DISINFECTANTS
Our Environment is Full of:“Microorganisms”
Bacteria
Bacteria
Fungi
Disinfectants:They are Chemical Agents that inhibit or kill microorganisms .
They prevent infection by:-Killing,
-Removing,-Diluting microorganisms.
Disinfection can be accomplished also by application of Physical Agents:
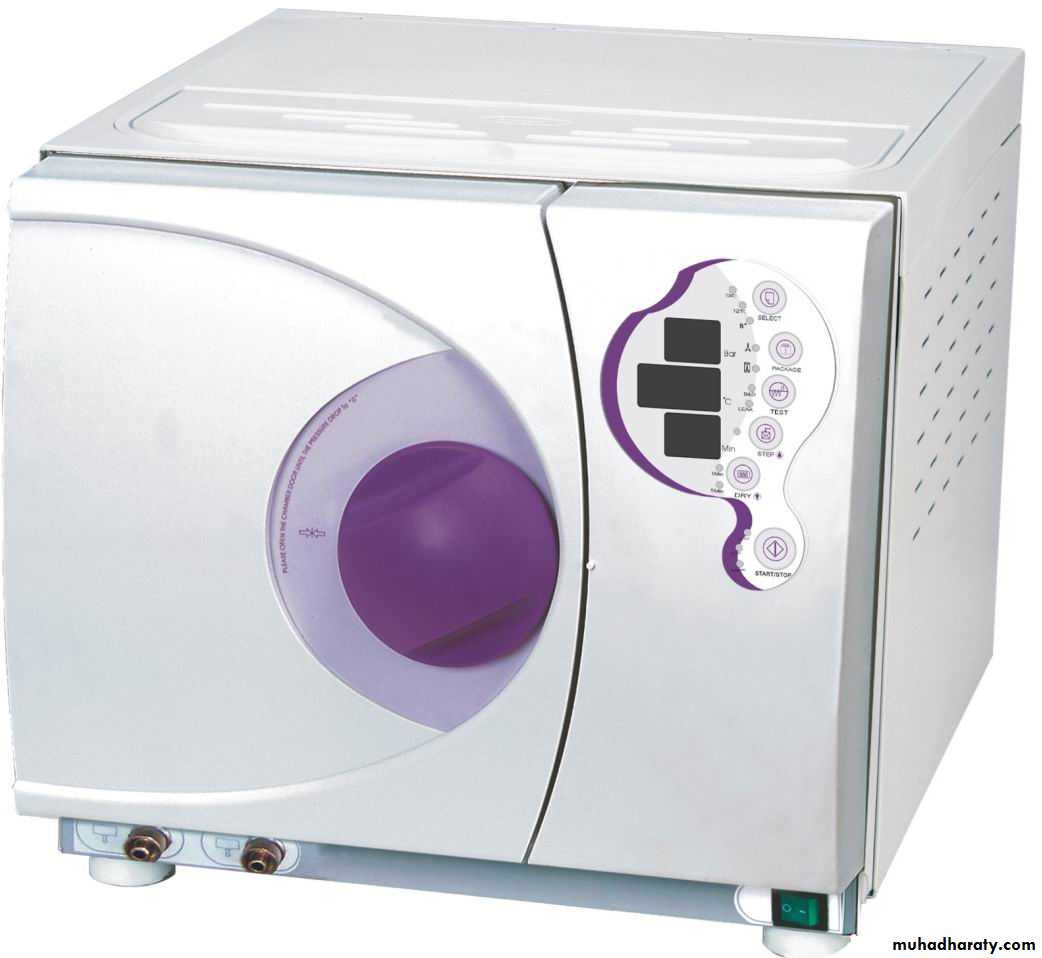
e.g. Super heated steam 120-160 degree centigrade (Autoclave).Autoclave
Autoclave
Autoclave
Antisepsis: (Antiseptic)Application of an agent to “Living Tissue” for the purpose of preventing infection .
Sterilization:
A process intended to kill or remove “All Types” of microorganism including spores and uncoated viruses.Can we sterilize living tissue?
SterilizationNO !
Sterilization involves application of physical or chemical agents too harsh
to be applied to a living tissue.Factors that affect the effectiveness of disinfectants are:
-Intrinsic resistance of the microorganism.-Number of the microorganisms present.
-Availability of mixed population.
-Amount of the organic material present.
-Concentration & stability of disinfectants.
-Time & temperature of the exposure.
-PH, hydration & binding of the agent to surfaces.
Three Types of Disinfection:
1-Tissue Disinfection (Antiseptic).2-Instrument Disinfection.
