1
Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-8
.د
هديل
5/4/2016
Computerized tomography (CT scan)
Introduction
Tomography is one of the imaging investigation, it present from 1960.
Mechanism of Action:
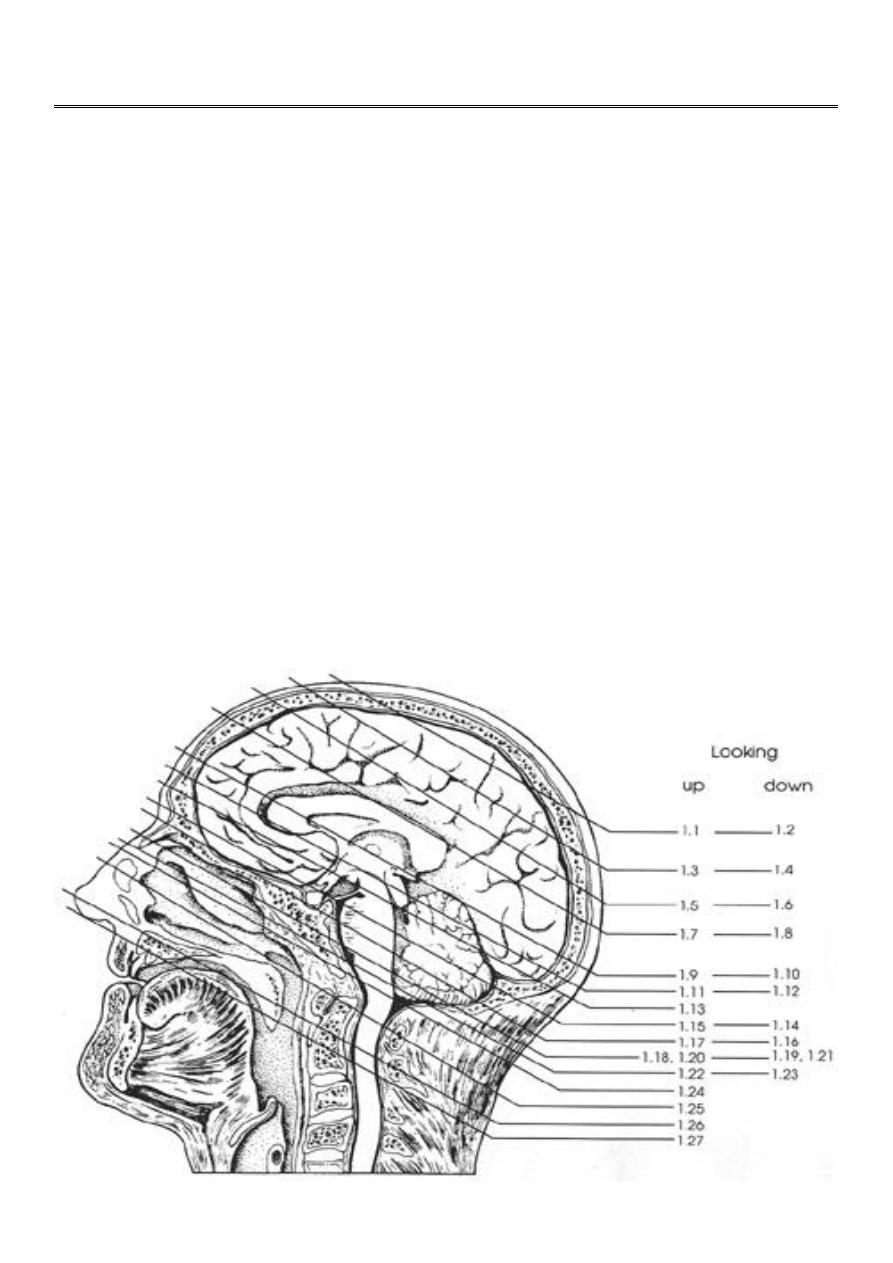
Tomography is the technique of rotating a radiation detector around the patient so that the
image obtained gives additional three- dimensional information.
In plain film tomography the source of XR ray & the photographic film move around the
patient to produce an image of the structures at a particular depth within the body, bringing
them into sharp focus, while deliberately blurring (unclear) structures above & below them.
In computerized tomography, the same technique of usual tomography, but instead of film,
there is detectors which attach to computer, this detector will catch the signal & convert it
into pulse, then to computer as image of different section.
So CT scan is a form of XR examination , in which the source & detector ( CT scanner ) & the
information obtained can be used to produce cross sectional image ( i.e. CT scan can produce
an image of slice through the body at a particular level)
2
N.B. when the no. of the detector increase, the clearance of the image is increase, the
usual no. of detectors is used now about 400.
What is the principle of CT scan?
The principle of CT scan is XR penetration & XR attenuation.
The XR can penetrate any organ & when penetrate it, it will face many different density
tissues like bone, muscle, fat, fluid or CSF.
Absorption of X-ray by these different tissues depend on:
Thickness
Conc. Of material
Molecular weight of the substance
The higher the thickness, the higher the Molecular weight, the more the absorption of the
XR & more attenuation examples:
Bone: is highly attenuated material, because it absorbed much XR so it appear white
in color.
Soft tissues have less attenuation, so appear gray in color.
Air has low absorption & low attenuation so it appear black in color.
3
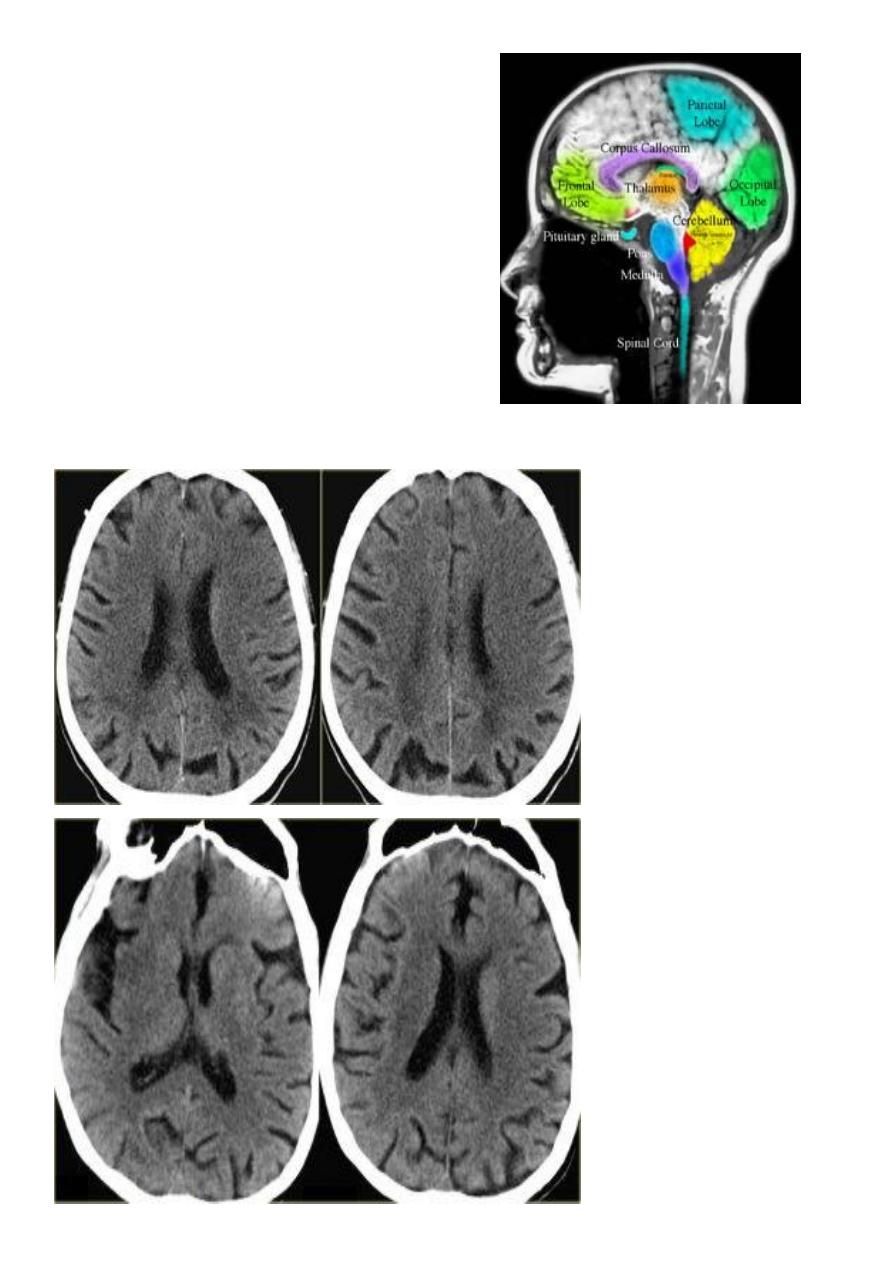
Normal brain (anatomy)
