1
1
Sub-phylum Sarcodina
The parasitic amoeba of man
Genera
Troph Cyst
Habitat
Pathogeniciy
Genus Entamoeba:
Entamoeba Histolytica
+
+
Large intestine of man
+
E. dispar
+
+
L.I of man
–
E. polecki (hog)
+
+
L.I of hog
–
E. coli
+
+
L.I of man
–
E. gingivalis
+
–
mouth
–
Genus Iodamoeba
I. Butschlii
+
+
L.I
–
Genus Endolimax
E. nana
+
+
L.I
–
Genus Dientamoeba
D. Fragilis
+
–
L.I
±
Free-living Pathogenic
amoeba
Naegleria Fowleri
+
+
CNS
+
Acanthamoeba
+
+
CNS eye
+
Entamoeba Histolytica
Named by Schaudin in 1903. This amoeba causes a disease known as
amoebiasis, amoebic colitis or amoebic dysentery.
It occurs in all areas of the world but it is more prevalent in tropical and sub-
tropical areas and the rates of infection are higher in crowded areas with poor
personal hygiene and low socioeconomic status e.g. mental hospitals, prisons and
children homes.
Lec. 1
أ
.
صباح النجار
2
2
This amoeba inhabits the large intestine (colon) mainly in cecum and
sigmoid - rectal regions. There are 4 forms in the life cycle of E. histolytica but
only two forms are seen in stool specimen.
Trophozoite (vegetative form): A stage in the life cycle of a protozoan parasite in
which the cells are taking in nourishment and divided by binary fission.
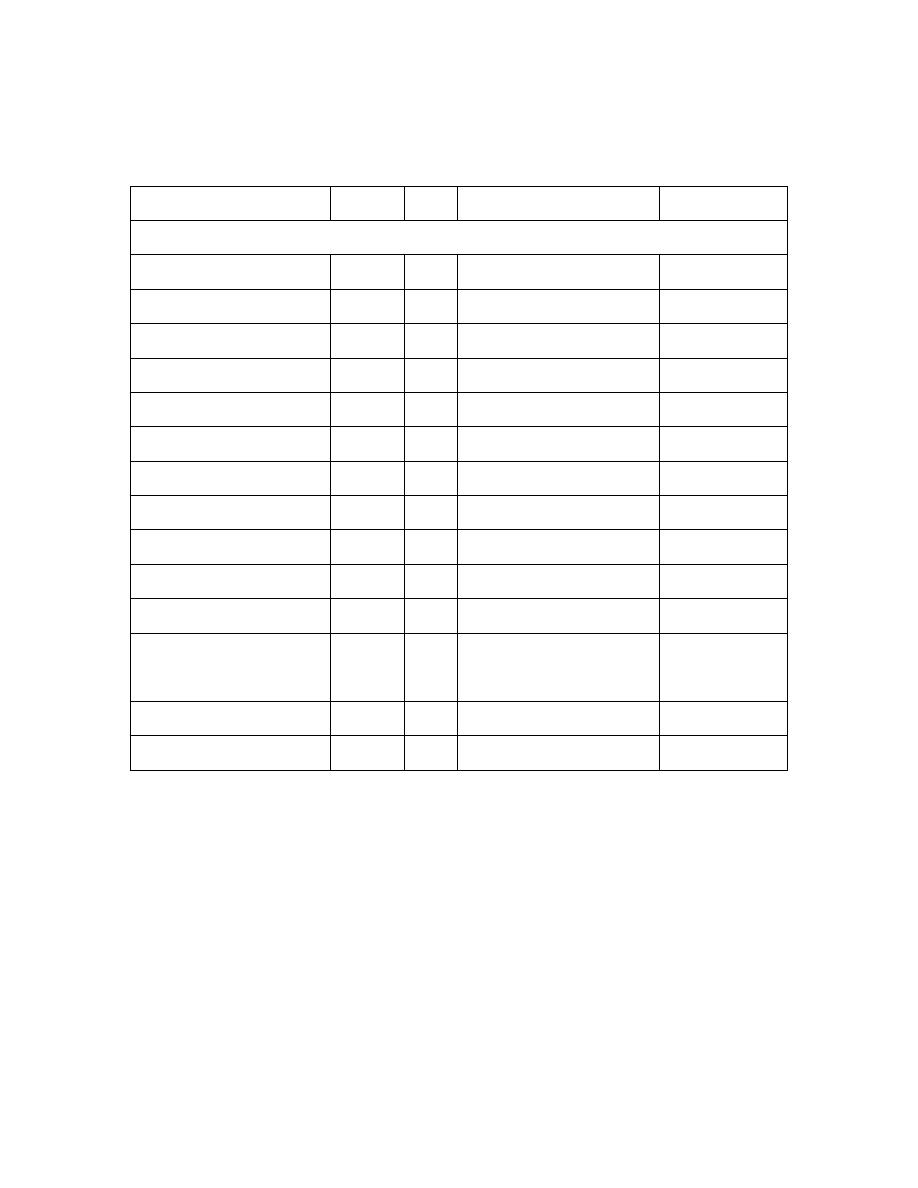
In fresh unstained smear, E. histolytica trophozoites are active, progressive
with directional motion. Ectoplasm clear, well differentiated from granular
endoplasm, pseudopodia are elongated with finger – like projection. The
trophozoite contain single spherical nucleus surrounded by nuclear membrane. The
chromatin materials found on inner surface of nuclear membrane with regularly
distributed granule and in the center of the nucleus there is a karyosome.