3-Enviromental Disinfection (Hospital setting).
1- Alcohols.
2- Biguanides.3- Halogens.
4- Phenols.
5- Aldehyds.
6- Quaternary ammonium compounds.
7- Superoxides.
Chemical classes of Disinfectants
1-Alcohols:*Antiseptic
The two alcohols most frequently used are:
-Ethanol.
-Isopropanol.
They are rapidly active (30 sec.) ,killing vegetative bacteria ,mycobacterium tuberculosis, many fungi & lipophilic viruses.
The optimum bactericidal concentration is:
70-90 % by vol. in water
-They act by denaturation of proteins.
-Their skin drying effect can be partially alleviated by addition of some emollients to the formulation.
-Alcohols are flammable & must be stored in cool ,well ventilated areas.
2-Chlorhexidine:
*AntisepticIs a Cationic Biguanide with very low water solubility ,it is active against vegetative bacteria & mycobacterium &has moderate activity against fungi & viruses.
strongly adsorbs to bacterial membranes causing leakage of small molecules & hence precipitation of cytoplasmic proteins.
they act at PH=5.5-7.0
Chlorhexidine digluconate resist inhibition by blood & organic materials especially the formulation of 4% solution.
0.2% -0.4 % are used as mouth washes
3-Halogens:
*AntisepticA.Iodine:
Iodine in a 1:20.000 sol. Is a bactericidal in 2-3 minutes & kills spores in 15 min.
It is the most active antiseptic for intact skin but have staining property with serious hypersensitivity reaction so not commonly used.B.Iodophores :
Are complex of iodine with surface active agent such as povidone –iodine .They kill vegetative bacteria ,mycobacterium ,fungi & lipophilic viruses &could be sporicidal upon prolonged exposure
They are less irritant &less likely to produce hypersensitivity than iodine.
Povidone Iodine
Povidone Iodine
Povidone Iodine
C.Chlorine*Environmental Disinfectant
Is a strong oxidizing agent & universal disinfectant that is most commonly provided as 5.25% sodium hypochlorite solution.
(typical formulation for household bleach)
Household bleach
6%Because formulation may vary ,the exact concentration Should be verified on the label.
A 1:10 dilution of household bleach provide 5000 ppm of chlorine which is sufficient to kill spores.where as less than 5ppm enough for bacterial disinfection.
200-500ppm for lipophilic & hydrophilic viruses.
4-Phenol:*Environmental Disinfectant
The oldest of the surgical antiseptics, it is no longer used because of its corrosive effect on the tissues.
*its toxicity when absorbed
*its carcinogenic effects
Phenols
*Environmental DisinfectantPhenolic compounds disrupt cell walls & membranes ,so precipitate proteins and inactivate enzymes.
They are bactericidal including mycobacterium bacilli & fungicidal, also capable of inactivating lipophilic viruses but not sporicidal.
Phenolic compounds mainly used for hard surfaces decontamination in hospitals & laboratories and hospital beds.
5-Aldehyds:
*Instrumental DisinfectionFormaldehyde & glutaraldehyde are used for disinfection & sterilization of instruments such as fiberoptic endoscopes & respiratory therapy equipments that can not withstand exposure to high temperature of steam sterilization.
These agents have abroad spectrum of activity against microorganisms & viruses.
They act by alkylation of proteins & nucleic acids.
An 8% formaldehyde solution in water has abroad spectrum activity against bacteria, viruses & fungi.
A 4% form used for fixation of tissues.
Formaldehyde is highly irritant to respiratory mucous membranes & eye at high concentration.same thing for glutaraldehyde, so protection is important.
6-Quaternary ammonium compounds :*Environmental Disinfectant
Their bactericidal action has been attributed to:
-Inactivation of energy producing enzymes.-Denaturation of proteins.
-Disruption of the cell membrane.
Used as disinfectant for floor ,bench……etc.
Benzalkonium chloride is the active ingredient of Dettol
*Environmental Disinfectant7-Peroxygen compounds:
e.g. Hydrogen peroxide(H2O2), these agents have the advantage that their decomposition product are not toxic & do not injure the environment.
Used as tissue disinfectant as well as for certain instruments(respirators).
Washing hands with soap and water remains one of the most important ways of disinfection and prevention of contamination!
Soup reduces the number of vegetative bacteria to a very large extent.
Soap and waterHBV and HIV
(Hepatitis B virus and Human immunodeficiency virus).Cloths, furniture…etc can be disinfected with:
1-1:10 dilution of household bleach for 10 minutes.
or2-High iodine content iodophor 70% in 70% isopropanol for 10 minutes.