Prof. Dr. Huda Al-khateeb
Lec. One
The Circulatory System

1.Study the layers and the sub-layers of the heart
2.Study the impulse conducting system structure and ultra-structure
3.Study the types of blood vessels
4.Study the classification of the arteries
5.Study the sorting of veins
6.Study the light and electron microscopical features of the
capillaries
7.Classification of capillaries according to their ultra structures
8.Throw light on the lymphatic vessel
Objectives:

•
blood vascular system: Consists of:
Heart
Blood vessels
: A. arteries
B. capillaries
C. veins
•
Lymph vascular system: Consists of:
Lymph vessels
Lymph organs
(lymph nodes, tonsils,
spleen………)
The circulatory system is categorized as:

1. Macro-vasculature (includes vessels with
more than 0.1mm in diameter).
These vessels are seen grossly.
2. Micro-vasculature (includes arterioles,
capillaries and post-capillary venules).
These vessels are seen by microscope.
Circulatory system can be divided into:
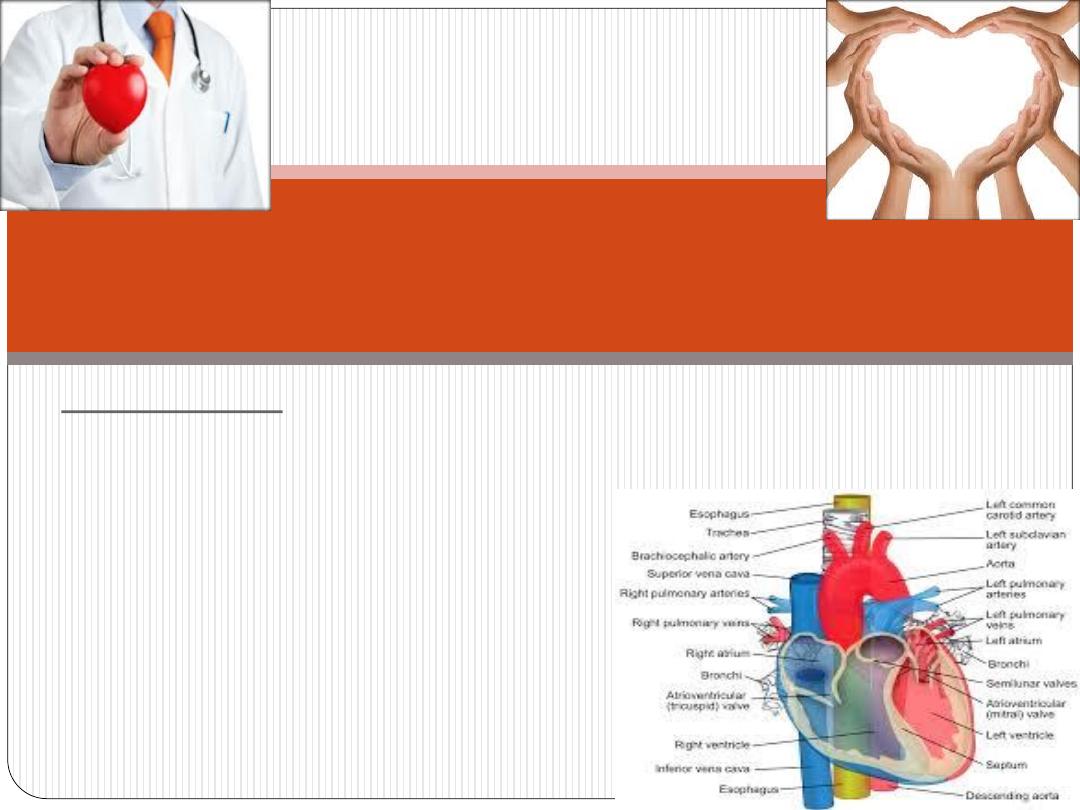
The heart
-it is a muscular, highly specialized portion of the
vascular system.