Immediately arround the karyosome there is a clear halo and a chromatic
fibrils extend between nuclear membrane and a halo. The nucleus is called
histolytica type nucleus. The trophozoite ingests RBCs which may be seen in fresh
preparation or in stained smear.
E. histolytica trophozite
3
3
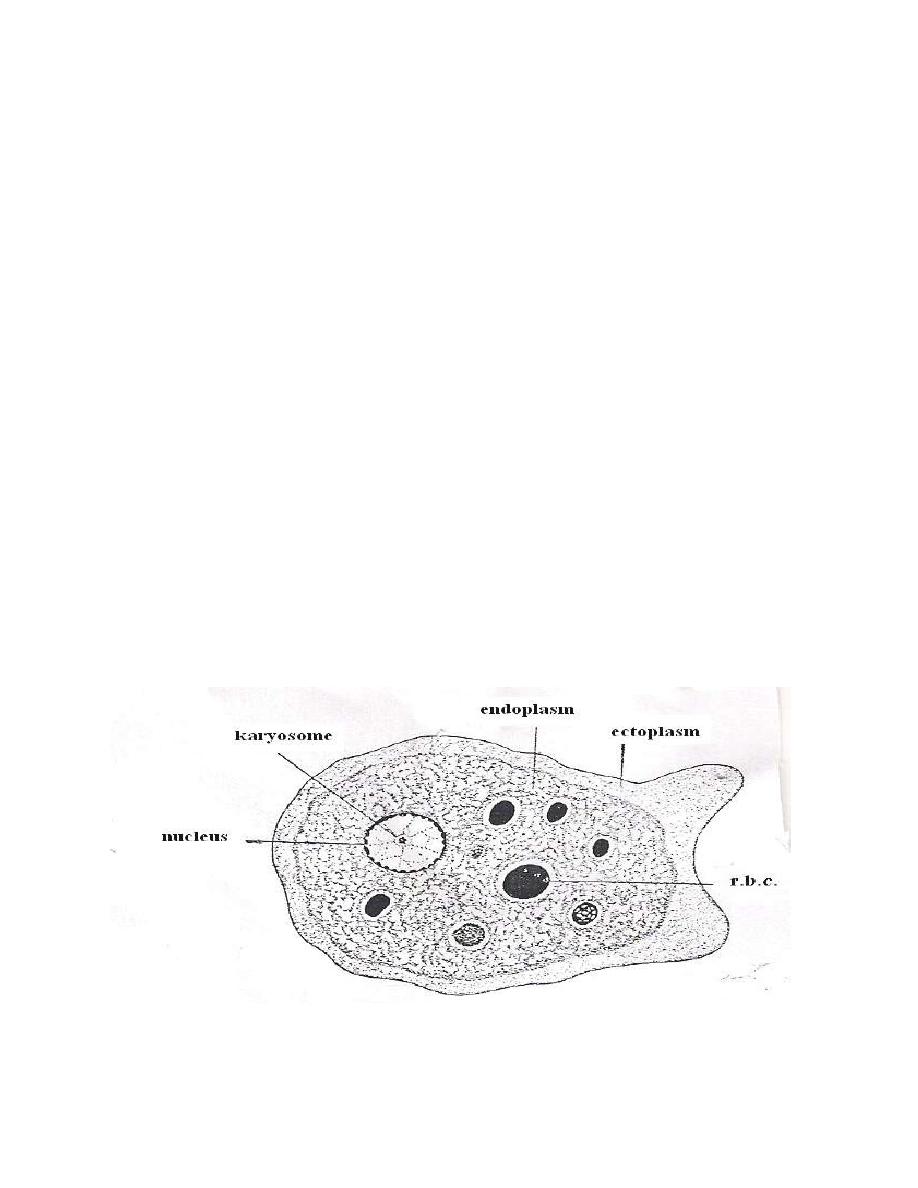
Cyst: rounded or spherical in shape with smooth cystic wall, the cytoplasm
contains glycogen mass and one or two occasionally more dark-staining sausage or
cigar shaped with rounded ends chromatoidal bodies. Chromatoidal bodies become
smaller and disappear as the cyst mature.
