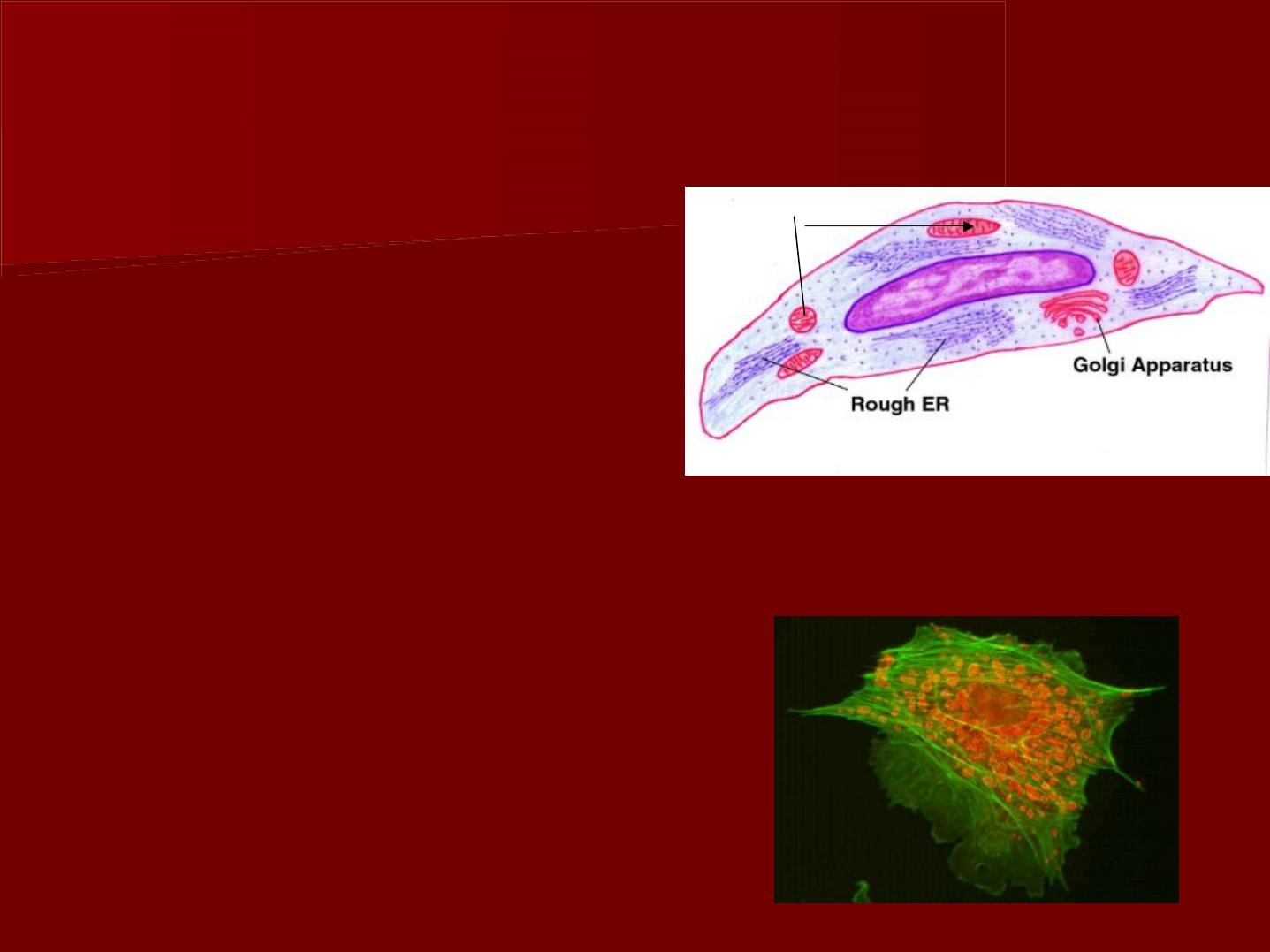
These cells have a dual function: synthesize and
degradation of fibers and ground substances in the
same cell .
I
I
n
n
y
y
o
o
u
u
n
n
g
g
p
p
u
u
l
l
p
p
,
,
t
t
h
h
e
e
y
y
a
a
r
r
e
e
:
:
*
*
l
l
a
a
r
r
g
g
e
e
c
c
e
e
l
l
l
l
s
s
.
.
*
*
w
w
i
i
t
t
h
h
l
l
a
a
r
r
g
g
e
e
m
m
u
u
l
l
t
t
i
i
p
p
l
l
e
e
p
p
r
r
o
o
c
c
e
e
s
s
s
s
e
e
s
s
*
*
c
c
e
e
n
n
t
t
r
r
a
a
l
l
l
l
y
y
l
l
o
o
c
c
a
a
t
t
e
e
d
d
o
o
v
v
a
a
l
l
n
n
u
u
c
c
l
l
e
e
u
u
s
s
,
,
*
*
n
n
u
u
m
m
e
e
r
r
o
o
u
u
s
s
m
m
i
i
t
t
o
o
c
c
h
h
o
o
n
n
d
d
r
r
i
i
a
a
,
,
*
*
w
w
e
e
l
l
l
l
d
d
e
e
v
v
e
e
l
l
o
o
p
p
e
e
d
d
G
G
o
o
l
l
g
g
i
i
b
b
o
o
d
d
i
i
e
e
s
s
*
*
w
w
e
e
l
l
l
l
d
d
e
e
v
v
e
e
l
l
o
o
p
p
e
e
d
d
R
R
E
E
R
R
m
m
i
i
t
t
o
o
c
c
h
h
o
o
n
n
d
d
r
r
i
i
a
a
F
F
i
i
b
b
r
r
o
o
b
b
l
l
a
a
s
s
t
t
(
(
p
p
r
r
o
o
t
t
e
e
i
i
n
n
s
s
e
e
c
c
r
r
e
e
t
t
i
i
n
n
g
g
c
c
e
e
l
l
l
l
)
)
.
.
i
i
n
n
p
p
e
e
r
r
i
i
o
o
d
d
s
s
o
o
f
f
l
l
e
e
s
s
s
s
a
a
c
c
t
t
i
i
v
v
i
i
t
t
y
y
a
a
n
n
d
d
a
a
g
g
i
i
n
n
g
g
t
t
h
h
e
e
s
s
e
e
c
c
e
e
l
l
l
l
s
s
a
a
p
p
p
p
e
e
a
a
r
r
s
s
m
m
a
a
l
l
l
l
e
e
r
r
a
a
n
n
d
d
r
r
o
o
u
u
n
n
d
d
o
o
r
r
s
s
p
p
i
i
n
n
d
d
l
l
e
e
-
-
s
s
h
h
a
a
p
p
e
e
d
d
w
w
i
i
t
t
h
h
w
w
o
o
r
r
g
g
a
a
n
n
e
e
l
l
l
l
e
e
s
s
,
,
t
t
h
h
e
e
y
y
a
a
r
r
e
e
t
t
e
e
r
r
m
m
e
e
d
d
f
f
i
i
b
b
r
r
o
o
c
c
y
y
t
t
e
e
s
s
.
.
