BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION(B.O.O.)BLADDER OUT FLOW OBSTRUTION (B.O.F.O.)
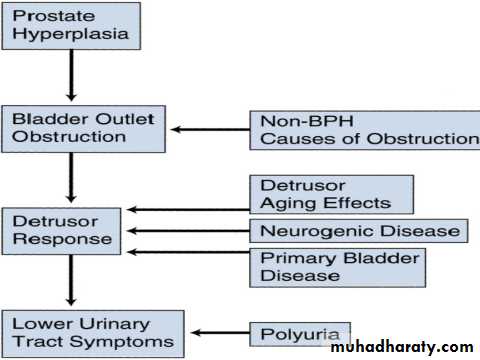
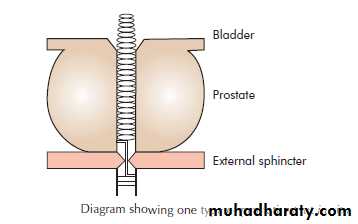
BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTIONIt’s urodynamic concept of low flow rates and high intravesical pressures.
The complex of symptoms referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) is not specific for BPH.
Causes:
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (B.P.H.)
Carcinoma of the prostate (CAP)
Prostatitis
Bladder neck stenosis or contracture.
urethral stricture.
Urethral stones
Bladder tumors (if presents at the bladder neck)
Neuropathic bladder.
Pathophysiology
BOO over time will result in increase in the intravesical pressure, bladder muscle hypertrophy (trabeculation, sacculation and diverticulum formation).High pressure may transmit to the upper tract causing hydroureter, hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency.
BOO results in incomplete bladder evacuation (residual urine) which predisposes to UTI and stone formation.
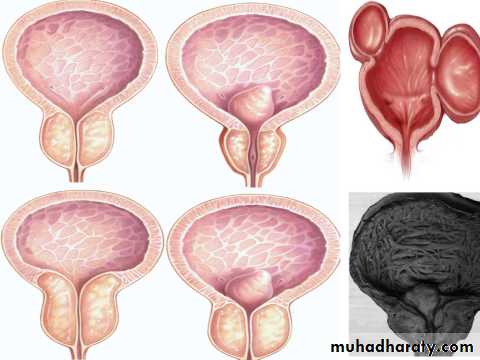
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
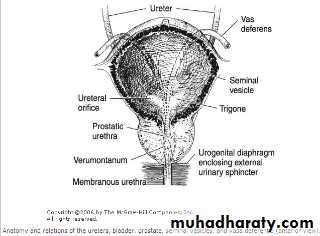
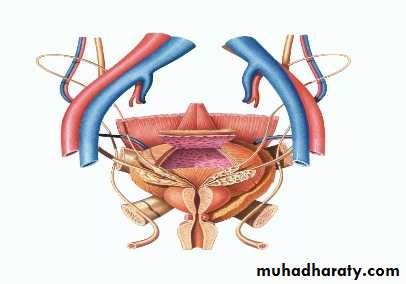
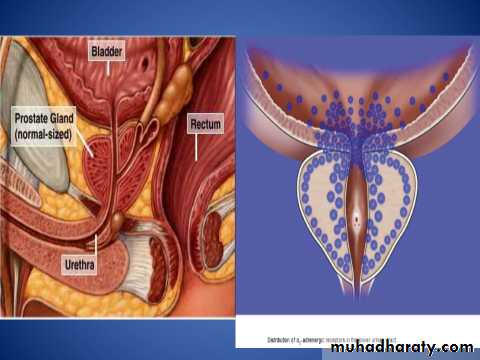
Definition: BPH describes a proliferative process of the stromal and epithelial (stromoglandular) elements of the prostate.Anatomy
fibromuscular & glandular organ
The bladder neck & prostatic bed is abundantly supplied by
1a sympathetic receptors
weighs : 20 gm
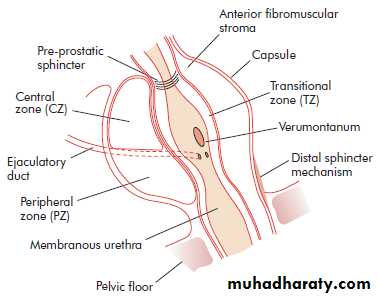
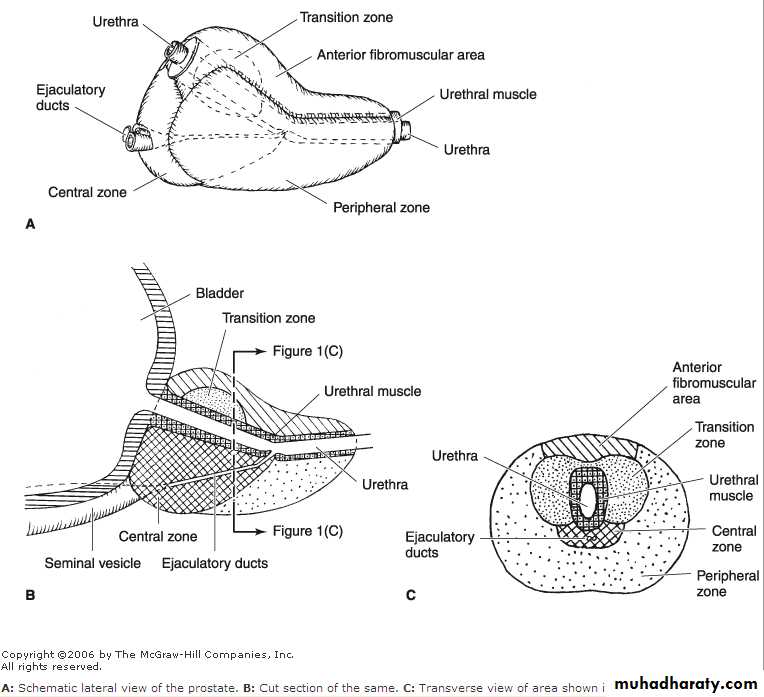
SURGICAL ANATOMY
McNeal classification ofthe prostate into zones:
The central zone
The peripheral zone
The transitional zone
BPH Typically affectssubmucosal glands at transitional zone
Etiology:
Multifactorial and endocrine controlled (Hormonal imbalance)Serum testosterone levels decrease with advancing age.