Cerebral hemisphere
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe
Temporal lobe
Occipital lobe
Posterior fosse
Cerebellum & brain stem
4
Ventricular system
1. Lateral ventricle ( frontal horn , body ,temporal horn ,& occipital horn ) .
2. Third ventricle .
3. Fourth ventricle .
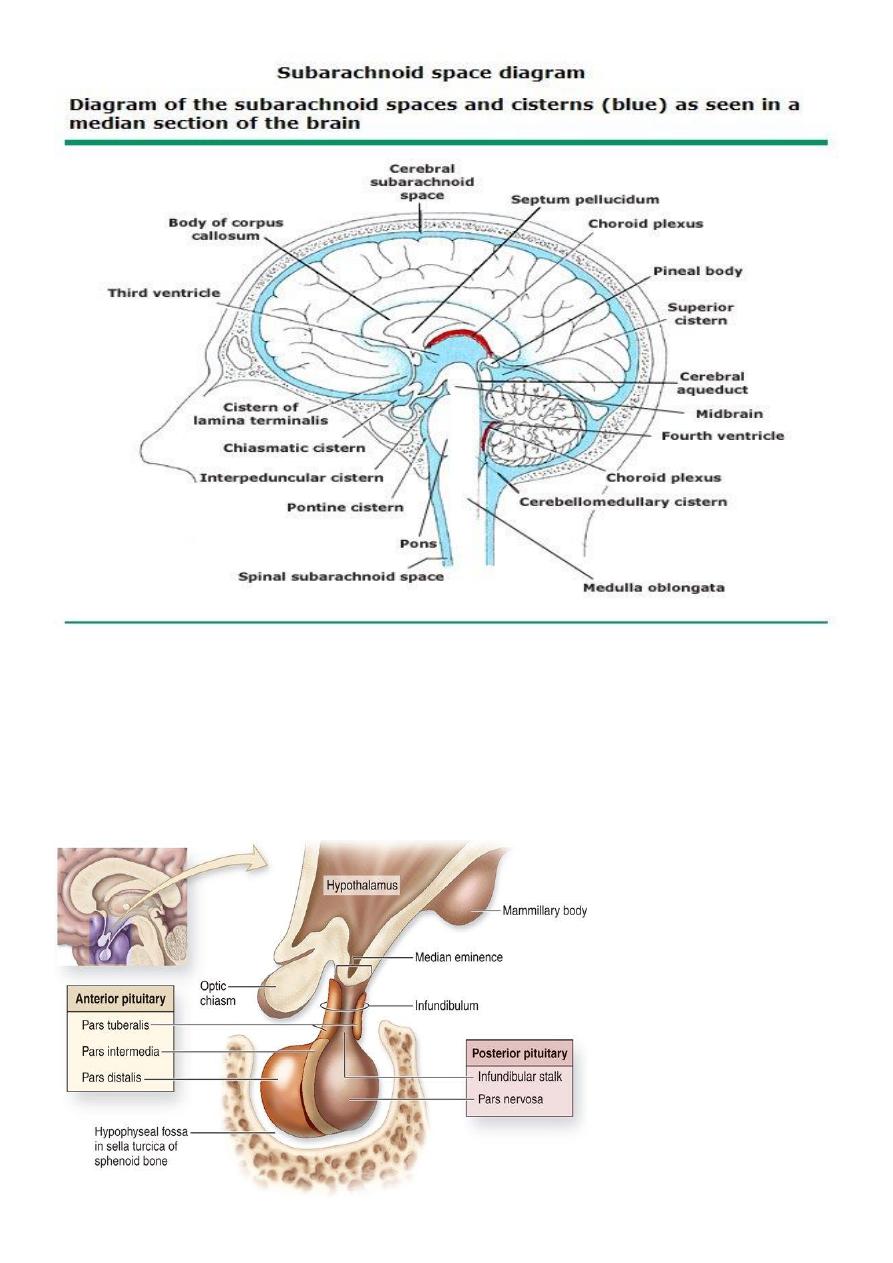
5
Pituitary fosse
Anterior cliniod process
The region of the sella tursica
Posterior cliniod process
Channel like area black in color ( cerebello pontine angle )
Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone & below it immediately the greater wing of spheniod.
6
CT terms
Iso dense, same density to organ examine
Hyper dense higher than the organ examined
Hypo dense lower than the organ examined
Density levels of different types of tissues
Density levels of almost all soft tissue organs lie within a range 10-90 HU, Water density 0
HU, fluid 10-15 HU depending on their density , air -1000 HU, fat -100 - -50 HU , bone &
calcification 100 & above HU , ossification 1000 & even more HU depending on the density
Encephalitis
Age : young & adolescence mostly .
Clinical picture : patient come with headache , vomiting , blurring of vision .
Usually the disease preceded by flue or vaccination , HS virus can also cause
encephalitis .
CT finding
Low attenuation of white matter ( due to the edema)
Compressing the ventricular system ( also due to edema ) specially the frontal & the
body of the lateral ventricle become slit like .
Complication
Brain destruction ( because the disease cause brain necrosis ) .
Atrophy of the brain tissues with subsequent loss of volume & dilatation of the
ventricular system .
Hydrocephalous .
