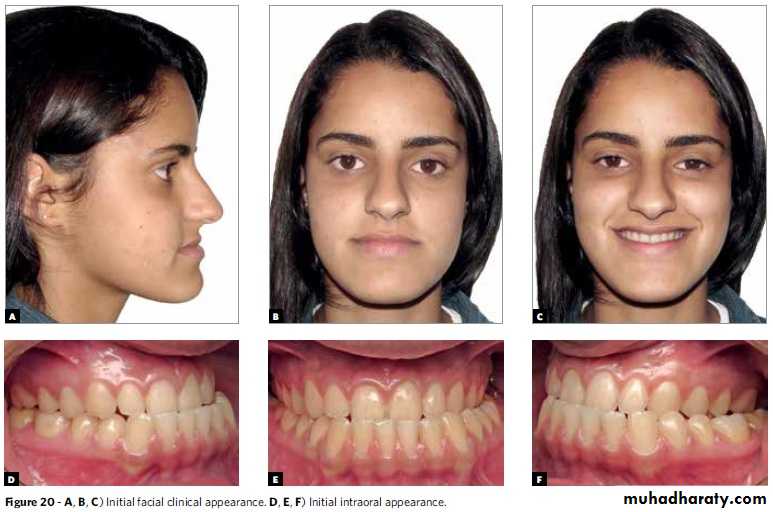
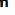Extra oral appliance in Treatment of Skeletal Problems in Preadolescent Children
The Timing for Growth Modification
Patient is growing (with in growth Period)The growth become
• faster from (birth till 5 years) then
• it become slow till the onset of growth Spurt which is about (10-11½) years in girls, (12½-13) years in boys & the spurt last for about (2-2½) years in both sex. Then the growth become slow till end at (18 years in girls & 20 years in boys)
The Timing for Growth Modification
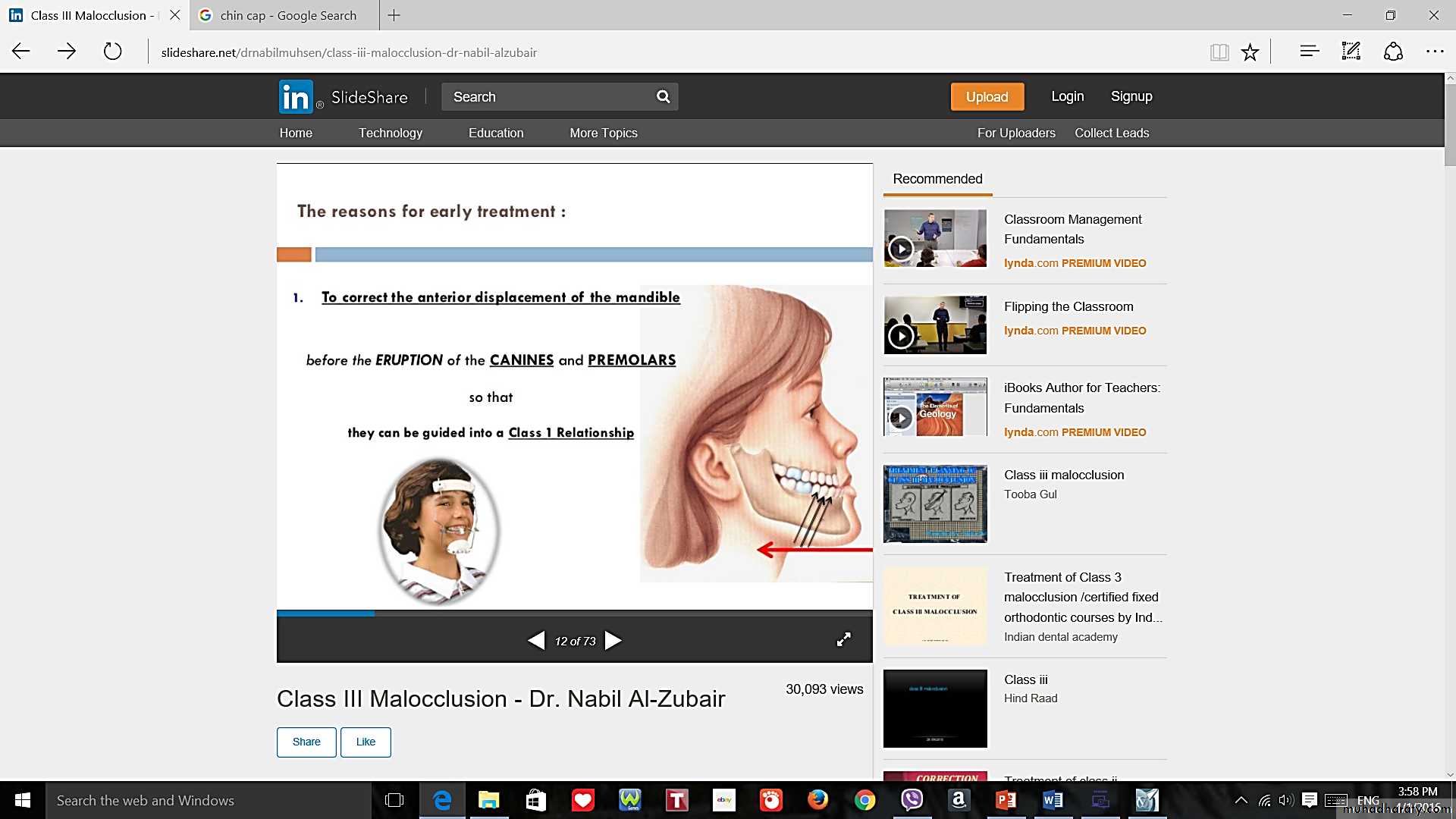
