
Classification Helminths
Phylum:Nemathelminthes (Round)
Class: Nematoda
Phylum: Platyhelminthes (flat)
Class: Cestoda & Trematoda

Objectives:
study the general characteristics of
medically important tapeworms including their
morphology, life cycle, pathogenesis and
laboratory diagnosis
Tapeworms (cestodes)

General characters
of tape worms
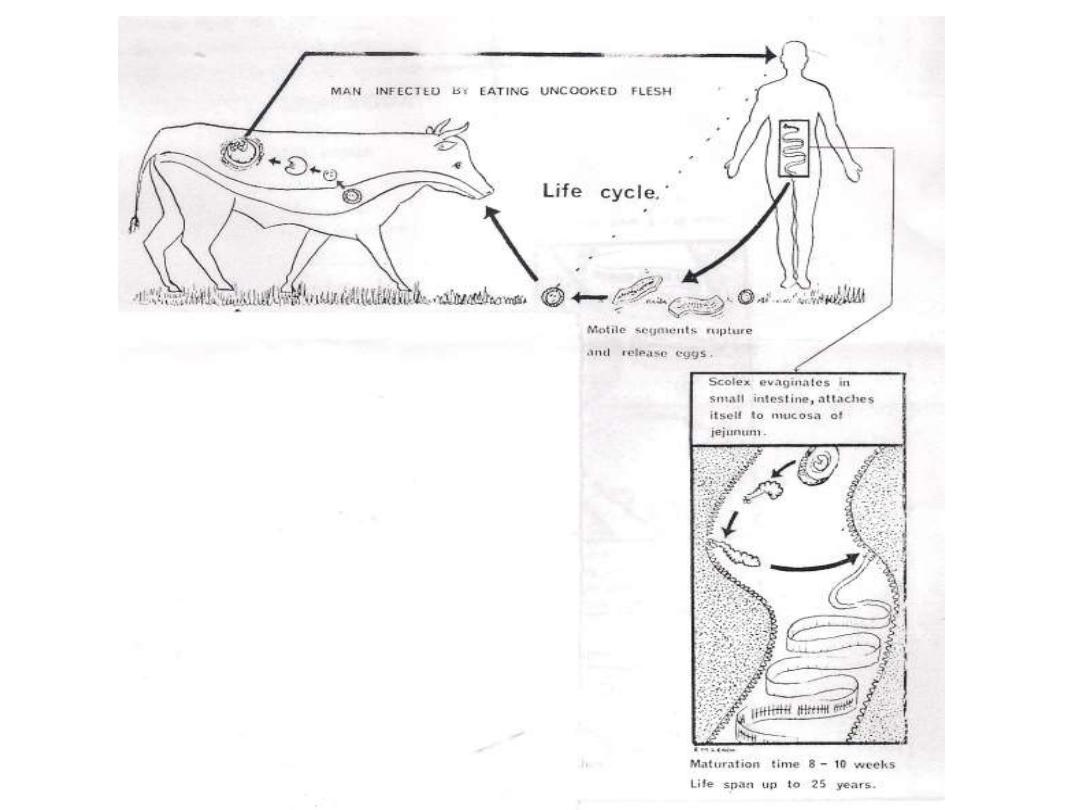
All tapeworms have indirect life cycle except
Hymenolepis nana
.
•They have ribbon- like shape, flattened dorsoventrally &
segmented .
•Adult tapeworm inhabits the small intestine of vertebrates. While
the larvae inhabit the tissues of vertebrates & invertebrates.
•All tapeworms are hermaphrodites,
•They have no gut or digestive tract,absorbtion takes place
through tegument.
.
Adult tapeworms produce minimal intestinal irritation and few
systemic effects(mechanical and chemical effects
).

Morphology of adult tapeworms ;
Adult tapeworm divided in to ;
-
Scolex
or head provided with attachment organs .
-
Neck
or region of growth .
-
Strobila
or chain of segments or proglottids ;
1-Immature proglottids .
2-Mature proglottids.
3-Gravid proglottids
.

