DISEASE OF THE VEINS
Assistant prof.Abdulameer M. Hussein
• Venous disease refers to all conditions related to or caused by veins that become diseased or abnormal.
• Venous disease is quite common.
• Mild venous disease is usually not a problem for patients, but as venous disease worsens, it can become crippling chronic venous insufficiency.VEINS
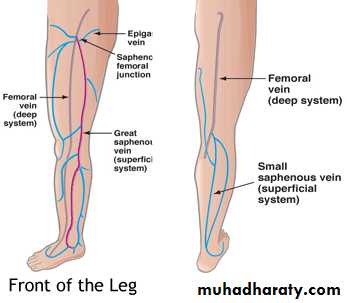
Deep SystemNamed for by associated arteries
Found running along the arteries
Predictable anatomy
Causes most of the Morbidity
• DVT
• PE
• Severe Leg Swelling
• Ulcerations
Little Surgical interventions (IVC Filter)
Medical Management
Anticoagulation
Thrombolytic therapy
Systemic vs. Catheter directed
Elevation and Compression
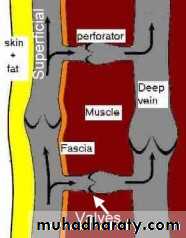
Superficial Venous System
• These are the veins we see
• Two main named branches
• Greater saphenous
• Small saphenous
