DR.RIADH ABDULATIF ALOBAIDYASS.PROFF.CONSULTANT PEDIATRICIANCOLLEGE OF MEDICINEUNIV.OF MOSUL
Hematology
Hemoglobin; normal HB consists of 4globin chains and 4 heme groups. These globins chains are inhereted from parents..At birth newborn has HbF made of 2alpha and 2 gama chains form74% of total Hb and adult type of HB (HbA) forming25% (2alpha and 2beta), and HbA2 of( 2alpha and 2 delta) chains form 1%.
Any abnormal Hb formed due to deletion of gene coding for the globin chain lead to change in Hb structure and lead to hemolytic disease as life span of the RBC will be shortened giving the name Hemoglobinopathies .like HbS and HbC, and absence of HbA as in thlassemia.
Hemoglobin
Fetal Hb gradually replaced by HbA and reaches adult kind by 1 yr.as HbA 97%,and HbA2 2-3%.At birth full term Hb >14 g-21 g/dl. then reduced gradually over the first weeks of life to reach a nadir around 10g/dl at 2 months.
preterm babies have more fall in Hb reaching 7-9 g/dl. Then after that age the HB increases with age.
Folic acid and Vit B12 store for preterm and term babies at birth are adequate for many months.
The iron store is adequate till first 6 mon in fullterm and for 2 mon in preterms, so should have iron supplement after this age because breast milk alone is not enough in iron supply after this age,in form of complementary weaning semisolid food or cereals fortified with iron or even iron drops.
anemia
Defined as; reduction in Hb concentration or RBC volume (packed cell volume)below the accepted range for that age resulting in a lower ability for the blood to carry oxygen to the tissue.. The anemia considered if;Newborn (0-28 days) Hb <14g/dl
Infant1-12 monthes ;<10 g/dl
Children > 1 yr <11 g/dl.
Anemia is either due to ;
A. Inadequate RBC production ;as due to iron def. anemia or folic acid defeciency or vit. B12 deficiency or bone marrow depression as aplastic anemia.
B.Loss of blood due to bleeding.
C. Destruction of RBCs in the spleen and consumption as in chronic hemolytic anemia or intravascular destruction as in favism (G6PD deficiency).
Anemia usually classified according to blood film.
Hypochromic microcytic: iron def.anemia, thalassemia.
Normochromic normocytic anemia:sickle cell anemia,anemia of chronic diseases.
Macrocytic anemia: Folic acid or B12 deficiency,or bone marrow suppression .
Anemia is either mild or moderate or severe ...
Approach to the diagnosis of the cause of anemia
If child present with pallor and other features like pica or koilonychia or jaundice or fatigue or anorexia ; you should search for diagnosis ;
A)History ;as family Hx of hemolytic anemia and nutritional Hx and bleeding Hx or malabsorption diseases.
B) Full physical examination for pallor, growth status, jaundice,splenomegaly and other possible causes
C)Investigations; includes total serum bilirubin, complete blood count CBC; HB,RBCs count (5 million), MCV(80-100fl), MCH(27-32pg ) reticulocyte count( 1-2%). RDW%; (increased above 14%.,like in thalassemia major and iron def. anemia) but normal in thalassemia trait.normal value(13- 14%)
Serum Ferritin, serum iron and Total iron binding capacity TIBC (serum transferrin).
Stool examination for occult blood, and ova of parasites.
HPLC OR HB ELECTROPHORESIS to identify the type of HB and it’s quantity.
koilonychia
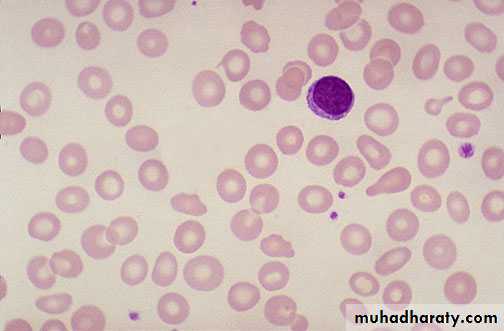
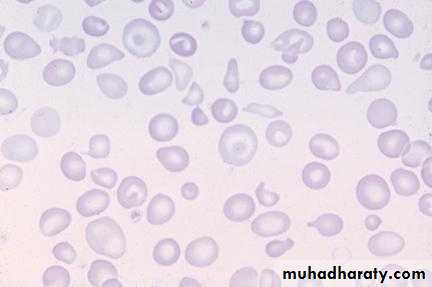
Blood film iron def. anemia
Iron def. anemia blood film
Laboratory studies differentiate most common microcytic anemia
Study normal
Iron deficiency an
Alpha and beta Thalassemia trait
Anemia of chronic diseases
HEMOGLOBIN
DECREASED
DECREASED
DECREASED
RBC count
<5X10*9/L; reduc.