Skeletal Treatment should begin before the end of growth Spurt which is about 13 years in girls & 14 years in boys.The Timing for Growth Modification
• Rapid growth That occur during primary dentition (4-6) years indicate successful result for growth Modification but it need retention for prolonged period till completion of growth (till end of growths spurt) unless relapse will occur.The Timing for Growth Modification
Delay treatment has a problem:no growth Sufficient remain specially after eruption of 3,4,5 & 7.
Principles of Growth Modification
Accelerate growth Of deficient bone.
Restrain growth Of excessively growing bone
Redirect the growth Of some difficult to be restrained like excessively growing Mand.
Classification of Skeletal Problems
Mand. Excess.Mand. Deficiency
Max. Excess (sagital & vertical)
Max. Deficiency (sagital, vertical & transverse)
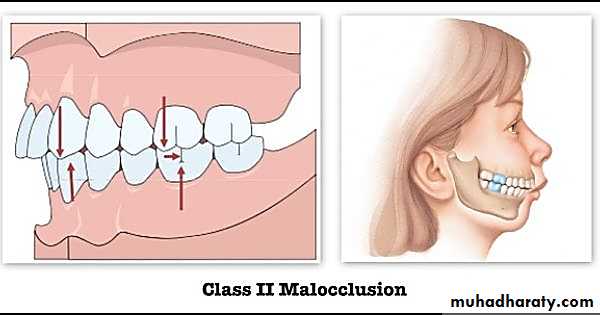
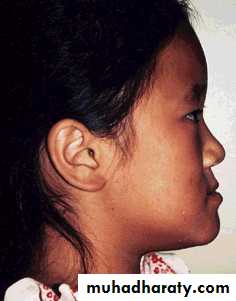
Cl. III malocclusion due to excessively growing mand.
Mand. ExcessMand. Excess
Options of treatmentsExtra Oral Force to Mandible: (Chin Cup or Cap)
Intra Oral Force to Mandible: Functional Cl.III or Frankle Cl.III Appliance
Mand. Excess
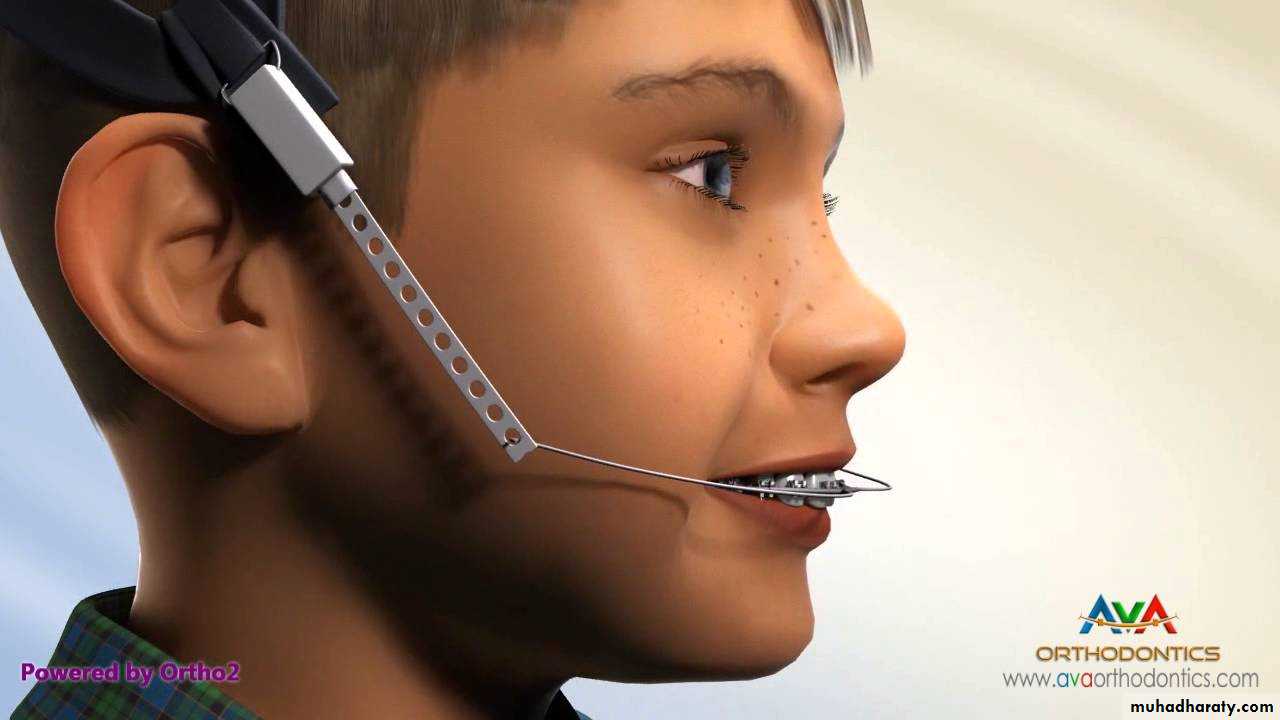
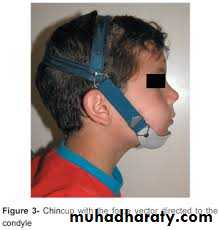
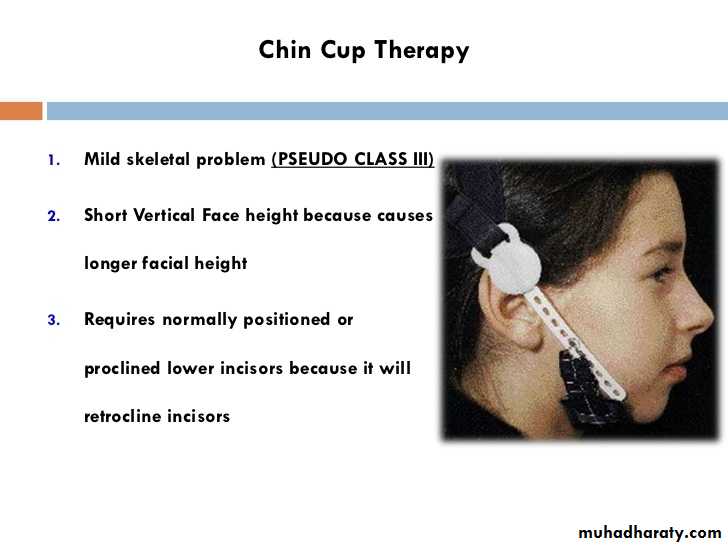
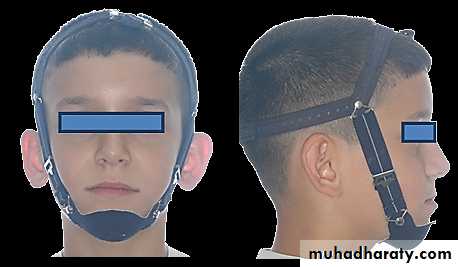
