Seasonal Influenza and Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1, H5N1) Virus
Dr. Alaa kuttar musaDepartment of Medicine
College of Medicine/ Basra University
Circulating Influenza Strains and Pandemics in The 20th Century
1920 1940 1960 1980 2000H1N1
H2N2
H3N2
1918: “Spanish Flu”
1957: “Asian Flu”1968: “Hong Kong Flu”
20-40 million deaths
1-4 million deaths1-4 million deaths
3
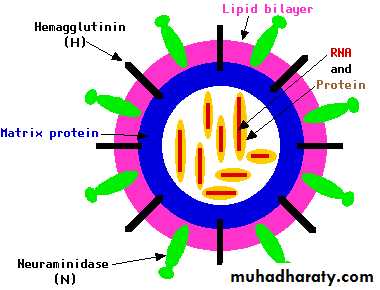
Influenza VirusTypes A and B
• Type A
• (Seasonal, avian, swine influenza,….)
• Type B
• (Seasonal influenza)
• Can cause significant disease
• Generally causes milder disease but may also cause severe disease
• Infects humans and other
• species (e.g., birds; H5N1)
• Limited to humans
• Can cause epidemics and pandemics (worldwide epidemics)
• Generally causes milder epidemics
The InfluenzaVirus
is an acute systemic viral infection that primarily affects the respiratory tract; it carries a significant mortality
Avian influenza
is caused by transmission of avian influenza A H5N1 from poultary .Infections with H5N1 viruses have been severe, with enteric features and respiratory failure.
Swine influenza
