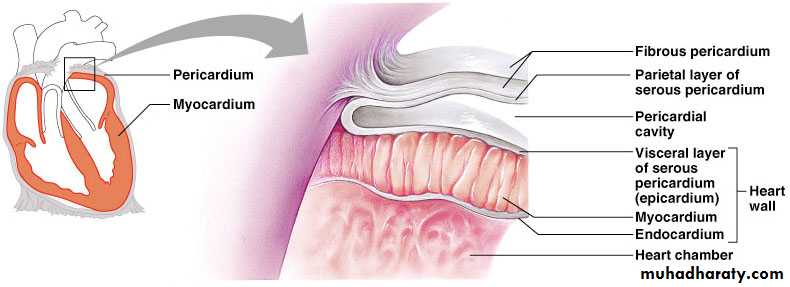
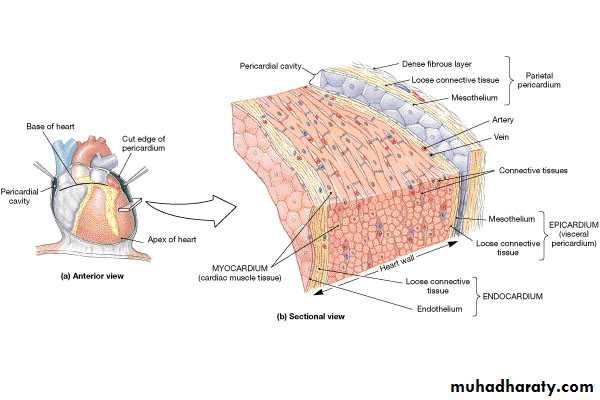
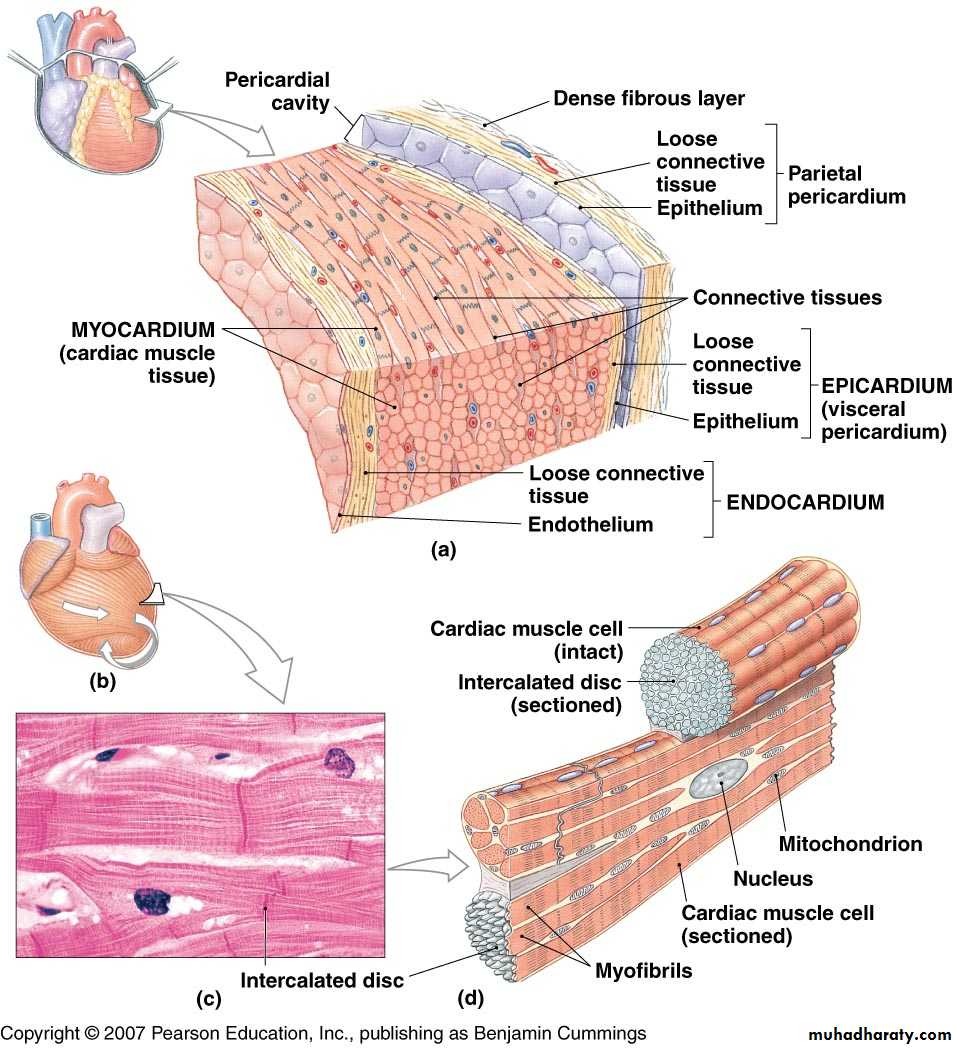
Pericardium
The heart lies enclosed within pericardial membranesFibrous pericardium (pericardial sac) – outer layer of dense CT that protects & anchors
Serous pericardium – double layered membrane with “pericardial fluid” between
Parietal pericardium – lines the pericardial sac
Visceral pericardium – covers the heart; also known as the “epicardium”
Pericardium
Double walled sac around heart composed of:Superficial fibrous pericardium
Deep two-layer serous pericardium
Parietal layer lines internal surface of fibrous pericardium
Visceral layer (AKA epicardium) lines surface of heart
Parietal and visceral layers separted by fluid filled pericardial cavity
Pericardium
Protects and anchors heartPrevents overfilling
Provides friction free environment for heart
Constituents of Heart Wall
Epicardium: the visceral layer of serous pericardiumMyocardium: muscle layer
Fibrous skeleton: interlacing, criss-crossing layer of connective tissue
Endocardium: endothelial layer of inner myocardial surface
Cardiovascular SystemThe HeartAnatomy