Types of Cestodes larvae
A - Bladder larvae :
1-Cysticercus : e.g.
T. solium, T. saginata.
2-Cysticercoid: e.g.
Hymenolepis spp.
3-Hydatid cyst : e.g.
Echinococcus spp
.
4-Coenurus: e.g.
Taenia multiceps.
B – Solid larvae:
1-Procercoid: e.g.
D. latum.
2-Plercercoid: e.g.
D. latum.
Bladder larvae :
•Cysticercus
: a true bladder worm, It is oval in
shape, has fluid- filled membranous bladder with
invaginated scolex. e.g. larvae of
Taenia solium
&
Taenia
saginata
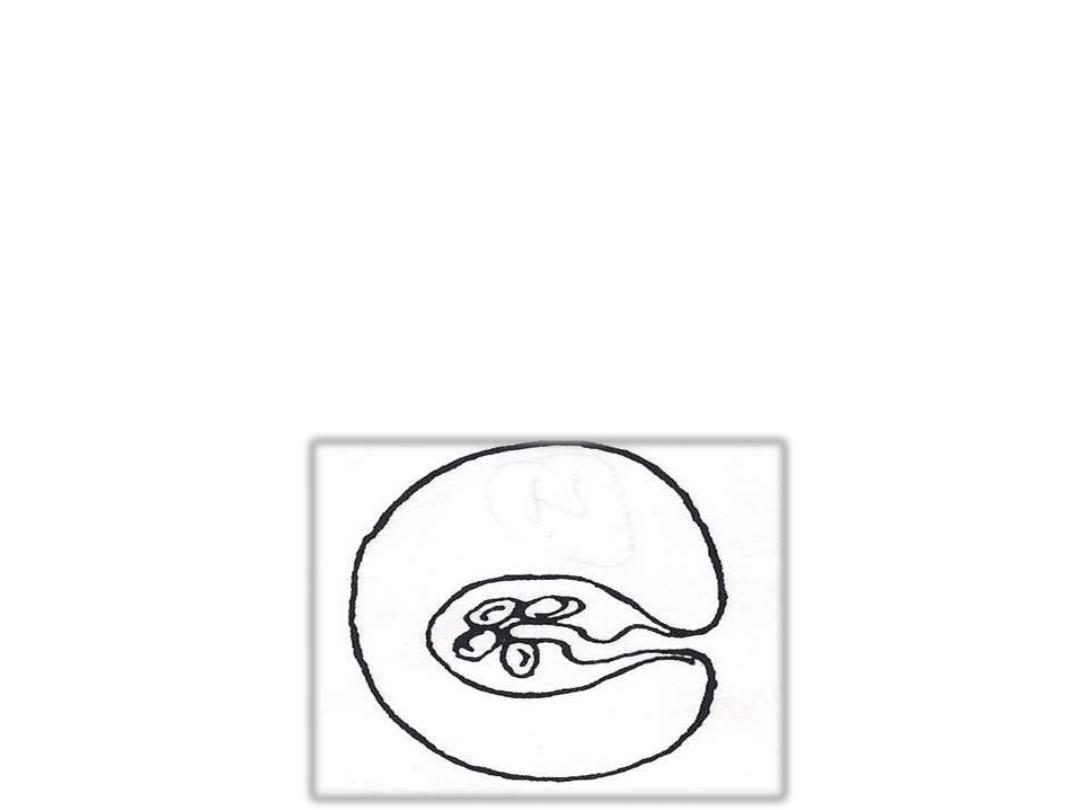
•
Cysticercoid
;is not a true bladder worm, it has
bladder filled with parenchyma cells and
invaginated scolex and a caudal appendage . e.g
.
larva of Hymenolepis spp
.
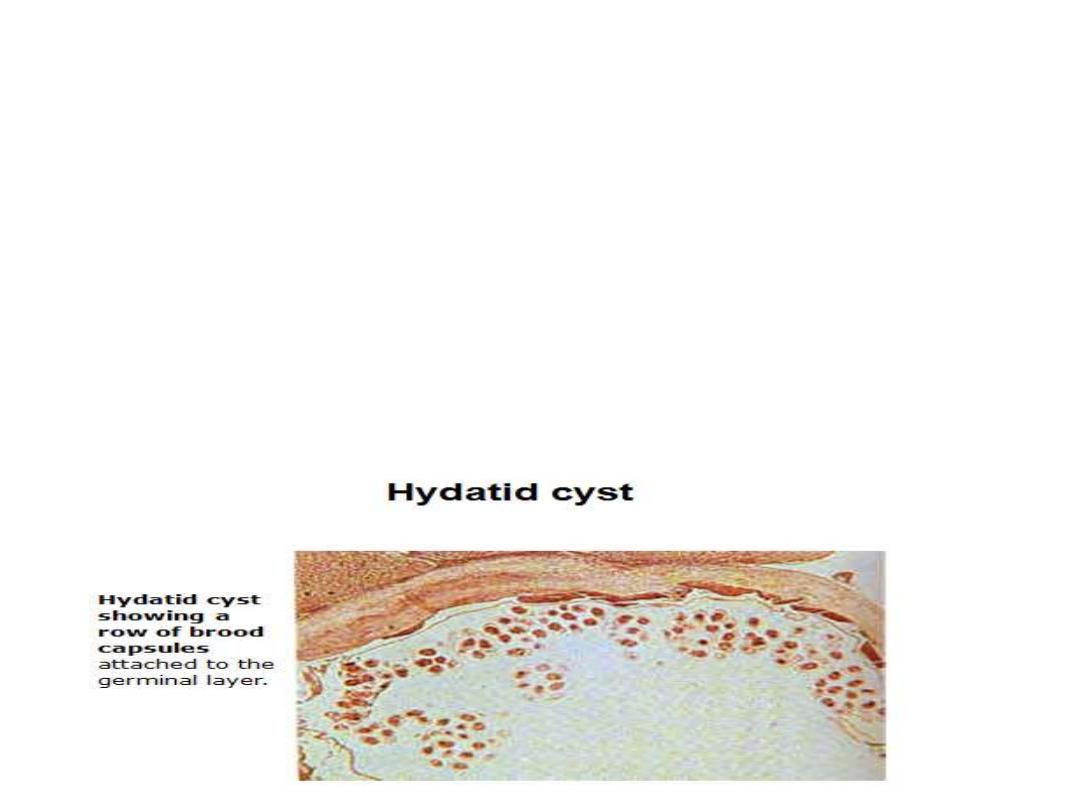
Hydatid cyst:
large bladder composed
of, outer laminated and inner
germinal layers and filled with
hydatid fluid . It is form multiple
scolices and numerous daughter or
brood capsules. e.g. larva of
Echinococcus spp
.