• Perforators connect superficial and deep systems
• Highly variable anatomy
• Many unnamed branches and Tributaries
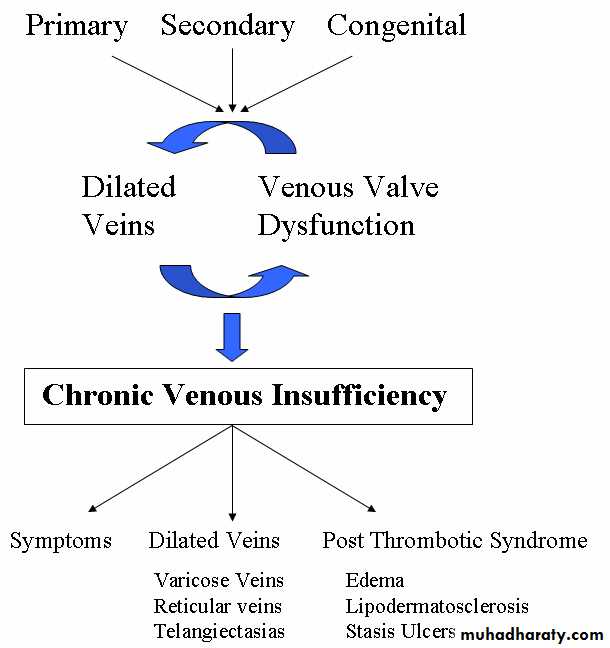
Venous Disease
• Superficial System• Varicose Veins
• Spider Veins
• Venous Malformation
• Venous Reflux
• Leg Swelling
• Venous Ulceration
• phlebitis
• Family history
• Obesity
• Pregnancy
• Prolonged standing
• Prior history of blood clot formation in the veins
• Trauma
• Surgery
• Medications
• Lifestyle
Risk factors for venous disease include:
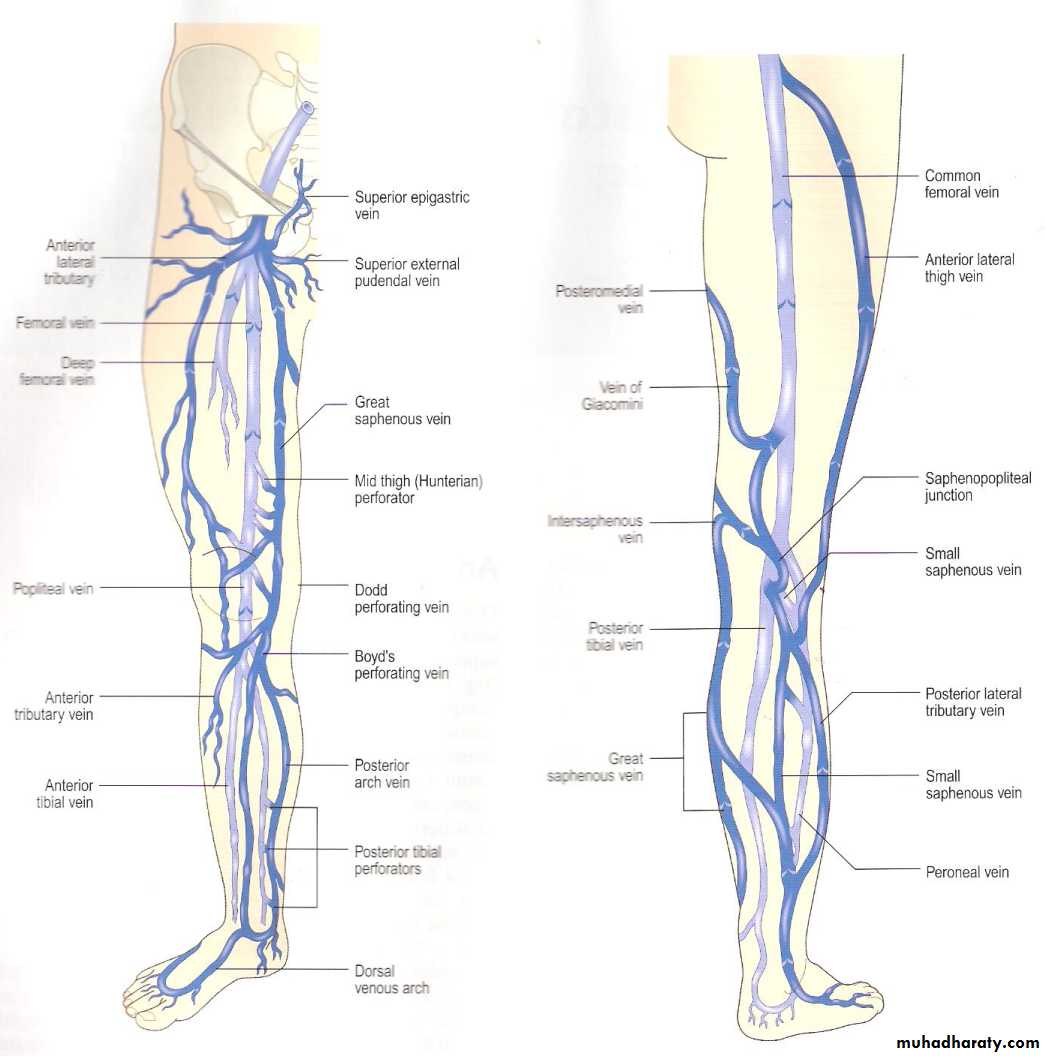
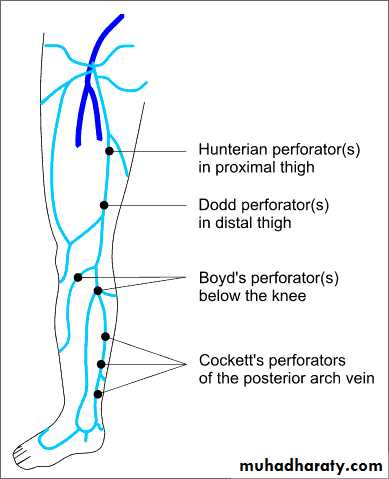
Superficial Anatomy
• Deep System = Light blue
• Superficial System = Dark blueComplex and variable anatomy
Named perforators along the greater saphenous distribution
Physiology
• Arteries deliver blood to tissue• Veins return blood to the heart
• Heart is the arterial pump
• What pumps the venous blood back to the heart?