H1N1 transmitted from pigs to humans. Re-assortment of swine, avian and human influenza strains can occur in pigs. Sometimes this can lead to an outbreak of swine ‘flu’ in humans( Maxico 2009)
Viral Re-assortment
Reassortment in pigsReassortment in humans
Pandemic Influenza VirusInfluenza Transmission Routes
• Infectious 1 day before and up to 7 daysFever, cough, headache, muscle aches
Sometimes lower respiratory
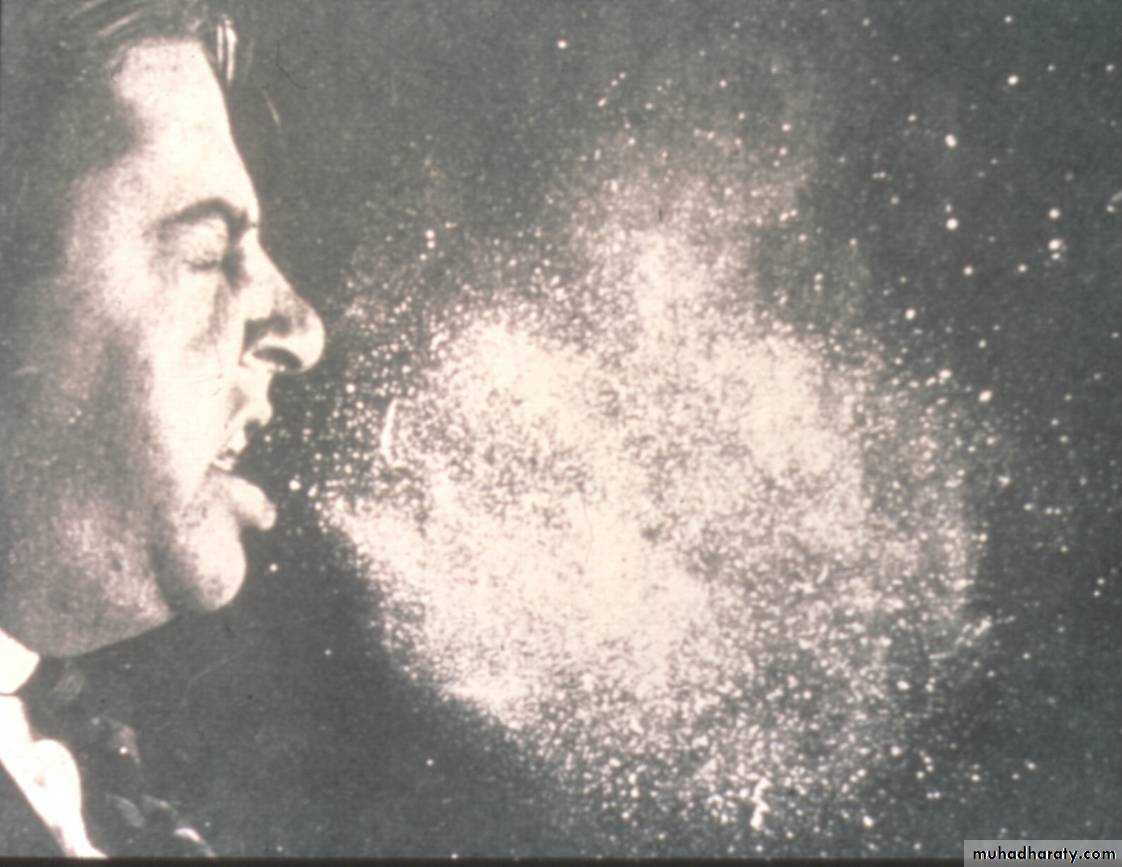
Transmission of influenza viruses
Air droplet from coughing or sneezing
* Person-to-person (H1N1)
* Poultry to human ( H5 N1)
Contact orally or MM with animal or animal products (meat, egg, discharges)
8
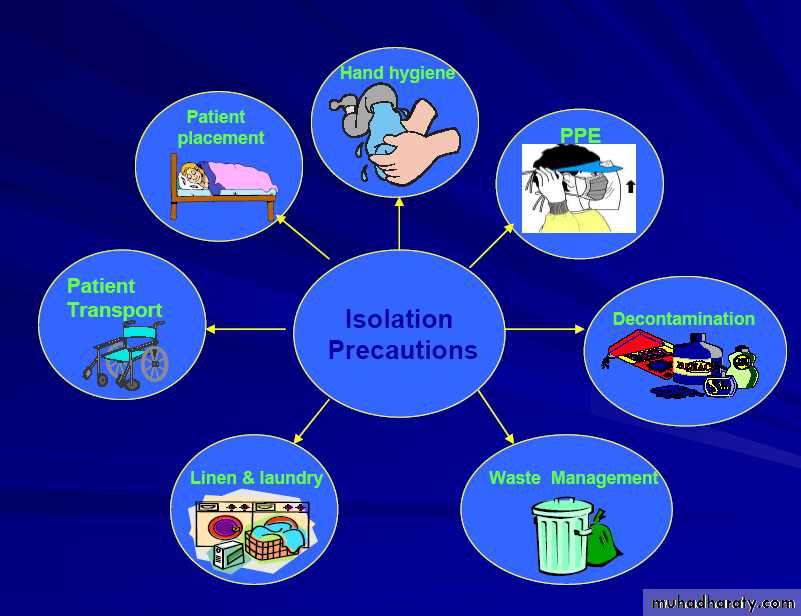
Isolation Precautions
Big droplets
fall on peoplesurfaces bed clothes
Courtesy of CDC
Clinical features
-incubation period of 1–3 days,
-fever, malaise and cough. May followed by Viral pneumonia.
- superinfection with Strep. pneumoniae, Staph. aureus or other bacteria
Complications
extrapulmonary manifestations include:
• myositis, myocarditis, pericarditis• neurological complications (Reye’s syndrome in children, encephalitis or transverse myelitis, fit).
• Mortality is greatest in the elderly, those with medical comorbidities and pregnant women.