Increas>5.5X10*9L
<5X10*9/L reduc.
MCV(80-100fl)
DECREASED
DECREASED
NORMAL
RDW(<14%)
INCREASED
NORMAL
NORMAL
MCH (>27pg)
DECREASED
DECREASED
NORMAL
SERUM FERRITIN(iron store)
DECREASED
NORMAL
INCREASED
Total iron binding capacity TIBC (transferrin)
INCREASED
NORMAL
DECREASED
RETICULOCYTE1-2%
DECREASED
NORMAL
NORMAL
BILIRUBIN indirect
NORMAL
INCREASED
NORMAL
SERUM IRON
DECREASED
NORMAL
DECREASED
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISof iron def. anemia
Alpha thalassemia trait (a,a/- ,-)cis,or trans (a,-/a,-
Due to deletion of 2 genes(alpha) coding foreach alpha globin chain
Beta thalassemia trait. Due to deletion of one gene inherited from one parent.
Both are like iron deficiency anemia in CBC indicies as low HB, low MCV ,low MCH but; in thalassemia minor; A-thal. or B-thal traits the;
serum iron is normal, and serum ferritin is normal, and RBCcount high, RDW is normal,iron binding capacity is normal; while in iron def. anemia; serum iron is low ,and ferritin level is low, and iron binding capacity is high and RBC count is low, RDW is increased. BOTH thalassemia traits are with mild anemia, like iron def. anemia which is usually mild and is uncommon to be moderate severe anemia .
Both A- thlassemia trait or B-thalassemia trait are called thalassemia minor ;
HB electrophoresis or HPLC, shows normal HB form in Alpha- thalassemia.
But in B-thalassemia trait ;HPLC ; shows elevated HBA2,and elevated HBF 1-3%, But both give hypochromic microcytic anemia, similar to iron def. anemia.
Iron defeciency anemia causes
Causes of iron def anemia in infants and children; nutritional when infant weaned on low iron food after 6 months or if there chronic blood loss as rectal polyp, or malabsorption as celiac disease, treatment in addition to search for the underlying cause and correct it, give oral iron as 6mg/kg daily for 3 months as to treat and to replenish the body store for iron.No nutritional iron def. anemia can occurs in infant full term below 6 months: but other causes YES, like if has thalassemia or congenital pure red cell aplasia(Diamond-Blackfan) or parvovirus infection in infants lead to transient pure red cell aplasia may cause anemia in first 6 months