Venous pressure is about 25mmHg at the foot
Pressure needed 80mmHg to return blood
• Two unique features of veins accomplish this
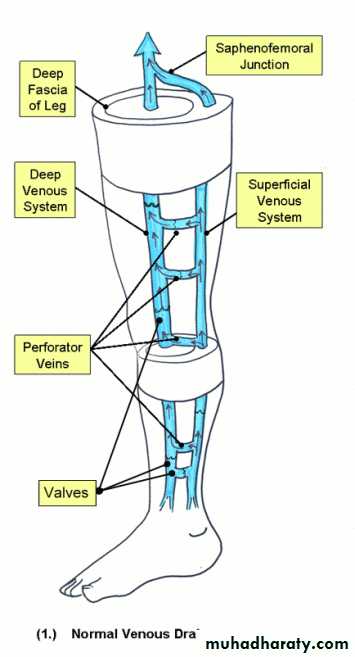
Most important is one-way Venous Valves
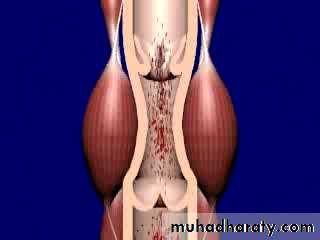
Easily compressible by surrounding muscle (calf pump)
Calf Muscle Pump
Normal venous flow in the LegNormal Flow
Superficial veins drain into the deep veins
From the foot up to the heart
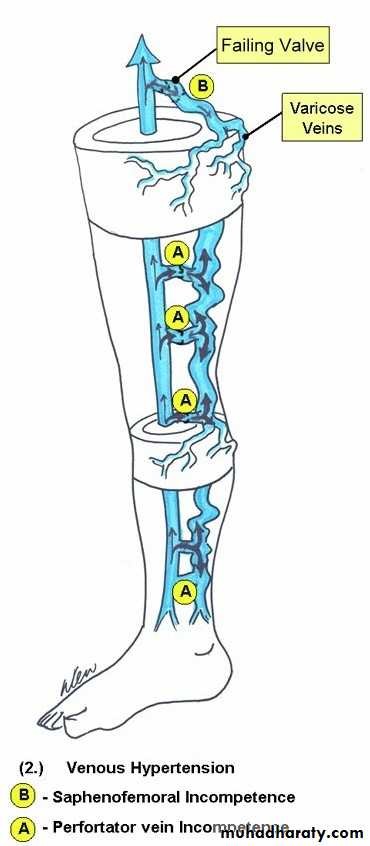
Superficial vein disease always starts with abnormal valves and interruption to normal flow called venous reflux
Abnormal flow = Venous Reflux
• Damaged Valves• Blood flows to the skin
• Blood is pushed distally and proximally
• Close loop recirculation
• Blood is retained in the leg
• Increased volume of blood (heaviness Fatigue)
• Increased venous pressure
• Veins Dilate (varicose veins)
Causes of Venous Reflux
Symptoms of venous reflux
• Leg Fatigue• Leg Heaviness
• Itching and pain along veins
• Varicose Veins
• Spider veins (not always 2nd to reflux)
• Leg swelling( think DVT 1st)
• Skin Discoloration (lipo dermatosclerosis)
• Venous ulceration
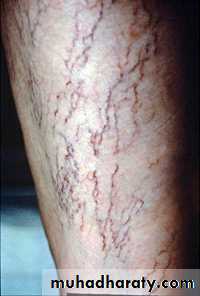
• Definition: Visible tortious bulging blue veins found in the lower extremities
Located in the Subcutaneous(between skin and fascia)• Remember this is only a manifestation of the underlying disease
• Mild Disease is cosmetic issue
• Advanced Disease significant medical problem
Pain
Swelling
Ulcerations
Varicose Veins
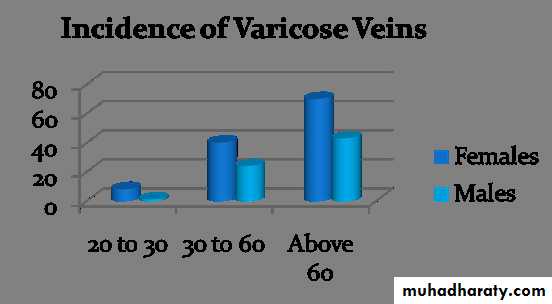
Incidence Increases with age
Females to male 3 to 1
50% of the population will affected in their life time
Varicose Veins
Spider Veins (Telangiectasia)These are non raised dilated veins located in the Dermis (deep layer of the skin)
Single layer endothelium, minimal muscleDo not cause major medical complications
Appears earlier than varicose veins (4% of teenagers , and 13 % in 18 to 20 year olds
More common in females
50 percent of adult females are affected with spider veins.