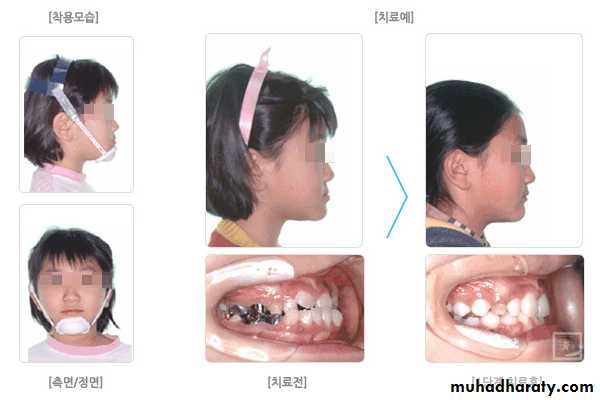
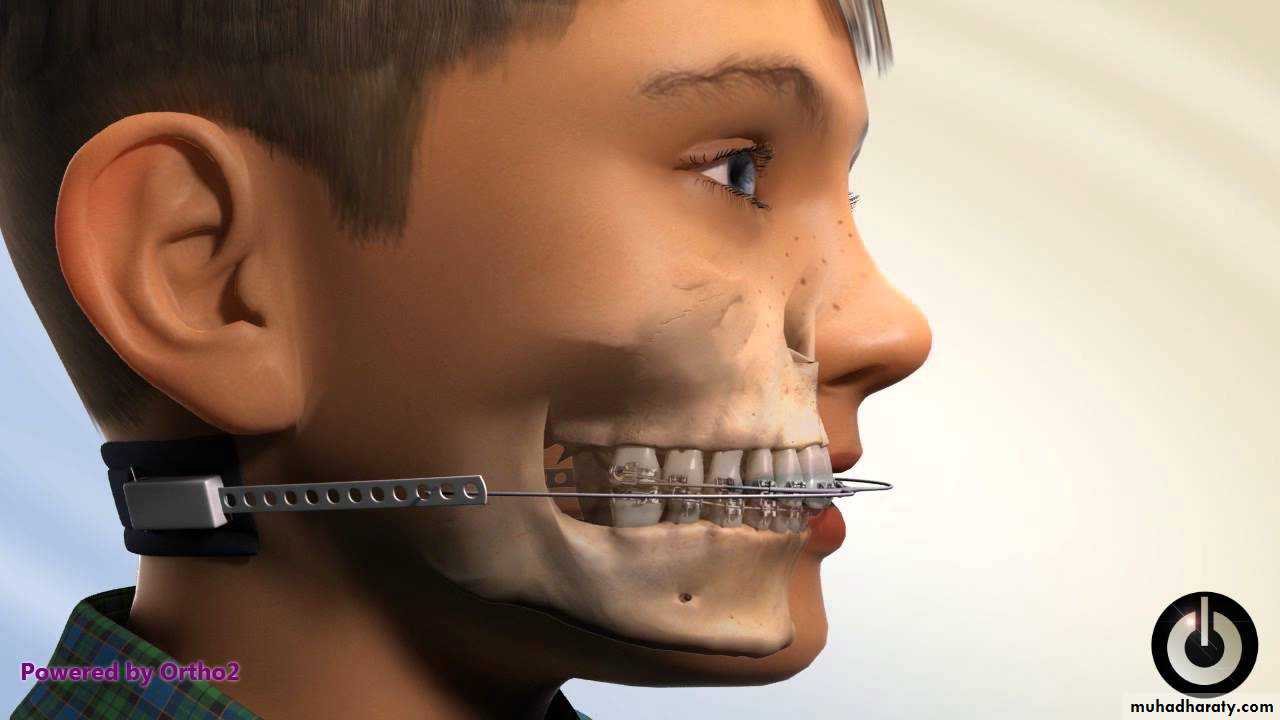
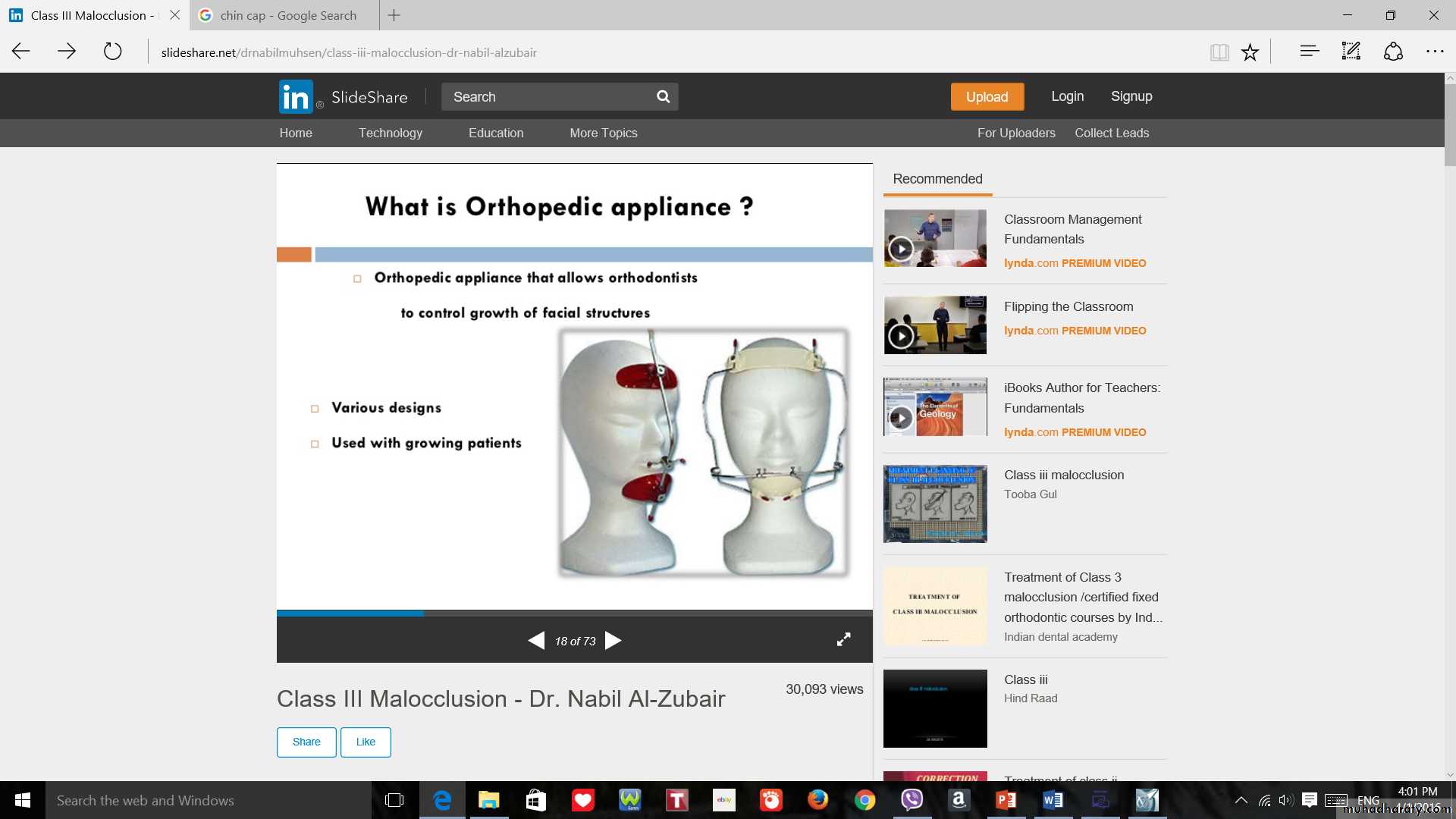
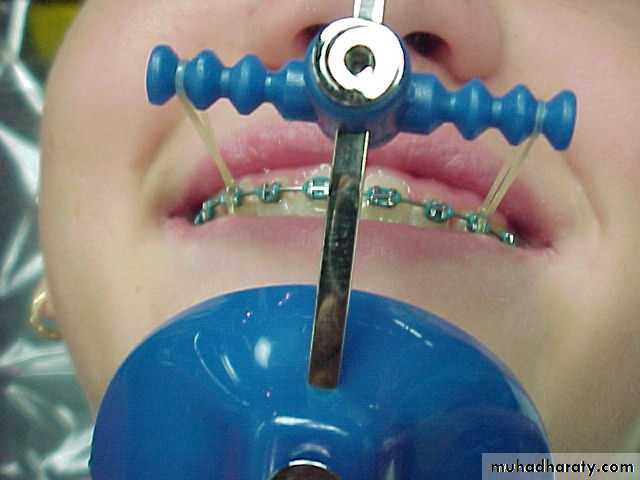
Chin cap (Chin cup) Appliance
Extra oral orthopedic appliance that consists of a cap that fits on the patient’s chin and a head strap.
It is designed to deliver a superiorly and posteriorly directed force to the mandibular condyles, via the chin.
The appliance has been used to correct mandibular prognathism in young patients by restraining or redirecting mandibular condylar growth.
Mand. Excess
Ideal Patients for chin cupMild problem with ability of patient to bring incisors into edge to edge relation.
Short vertical facial height.
Normally positioned or protrusive lower incisors but not retrusive.
Mand. Excess
Chin cupMode of actions as it attached to head cap, so it produced the followings:
A. Orthopedic effects :
via changing the forward downward rotation into backward & downward rotation so it will decrease the prominence of chin & profile.
It increase the anterior Facial height .
Chin cup
B. Orthodontic Effects:
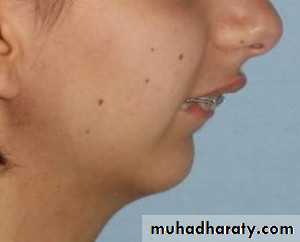
• a: it produce lingual tipping of lower incisors due to pressure on lip & teeth.b:labial tipping of upper incisors as lower one tipped lingually.