-it consists of 4 chambers:
RT< atria
RT< ventricles
Blood Vascular System
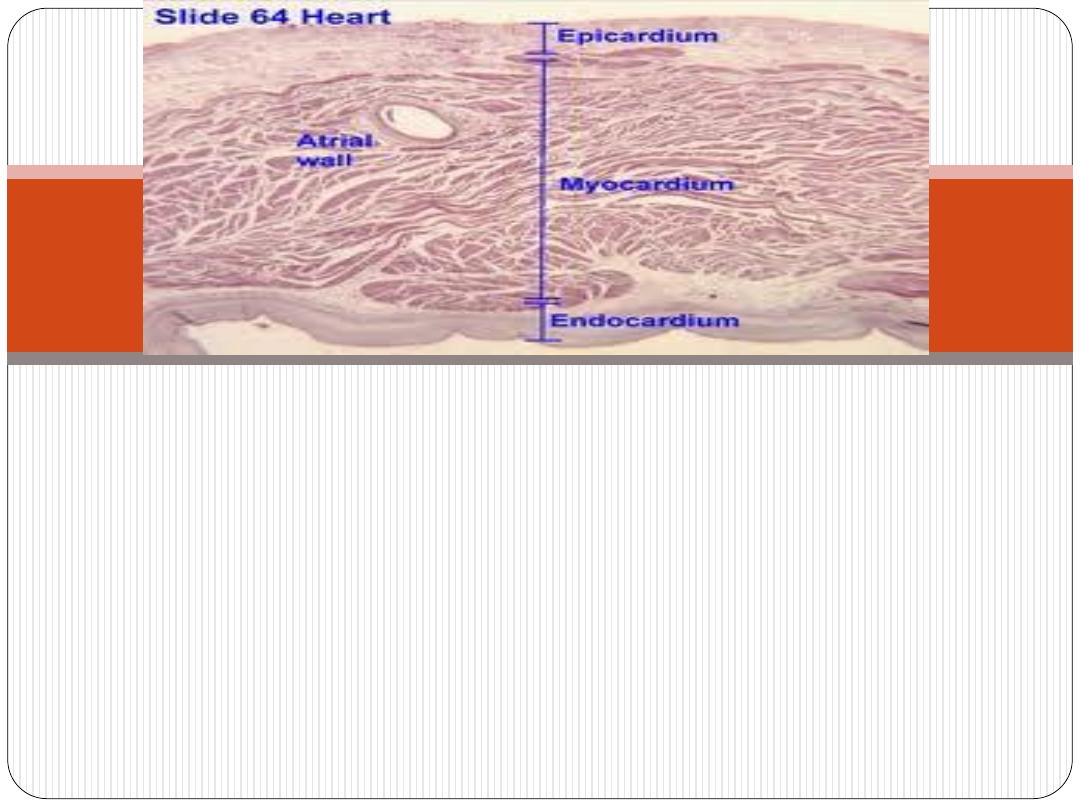
The heart wall consists of 3 layers
1. Endocardium (inner layer).
2. Myocardium (middle layer).
3.Epicardium (outer layer).
The fibrous central region of the heart is called
fibrous skeleton
, which serves as base of the valves
and site of origin and insertion of cardiac muscle
cells. Histologically, fibrous skeleton is composed of
dense irregular connective tissue, with separated
nodules of fibrocartilage.