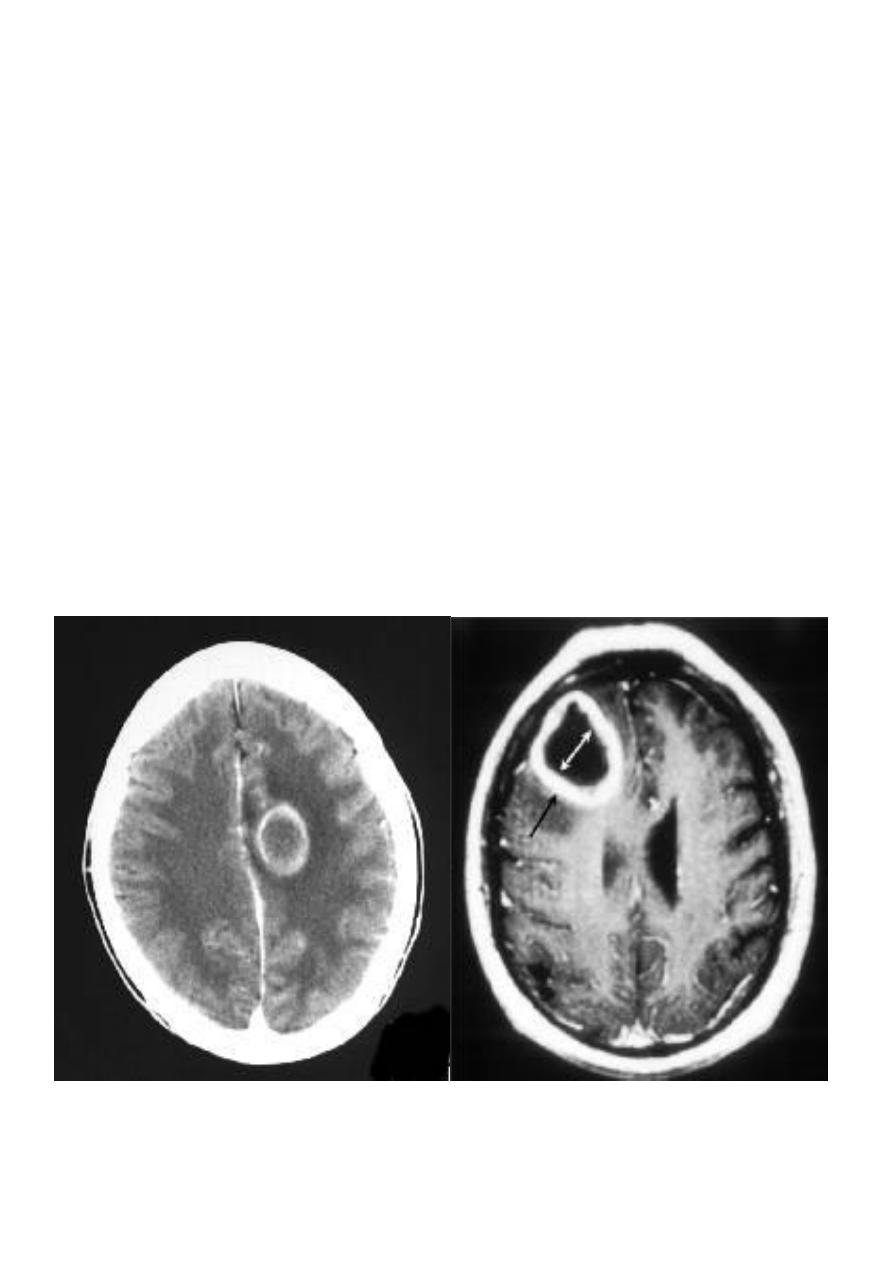
7
Herpes encephalitis
same as usual encephalitis but there will be low attenuation or hypo density area in the
tempo frontal or tempo priato frontal with evidence of patchy whitish area due to the clotted
blood ( hemorrhage ) .
Brain abscess
CP: high fever for long duration with focus of infection, patient may be toxic, or present with
epilepsy (focal)
CT finding
Hypo dense area surrounded by large area of peri focal edema, which may cause
shifting of the midline).
After injection the lesion show ring pattern of enhancement so the peripheral aspect
of the lesion become clearer.
DDx
Secondary metastasis, patient have history of primary malignancy, beside absence of
the fever.
Primary necrotic tumor, neither Hx of primary, nor fever are present.
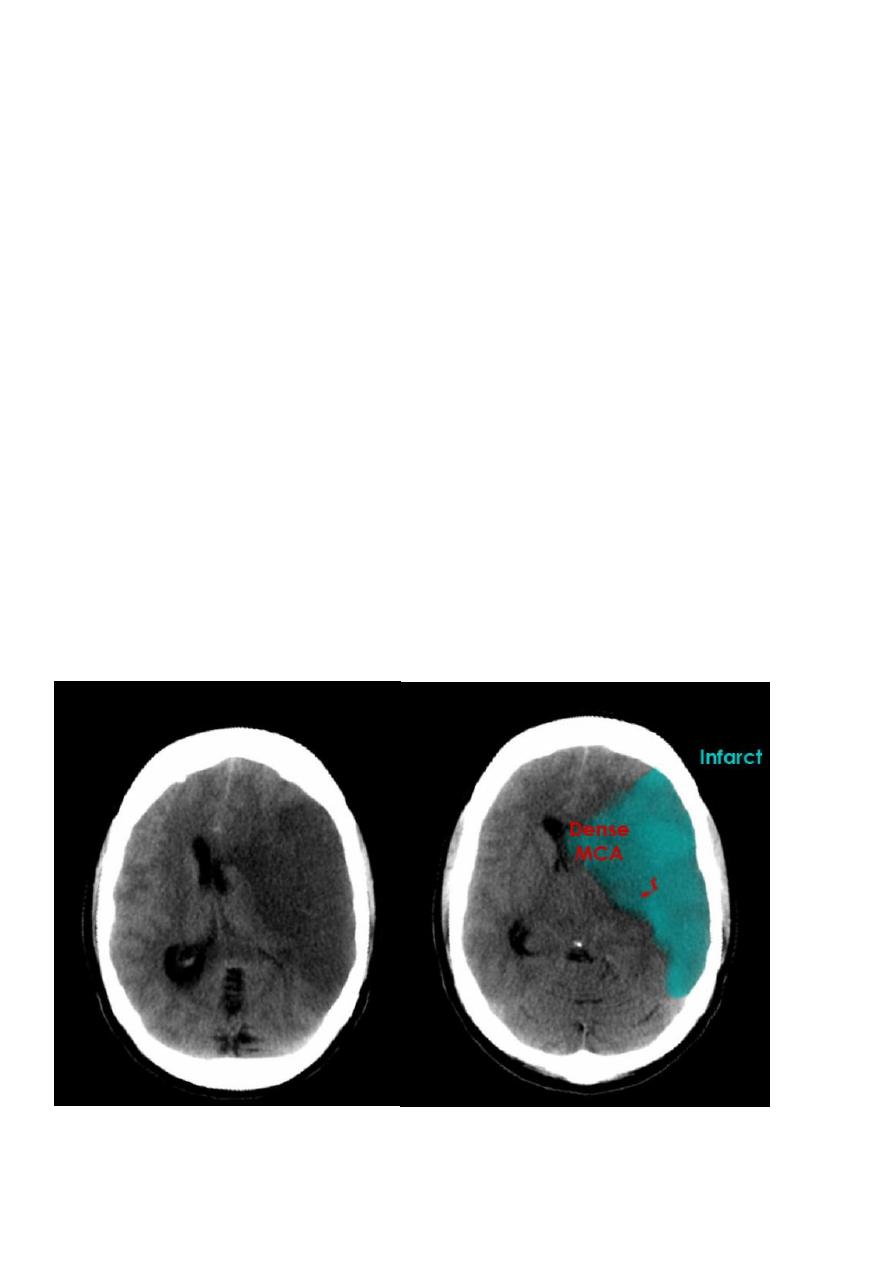