Megaloblastic anemia
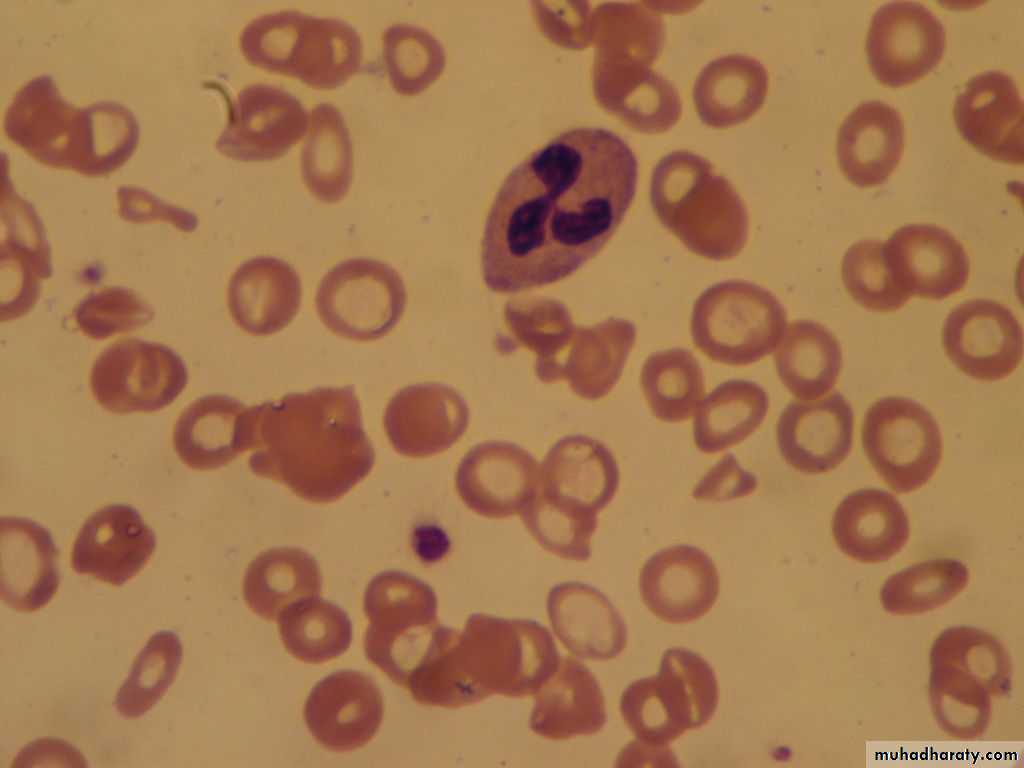
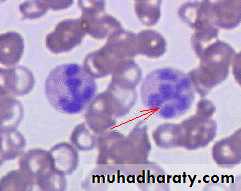
Uncommon .Is due to folic acid deficiency or vit.B12.deficiency ,either nutritional or due to malabsorbtion .Folic acid def.may be present in chronic hemolytic anemias if folic acid not supplied to the patient regularly. Megaloblastic anemia; CBC shows RBCs macrocytes ;MCV>110 fl, with hyper-segmented nuclei of the neutrophiles.
Megaloblastic anemiamacrocytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
1.Hemoglobinopathy as:B-thalassemia
A- thalassemia
Sickle cell anemia .
HBC,HBE,persistant HBF
2.red cell enzyme deficiency:
a. G6PD def.
b. pyruvate kinase deficiency
3. immune hemolysis with Coomb test +ve.
4.Hereditary spherocytosis. due to membrane disorder.
HB TYPES IN HEMOLYTIC DISEASES
CHILDHB A
HB A2
HB F
HB S
NEWBORN NORMAL
25%
1%
74%
--
ADULT NORMAL
97%
2-3%
--
--
B-THALASS TRAIT
>90%
5% increased
1-3% elevated
--
B-THALASS MAJOR
----
2-3%
>95%
--
A-THALASS TRAIT( like HB adult normal)
97%
2%
-----
-----
SICKLE CELL TRAIT
60%
2%
3-5%
40%
SICKLE CELL DISEASE
---
3%
10%
MAILY HB S
B-Thalassemia major
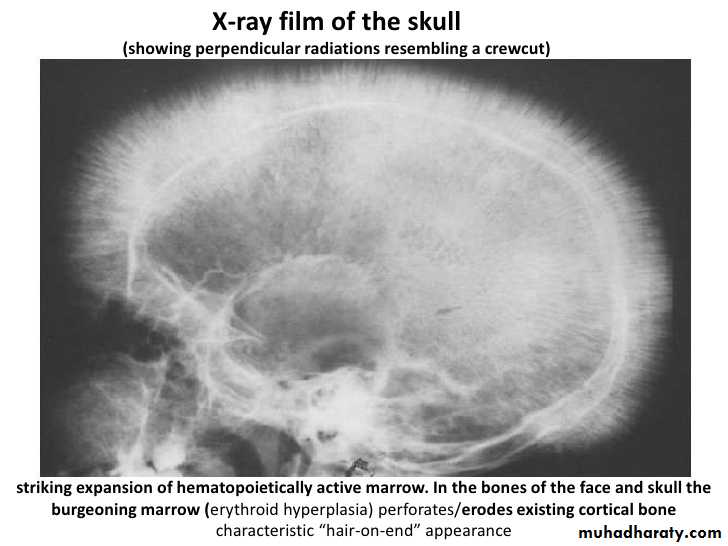
Autosomal recessive,with severe anemia and ineffective erythropoeisis due to rupture of RBC inside bone marrow due to toxic effect of alpha chains. it in common in middle east and Greece and Africa. It does not form HBA. RBC life span is short and rapidly destructed in the spleen and bone marrow. Definite diagnosis is by HPLC(high performance liquid chromatography) give mainly HBF in the patient blood.
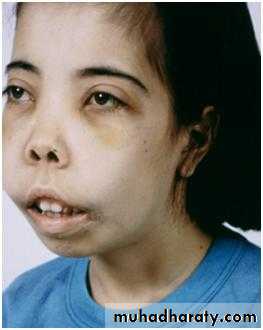
It is blood transfusion dependent for survival,and start early by3-6 months.Features includes jaundice anemia, boosing of maxilla due to thickening of flat bones as extramedullary erythropoeisis,hepatosplenomegaly, hyperpigmentation of skin due to iron overload .