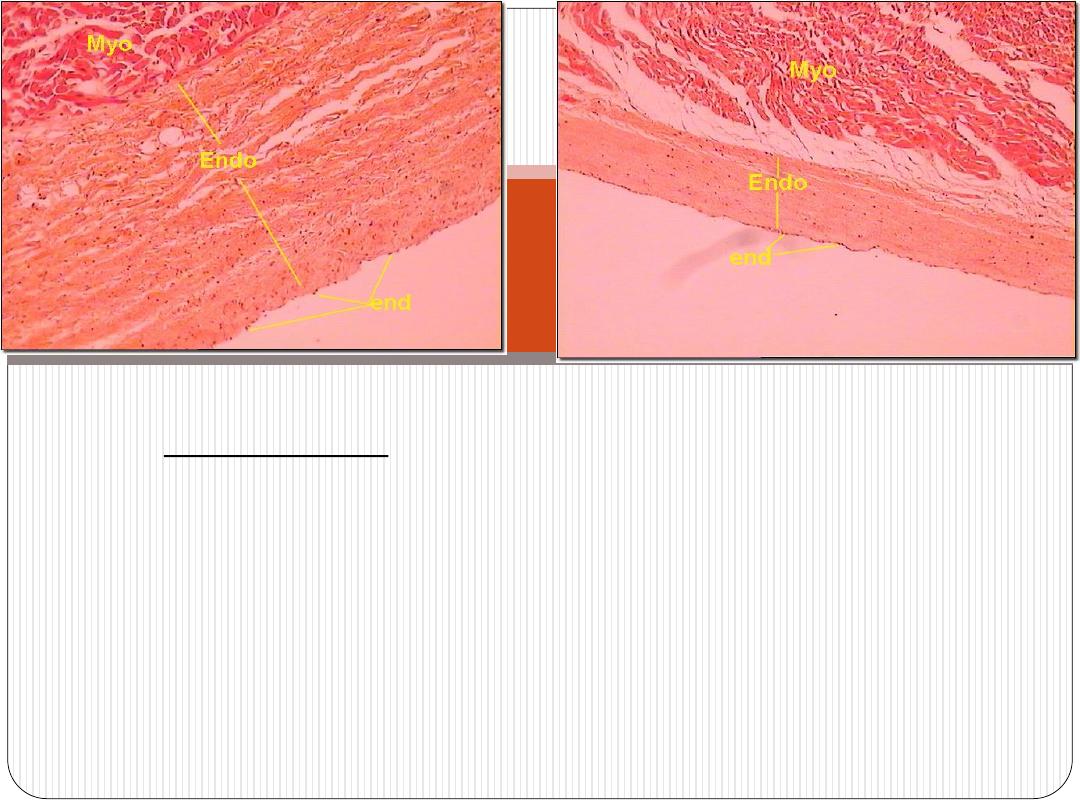
Endocardium
-it lines all internal surfaces of the heart.
-it is thicker in atria than ventricles
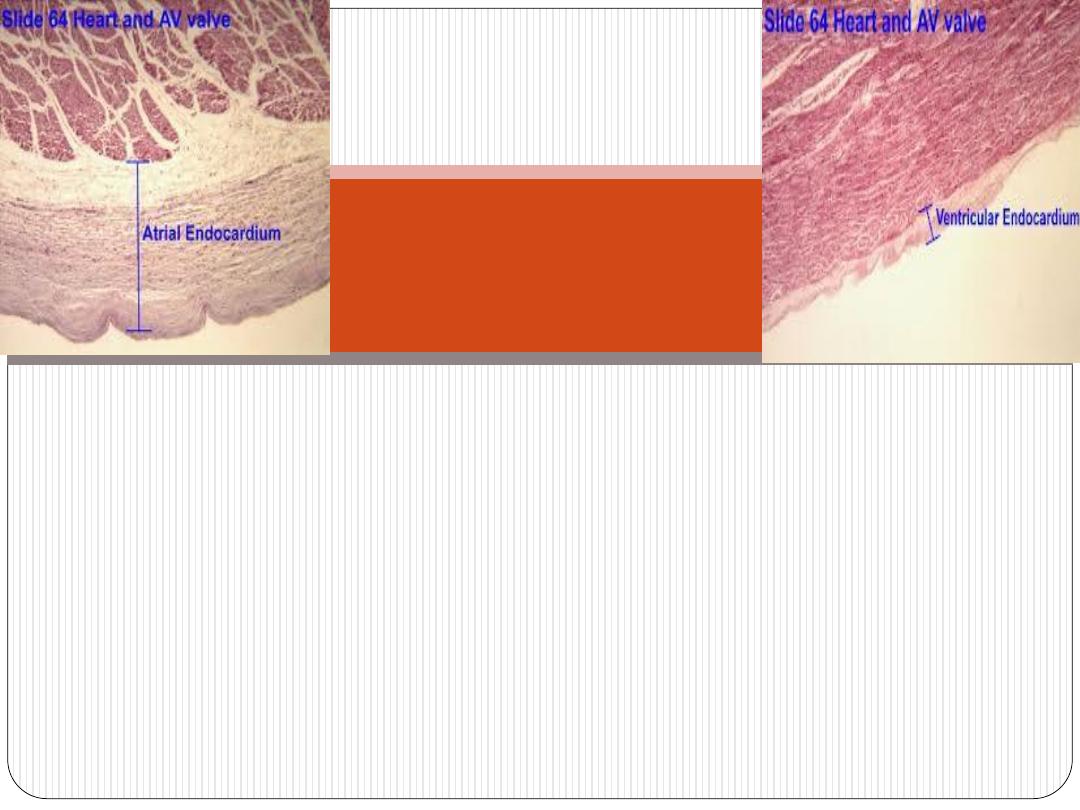
-it has three layers:
The endothelium-
it is the inner most layer. It is continues with that of
blood vessels entering and leaving the heart. It is composed of simple
squamous epithelium.
Subendothelial layer-
consists of narrow zone of loose connective t. that