The cyst may contain from 1 – 4 histolytica type nuclei and the infective
stage is mature quadrinucleated cyst.
E.histolytica cysts
Histolytica type nucleus
4
4
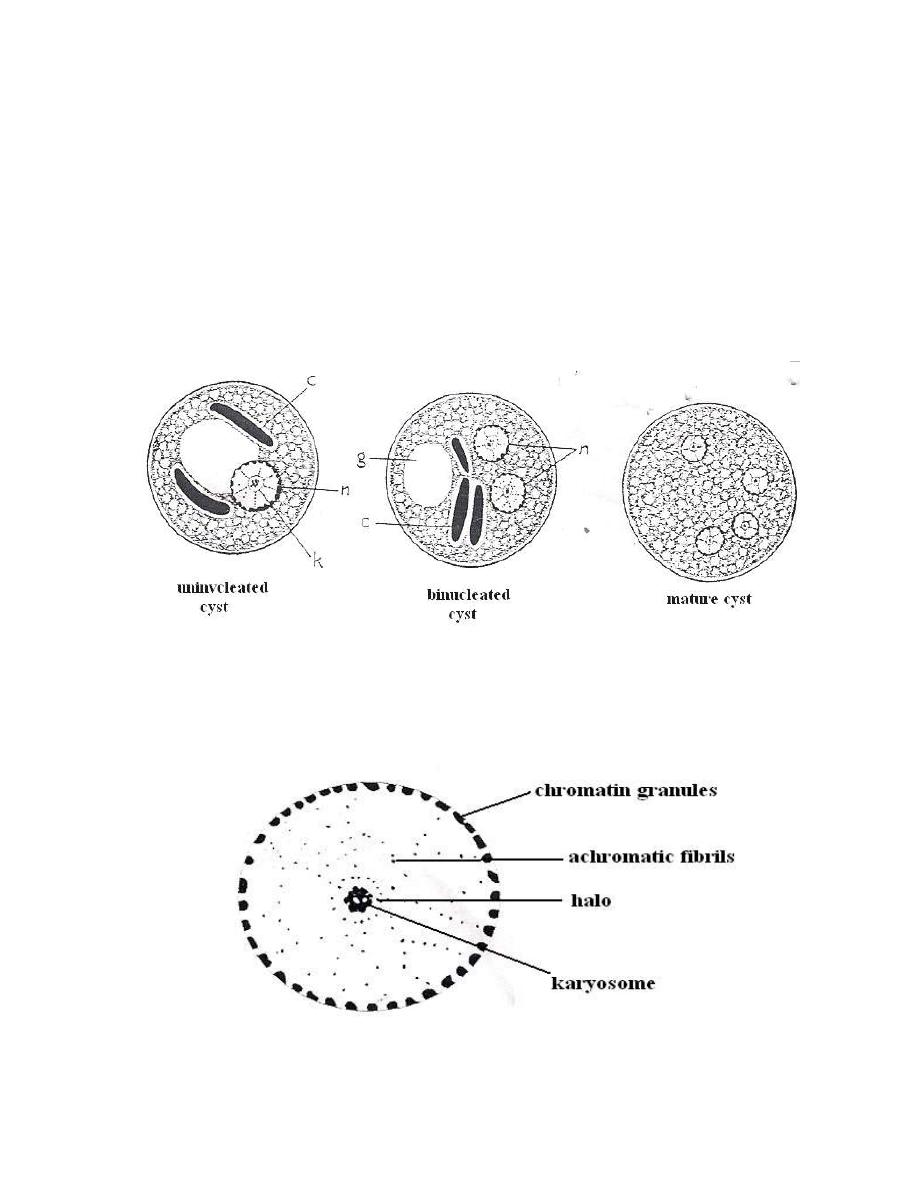
Life cycle
E. histolytica life cycle is simple and direct. The parasite has traphozoite,
precyst, cyst and metacystic stage during the life cycle but only
trophozoite and cyst stages are recognized in feces. Trophozoites are
easily destroyed in outside environment and degenerating within minutes.
Cysts can remain alive outside the host for weeks or months especially
under damp conditions. The cysts resist to routin chlorination and killed
by freezing and desication. This amoeba inhabits the lumen of the colon.