Mand. Excess
Mand. Excess
Chin cupForce applied is about: 16-24 ounce / side.
Direction of pull:
• A: through condyle as restraining device for Mand. growth Is impossible due to the nature of TMJ.
• B: Sub Condyle: rotation of Mand. Backward & downward that need lighter force.
Mand. Excess
Despite the many trial of modifying mand. growth Most of them need future surgery.Mand. Deficiency
Mand. Deficiency
Options of treatmentsAcceleration of Mand. growth & inhibit Max. growth Anter-posteriorly using Functional Cl.II Appliance which is the best.
Mand. Deficiency
Options of treatments• Inhibition of antero-posterior growth Of Max. & let Mand. growth anteriorly Using head gear with face bow, this method not greatly significant for Mand.
Max. Excess
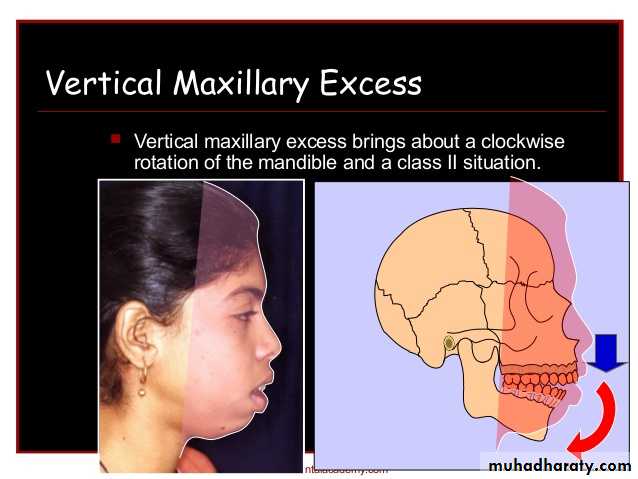
(Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
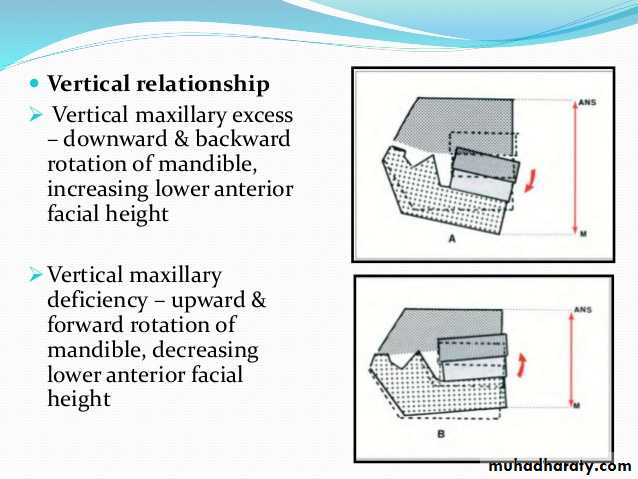
Usually the max. Excess or deficiency in anteroposterior Direction, are accompanied with vertical Excess or deficiency respectively. Due to too much or little growthManagement by face bow with head or neck gear.
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
really both forward & downward growth Max. lead to Cl.II malocclusions as:a: forward growth Lead to anterior Displacement of Max.
b: downward(vertical) growth Lead to downward & backward rotation of Mand.
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
5. Extra oral head gear effects:a: restrain forward & downward growth Of Max.
b: if well developed Mand., it’s forward growth Is necessary to correct cl. II but if not well developed mand. A functional Cl.II appliance is need to stimulate growth Of Mand.
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
6. Force application:
a: 10-12 H / day wearing of appliance.