Oestrogenic steroids do not decrease equally.
( the prostate enlarges because of increased oestrogenic effects.)
Risk factors
Genetic and Familial Factors:
BPH has an inheritable genetic component (autosomal dominant trait).
The first-degree relatives of surgically treated BPH carry an increased risk of developing BPH approximately 4-fold compared with controls.
Racial differences
Abdominal obesity may increase the frequency and severity of obstructive symptoms and may increase the likelihood to undergo prostatectomy.
Incidence & Epidemiology
-BPH is the most common benign tumor in men.-Its incidence is age-related (increases with age).
-The prevalence of Histologic BPH in autopsies:
-20% in men aged 41–50 YEARS.
-50% in men aged 51–60 YEARS.
-Over 90% in men older than 80 Years.
Clinical evidence BPH occurs less commonly:
-25% at age 55 years
-50% at age 75 years
Pathology
BPH affects both glandular epithelium and connective tissue stroma to variable degrees causing:- Glandular hyperplasia
- Fibromuscular hyperplasia
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The symptoms of BPH can be related to either:
1) The obstructive component of the prostate which is divided into:
-The mechanical obstruction.
-The dynamic obstruction.
2) The secondary response of the bladder to the outlet resistance (detrusor instability & low bladder compliance, trabeculation & diverticulae formation in the wall of the bladder & ultimately causes bladder decompensation).
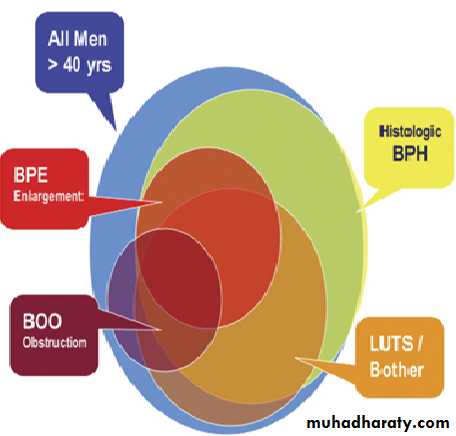
BPH: Is a histologic diagnosis & doesn’t necessarily implies prostatic enlargement (BPE)or presence of symptoms.
BPE
Bladder outlet obstruction(BOO or BOFO)
Lower urinary tract symptoms( LUTS) indicate all lower urinary tract symptoms that results from either outlet obstruction or bladder dysfunction & response of the bladder to a pathology in the prostate or urethra.
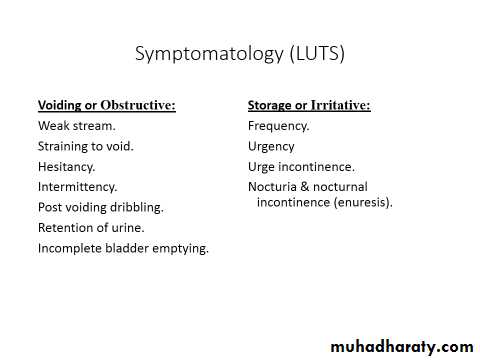
Symptomatology
Slowly progressive over years, worsening at winter time.LUTS: irritative and obstructive.
Urinary retention: inability to pass urine in spite of full bladder (Acute & chronic)
Recurrent UTI
Renal failure due to back pressure effect on the kidneys.
Hematuria.
Pain is not a symptom of BOO: its presence should prompt the exclusion of acute retention, urinary infection, stones.
N.B.: The size of the prostate has no relation to the severity of the symptom but the degree of urethral compression.