is mainly composed of fine collagen, elastic and smooth muscle fibers.
subendocardial layer-
which is composed of connective t. that contains:
+B.V.s
+nerves
+branches of impulse-conducting system of the heart (Purkinje
fibers)
Endocardium
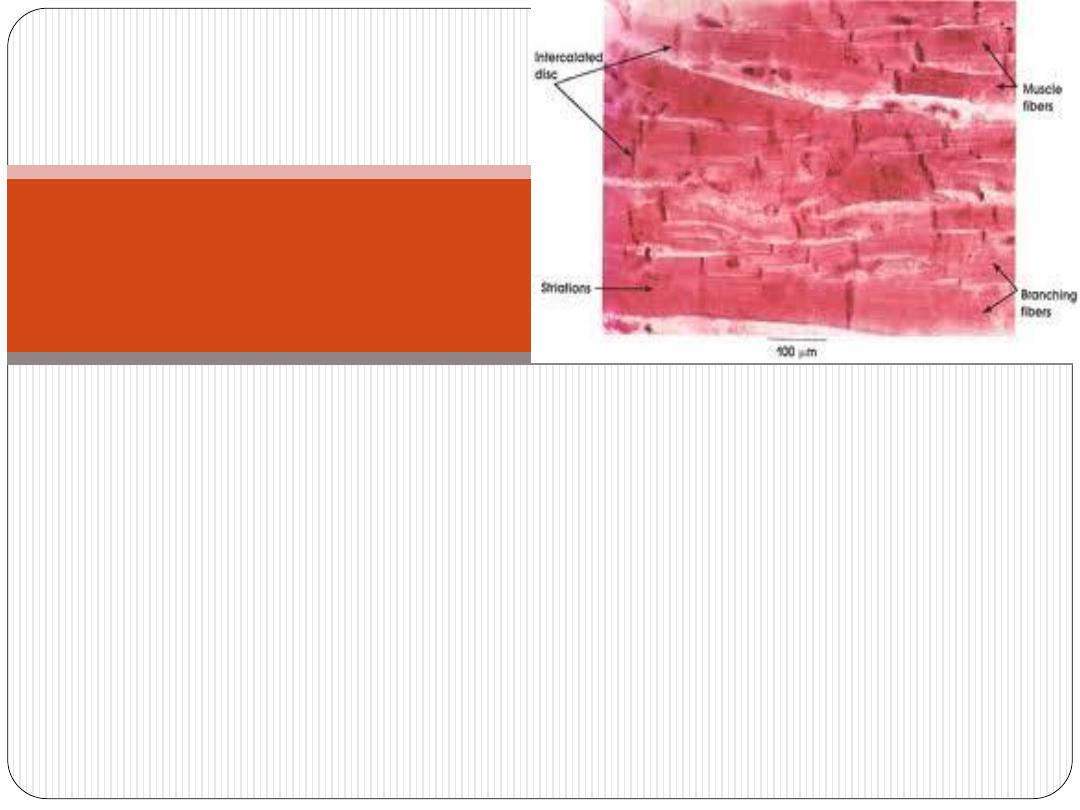
•
composed of
cardiac m. fibers
that run in different
directions (complex-spiral) and usually inserted into the
fibrous skeleton of the heart.