8
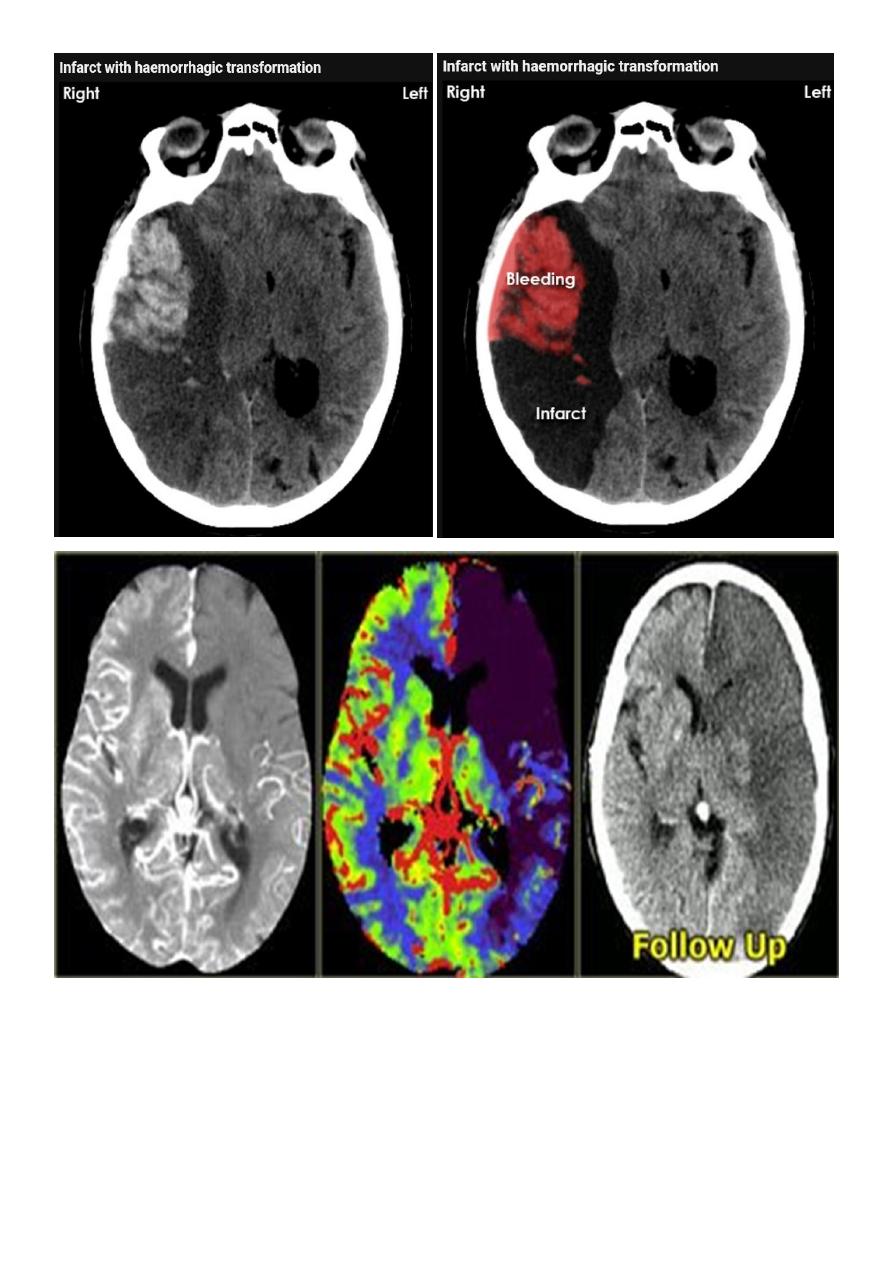
Infarction
Acute
Chronic
Acute infarction
History: sudden onset of hemiplegia , with slurred speech .
CT features:
Wedge shape area of hypo density involve the tributaries of anterior , middle or
posterior cerebral arteries , ( i.e. priato frontal & priato occipital area )
Shift of the midline to the other side .
Compression of the ipsi lateral aspect of the regional ventricle by the edema
Dense middle artery sign
Chronic infarction
• The necrotic area will be liquefy & change to the source of fluid ( por encephalon ) .
CT finding
Hypo density area as a result of blockage of AC , MC , & PC arteries .
The ventricle will be dilated to compensate for the loosed brain tissue .
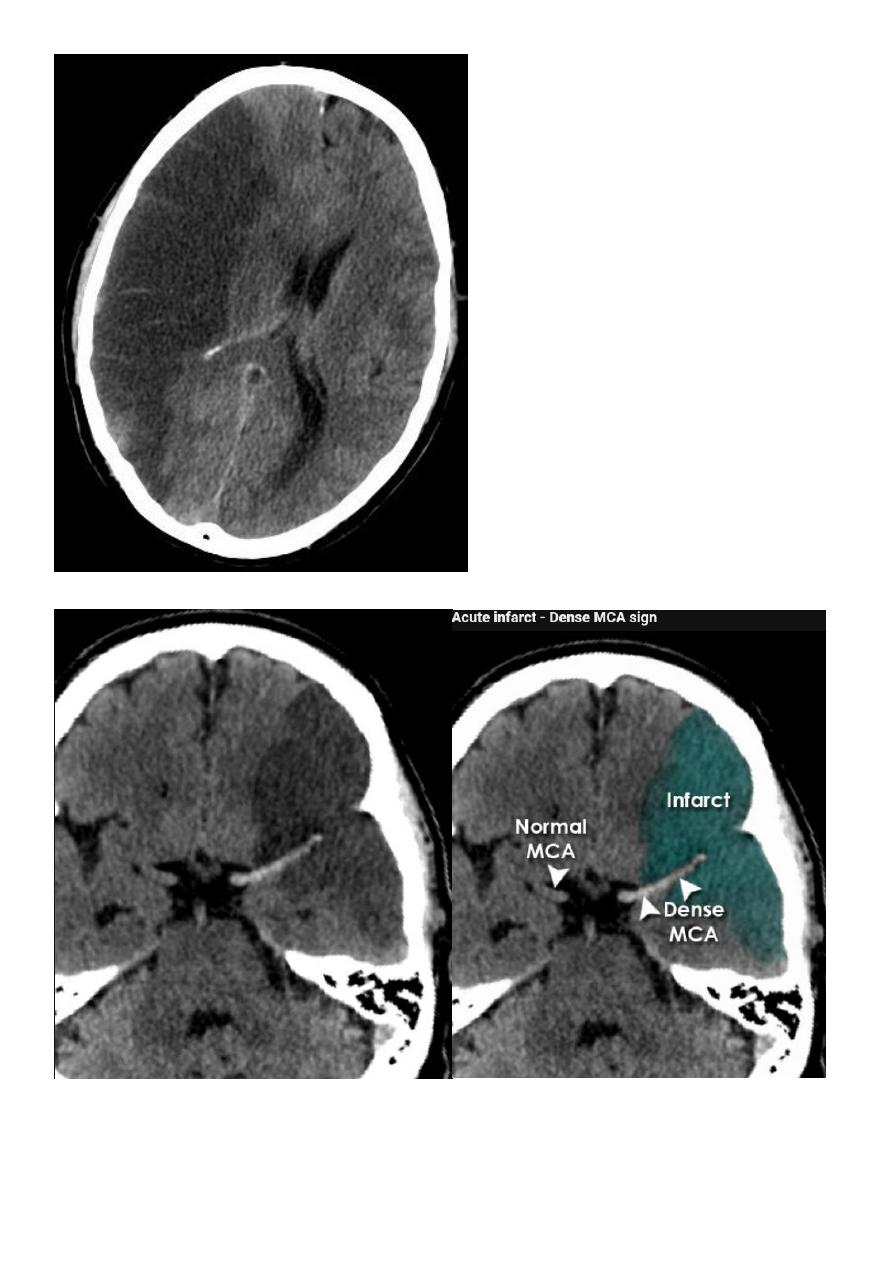
9
ACUTE INFARCTION
* wedge shape hypo density area.