Reticular Veins are lager feeding veins
Spider Veins
• Etiology: Multifactorial
• Venous Hypertension associated with varicose veins
• Congenital: vascular nevi, neonatal hemangiomatosis, others..
• Collagen Vascular Disease: lupus,
• Hormonal factors: pregnancy, estrogen therapy, topical steroids
• Trauma: contusion, incisions
• Infections
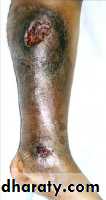
Venous Stasis Ulcers
• Differential Diagnosis• Venous ulcerations 50% on non healing ulcers
• Arterial ulcers in about 10%
• Malignancy : basal and squamous cell, lymphoma
• Infections: HIV, fungal
• Collagen vascular disorders: Lupus.
• Lymphatic obstruction
Venous Stasis Ulcers
• Etiology• Venous Hypertension
• Venous reflux
• DVT
• Varicose veins
• Edema
• Biological factors
• Leakage of proteins impedes diffusion O2
• Aggregation of white cells
• Block capillary flow
• Release on inflammatory proteins
Venous stasis ulcer
Diagnosis of venous disease• Physical exam
Appearance
Trendelenburg test
Palpation
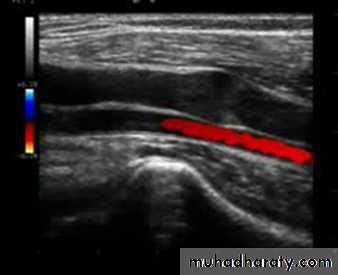
Hand Doppler
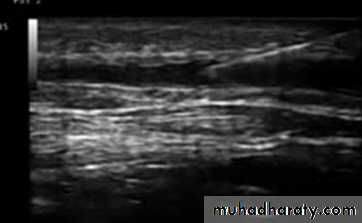
• Duplex Examination
DVT
Size of veins
Map out superficial veins
Locate the site of reflux
Find refluxing perforators
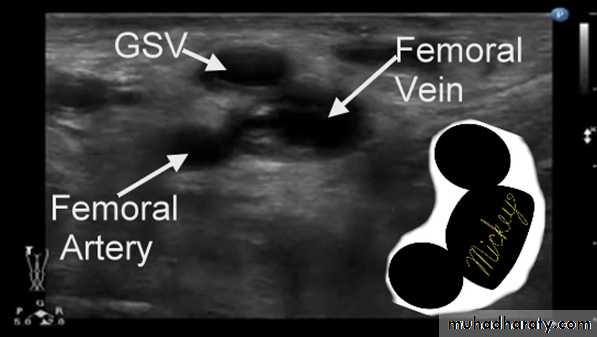
Duplex Anatomy
• Locate GSV Junction(FSJ)• Look for Mickey's
• Normal venous flow Look at valve
• Venous flow is opposite the artery
• Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV)
• Most sensitive & most specific test to find causes of anatomic obstruction.• This is expensive test used only as adjuvant when doubt still exists.