b: 350 – 450 gm / side (not greater than 1000 gm total)
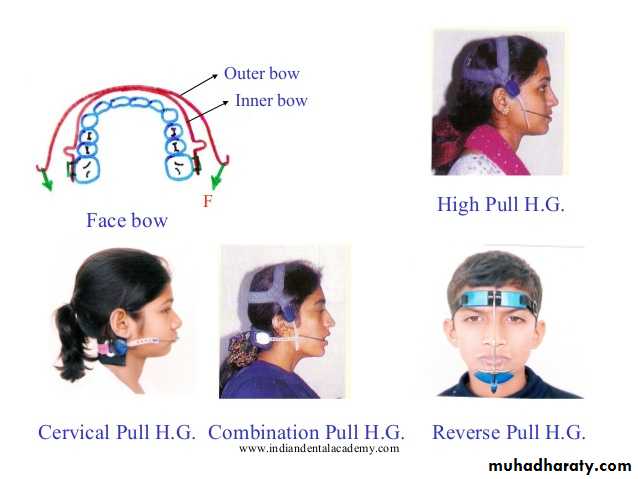
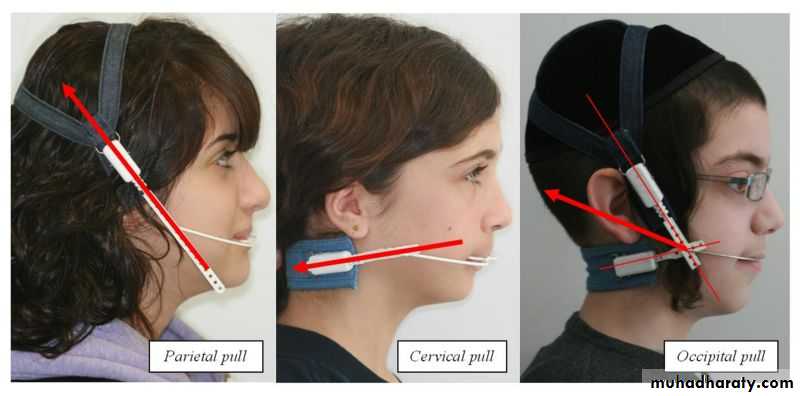
Selection of head gear type
3 major design are:1. At which cranial structures outer bow is attached:
a: head cap (gear)
b: neck cap (gear)
c: combination of above.
2. inner bow is attached to molar tube:
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
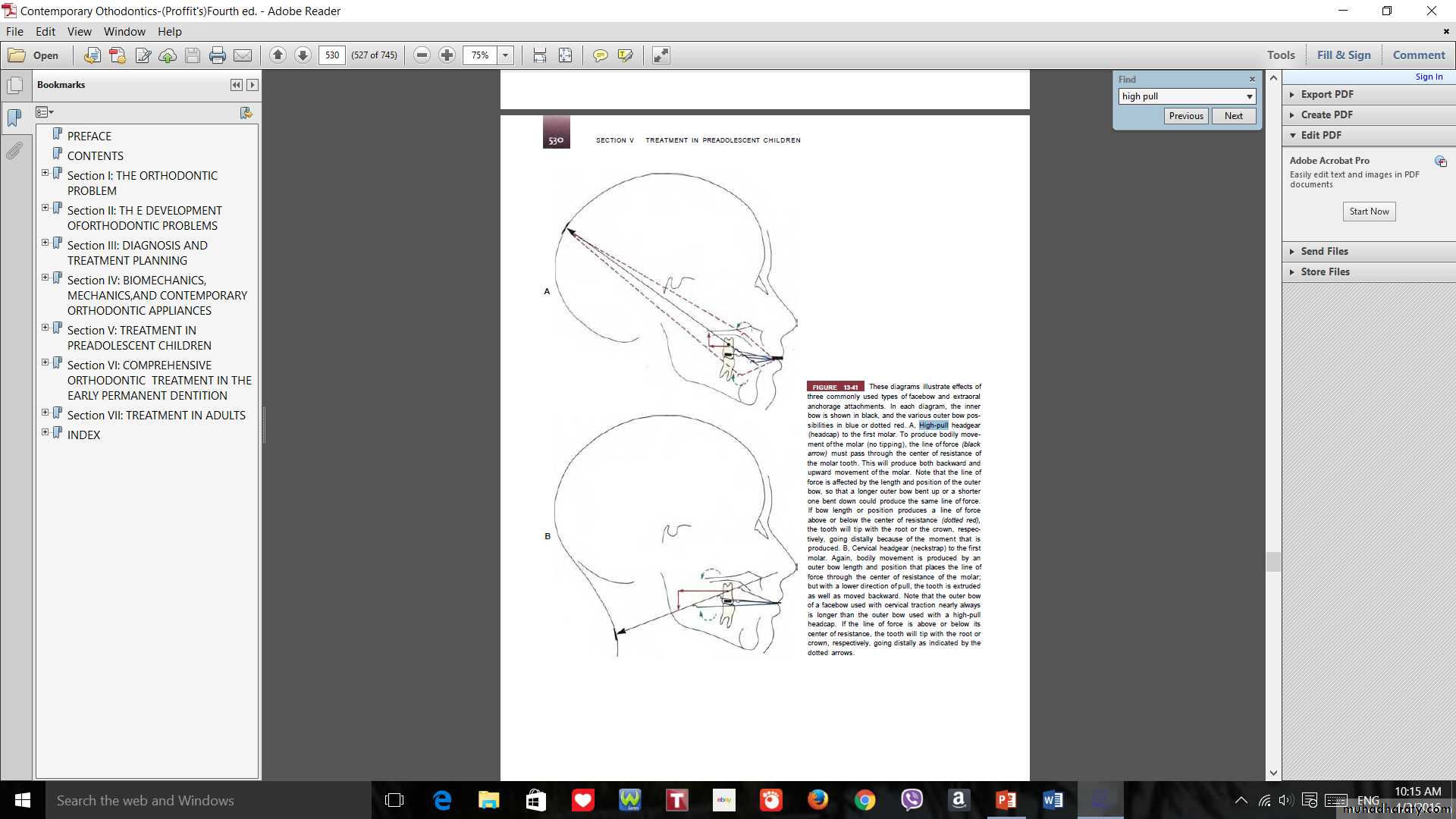
Selection of head gear type3 types of pulls are:
• High Pull (correction of open bite)
• Straight Pull (normal over bite)
• Low Pull (correction of deep bite)
1
2
3
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
Selection of head gear type2. At where in the oral cavity the inner bow is attached:
a: almost always upper 6 tube that prewelded into band.