* Shifting of the midline & frontal horn
10
11
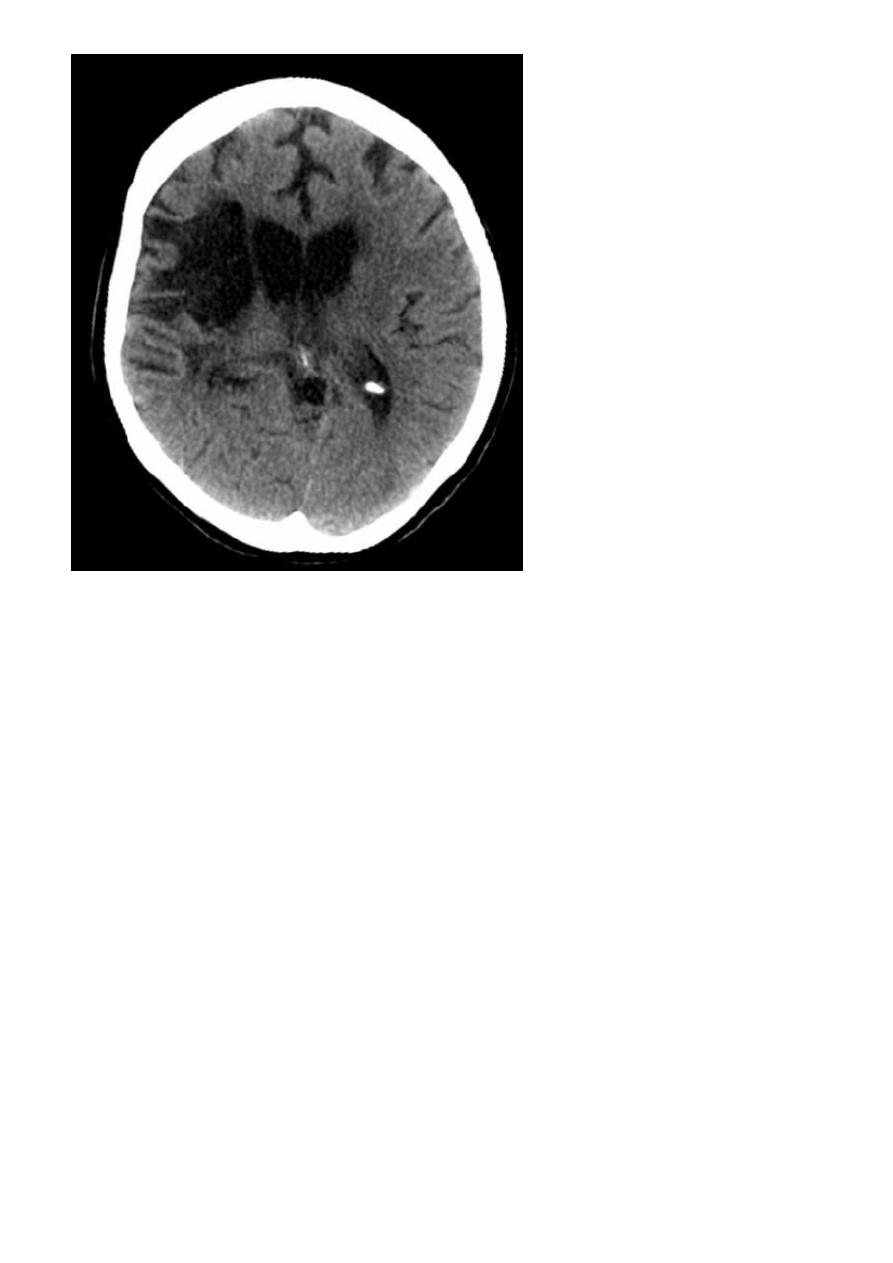
Chronic infarction
Hypo density area (pore encephalic
cyst)
Dilated ventricle
Hemorrhage
Classify the brain hemorrhage according to the site:
Epidural EDH
Subdural SDH
Sub arachnoids SAH
Intra cerebral ICH
Intra ventricular IVH
Other classification according to the onset of bleeding:
Acute
Chronic
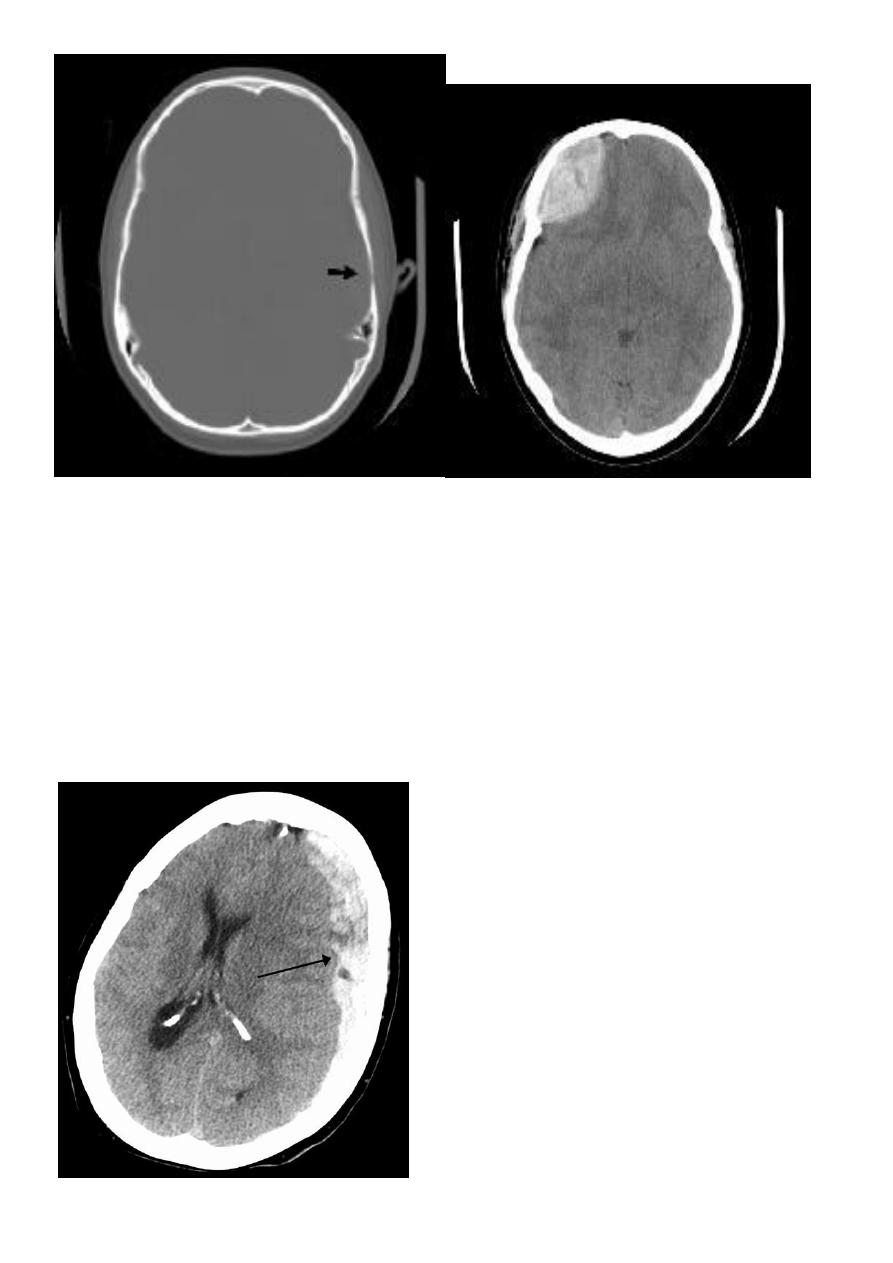
Acute EDH
CT finding
Hyper density area, 50-70 HU, due to the clotted blood, elliptical in shape, no edema
around the lesion, but may cause shifting of the midline, or compression of the ipsi
lateral ventricle if it is large enough.