f
f
i
i
b
b
r
r
o
o
c
c
y
y
t
t
e
e
f
f
i
i
b
b
r
r
o
o
b
b
l
l
a
a
s
s
t
t
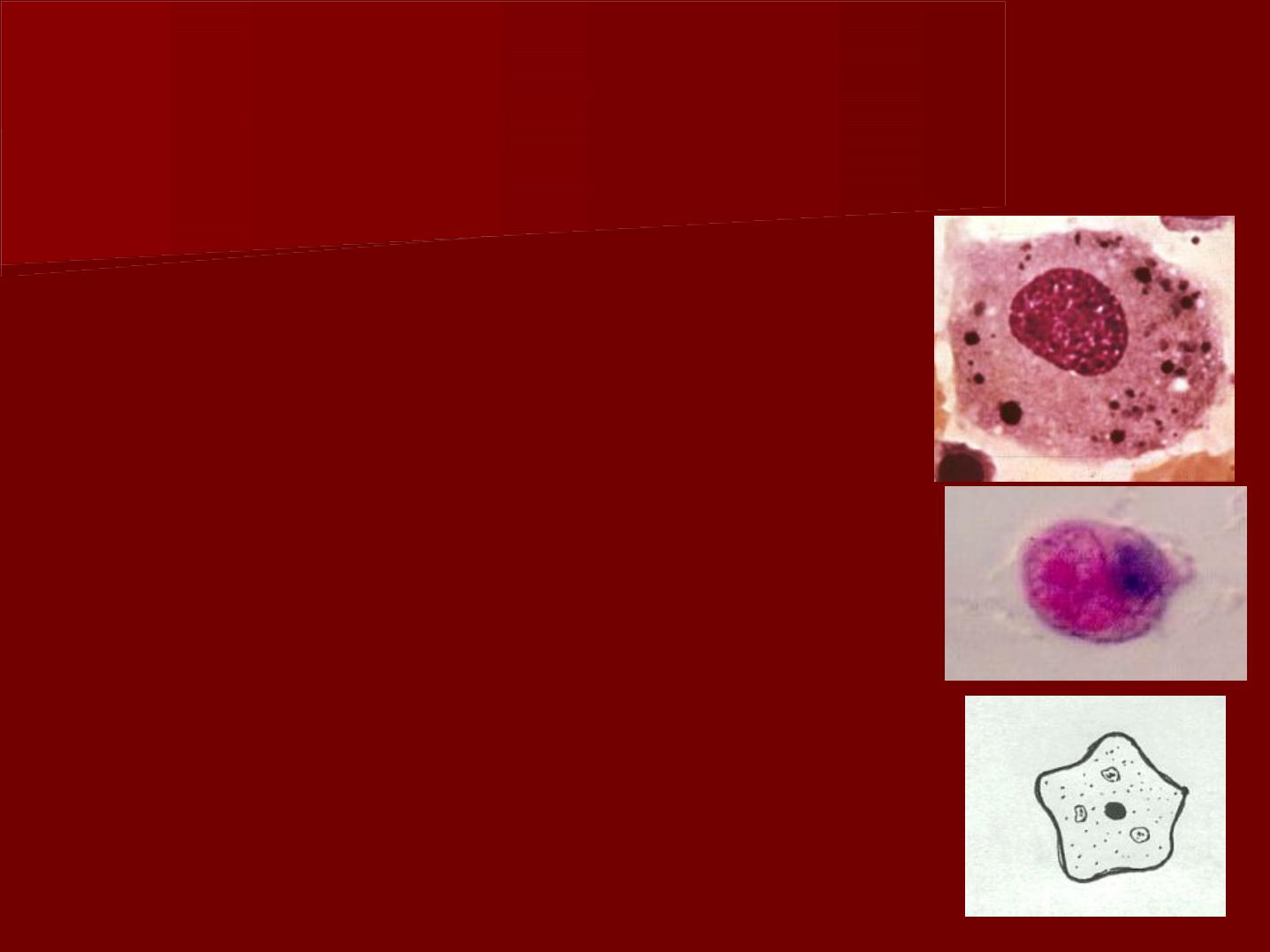
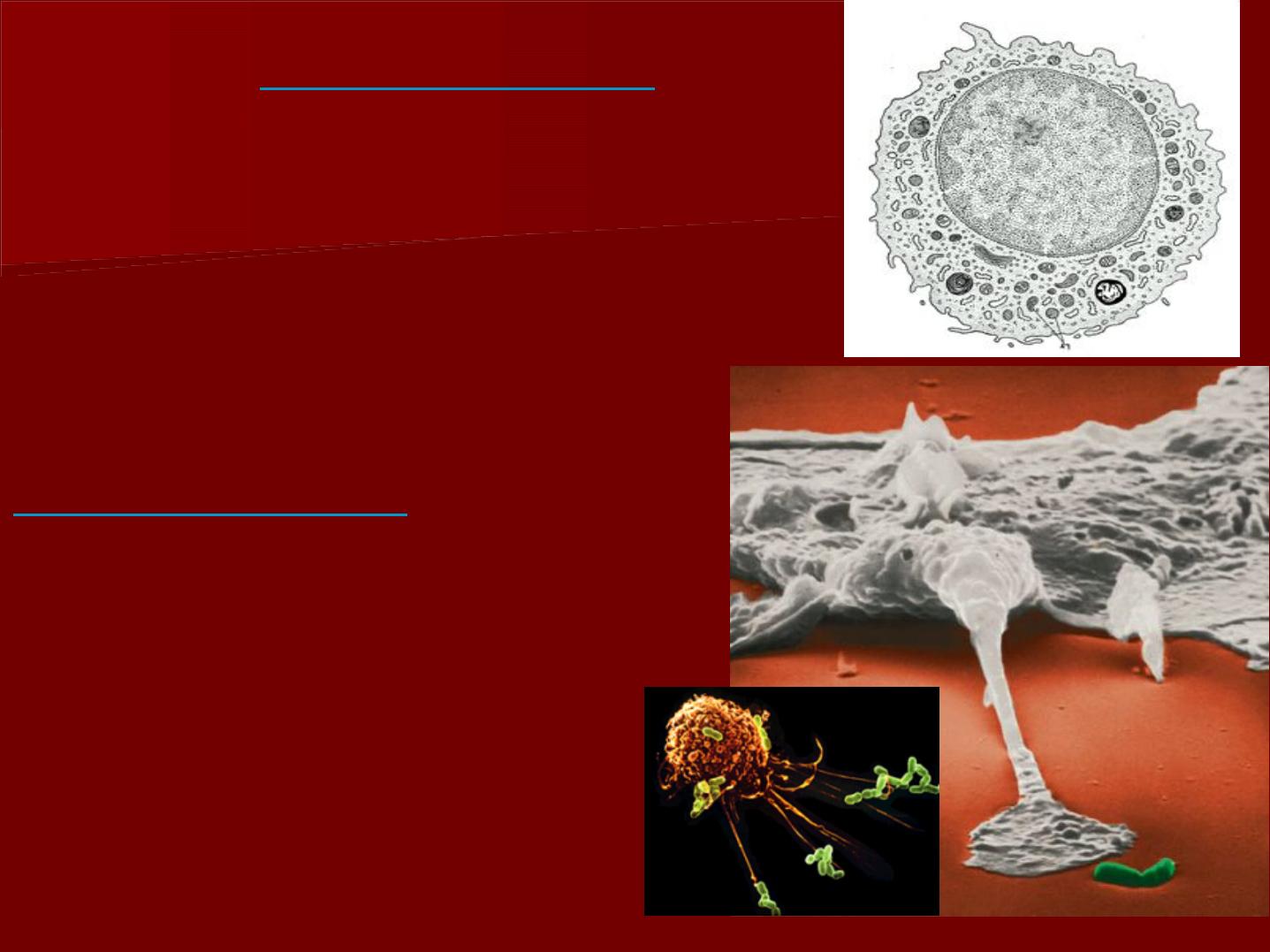
2- Defensive cells:
A- Histiocyte ( macrophage ):
In light microscope, the cells appear
irregular in shape with short blunt
processes.
The nucleus is small, more rounded and
darker in staining than fibroblast.
Their presence is obseved by intra-vital
dyes such toluidine blue.
These cells are distributed around the
odontoblasts and small blood vessels
and capillaries.
In case of
inflammation
,
*nuclei, increase in size and
exhibit a prominent
nucleolus.
it exhibits granules and
vacuoles in their cytoplasm
Invaginations
(infold)of
plasma membrane are
noted ultrastructurally with
aggregation of vesicles or
phagosomes .