•
form the main mass of the heart wall.
•
It is the thickest layer in the heart wall. Its thickness
varies in different parts of the heart being thinnest in the
atria, thickest in the LT ventricle.
Myocardium
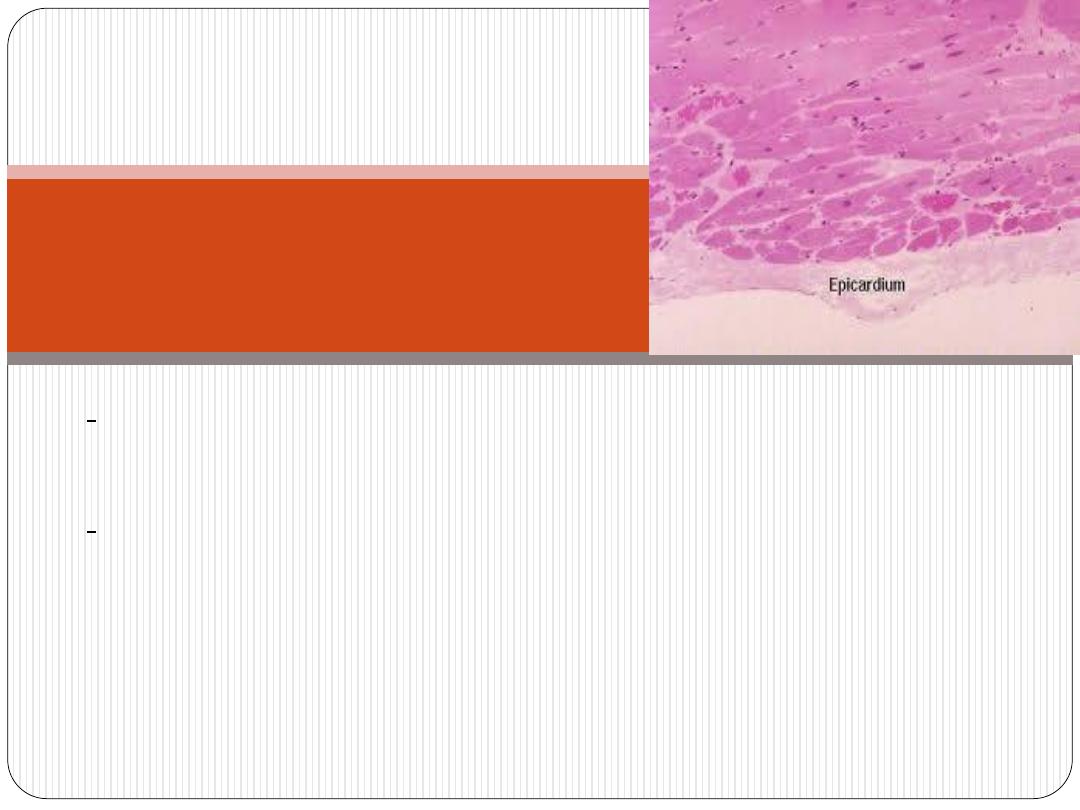
(it is the
visceral pericardium
)
-covered externally by a single layer of simple
squamous epithelium (
mesothelium
), that is supported
by very thin layer of connective t. containing elastic
fibers (
subepicardial
layer
), which is composed of loose
connective t. containing; B.V.S, N.s and adipose t.