Coenurus
: A bladder worm
resembles Cysticercus except
that its bladder generally is
much larger and bears
numerous scolices rather than
one e.g. larva of
Taenia
multiceps
.
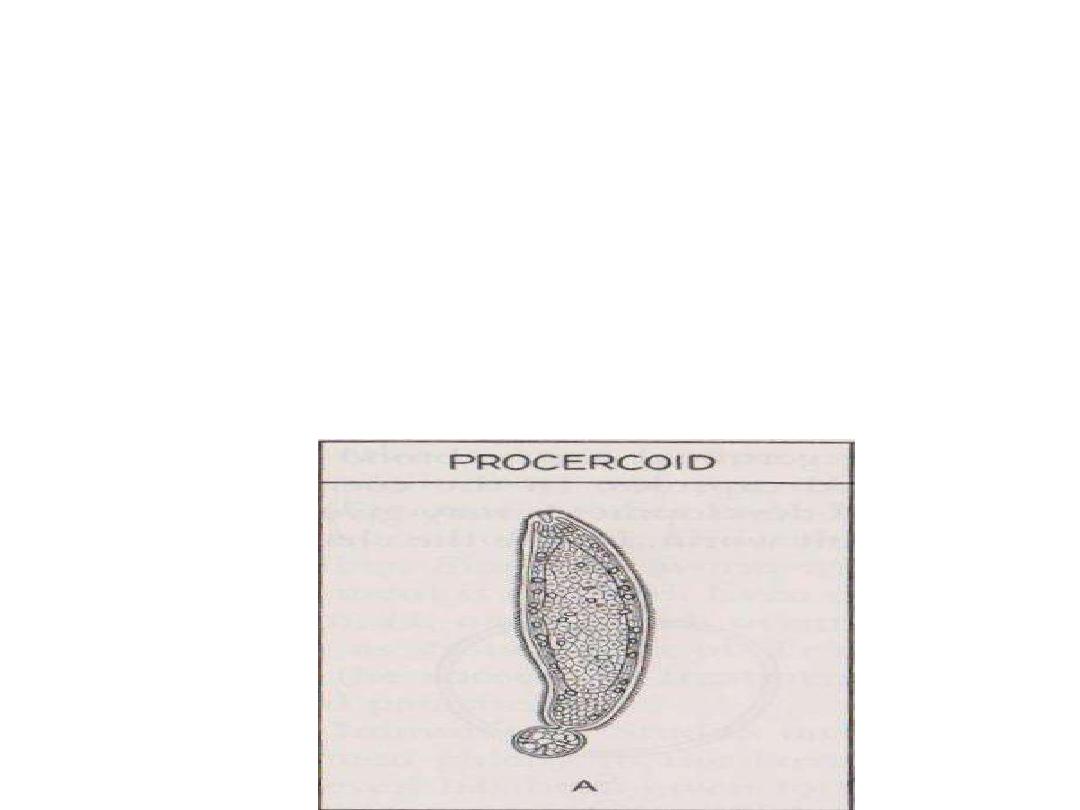
•B-solid larvae;
•Procercoid
: sac – like solid body with
cephalic invagination and caudal spherical
appendage at its posterior end which contain
6 hooks e.g.
Diphylobotherium latum
.