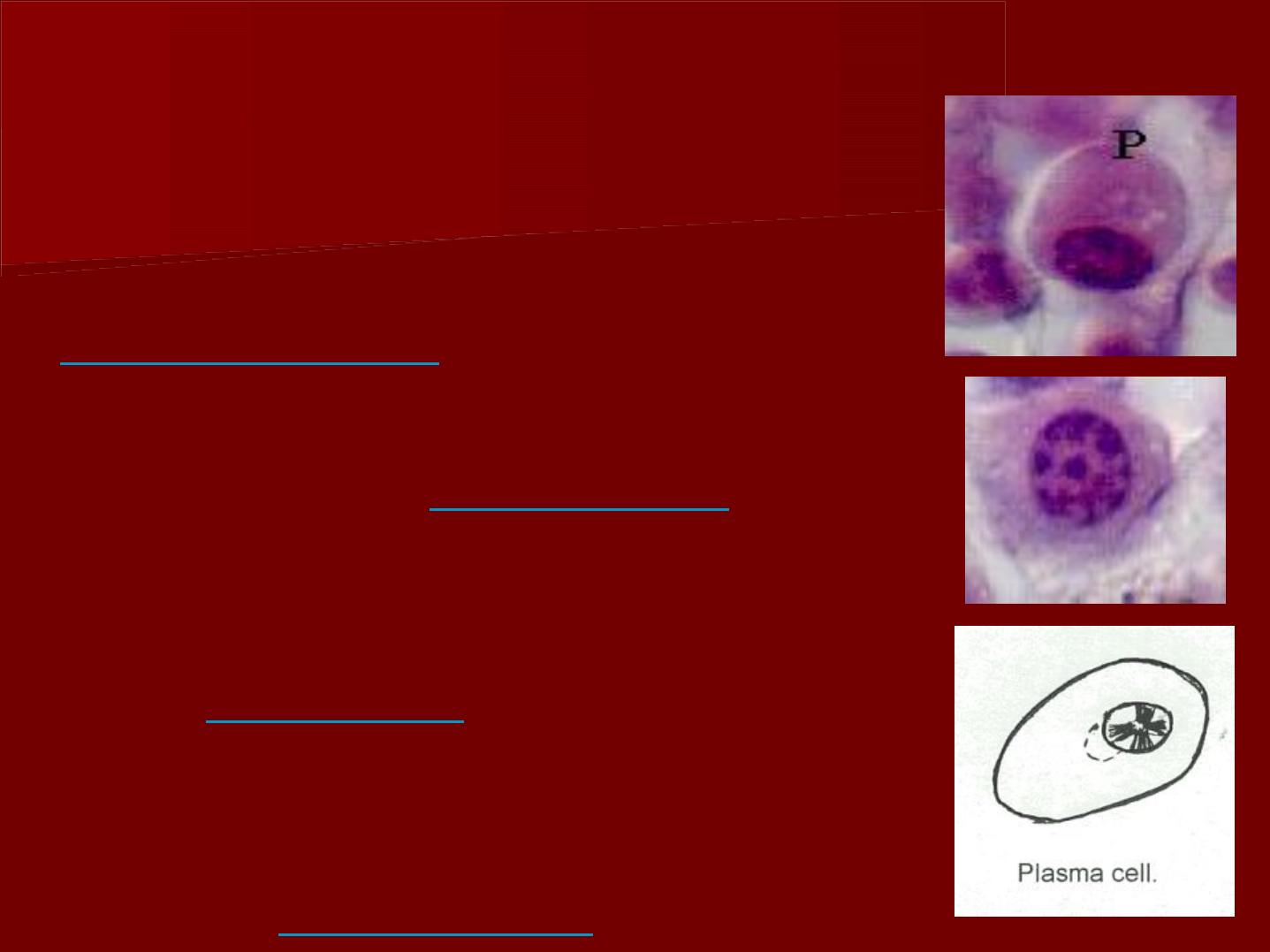
B- Plasma cells:
These cells are seen during
inflammation
.
The arrangement of chromatin gives
the nucleus a
cart wheel
appearance.
The mature type exhibits a typical
small
eccentric
nucleus and more
abundant cytoplasm.
The plasma cells are known to
produce
antibodies.
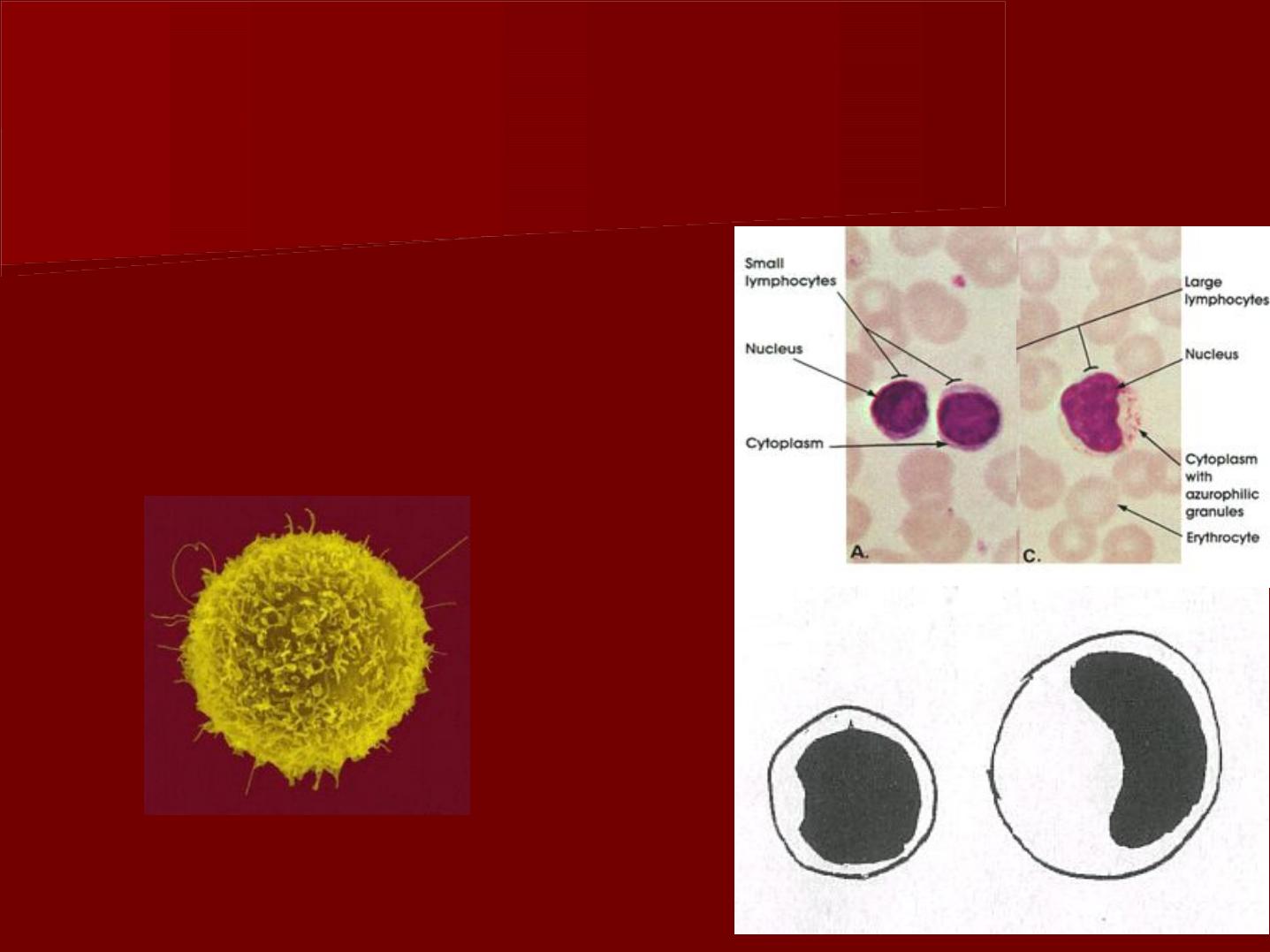
C- Lymphocytes
They are found in normal
pulp and they increase
during inflammation.