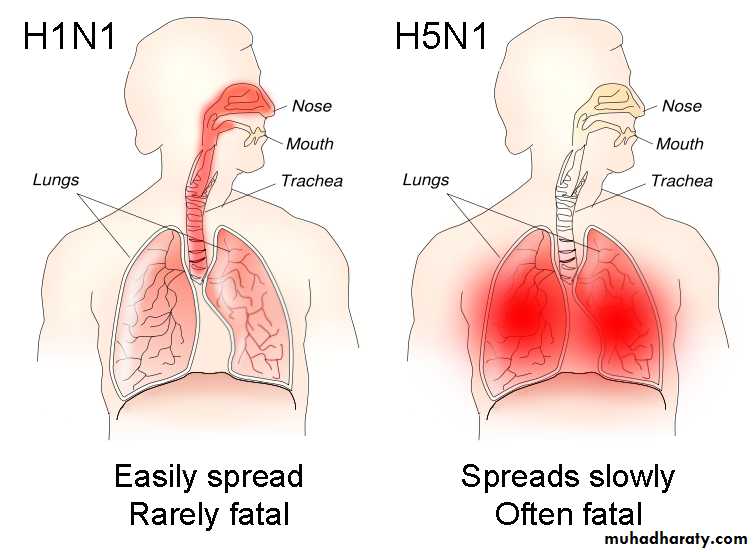
Seasonal Flu
Occurs every year during the winter.Affects up to 10% of the population.
Looks ill, but not life-threatening in most cases.
May complicated by pneumonia but not early
Very young, very old, and people with certain chronic illnesses most at risk.
Vaccines are available to prevent seasonal flu.
Antiviral drugs available to treat those at special risk.
How Do Pandemic Flu and Seasonal Flu Differ?
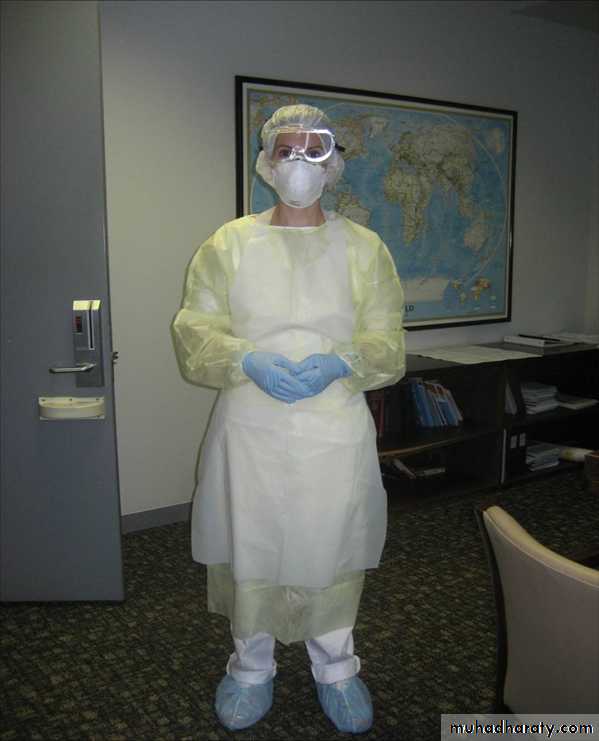
• Droplet precautions: Surgical Masks
• Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
• Ovoid contact with infected patients
• hand hygiene and preventing dissemination of infection by coughing and sneezing
• seasonal vaccination
Prevention
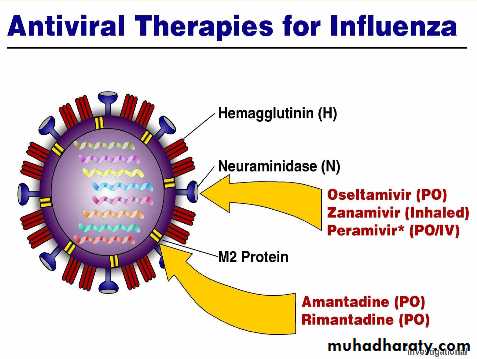
Antivirals- Oseltamivir
• Administration of neuraminidase inhibitor, oral oseltamivir (75 mg twice daily) or inhaled zanamivir (10 mg twice daily) for 5 days• Prophylaxis is 75 mg once a day for 7 days after last exposure
•