Plerocercoid (sparganum)
: chalky white solid
structure with pseudo segmentation composed of
caudal solid appendage and invaginated head in
the neck e.g.Diphyllobotherium latum
.

-Diagnosis.
1-Infection with adult:
-
Scolex, egg , segment
.
2-Infection with larvae:
-
Serology
-Histopathology
-Classification ;Class Cestoidea has two orders
1-Cyclophyllidea
2-Pseudophyllidea
.
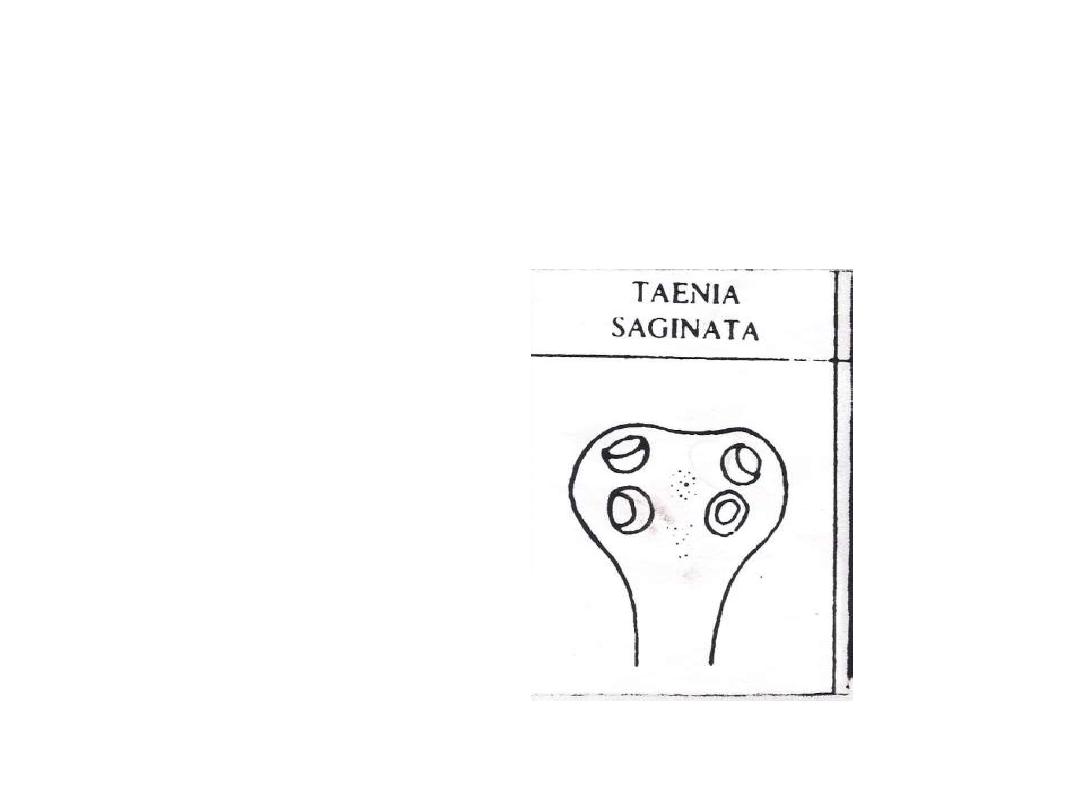
•
T
aenia saginata (beef tapeworm)
•
-Disease ; Taeniasis
•
Beef tapeworm infection
•
-Habitat ;Upper part of
•
small intestine
•
-Morphology
•
1-Scolex (unarmed)
•
2
-Neck
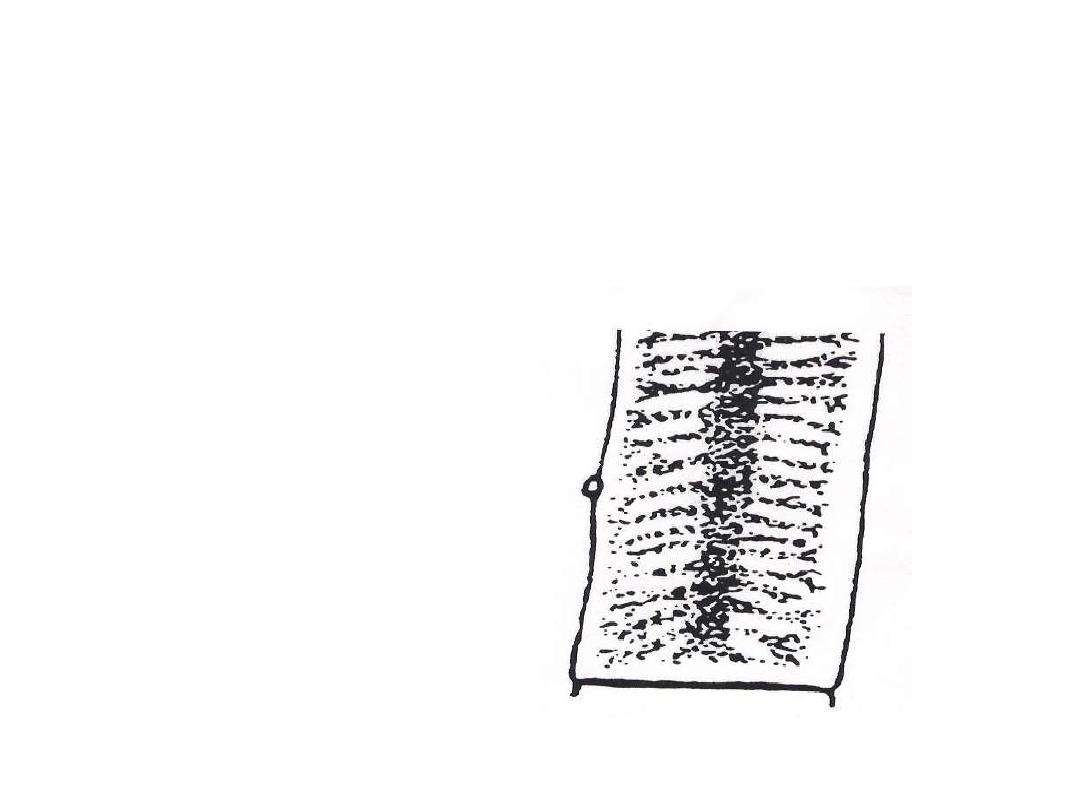