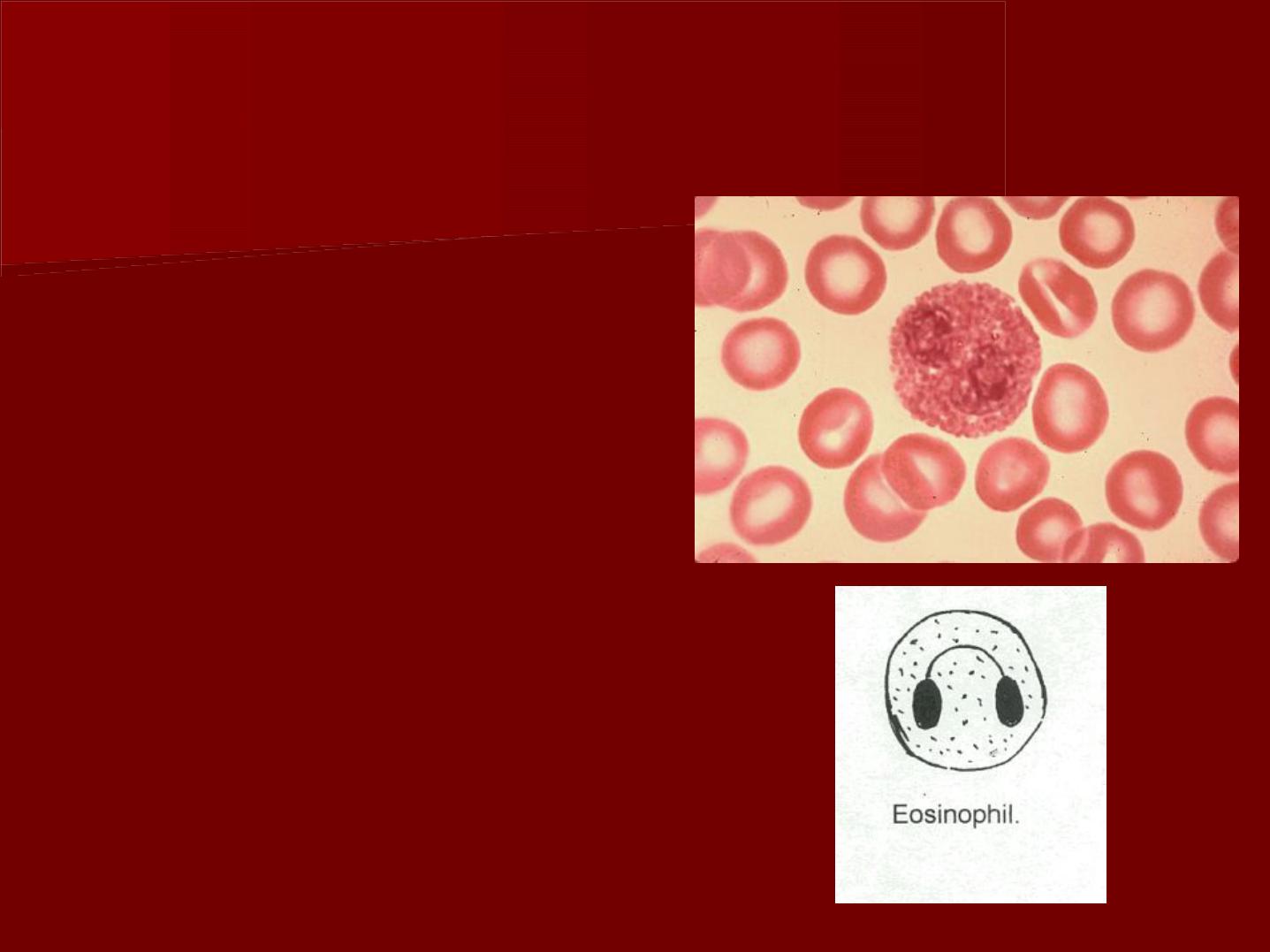
Eosinophils
T
T
h
h
e
e
y
y
a
a
r
r
e
e
f
f
o
o
u
u
n
n
d
d
i
i
n
n
n
n
o
o
r
r
m
m
a
a
l
l
p
p
u
u
l
l
p
p
a
a
n
n
d
d
t
t
h
h
e
e
y
y
i
i
n
n
c
c
r
r
e
e
a
a
s
s
e
e
d
d
u
u
r
r
i
i
n
n
g
g
i
i
n
n
f
f
l
l
a
a
m
m
m
m
a
a
t
t
i
i
o
o
n
n
.
.
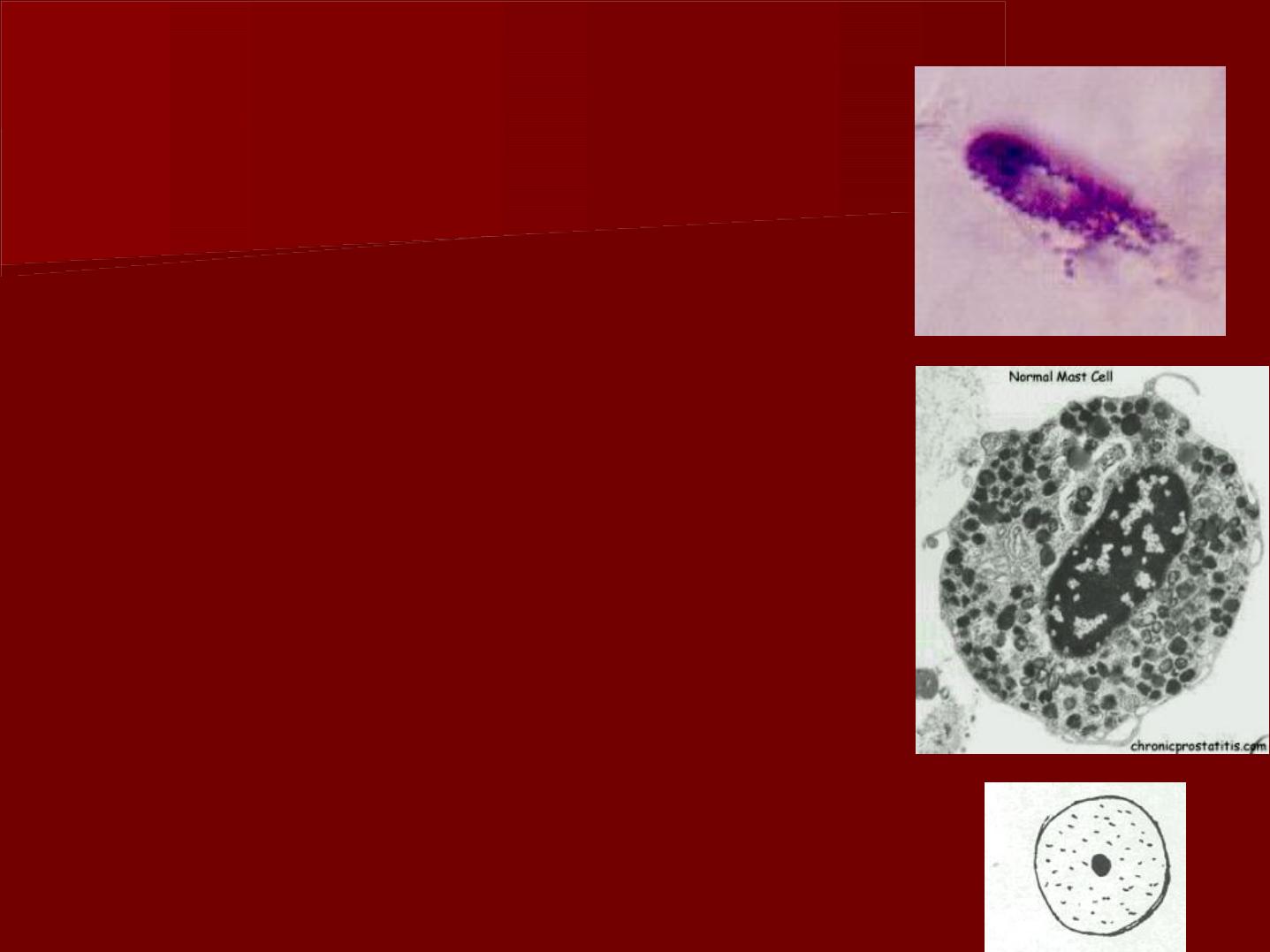
D- Mast cells:
*They have a round nucleus and their
cytoplasm contains many granules.
*They are demonstrated by using
specific stains as toluidine blue.
*They produce histamin& heparin.
