Heart Failure
Objectives1- to know the common causes of heart failure.
2- Types of heart failure .differentiation between systolic & diastolic failure. Staging of H.F
3- Clinical signs of heart failure & lab tests &their findings in diagnosis of H.F.
4- Treatment of systolic & diastolic failure.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERPathophysiology
Hemodynamic changes
Neurohormonal changes
Cellular changes
Congestive Heart Failure CHFSUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERNeurohormonal changes in CHF
RAS, renin-angiotensin system; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.
Myocardial injury to the heart (CAD, HTN, CMP, Valvular disease)
Morbidity and mortality
ArrhythmiasPump failure
Peripheral vasoconstriction
Hemodynamic alterations
Heart failure symptoms
Remodeling and progressive
worsening of LV function
Initial fall in LV performance, wall stress
Activation of RAAS and SNS
Fibrosis, apoptosis,hypertrophy, cellular/molecular alterations,myotoxicity
FatigueActivity altered Chest congestionEdemaShortness of breathCongestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERNeurohormonal changes
• N/H changes
• Favorable effect
• Unfavor. effect
• Sympathetic activity
• HR , contractility,
• vasoconst. V return,
• filling
• Arteriolar constriction
• After load workload
• O2 consumption
• Renin-Angiotensin –
• Aldosterone
• Salt & water retention VR
• Vasoconstriction
• after load
• Vasopressin
• Same effect
• Same effect
• interleukins &TNF
• May have roles in myocyte hypertrophy
• Apoptosis
• Endothelin
• Vasoconstriction VR
• After load
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER• Volume overload: Regurgitate valve
High output status
• Pressure overload: Systemic hypertension
Outflow obstruction—AS
• Loss of muscles: Post MI, Chronic ischemia
Connective tissue diseases
Infection, Poisons (alcohol,cobalt,Doxorubicin)
• Restricted Filling: Pericardial diseases,
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Tachyarrhythmia
Causes of CHF
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERTypes of CHF
Systolic & Diastolic
High Output Failure
• Pregnancy, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, A/V fistula, Beriberi, Pagets disease
Low Output Failure
Acute
• large MI, aortic valve dysfunction---
Chronic
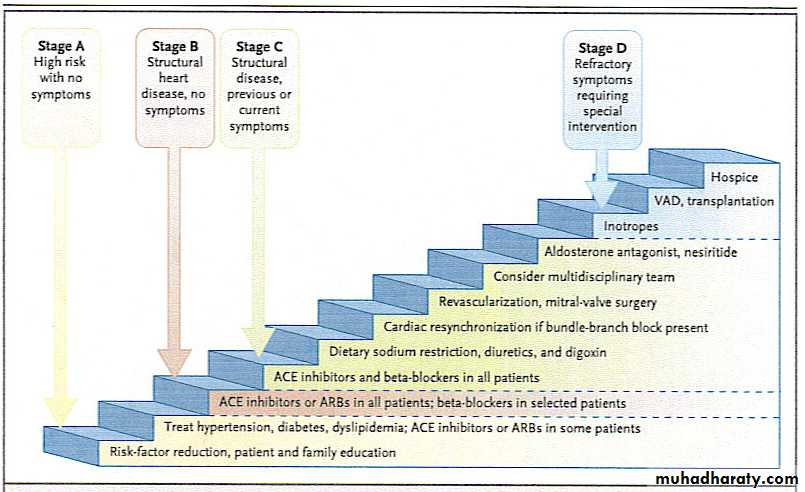
CLINICAL STAGES OF HEART FAILURE.
STAGE A: risk factors ,no structural disease or symptoms.STAGE B : structural disease but no symptoms.
STAGE C : structural disease with prior or current symptoms.
STAGE D : refractory disease with severe symptoms.
Precipitants of H F:1- Myocardial ischemia. As ACS.
2- Hypertension.
3- Arrhythmias.
4- Infections.
5- Drugs & Toxins.
6- Diet .
7- Noncompliance.
8- acute pulmonary embolism.
9- Anaemia.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
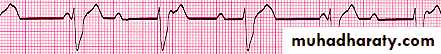
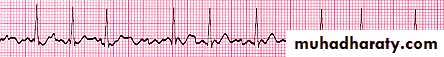
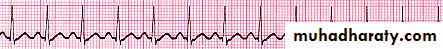
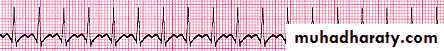
Rhythm problems leading to CHF
DIAGNOSIS OF HEART FAILURE
Signs & Symptomes Of H FDyspnea on exertion & later on at rest.NYHA 1 – 4 .