Thalassemic face in B-thalassemia
Hair on end in skull X-R
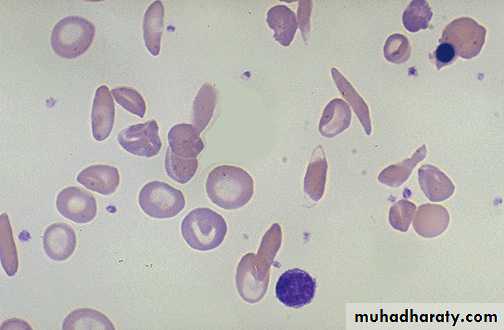
Blood film in B-thalassemia major
B-thalassemia complications
Monthly blood transfusion may be needed to keep Hb level above 10g,so to decrease bony changes and improve growth. Iron over load due to repeated transfusion may deposit in the pituitary lead to growth faillure, and infertility, and in pancreas lead to diabetes, and in the liver lead to cirrhosis, and in the heart leading to cardiomyopathy and a cause for rapid death. Other complications are hepatitis B and C. Even HIV infection due to repeated BT. Hypersplenism(increased consumption of RBCs,or other blood elements) may add more frequent need for BTs.Aplastic crises when pt. gets viral infection as parvovirus B19 ,leading to severe anemia as transient depression of erythropoeisis by the virus .
Diagnosis:
Thalassemia beta major usually with CBC shows Hb level< 6gm,slight increase in reticulocytes count as 5%.RBCs in smear shows are hypochromic microcytic and anisocytosis (size differences ),poiliocytosis(shape variations) with target cells ,and high RDW >14% due to variation in size= anisocytosis.
Serum ferritin, and serum iron are high due to Fe. over load
HPLC shows mainly HBF AND IS DEFINITE DIAGNOSIS
prognosis
Usually fatal, with aggressive and regular BTs, patient may live till forties.
Death occurs due to infections or severe anemia or cardiomyopathy.
Prenatal and neonatal diagnosis
Usually neonatal screening test at birth by HPLC to search for hemoglobinopathies to give clue for diagnosis by Guthrie test to take: spot of blood for the HPLC test on filter paper.PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS performed by taking chorionic villous biopsy for DNA test at 12wk of GA ,in case of both parents are known carriers for the gene of thalassemia ,and possible to get baby with thalassemia by ¼,so to give parents option whether to continue the pregnancy or to end it.
B-THALASS.TREATMENT
Regular blood transfusion to keep HB>10.Chelating therapy for iron load with either desferrioxamine; Subcutaneous infusion for 6 days in a week, or;
by oral drug ;deferasirox (Exjade) in start dose 20mg/kg/day. start when serum ferritin level more than 1000 micg/dl .
Exclusive curative treatment is by bone marrow transplantation from HLA identical sibling
donor.
ALPHA THALASSEMIA
Due mutant genes for alpha globin chains inherited from carrier parents.4-genes del. leads to absent alpha chains so forming 4-gama HB (forming HB BART); lead to rupture of RBC and hydrops fetalis.
For 3-alpha gene delesion can help forming HBH and go after birth and form HBH with 4-B chains with time; and is severe hemolytic condition.
For 2-alpha gene delesion(alpha trait) it leads to mild hypochromic microcytic like iron deficiency anemia. Alpha thalassemia major is rare but traits is frequent.
Immune hemolytic diseasesCoomb test positive
Rh isoimmunisation .
ABO incompatibility,.
hemolytic diseases like SLE ,drugs, certain virus infections like EB virus
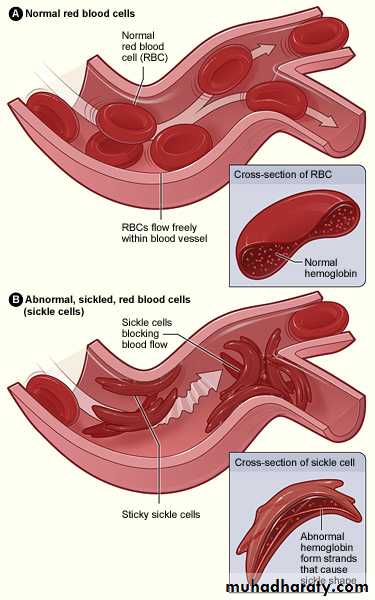
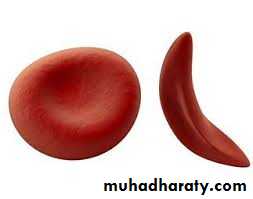
Sickle sell disease
It is also common in middle east. It is due to abnormal beta chain forming HBS.It is it is due to mutation in B- gene which cause a change in the amino acid in putting valine in place of glutamic acid in the globin. There are three forms of SCD :A) Sickle cell anemia HBSS ;pt. is homozygous for HBS, all his HB is formed of HBS due to 2 genes mutation for sickle HB.