Epicardium

(1)
Atrio-ventricular valves
(A-V valves):(tricuspid & mitral)
-they are composed of core of dense fibrous connective t.
(central core) that is lined on both sides by endothelium. The
bases of the valves are attached to the fibrous skeleton.
(2)
Semi lunar valves
(aortic and pulmonary valves):
are similar in structure to the A-V valves, but they have thinner
central core.
:
Cardiac valves
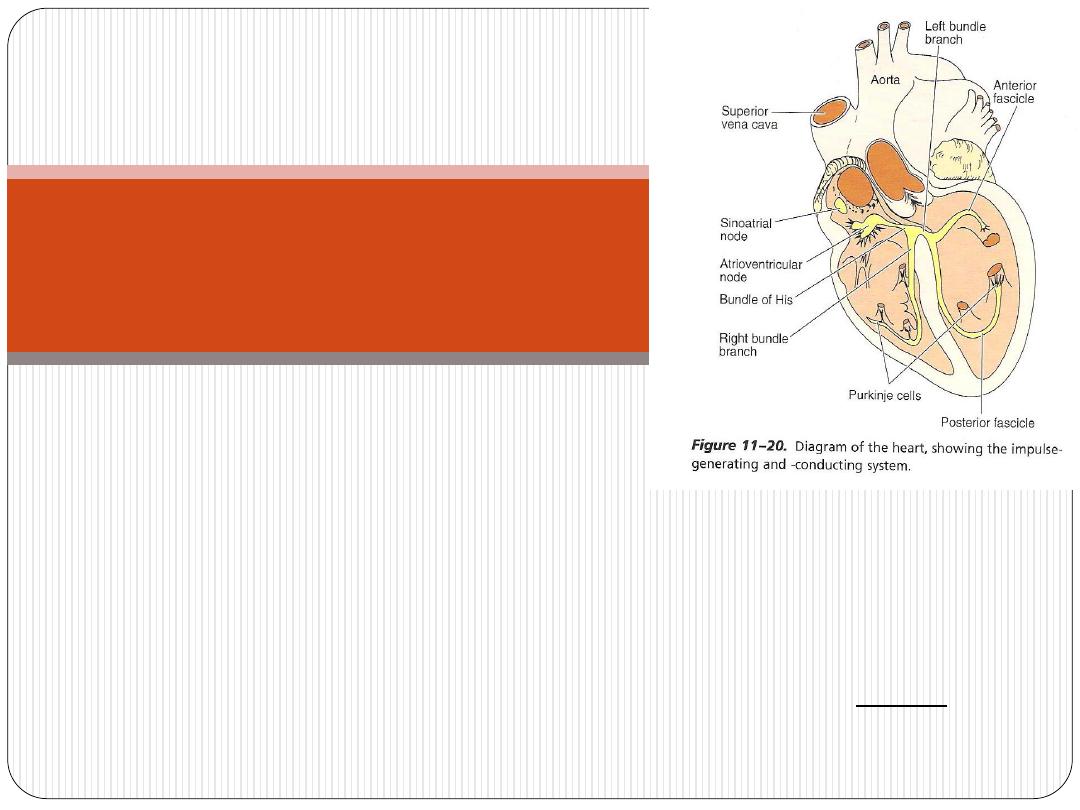
1. Sino-atrial node (SA node)
2. Atrio ventricular node (AV node)
3. Atrio-ventricular bundle (AV bundle);includes;
A. Bundle of His
B. Right and left bundle branches
C. Purkinji fibers
All cells of impulse-conducting system are modified cardiac muscle cells
(fuseform cells and
smaller
than atrial cardiac muscle fibers), except
Purkinji fibers, which are
larger.