The Cardiovascular system is comprised of the heart, blood vessels, & bloodThe heart acts as a “pump”, creating pressure which causes blood to move through the blood vessels of the body, allowing O2 & nutrients to be distributed to, & wastes removed from, body tissues
Cardiac Anatomy
Atria
Receiving chambers of heartEach has an auricle
Pectinate muscles
Ventricles
Discharging chambers of heart
Characterized by papillary muscles and trabeculae carneae muscles
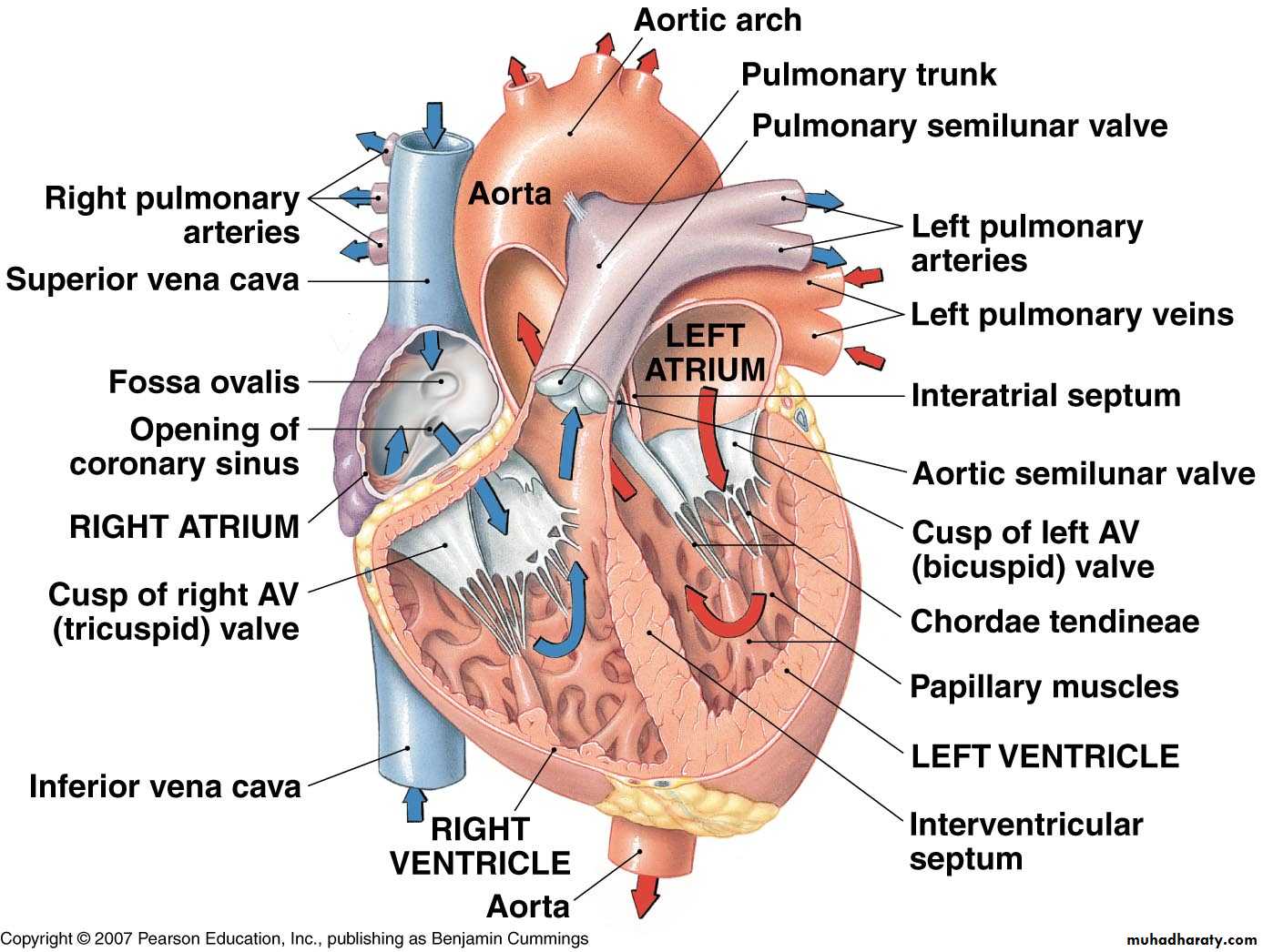
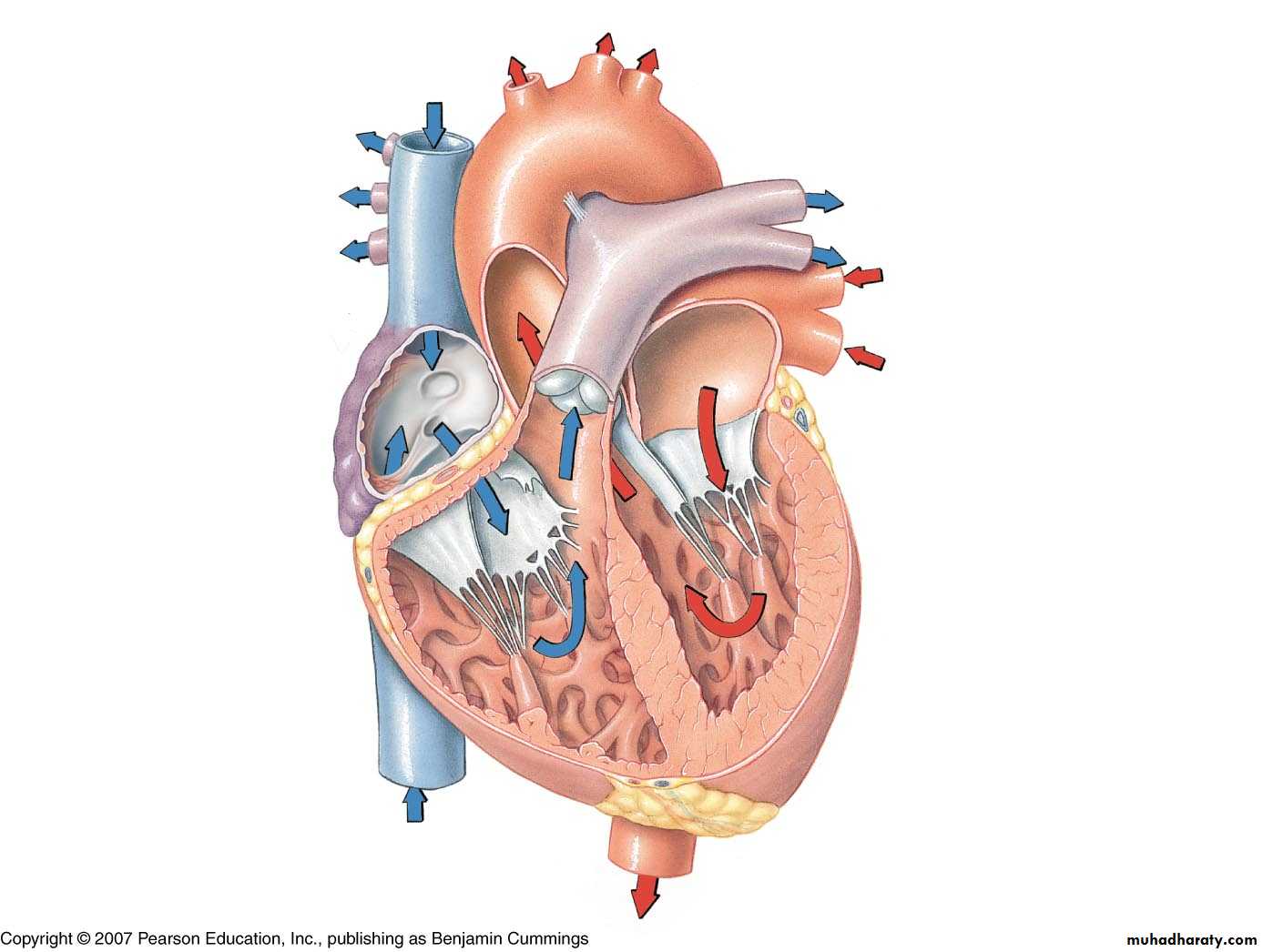
Overview of Blood Flow
Right AtriumTricuspid Valve
Right Ventricle
Pulmonary Valve
Pulmonary Artery
Lungs
Pulmonary Veins
Left Atrium
Mitral Valve
Left Ventricle
Aortic Valve
Aorta
Systemic Circulation
Anatomical Features of the Heart
The heart lies within the mediastinum of the thoracic cavity
Hollow muscular organ with four internal chambers
(2) atria (lt. atrium & rt. atrium)- receive blood from veins
(2) ventricles (lt. ventricle & rt. ventricle)- pump blood into arteries
Superior aspect of heart is the “base” (3rd intercostal space/sternal angle), where the blood vessels attach; Inferior is the “apex” (5th intercostal space), which rests on the relaxed diaphragm
External Features
AuriclesCoronary sulcus – contains the coronary sinus
Anterior interventricular sulcus – contains coronary vessels
Posterior interventricular sulcus – contains coronary vessels
Layers of Heart Wall