Orthopnea & PND.
Fatigue & poor exercise tolerance.
Plapitation & syncope.
Cough specialy at night.
Leg swelling.
Raised JVP.
Basal rales.
S3 gallop.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERFramingham Criteria for CHF
Major Criteria:
• PND
• JVD
• Rales
• Cardiomegaly
• Acute Pulmonary Edema
• S3 Gallop
• Positive hepatic Jugular reflex
• ↑ venous pressure >16 cm H2O
Minor Criteria
1- Bilateral leg odema.2- Dyspnea on exertion.
3- Pleural effusion.
4- Hepatomegaly.
5- Heart rate more than 120 per min.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
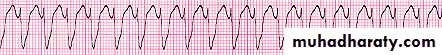
HEART CENTEREKG
Old MI or recent MI
Arrhythmia
Some forms of Cardiomyopathy are tachycardia related
LBBB→may help in management
Heart Block
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
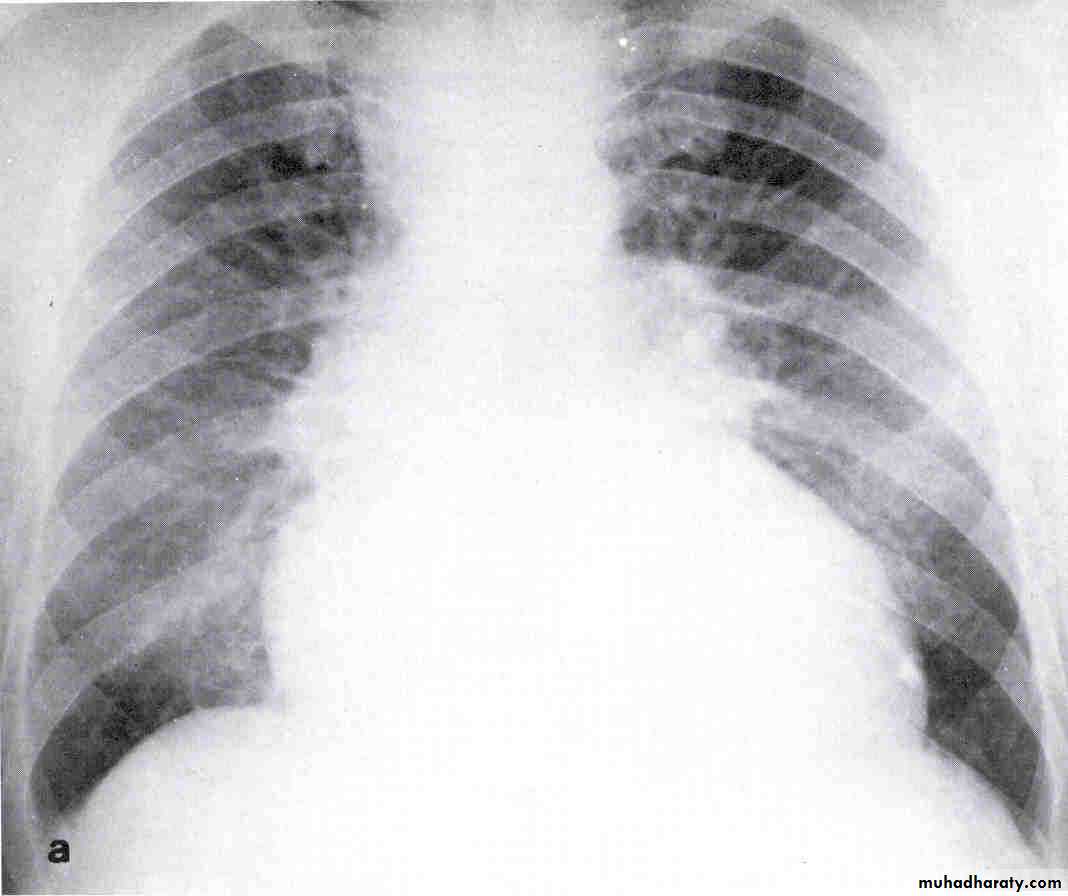
Chest X-ray
Look for Heart sizePulmonary vascular markings
COPD, pneumonia, Pneumothorax, widened mediastinum
Pleural effusions
Chest X- ray
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
Echocardiogram
Function of both ventricles
Wall motion abnormality that may signify CADValvular abnormality
Intra-cardiac shunts
Pericardial effusion
Restrictive pericarditis
Pulmonary hypertension
Diagnostic tests:
4- B-type natriuretic peptide ( BNP ).Cutoff level 150 pg / ml. senstivity =90 %
specificity 70%. Use in acute setting only.