Impulse-conducting
system
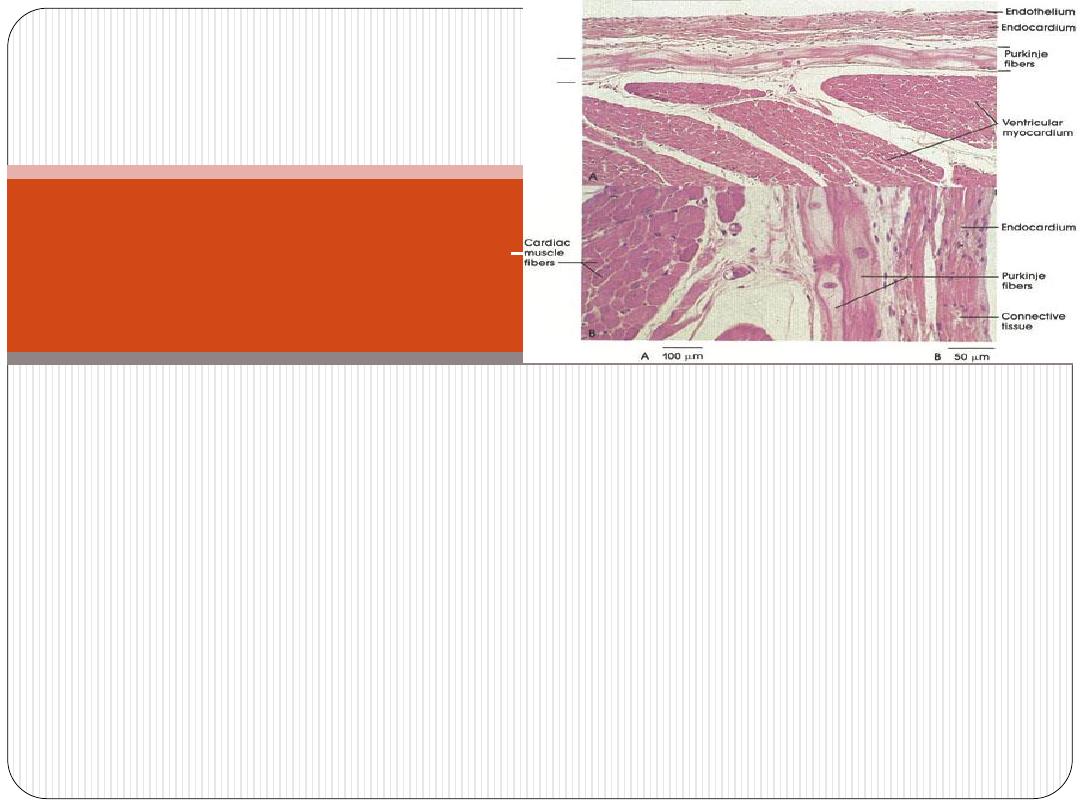
-they are modified cardiac m. fibers. They conduct impulses
faster than the ordinary heart m. fibers.
-After traveling in subendocardium, they penetrate
myocardium of ventricles. This arrangement is important
because it allows the stimulus to get into the outermost
layers of ventricular musculature.