Encystations occurs in the intestinal lumen after transformation of cyst to
precystic stage. Either before the stool is passed or soon therefore, the nucleus of
the cyst divides into two, then each of the two divides once again so that the
mature cyst typically has 4 nuclei. When mature cyst ingested with contaminated
food or drink by a new host, excystation occurs in the lumen of small intestine,
here, under the influence of neutral or alkaline digestive juices, and the activity of
the amoebae, the cyst wall disintegrates. The liberated 4-nucleated metacystic
amoeba divides into 8 small amoebulae and moves downward to the large
intestine.
Life cycle of E. histolytica
5
5
Types of E. histolytica Infection in Man
There are two types of amoebiasis:
1- Intestinal amoebiasis (primary infection).
2- Extra-intestinal amoebiasis (secondary infection).
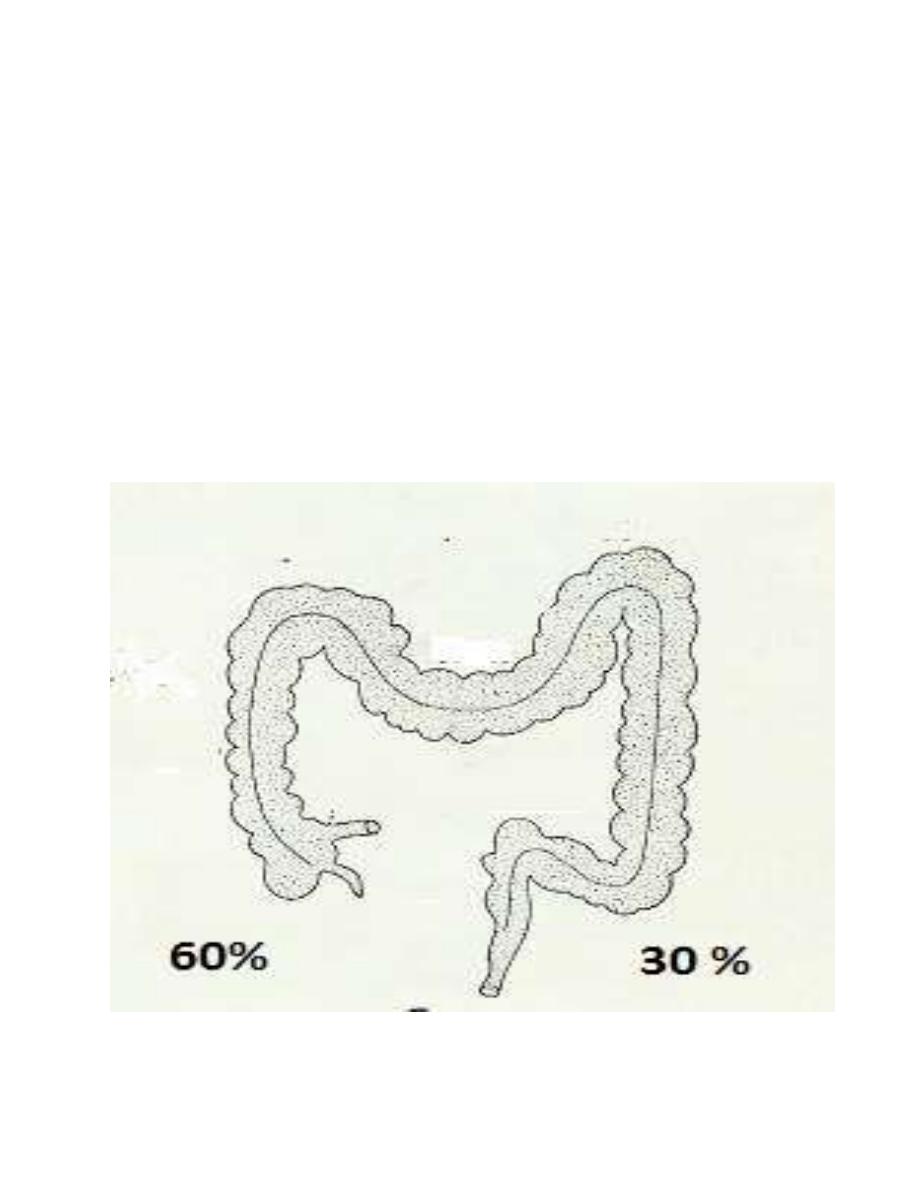
Sites of Intestinal Infection
The infection may occurs at any point of large intestine, but the most
frequent primary sites are the cecum (about 60%) and the sigmoidorectal region
(about 30%).

6
6
E. histolytica infection occur via fecal – oral route . food and
water becoming contaminated through exposure to human
feces or through flies . cyst carriers are the main reservoirs .
sexual transmission also occur mainly in homosexuals .