b: into tube inserted in acrylic of removable or functional appliance at level of premolar areas.
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
Selection of head gear type3. Type of movement of tooth or bone (Maxilla)
a: bodily movement of upper molar
b:crown tipping movement of upper molar
c: root tipping movement of upper molar
d: extrusion movement of upper molar
e: intrusion movement of upper molar
Max. Excess (Cl. II Skeletal discrepancy)
Head gear mechanicsIt has loop before it’s insertion in tube of 6, this loop for adjustment to expand or contract it.
Max. Excess (vertical Excess)
Long face syndrome (anterior Open Bite)also referred to as skeletal open bite is a condition generally caused by childhood mouth breathing.
Max. Excess (vertical Excess)
Long face syndrome (anterior Open Bite)as vertical growth is continued for post adolescent period so that retention is mandatory.
Ideal treatment via controlling of vertical growth of Max. so need to rotate mand. forward & upward,Max. Excess (vertical Excess)
Long face syndrome (anterior Open Bite)Options of treatments
1. High pull head gear to the molar, this inhibit vertical eruption of post. Teeth
Functional appliance with bite block: that applies intrusion forces on post. Teeth & allow anterior Teeth for further eruption, & so mand. Will rotate forward & upward.
Max. Deficiency (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
Such deficiency usually affect sagital & vertical dimension & sometime affect transverse plane also.Max. deficiency of sagital & vertical dimension (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
Max. deficiency of sagital & vertical dimension (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
ant.post max. Deficiency has direct effect on Cl.III production either due to small size or post. Positioned max.Vertical deficiency has indirect effect on Cl.III production as it lead to upward & forward rotation of Mand. Rather than increasing in the size of mand.
Options of treatments
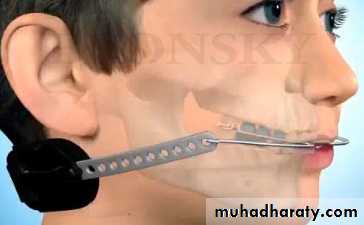
Extra Oral Force to Maxilla: (reverse facial mask) (Delaire)
Intra Oral Force to Maxilla: Functional Cl.III or Frankle Cl.III Appliance
Max. deficiency of sagital & vertical dimension (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
Extra Oral Force to Maxilla: (reverse facial mask) (Delaire)
is an orthodontic appliance to correct (Class-III orthodontic problems) by pulling forward and assisting the growth of the upper jaw (maxilla), allowing it to catch up to the size of the lower jaw (mandible).Max. deficiency of sagital & vertical dimension (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
Extra Oral Force to Maxilla: (reverse facial mask) (Delaire)
EFFECTS
Orthopedic effects: on max. & mand.
max: it pull the max. Forward & downward that lead to rotation of mand. Backward & downward., so the mask is contraindicated in long face syndrome.
Orthodontic effects:
a. Protraction of max. Teeth.b. Retraction of mand. Teeth.
Max. deficiency of sagital & vertical dimension (Cl. III Skeletal discrepancy)
Mechanicsanchorage is achieved from frontal & chin bones.
Forces applied to pull max. via attaching extraloral appliance, into either:
a: fixed appliance.
b: removable appliance
c: expander (W-Arch)