Treatment of Varicose Veins
• Conservative managementExercise
Leg elevation
Compression stocking
• Surgical treatment
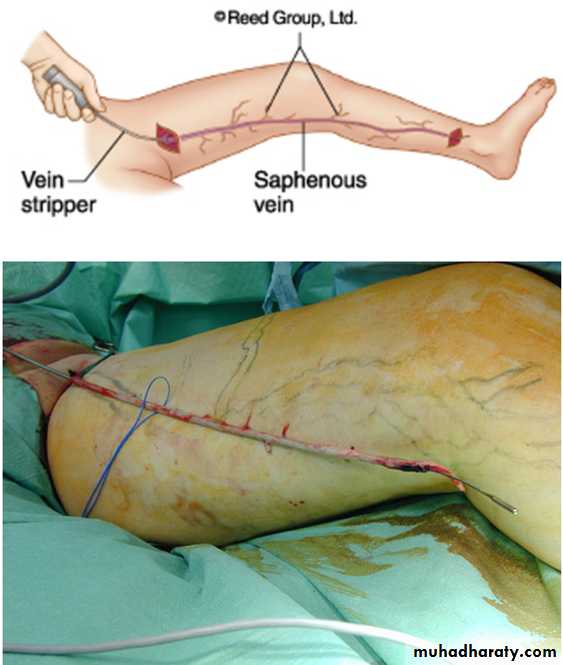
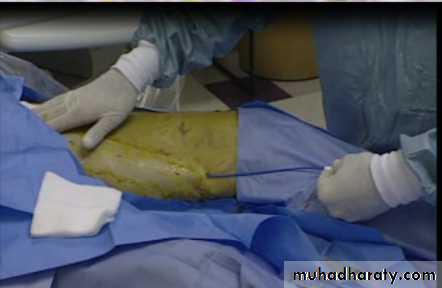
Standard Ligation and stripping
Phlebectomies
• Minimally invasive procedures (Currently accepted standard)
Laser Ablation
Radio Frequency ablation
Sclerotherapy