:
Purkinje fibers
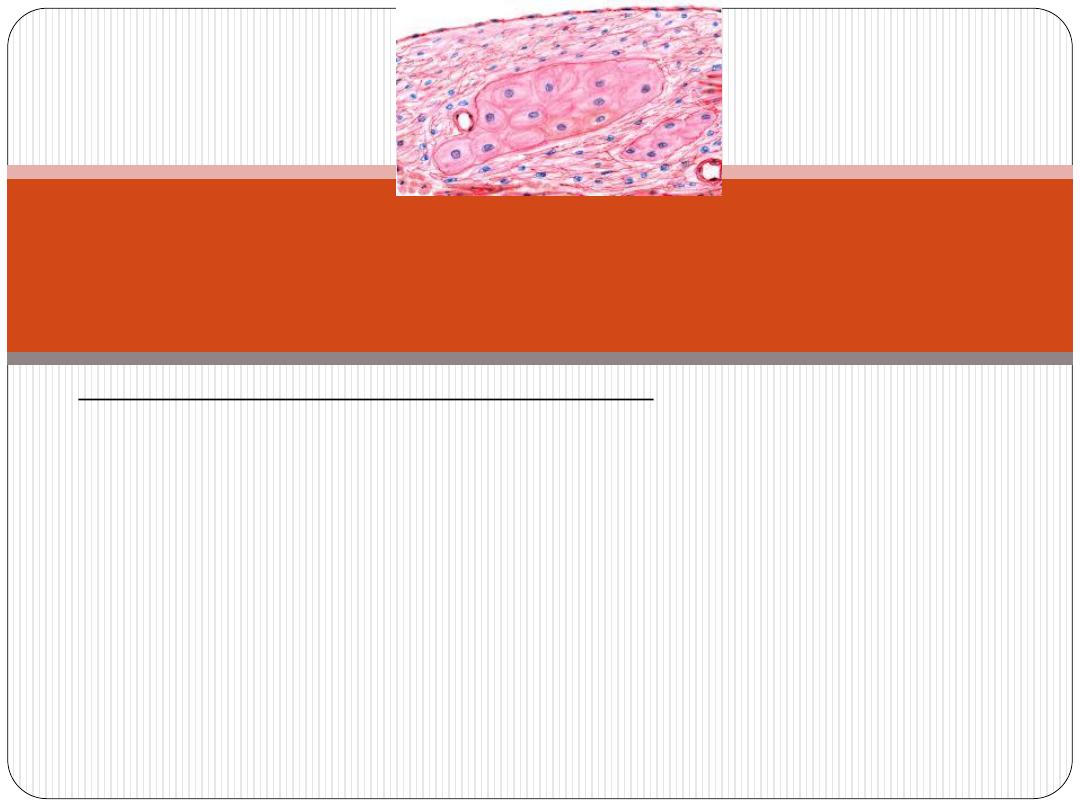

I. Light microscopical (L.M.) features:
Purkinje fibers
resemble
ordinary cardiac m. in that:
they have central nuclei.
they have cross striation.
However they
differ
from them in that:
they are generally larger and paler.
they have more sarcoplasm.
their nuclei are surrounded by clear perinuclear area.
Histological features of
Purkinji fibers:

II. Electron microscopical (E.M.) features:
Ultrastructurally Purkinje fibers have the following features:
•
they contain large amount of
glycogen
and mitochondria.
•
they contain less amount of
myofibrils
which tend to lie
peripherally (this explain the presence of clear perinuclear
area).
•
sarcoplasmic reticulum
is not well developed as in cardiac m.s
Histological features of
Purkinji fibers:
Heart is innervated by:
•
Parasympathetic nerve (vagus)
- ends near SA node. Its
stimulation leads to reduction of the heart rate.
•
Sympathetic nerve
- ends near SA and AV nodes. Its
stimulation leads to increase of heart rate.
•
Free nerve ending
- ends between cardiac muscle fibers.
It is related to pain sensation.
INNERVATION OF THE HEART

-
Partial (temporary)
obstruction
of coronary artery or any
of its branches leads to reduction of O
2
supply to
myocardium that leads to temporary pain(conducted by
free nerve ending). This case is called Angina Pectoris.
-
Complete
obstruction
of coronary artery or any of its
branches (by a thrombus ) leads to sever pain (conducted by
free nerve ending). This case is called myocardial infarction.
CLINICAL NOTES

Thank you