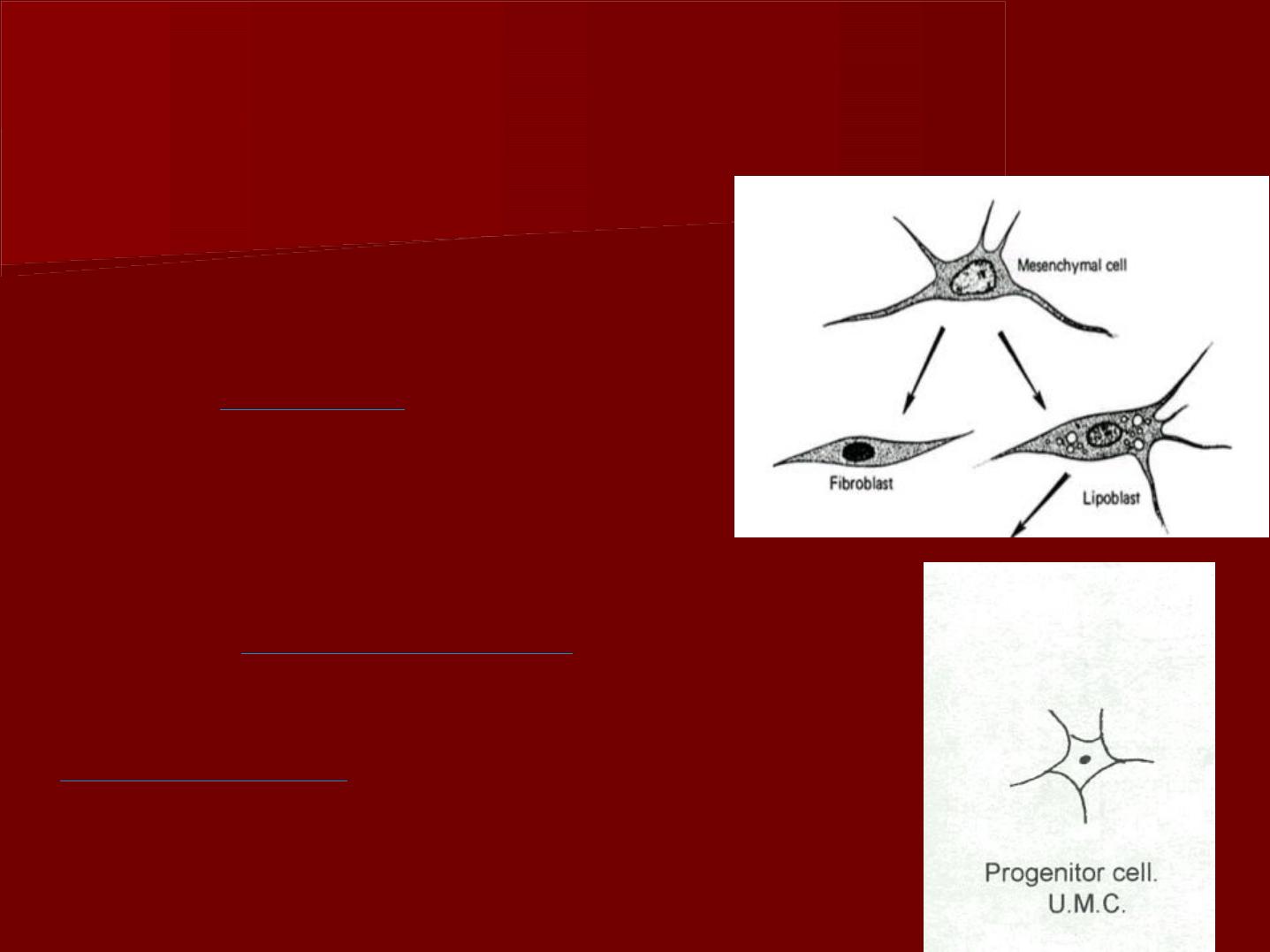
3- Progenitor cells:
(The undifferentiated
mesenchymal cells):
They are
smaller
than
fibroblasts but have a similar
appearance.
They are usually found along the
walls of
blood vessels
.
These cells have the
potentiality
of forming other
types of formative or
defensive connective tissue
cells.
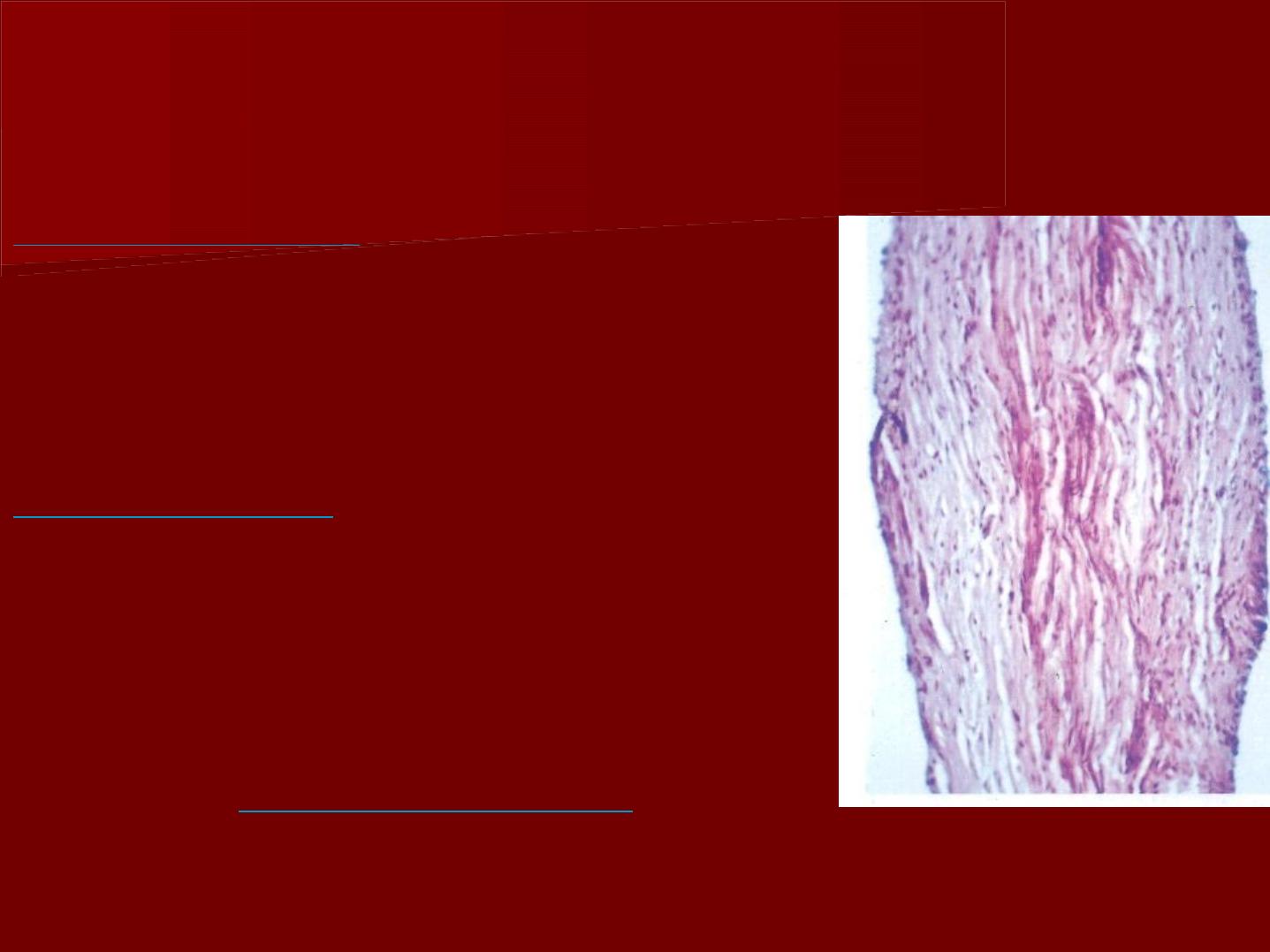
Fibers of the pulp
In young pulp
the fibers are
relatively sparse (few) and
delicate throughout the pulp and
gradually the bundles increase in
size with advancing age.
In older pulp
two patterns of
collagen distribution can be seen:
one is a diffuse collagen network
with no definite orientation,
the second is bundles of collagen.
There are
no elastic fibers
in the
pulp except those present in the
walls of the larger blood vessels.

The ground substances of the pulp:
The ground substances consists of acid
mucopolysaccharides and neutral
glycoprotein.