Surgical ligation and Stripping
• Standard treatment for a century• General anesthesia
• Pain
• Long recovery
• Some complications
• Good cosmetic results
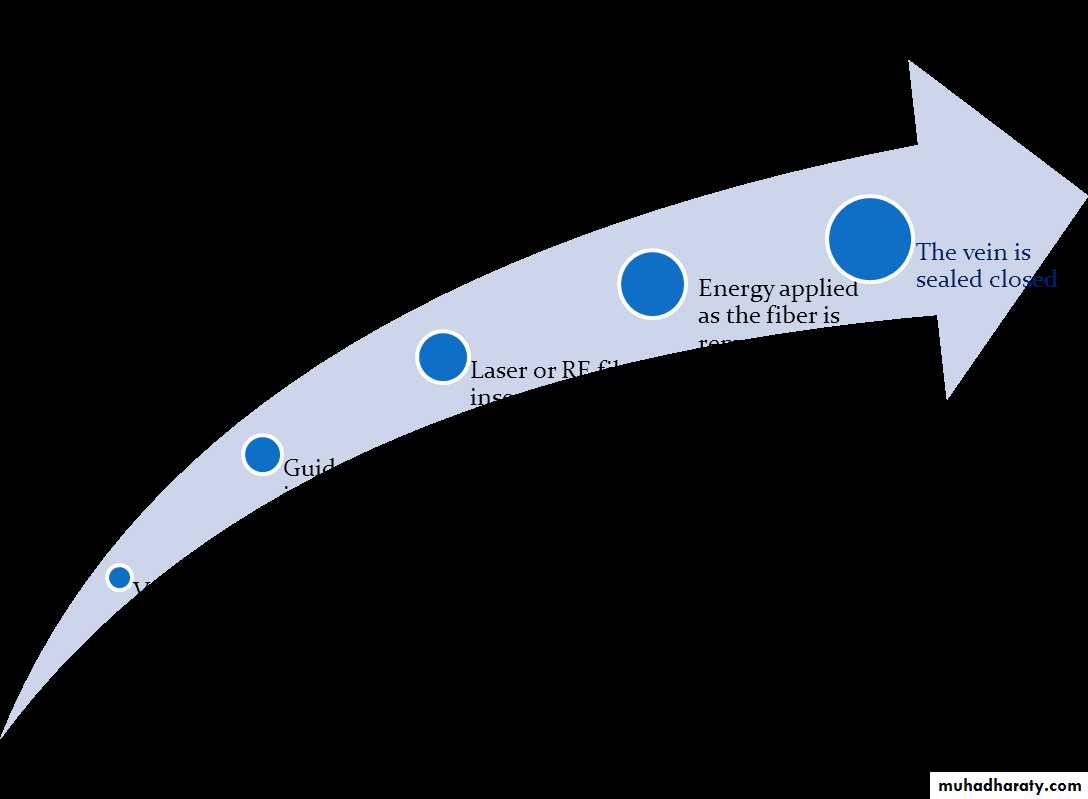
Vein Ablation
• Laser Ablation (EVLA or EVLT)Uses light to heat the vein
• Radio Frequency
Uses radio frequency to heat the vein
• Office based procedure
• Done under local anesthesia