Causes of frequency in BPH
Bladder irritation by enlarged prostate.
Residual urine.
Vesical stone.
Cystitis.
Vesical diverticulum.
Chronic retention and overflow incontinence.
Precipitating causes for acute retention
Constipation.Anticholinergics, antihistaminics & diuretic medication (sudden bladder over distention).
Ignoring first desire for urination.
Cold exposure.
Severe pain: MI, joint pain, pelvic or perineal pain.
Psychological upset.
Clinical Exam:
Usually normal.
Distended bladder.
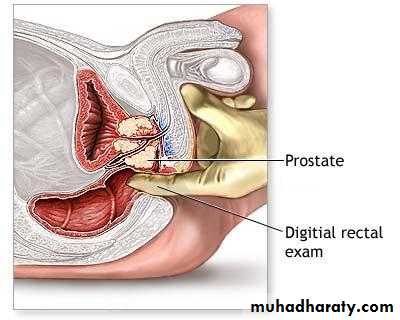
A digital rectal examination (DRE) and a focused neurologic examination should usually be performed
Digital rectal examination (DRE):
enlarged prostate, painless, smooth surface, regular, firm consistency,regular, sulcus, and mobile rectal mucosa over the prostate.
Investigations:
LaboratoryGUE: to rule out UTI and hematuria
RFT: Urea, Creatinine measurement
Serum PSA: (prostate specific Ag) normal value up to 4.0 ng/mL
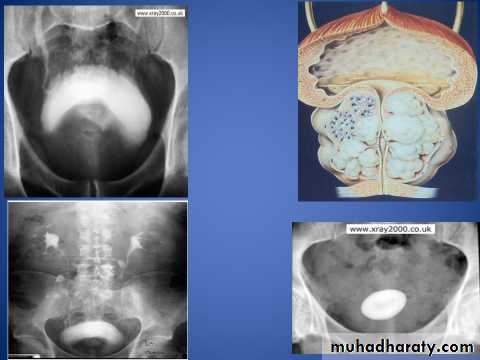
Radiological
U/S: abdominal (conventional) & transrectal(TRUS): Prostatic enlargement, vesical stone, post void residual urine and hydronephrosis.IVU: elevation of bladder base, irregular bladder out line, bladder diverticulum, fish hook lower ureter, vesical stones and residual urine.
Cystoscopy: enlarged prostate, vesical trabeculation & stones.
Urodynamic studies: uroflowmetry
cystometry
Complications of BPH
Recurrent urinary tract infections.Bladder stones.
Recurrent hematuria.
Hydroureteronephrosis & renal impairment.
Refractory urine retention (failing at least one attempt at catheter removal).
Treatment:
Watchful Waiting (conservative)Medical therapy
Surgical Therapy
Conservative:
Indications: mild symptom, reasonable flow rates, and good bladder emptying
Waiting for a period of 6 months
Avoid precipitating factors:
Treat pains.
Treat UTI.
Avoid constipation
Avoid rapid overfilling of the bladder (diuretics)
Avoid anticholinergics & antihistamines.
Do not postpone micturition
Avoid cold exposure
Medical therapy
α-Adrenergic blocking agents: work quickly eg.: prazocin, terazocin, doxazocin , alfuzocin, tamsulosin
S/E : hypotension, retrograde ejaculation,1st dose syncope.
5 α- reductase inhibitors: inhibit the conversion of testosterone to DHT (the most active form of androgen).eg.: Fenasteride, Dutasteride
Need to be taken for at least 6 months, and their effect is greatest in patients with large (> 40 g) glands.
S/E: Impotence.
Phytotherapy: eg. Pumpkin seeds
Surgical (Operative) treatment
Absolute indications for surgical intervention:Refractory urinary retention.
Recurrent UTIs.
Renal insufficiency.
Bladder calculi &\or large bladder diverticula.
Recurrent gross hematuria.
Surgical treatment includes:
Endoscopic: -TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate ), constitutes 95% of simple prostatectomies-TUIP (Transurethral Incision of the Prostate)
Open simple prostatectomy:
- Transvesical prostatectomy. - Rertopubic prostatectomy.
- Perineal prostatectomy.
Minimally Invasive Therapy
TULIP: Transurethral laser-induced prostatectomy
Transurethral Electrovaporization of the Prostate
TUNA: Transurethral Needle Ablation of the Prostate through Interstitial radiofrequency needles
TUMT: trans urethral microwave thermotherapy delivered with a transurethral catheter
HIFU ( high intensity focused u/s)
Urethral stents
Transurethral balloon dilatation of the prostate
TURP syndrome (water intoxication). Dilutional hyponatremia.)
Etiology: absorption of water into the circulation at the time of TURPCausing: congestive cardiac failure, hyponatraemia and haemolysis, confusion, convulsion, sudden death.
Dx.: serum sodium
Treatment: diuretics & normal saline.