The source of bleeding of the haematome is injured middle meningeal artery so the
lesion > 90 % associated with skull # at the site of the previous mentioned artery.
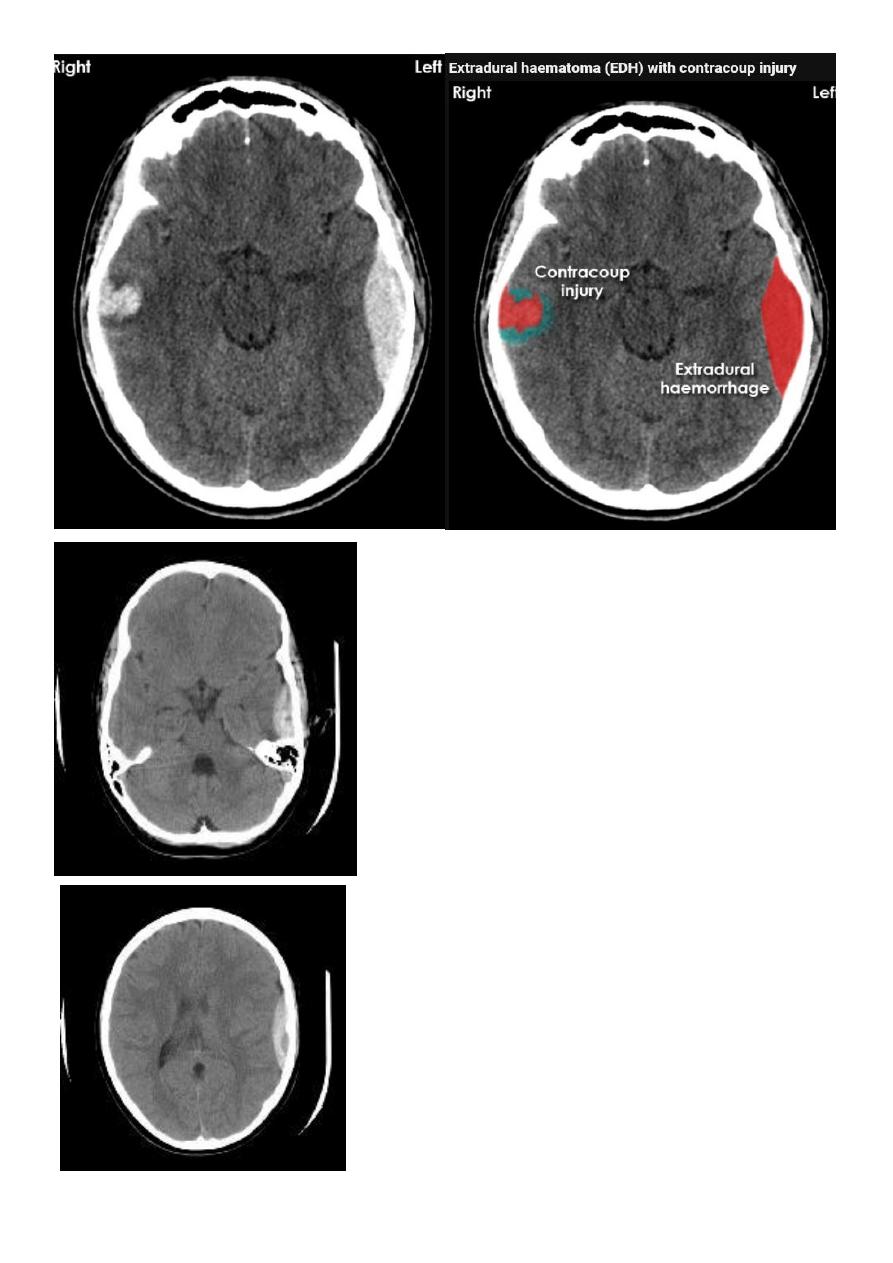
12
EDH
Biconvex hyper density area
Shifting of the midline
Compression of the ventricles
13
Acute SDH
CT finding
Crescent shape or oval shape of hyper density area their inner medial margin is
irregular shaggy
Associated with edema which cause shifting of the midline .
The source of bleeding hematoma is venous , not associated with # , but occur as a
result of disruption of subdural vein , more commonly to occur in the old age group ,
due to brain concussion , ( brain atrophied wide SAS ) & in the pediatric age group the
SAS &cistern are wide also .