• One needle puncture at the level of the knee
• Takes about 1 hour
• Patient resumes normal activity same day
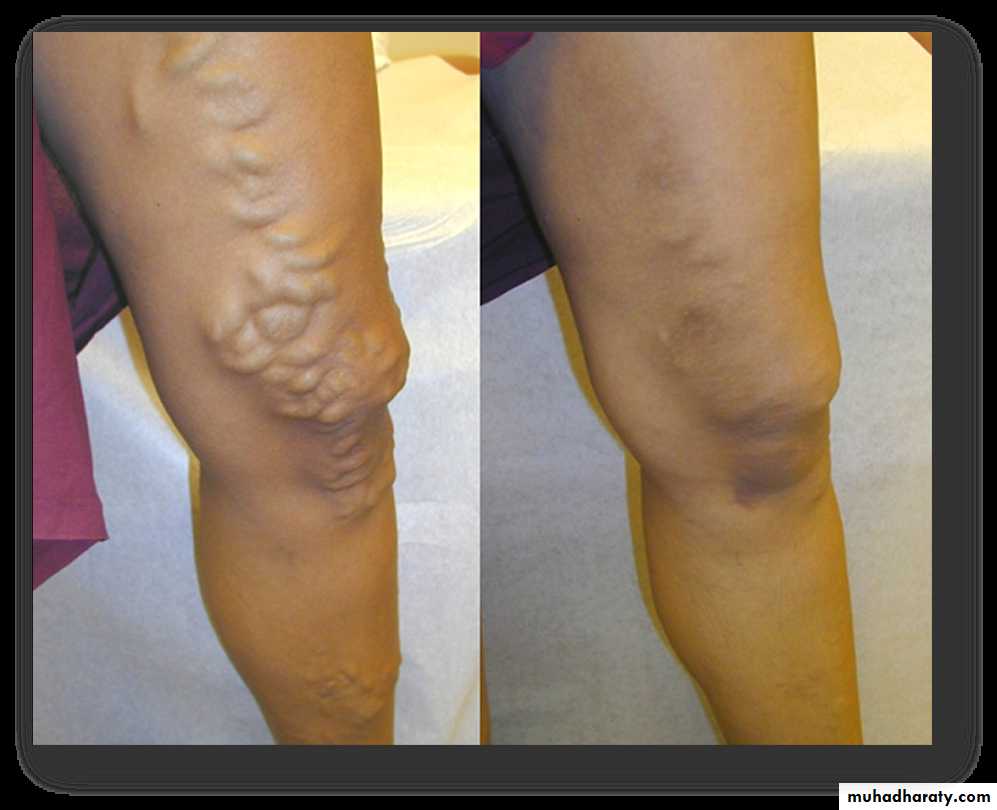
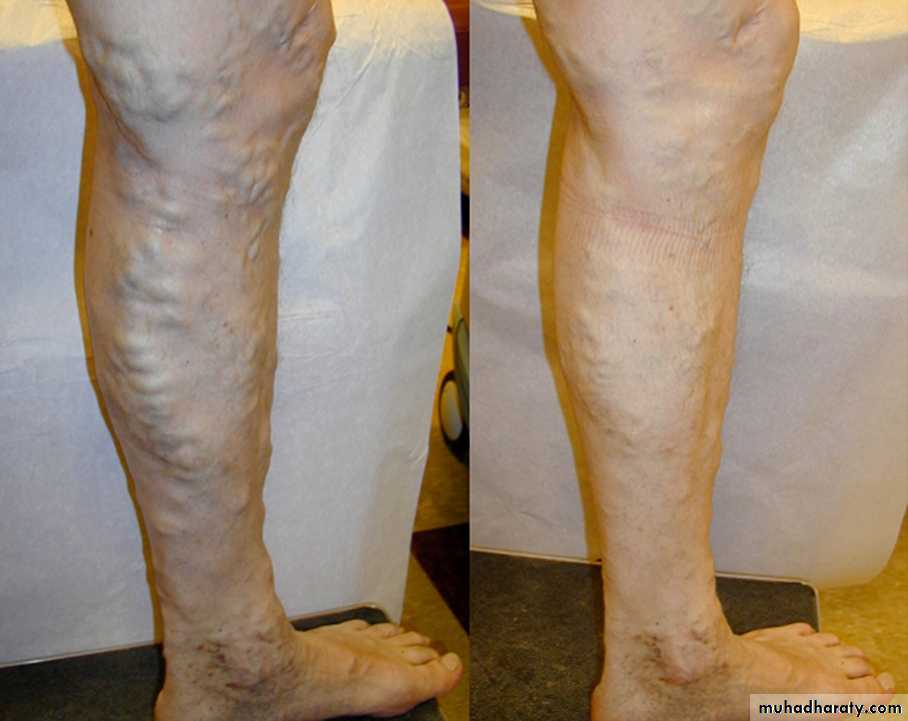
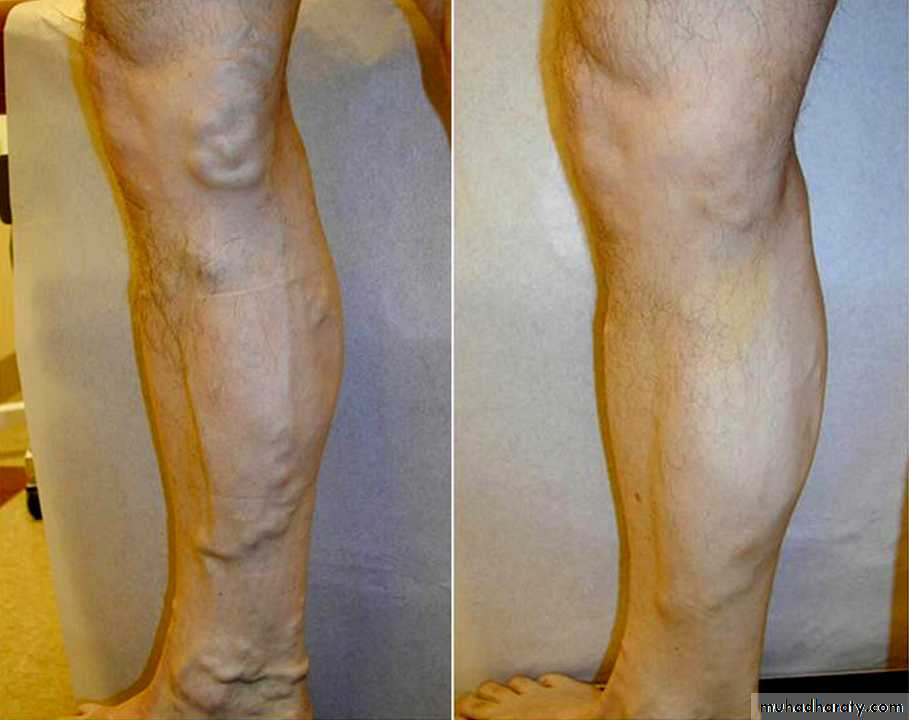
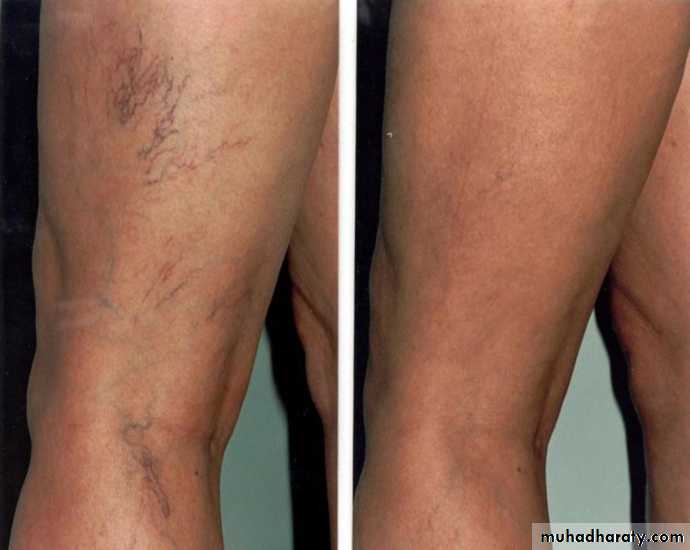
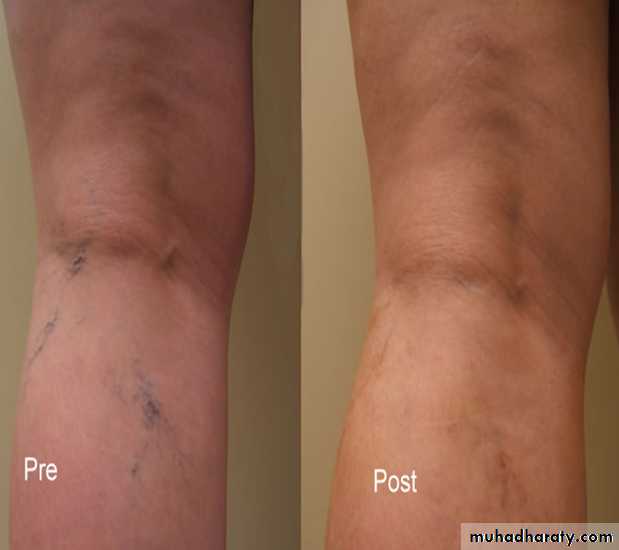
EVLA Results
EVLA Results
EVLA Results
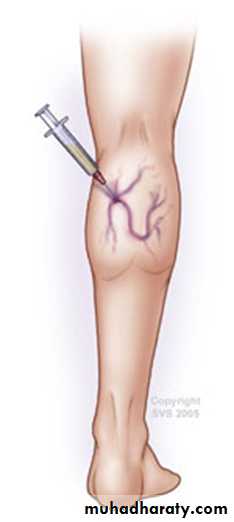
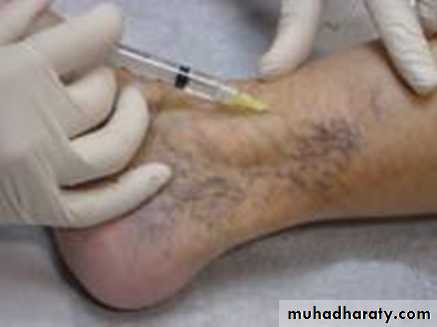
Sclerotherapy
• Cumulate vein with needle• Inject Sclerosing Solution
• Hyper tonic Saline
• Intravenous injection causes intima inflammation and thrombus formation
Sclerotherapy
• Perforators• Spider veins
• Reticular veins
• GSV: can closure the, but has high recurrence rate