These substances are the environment that
promotes life of the cells
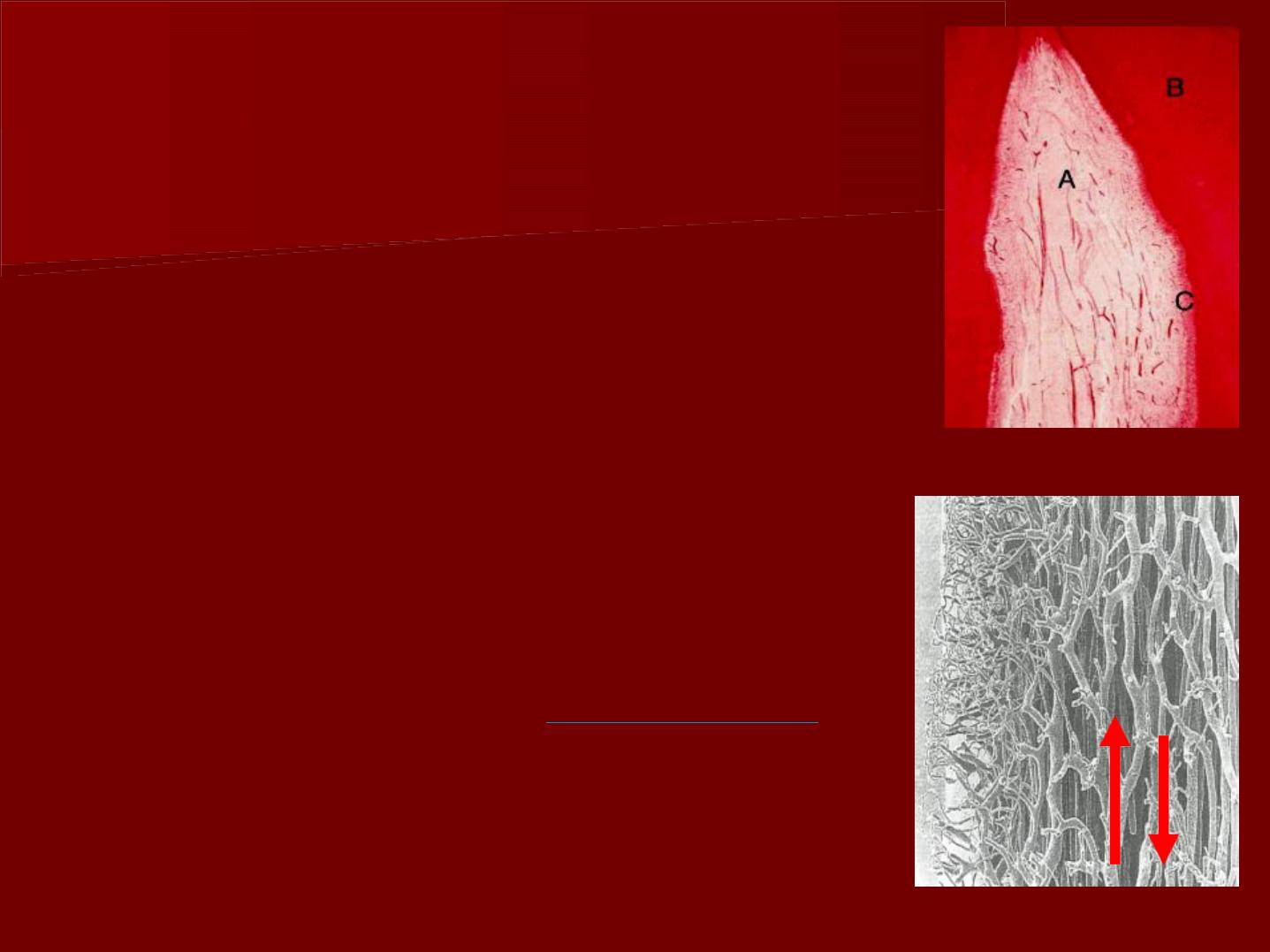
III-Blood vessels
The pulp is highly vascularized.
It is supplied by the inferior and superior
alveolar arteries
As the vessels enter the tooth, their walls
become considerably thinner than
those surrounding the tooth.
Along their course they give numerous
branches in the radicular pulp that
pass peripherally to form a plexus in
the odontogenic region.
The pulpal blood flow is
more rapid
than in most areas of the body.
D
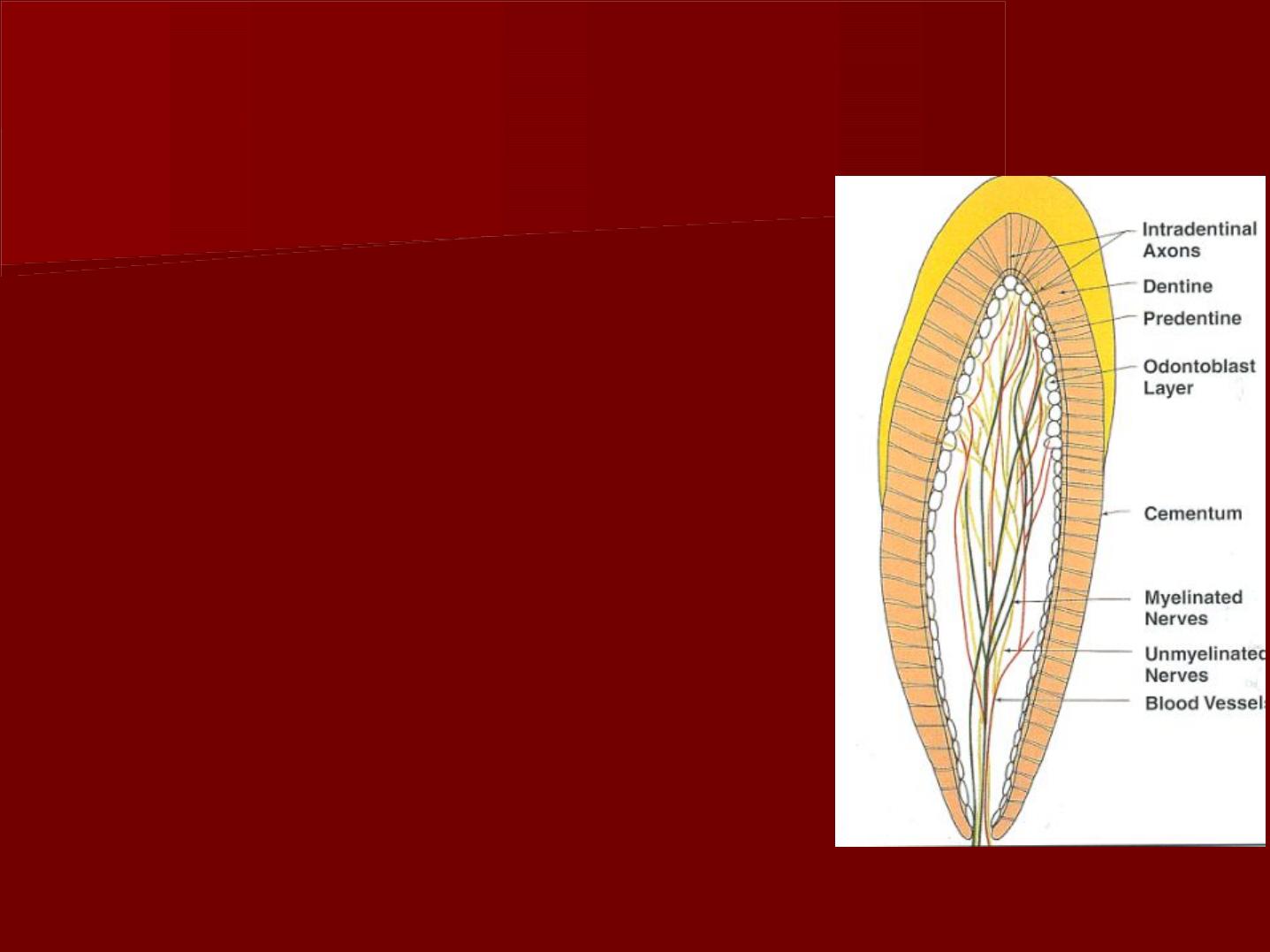

Nerves:
The pulp has an abundant nerve
supply which follows the
distribution of the blood vessels.
Two types of nerve fibers are
present:
The nonmyelinated nerves, are
sympathetic in nature, they
control the contraction of the
smooth muscles of the blood
vessels
Myelinated fibers which are sensory
parasympathetic nerves.