Affected by age ,renal function & BMI.
5- other tests : BUN, s.electrolytes, CBC, thyroid function test, s.iron & s.ferritin.
Congestive Heart Failure CHFSUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERCardiac Catheterization
Coronary artery disease
Dilated ventricleHyperdynamic small ventricle
Wall motion abnormality that may signify CAD
Valvular abnormality
Intra-cardiac shunts
Pulmonary hypertension
Systolic versus diastolic failure
SYSTOLIC DYSFUNCTIONDIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION
Dilated cardiac chambers.
Cardiomegaly on CX-ray.
Low EF < 40 %.
Worse prognosis.
Normal size or LVH.Pulmonry congestion +normal cardiac size.
Normal EF > 40 % ,E/A< 1Good prognosis.
Congestive Heart Failure CHFSUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERGoals for CHF management in a hospital
• Relieve symptoms rapidly
• Reverse hemodynamic abnormalities
• Prevent end-organ dysfunction
• Initiate patient education and survival-enhancing medications before discharge
• Optimize survival-enhancing oral medications (ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, aldosterone receptor antagonist)
• Optimize patient education and HF disease management
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERCHF Management-long term
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERDiet and Activity
Salt restriction (2 grams per day)
Fluid restriction (Less than 1-2 liters per day)Daily weight (tailor therapy)
Gradual exercise programs
Blood sugar monitoring
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERTreatment of CHF
Correction of reversible causes
• Medications
• Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blokers etc.
• Ischemia
• Arrhythmia: A fib, flutter, PJRT
• Valvular heart disease
• Thyrotoxicosis and other high output status
• Shunts
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERCHF treatment-Acute
Pharmacological
Morphine sulfateNitrates
Diuretics
ACE inhibitors
Beta blockers
Aspirin therapy
statins
Vasodilators
Neurohormonal antagonists –
Anticoagulant therapy –
Antiarrhymics
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERDiuretics
Loop diuretics for more severe heart failure
• Lasix (20 – 320 mg QD), Furosemide
• Bumex (Bumetanide 1-8mg)• Torsemide (20-200mg)
• Mechanism of action: Inhibit chloride reabsortion in ascending limb of loop of Henle results in natriuresis, kaliuresis and metabolic alkalosis
• Adverse reaction:
• pre-renal azotemia
• Hypokalemia
• Skin rash
• Ototoxicity
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERDiuretics
K sparing diuretics
Triamterene
Amiloride – acts on distal tubules to ↓ K secretionSpironolactone (Aldosterone inhibitor)
Recent evidence suggests that it may improve survival in CHF patients due to the effect on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system with subsequent effect on myocardial remodeling and fibrosis
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
Renin, angiotensin, aldasterone blockers• Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is activation early in the course of heart failure and plays an important role in the progression of the syndrome:
• Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors)
• Angiotensin receptors blockers (ARBS)
• Spironolactone
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERRenin-angiotensin blockers
They block the R-A-A system by inhibiting the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II:
→ Vasodilation
→ Na retention ↓
→ Decreased Bradykinin degradation ↑ its level → ↑ PG secretion & nitric oxide
Ace Inhibitors improve survival in CHF patients
• Delay onset & progression of HF in pts with asymptomatic LV dysfunction
• ↓ cardiac remodeling
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERBeta Blockers
Has been traditionally contraindicated in pts with CHF
Now they are the main stay in treatment on CHF & may be the only medication that shows substantial improvement in LV function
In addition to improved LV function multiple studies show improved survival
The only contraindication is severe decompensated CHFCongestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
Inotropic agents-DigoxinThe role of digitalis has declined somewhat because of safety concern
Recent studies have shown that digitals does not affect mortality in CHF patients but causes significant
• Reduction in hospitalization
• Reduction in symptoms of HF
• Rate control in At fib.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERInotropic agent-Digoxin action
+ve inotropic effect by ↑ intracellular Ca & enhancing actin-myosin cross bride formation (binds to the Na-K ATPase → inhibits Na pump → ↑ intracellular Na → ↑ Na-Ca exchange
Vagotonic effect
Arrhythmogenic effect
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERInotropic agent-Digitalis toxicity
Narrow therapeutic to toxic ratio
Non cardiac manifestations
• Anorexia,
• Nausea, vomiting,
• Headache,
• Xanthopsia sotoma,
• Disorientation
• Treatment: Digibind (Fab antibody)
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERAntiarrhythmics
Most common cause of SCD in these patients is ventricular tachyarrhythmia
Patients with h/o sustained VT or SCD → ICD implantPatients with CHF with an ejection fraction of less than 30% may receive ICD implant
Amiodarone for patients with frequent VPCs and at fibDranedone for patients with recurrent paroxysmal at fib.