Epicardium (visceral pericardium)Myocardium
Endocardium
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001Internal Anatomy of the Heart
Chambers of the heart
Right & left atrium
Separated by the interatrial septum
Right & left ventricle
Separated by the interventricular septum
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001Structure of the Heart Wall
Epicardium = “upon the heart” = visceral pericardium
Dense fibrous connective tissueMyocardium is the middle layer
Cardiac muscle
Endocardium = “inside the heart”
Simple squamous epithelium
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001The Great Vessels
Superior & inferior vena cava
Return blood from body to right atrium
Coronary Sinus
Returns blood from heart wall to right atrium
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001The Great Vessels
Pulmonary veins
Return blood (oxygenated) from lungs to left atrium
Aorta
Takes blood from left ventricle to body
Pulmonary artery
Takes blood (deoxygenated) from right ventricle to lungs
Cardiac muscle tissue
Rt Atrium
Lt Atrium
Pectinate muscles
SVCIVC
Coronary sinus (opening)
Deoxygenated blood
Pulmonary veins
Oxygenated blood
Tricuspid valve
Bicuspid (mitral) valve
Chordae tendoneaePapillary muscle
Chordae tendoneae
Papillary muscleInteratrial septum
Fossa ovalis
Atrioventricular (AV) valves
TricuspidBicuspid
Rt ventricle
Lt ventricleInterventricular septum
Trabeculae carneae
AortaAortic semilunar valve
Pulmonary semilunar valvePulmonary trunk
Pulmonary arteryLigamentum arteriosum
Brachiocephalic trunkLeft common carotid artery
Left subclavian arteryHuman Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001Internal Anatomy of the Heart
Chambers of the heart
Right & left atrium
Separated by the interatrial septum
Right & left ventricle
Separated by the interventricular septum
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001Structure of the Heart Wall
Epicardium = “upon the heart” = visceral pericardium
Dense fibrous connective tissueMyocardium is the middle layer
Cardiac muscle
Endocardium = “inside the heart”
Simple squamous epithelium
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001The Great Vessels
Superior & inferior vena cava
Return blood from body to right atrium
Coronary Sinus
Returns blood from heart wall to right atrium
Human Anatomy, 3rd edition
Prentice Hall, © 2001The Great Vessels
Pulmonary veins
Return blood (oxygenated) from lungs to left atrium
Aorta
Takes blood from left ventricle to body
Pulmonary artery
Takes blood (deoxygenated) from right ventricle to lungs
74
The End
The End