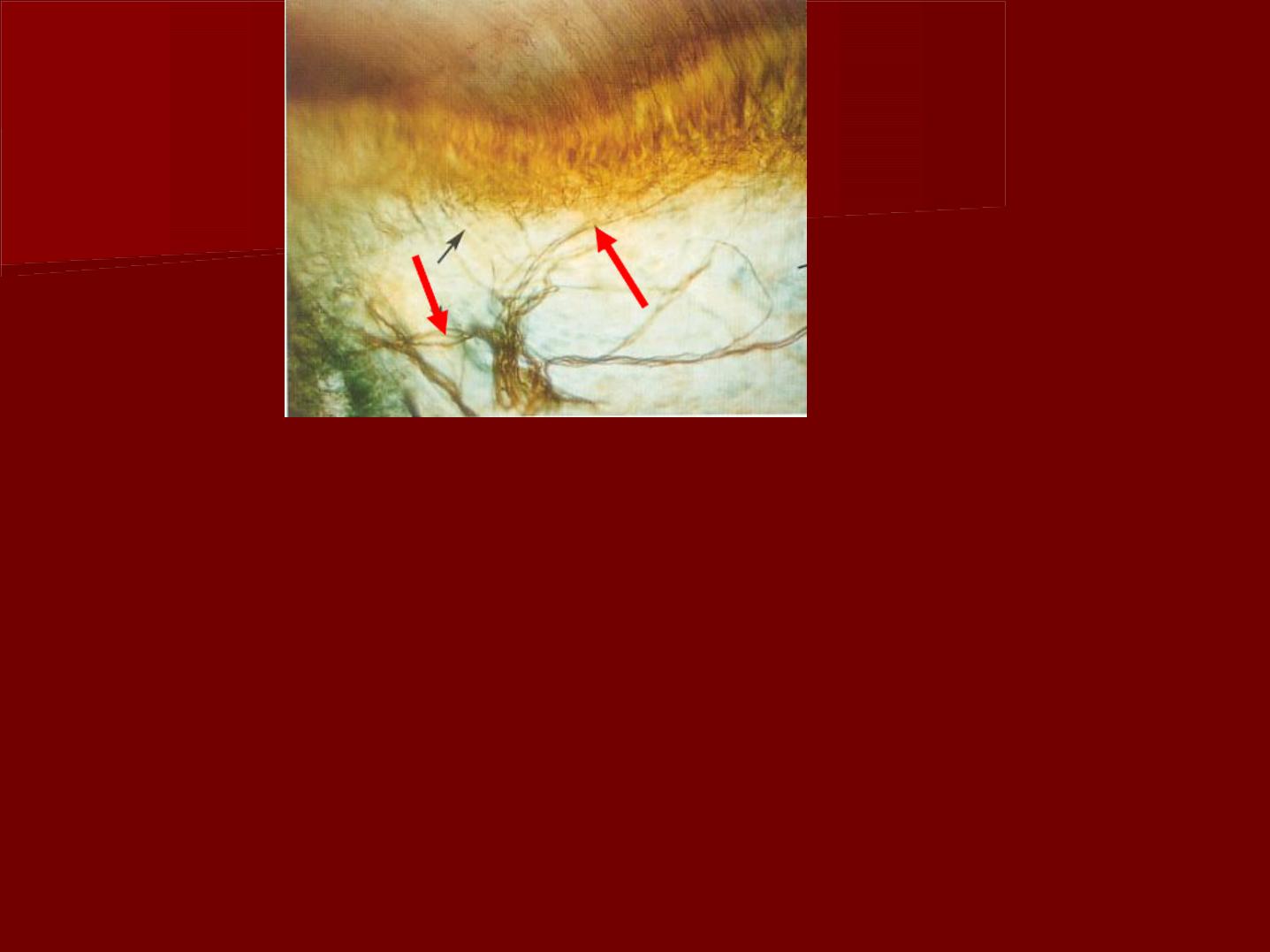
The peripheral non mylinated axons
form a network of nerves located
adjacent to the cell-rich zone. This
is termed the " parietal layer of
nerves" or plexus of Raschkow.

More nerve endings are found in the
pulp horns than in other peripheral
areas of the coronal or radicular
pulp.
Sensory response in the pulp cannot
differentiate between heat, touch,
pressure, chemicals. This is
because the pulp lacks those types
of receptors.
So the sensory nerve ending in the
pulp are presumed to function in
pain reception.

Functions of the pulp:
1- Inductive:
Dental papilla induces the enamel organ formation
and also determines the morphology of the tooth.
2- Formative :
Pulp organ produces dentin. Odontoblasts develop the
organic matrix and function in its calcification.
3- Nutritive :
The pulp nourishes the dentin. Nutrition is mediated
through the odontoblasts and their processes.

4- Protective:
The sensory nerves in the tooth respond with pain to
all stimuli, Pain sensation is a useful alarm system of
the pulp.
5- Defensive or reparative:
The pulp responds to irritation by producing reparative
dentin and mineralizing any affected dentinal tubules.
These reparative reactions are an attempt to wall off
the pulp from the source of irritation.
The presence of macrophages, lymphocytes and
leucocytes aid in the process of repair of the pulp.
Age changes in the pulp
The size of the pulp
The apical foramen
The cellular elements
The bl. vessels & nerves.
The Vitality
Reticular atrophy:
The total affect is the
production of a lessened vitality (power to live)