•
3-Strobila
•
-Immature segment
•
-Mature segment
-Gravid segment
15-30 lateral branch.
Gravid segment t

Egg
of Taenia spp
.(S S C C)
size;36 micron,
shape;globular or spherical,
color; yellowish brown
contents;
Taenia spp. eggs contain an embryo that is
called an
oncosphere
or
hexacanth embryo
,surrounded by striated
embryophore.
The egg
surrounded by delicate
egg shell.
Echinococcus granulosus
Egg
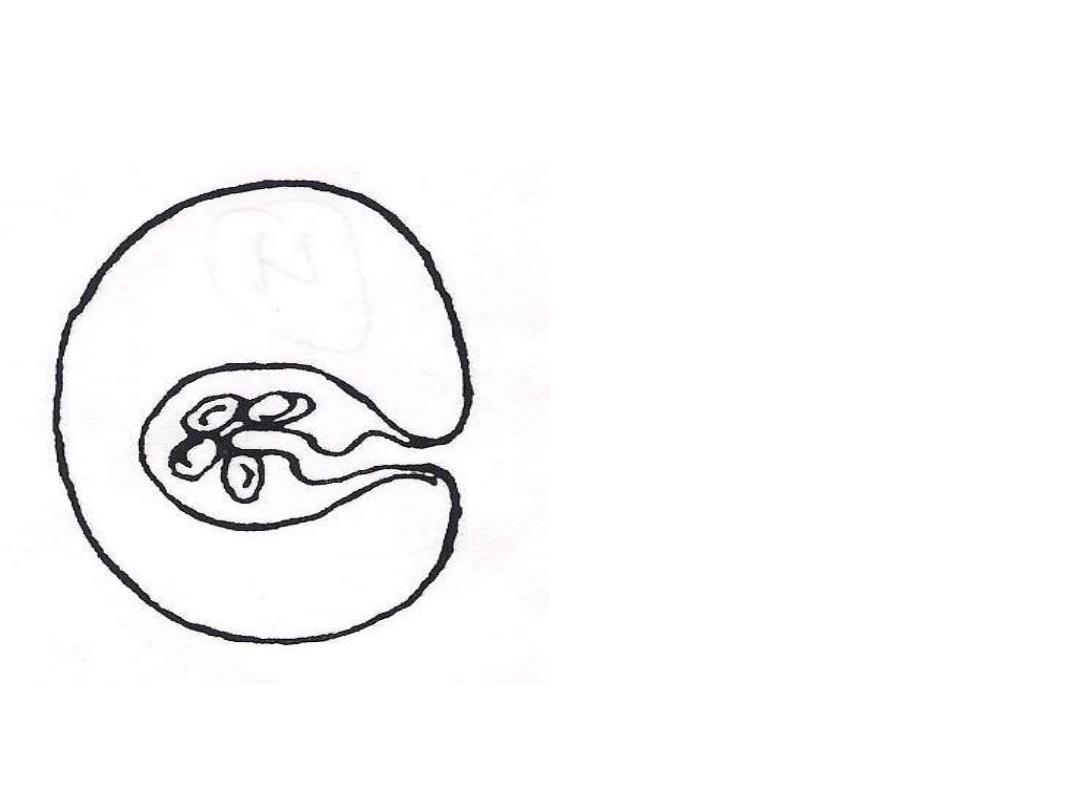
Cysticercus bovis
Membranous bladder filled with
a fluid with invaginated
unarmed scolex
.

•
symptomatology
Pathogenesis, pathology &
-
•
of adult
presrnce
Little damage result from the
worm in small intestine
•
-Intestinal disturbance
•
-Acute intestinal obstruction
•
-Appendicitis
•
-Hunger pain
•
-Systemic intoxication
-Mental worried and embarrassment ,the proglottids
are motile and may cause anal purities as they move
on the skin adjacent to the anus.

•
Diagnosis
•
1-General stool examination ( egg and gravid
segment )
•
2-Perianal swab (Scotch tape slide technique)
•
3-Examination of scolex (after medication
)
•
Treatment
•
Niclosamide, praziquantel and mebendazole
.