Congestive Heart Failure CHFSUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
AnticoagulationAtrial fibrillation
H/o embolic episodesLeft ventricular apical thrombus
Low LV ejection fraction
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERInotropic Agents
These are the drugs that improve myocardial contractility (β adrenergic agonists, dopaminergic agents, phosphodiesterase inhibitors),
Dopamine
Dobutamine
Milrinone,
Aamrinone
Several studies showed ↑ mortality with oral inotropic agents
So the only use for them now is in acute sittings such as cardiogenic shock
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERNew Treatment Choices
Implantable ventricular assist devices
Biventricular pacing (only in patient with LBBB & CHF)Artificial Heart
Congestive Heart Failure CHFSUGAR LAND
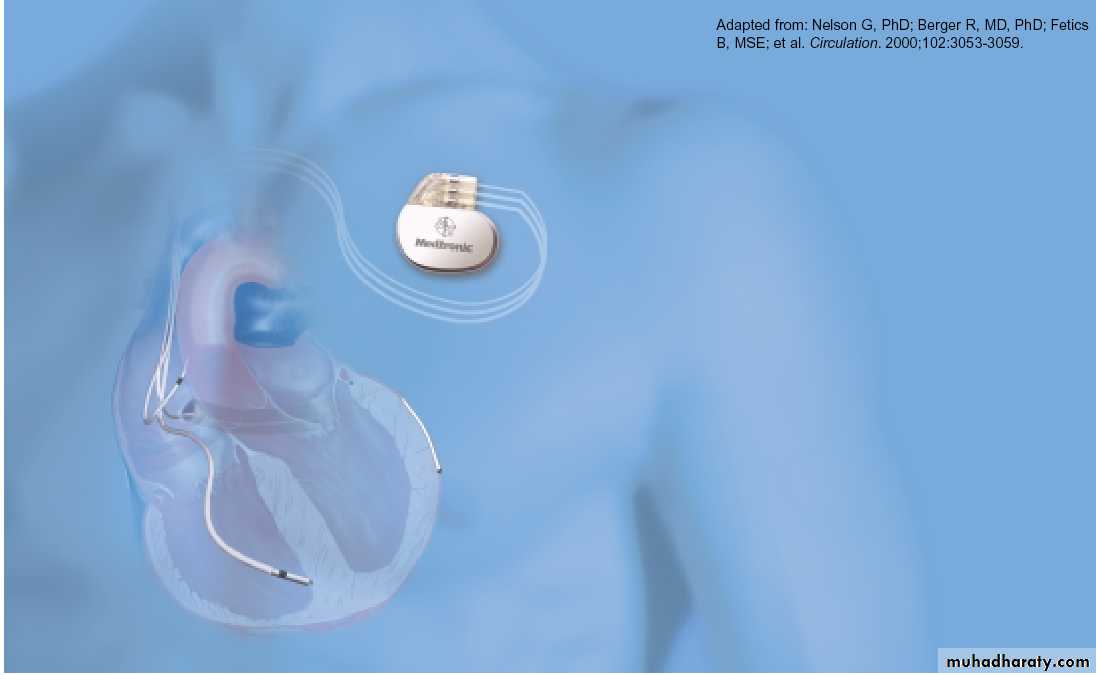
HEART CENTERAchieving Cardiac ResynchronizationMechanical Goal: Atrial-synchronized bi-ventricular pacing
• Standard pacing lead in RA
• Standard pacing or defibrillation lead in RV
• Specially designed left heart lead placed in a left ventricular cardiac vein via the coronary sinus
Right AtrialLead
Right VentricularLeadLeft VentricularLead
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTER
PacingCongestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERCHF treatment-Acute
• NTG- SL and IV infusion
• Morphine sulfate: 2-6 mg IV
• Lasix 40-80 mg IV
• O2—High flow O2
• CPAP
• Foley catheter
Congestive Heart Failure CHF
SUGAR LAND
HEART CENTERDifferential Diagnosis of CHF
Pericardial diseases
Liver diseasesNephrotic syndrome
Protein losing enteropathy