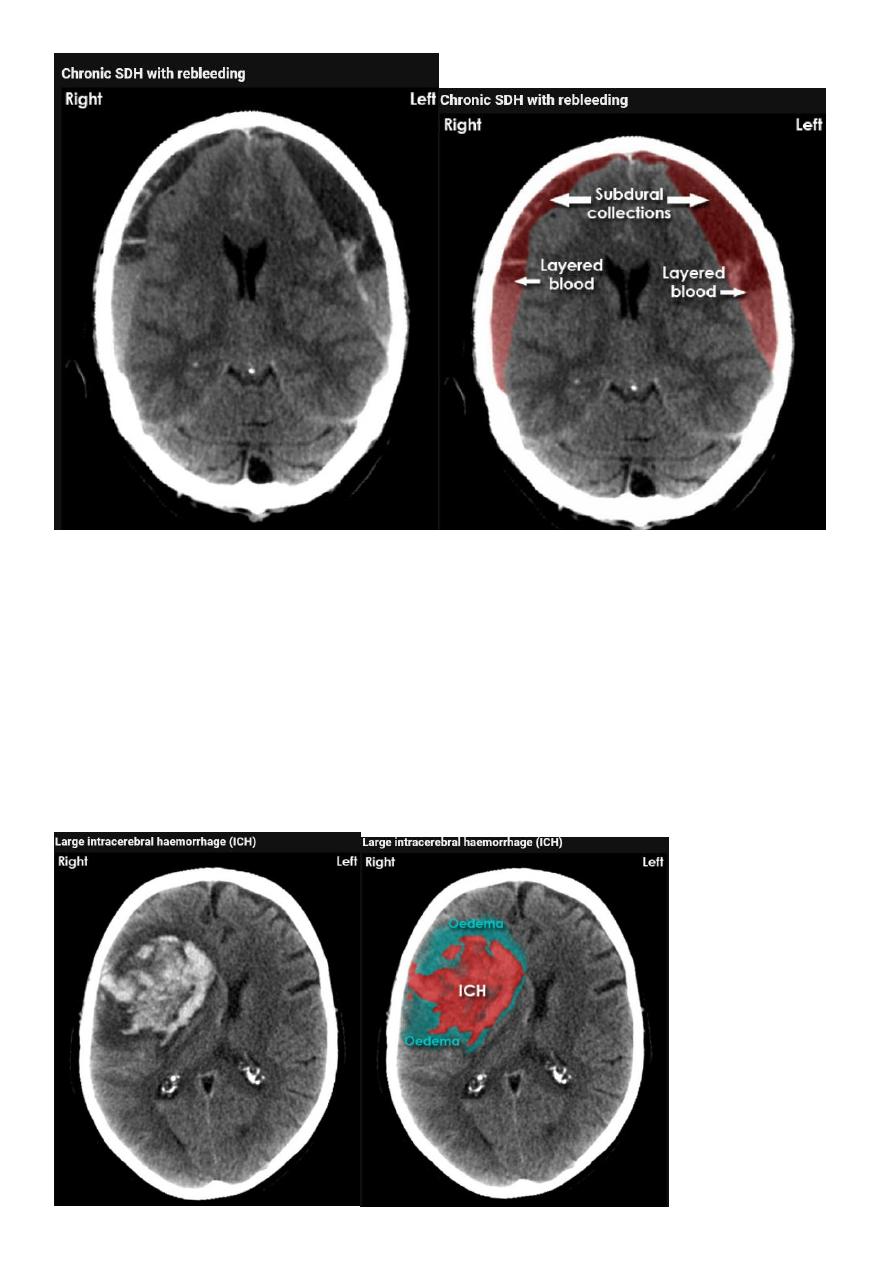
14
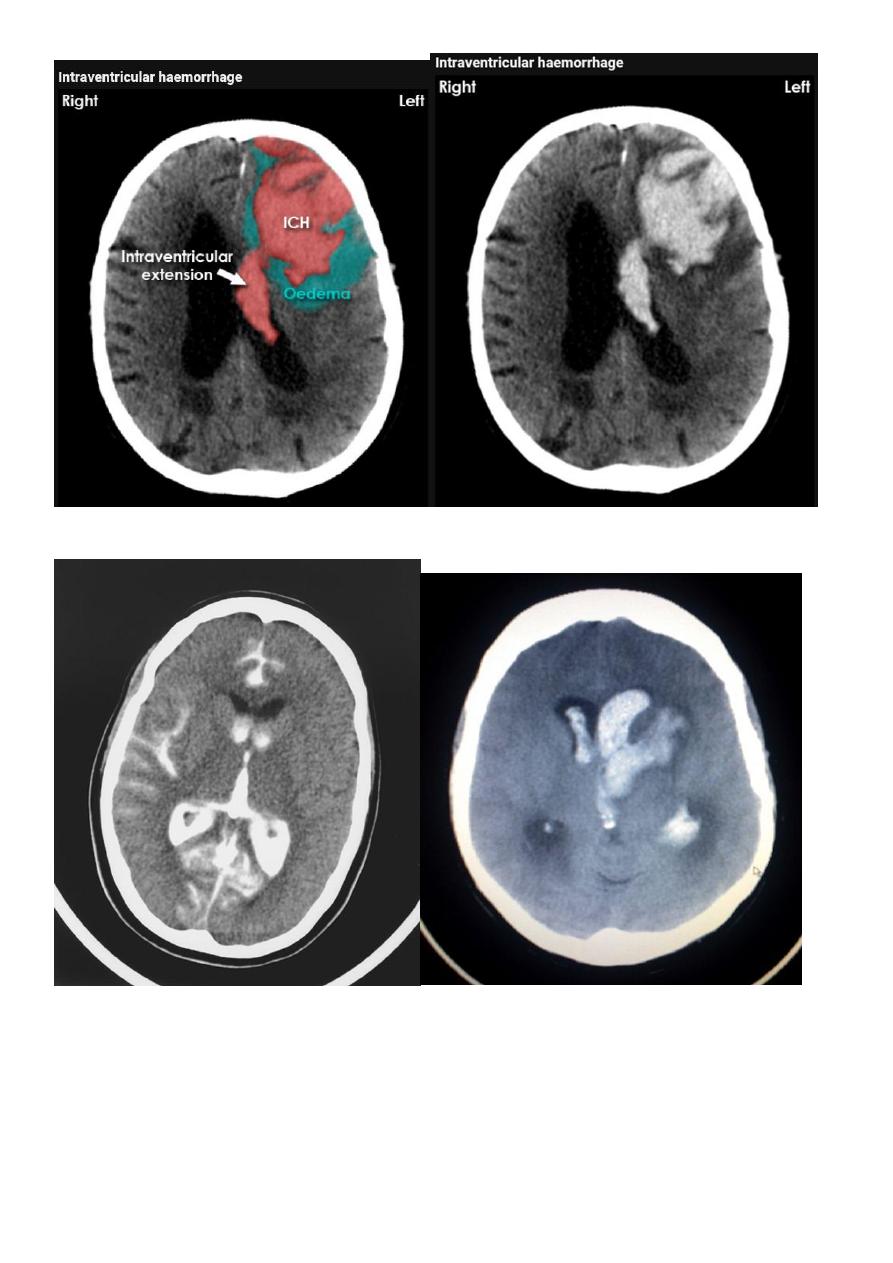
Acute Intra cerebral hematoma
CT finding :
Hyper dense area , surrounded by edema , any where within the brain parenchyma.
Shifting of the midline
Compression of the ipsi lateral ventricle .
Associated with infarction , # , trauma concussion , tumor …..