of the pulp tissue and a lessened response to
stimulation.
decreased
Pulp clacification
l
l
o
o
c
c
a
a
l
l
i
i
z
z
e
e
d
d
(
(
p
p
u
u
l
l
p
p
s
s
t
t
o
o
n
n
e
e
s
s )
d
d
i
i
f
f
f
f
u
u
s
s
e
e
F
F
a
a
l
l
s
s
e
e
d
d
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
c
c
l
l
e
e
T
T
r
r
u
u
e
e
d
d
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
c
c
l
l
e
e
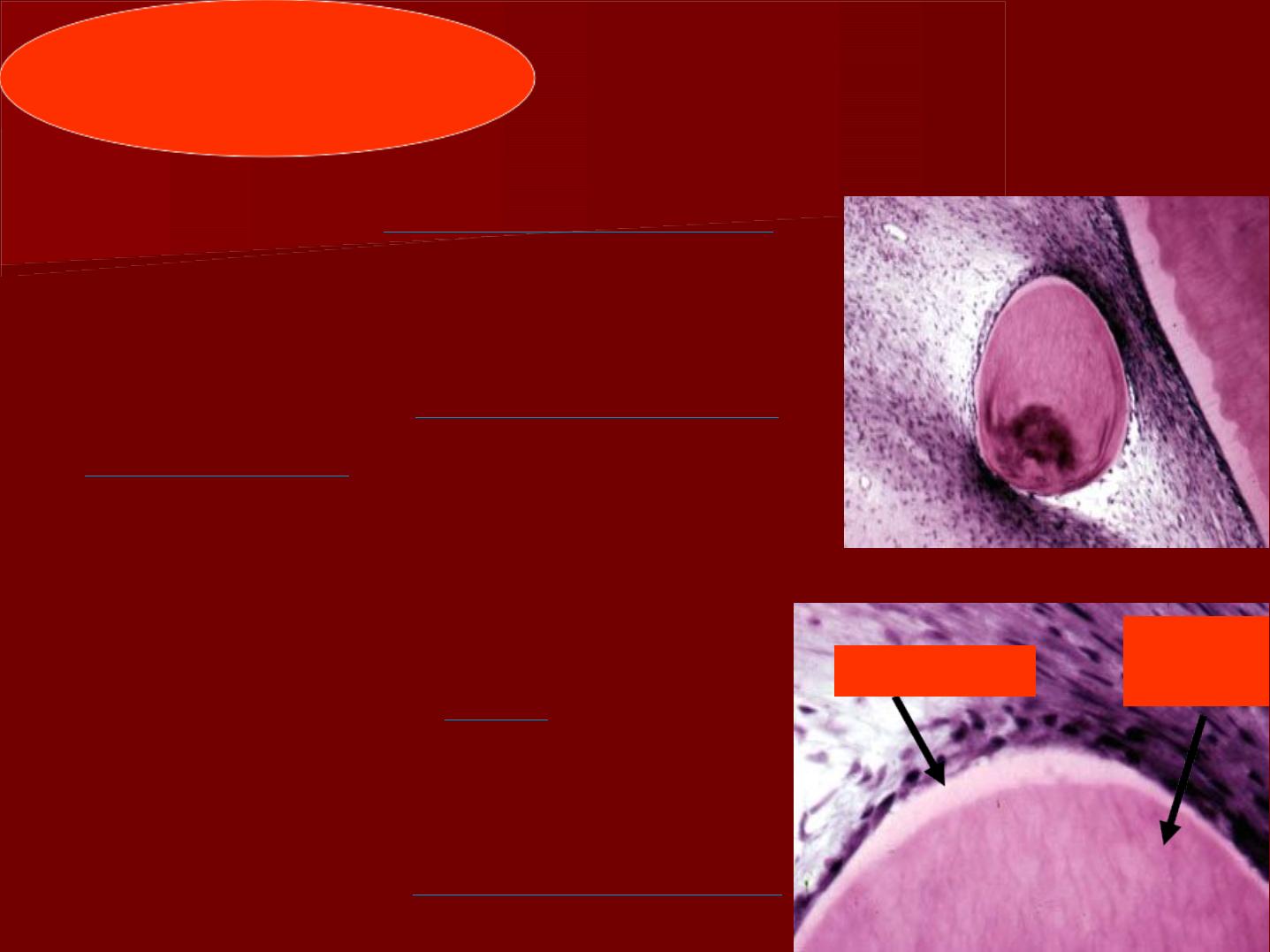
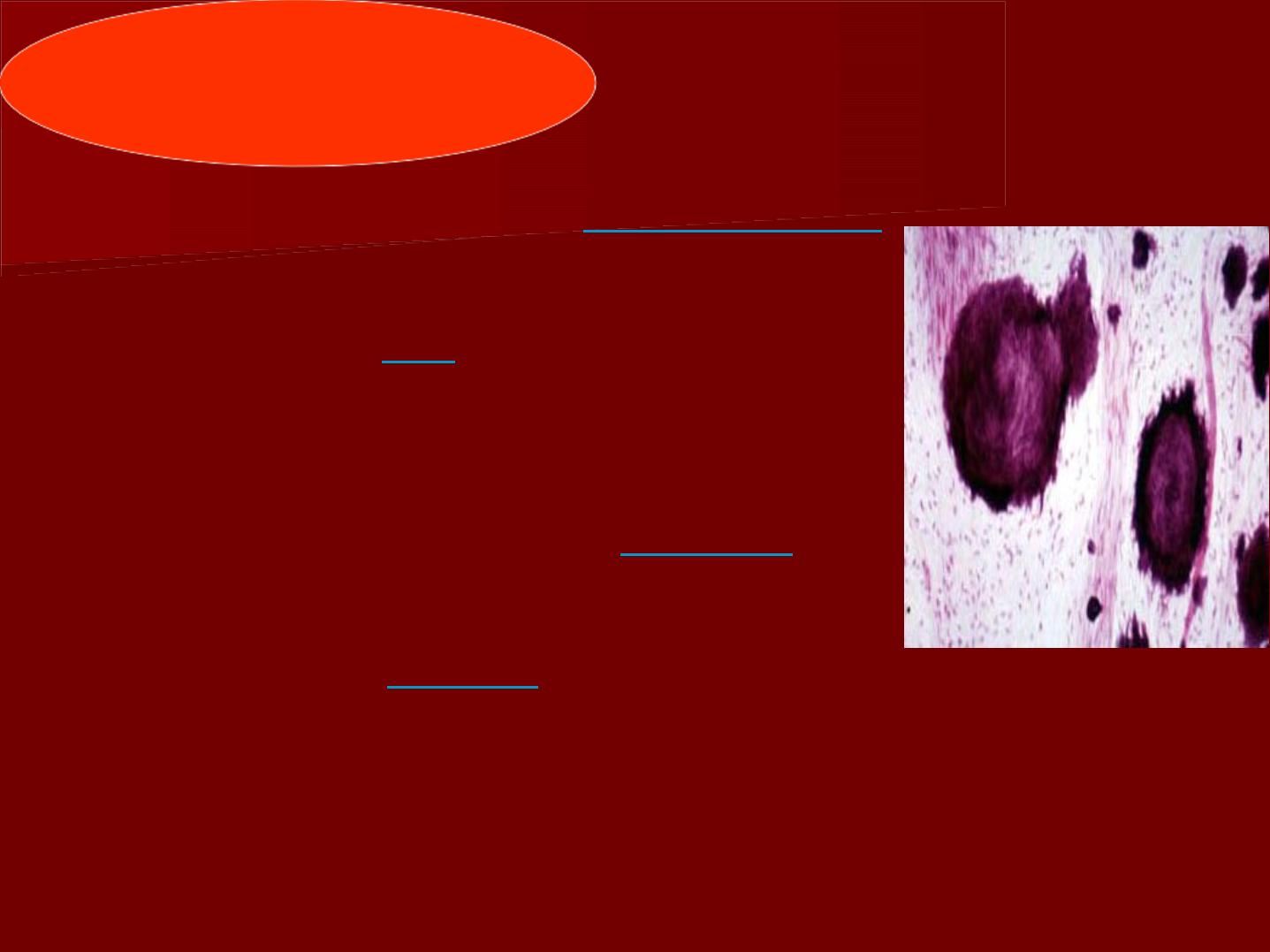
True denticles
They consist of
irregular dentin
containing traces of dentinal
tubules and few odontoblasts.
Remnants of the
epithelial root
of Hertwig
invade the pulp
tissues causing UMC of the pulp
to form this irregular type of
dentin.
True denticles are
rare
to occur,
they are small in size and
commonly found in the root
canal near the
apical foramen.
o
o
d
d
o
o
n
n
t
t
o
o
b
b
l
l
a
a
s
s
t
t
d
d
e
e
n
n
t
t
i
i
n
n
a
a
l
l
t
t
u
u
b
b
u
u
l
l
e
e
s
s
False denticles
*They are evidence of
dystrophic
calcification of the pulp tissue .
*They contain
no
dential tubules.
*They are formed of degenerated
cells or areas of hemorrhage
which act as a central
nidus
for
calcification.
*Overdoses of
vit. D
, may favor
the formation of numerous
denticles.
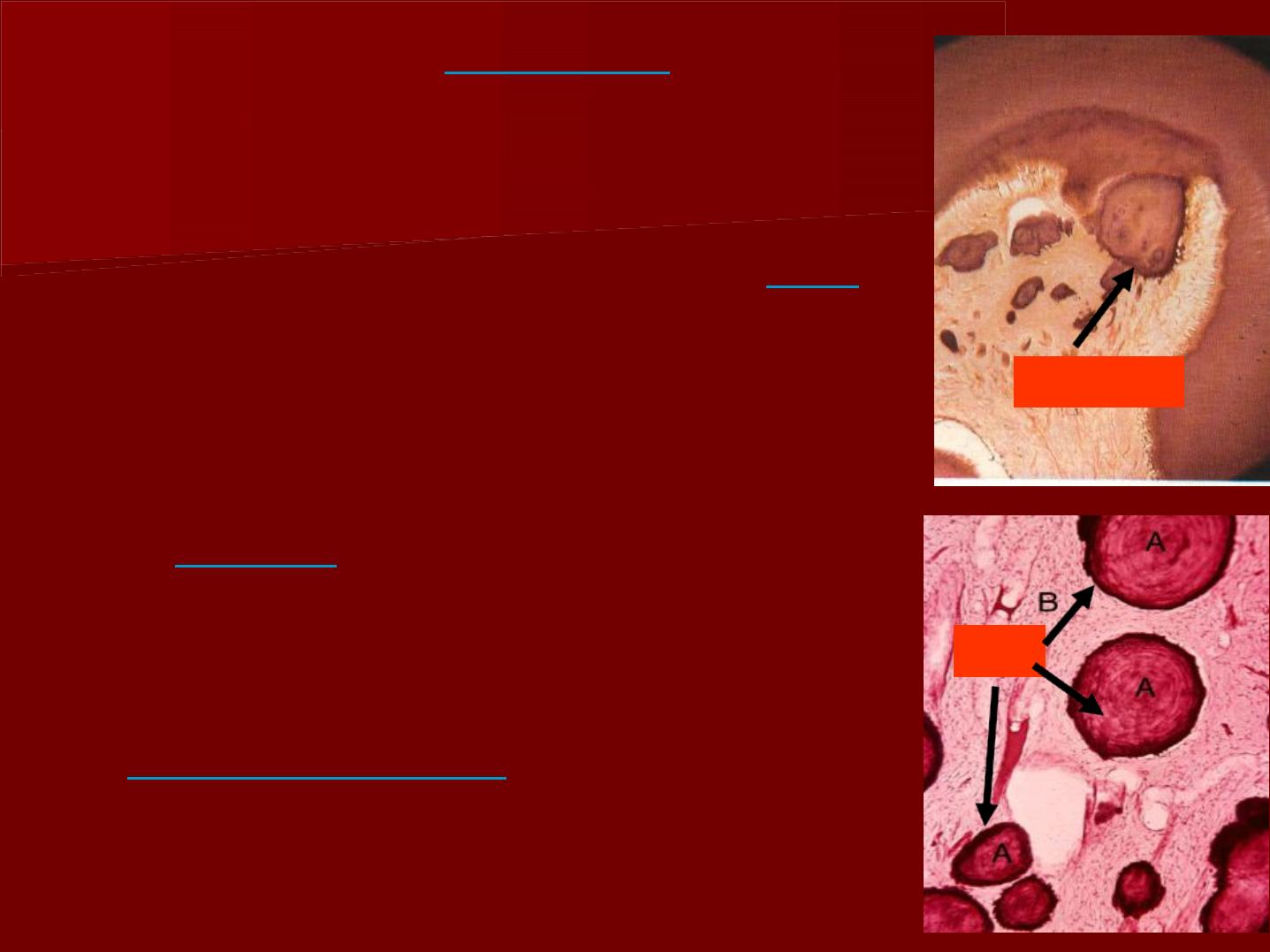
*Pulp stones are
classified
according
to their location into: free,
attached and embedded.
*They continue to increase in
size
and in certain cases they fill up
the pulp chamber completely.
*If pulp stones come close enough
to a
nerve
bundle pain may be
elicited (bring out).
*The close proximity of pulp stones
to
blood vessels
may cause
atrophy of it.
f
f
r
r
e
e
e
e
a
a
t
t
t
t
a
a
c
c
h
h
e
e
d
d