B) HBSC ;child inherits HbS gene from one parent and HbC gene from another. So also no HBA can be formed .
C) Sickle B- thalassemia. Affected child inherits gene for beta- thalassemia from one parent and sickle gene from the other. The pt. has no HBA . And has similar symptoms like sickle anemia.
Sickle trait; inherit one mutant sickle gene from one parent. Nearly 40% of HB is HBS and 50% HB A. The pt. Has no sickle disease but pt. is carrier for HBS. They are asymptomatic and can only be detected by blood test, and can transmit HBS gene to their offspring.
Blood film in sickle anemia
Pathogenesis of sickle cell disease
HBS polymerizes within the RBC and crystaline lead to red cell deformity in form of sickle shape.RBC has short life span and is trapped in the small vessels resulting in vaso-occlusion and so ischemia and infarction of organs or bones. This is induced and increase with hypoxia ,dehydration ,and cold. Clinical features depend upon the site and the severity of vaso-occlusive crises. Most pts. Have all his HB as HBS and only 1% of HBF. While some have high HBF as 10-15% and so they have milder symptoms. Peripheral blood smear shows sickle cells and increased reticulocyte count With low ESR .Sickle B-Thalassemia
MODERATE SEVERE ANEMIA SIMILAR TO SICKLE CELL ANEMIA IN SYMPTOMS.Patient inherits HBS gene from one parent and B-thalassemia gene from the other. Absent HBA, normal HBA2 3%, HBS 60%, HBF 40%.
SICKLE CELL TRAITS,B-THALASSEMIA TRAIT ,AND G6PD DEF. ARE PROTECTIVE AGAINST FALCIPARAM MALARIA.
Normal and sickle cells inside vess.
Normal and sickle cell
Clinical feature
Anemia moderate HB 6-8/dl and jaundice due to chronic hemolysis .Infections due to hyposplenism as it exposed to repeated infarctions and shrink, and child will have low splenic opsonisation for encapsulated bacteria specially pneumococcus,H.influenza,meningococcus.So high risk for meningitis, peritonitis and septicemia. Also increase possibility for osteomylitis caused by salmonella.
Painful crises; usual presentations as bone pains, dactylitis and finger swelling,abdominal pain , CVA due to brain infarction, Acute chest syndrome (severe and may be fatal due to vasooclusive crises leading to hypoxia and needs urgent exchange blood transfusion and ventilation).
Acue anemia due to aplastic crises when get viral infection as in parvovirusB19.,and also may be due to Sequestration crises due to rapid pooling of huge volume of blood inside the spleen leading to shock and splenomegaly and needs urgent blood transfusion.
Priapism due to occlusion of corpora cavernosa; needs treated urgently by exchange blood transfusion otherwise may lead to damage and fibrosis.
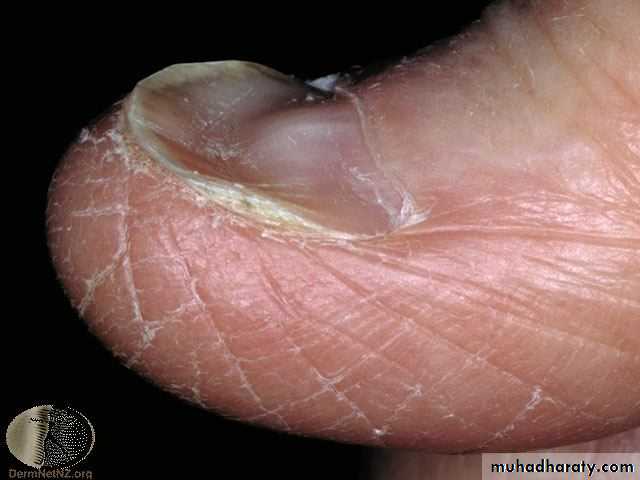
Dactylitis in sickle cell anemia
Long term treatment
Treatment of chronic recurrent problems like acute chest syndrome ,priapism, CVA, splenic sequestration crises needs regular monthly blood transfusion to dilute the sickling cells and prevent recurrence. Also give hydroxurea to increase HBF,and help these patients .Pneumococcal vaccine should be given and also routine vaccination for H.influenza .