Hypertensive Hemorrhage
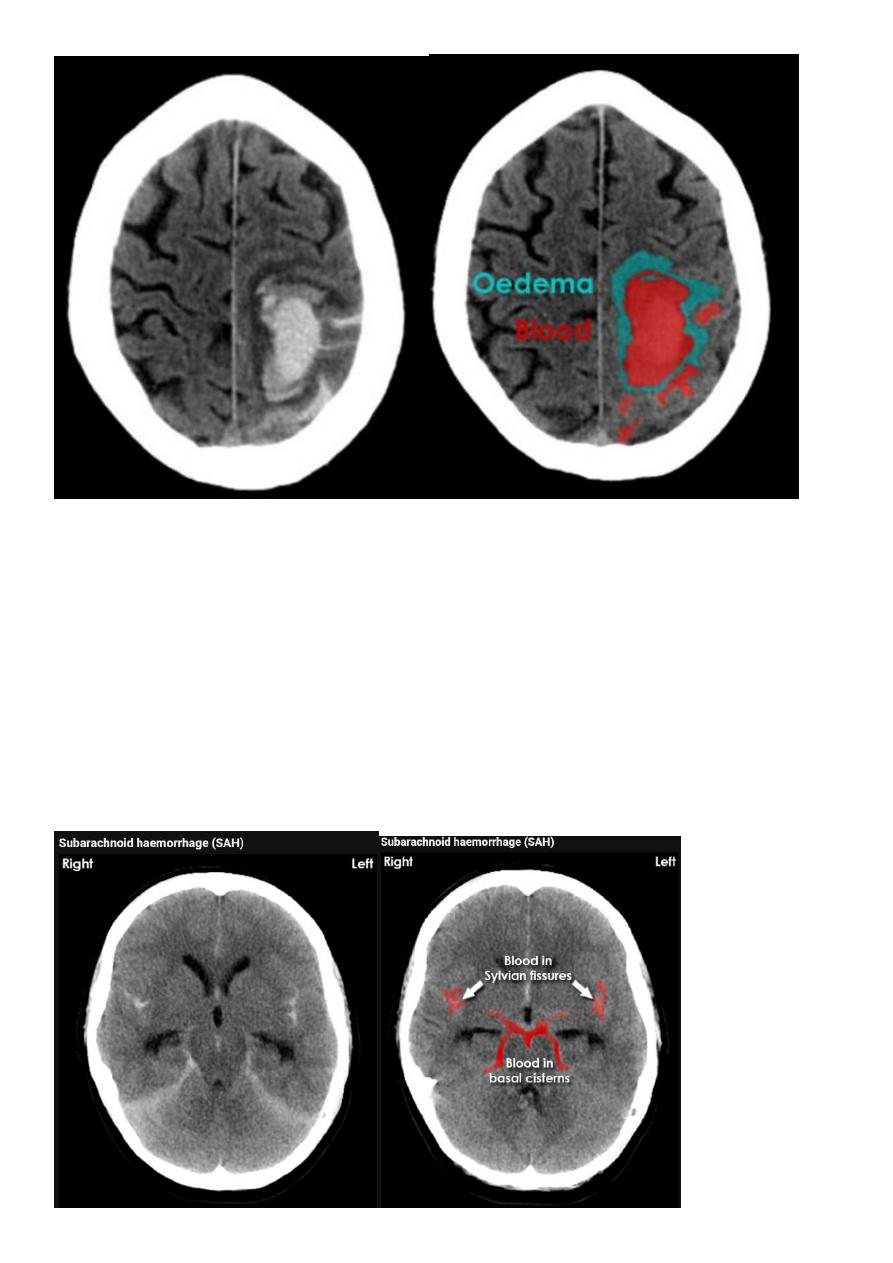
15
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
causes
due to ruptured aneurysm over 90 % of cases spcially at the circle of Willis .
ruptured AV malformation .
trauma .
CT finding
hyper density is seen within the SAS ( hyperdense sulci , being filled with clotted blood)
opacified inter hemispheric fissure ( become white & more dense )
opacification of the falx cerebri .
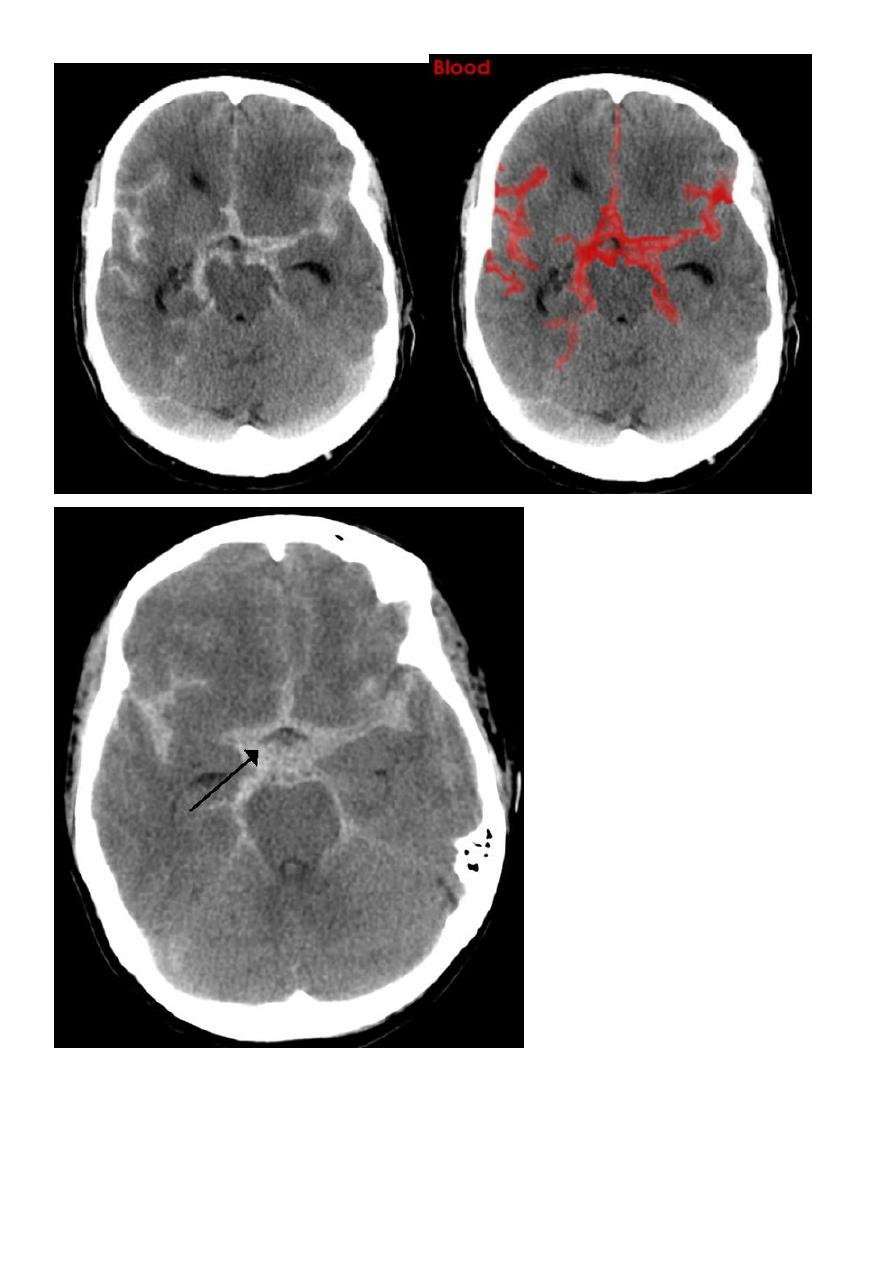
16
SAH
White sulci
Opacified IHF
17