Exclusive curative treatment is by BMT. Most pts.can survive with SCD till forties with usual management.
Neonatal screening for sickle Hb ,and prenatal DNA study for sickle gene from chorionic villous tissue, is available.
PENECILLIN PROPHYLAXIS
Children during first 5 yrs depend upon spleen for protection against encapsulated bacteria especially pneumococcus by its filtering and opsonizing function.after 5 yr,the immunity to these bacteria established from RES. In SCD,child will has hyposplenism due to repeated vasooclusive infarctions of spleen,So his immunity is low, and so pt. should be given prophylaxis oral penicillin since 2 months till 5 years together with usual schedule of peumococcal vaccine.After 5 years booster doses of vaccine should be given every 5 yrs . Usually PCV 13 type is used.
Hereditary spherocytosis
Autosomal dominant. uncommon in IRAQ, but common in U.KMay cause neonatal jaundice.
It cause anemia, splenomegaly ,jaundice, gall stones in older children but often asymptomatic.
Aplastic crises due to viral infection.
Diagnosis by blood film to see spherocytes with reduced central pallor.
Treatment folic acid .
splenectomy in symptomatic patients
spherocytosis
G6PD DEFICIENCY; FAVISM
Common in our countries. It is X-linked disease mainly males but also female can be express the problem as explained by Lyon hypothesis as by chance random inactivation of normal X chromosome more than the abnormal X containing the mutant gene,or if both parents transmit the X-mutant gene to their daughter as homozygous 2-genes.Clinically child is normal but he develops intravascular severe hemolytic crise if exposed to fava bean ,hinna, certain drugs like sulpha,naphthalines, antimalarial primaquine, and others called: oxidants as the RBC without G6PD enzyme cannot tolerate oxidants and RBC membrane will readily rupture if exposes in the blood to these oxidant antigens.Patient should not take these agents and should be given the list of oxidants. It may lead to severe spontaneous jaundice and hemolysis in the newborn.Children present after 3-5 days of exposure to fava beans; with severe anemia and dark cola- coloured urine due to hemoglobinuria,even may lead to renal tubular block, and jaundice , acidosis , splenomegaly, and even in shock. So immediate IV fluid hydration,and blood transfusion should be given, to prevent renal shutdown, and severe anemia. Usually onset is 3-5 days after exposure.
G6PD DEFICIENCY PATHOGENESIS
G6PD enzyme of pentose monophosphate shunt in RBC acts to catalyse reduction of NADP+ to NADPH (reduced form) that keep glutathione in reduced form .This glutathione act as scavenger to remove oxidants .In its absence ,oxidants can destroy the lipid in RBC wall leading to hemolysis; patient has dark urine due to hemoglobinuria with no RBCs in the urine;( no hematuria), and Negative bile pigment in the urine. Level of haptoglobin decreased in the blood due to its combination with free HB in the blood and excreted in urine. To be differentiated from hepatitis A illness which may be confused with G6PD def. in its clinical features:pt. with infectious hepatitis, has dark urine and also jaundice, but; no anemia or pallor ,and has positive urine test for bile pigment and and no RBCs urine.
Bone marrow failure
Bone marrow supression or aplastic anemia is condition of reduction of production of all tree lineages of blood precursor cells leading to pancytopenia; RBC ,leuckocytes ,and platelets, due to congenital inherited or acquired causes. The acquired causes like viral infection, chemotherapy, drugs,or toxins.
Inherited; Fanconi anemia is autosomal recessive present with pancytopenia by 5-6yrs.and has congenital anomalies like absent radius and thumb, microphthalmia, renal anomalies and skin hyperpigmentation. Recommended treatment is bone marrow transplantation. Has a tendency to change to acute leukemia
Shwachman –diamond syndrome; rare bone marrow failure, anemia,neutropenia,with or without thrombocytopenia, pancreatic exocrine failure, skeletal abnormalities and short stature.Has a risk to change to acute leukemia.
Pure red cell anemia
Due to bone marrow failure of erythropoiesis; causes1. transient erythrocytopenia of childhood TEC, may be idiopathic or due to parvovirus B19 infection(erythema infectiosum) occur in children age 2-10 yrs.
2. autoimmune pure red cell anemia; due to autoantibodies to RBC precursors in bone marrow.
3.Idiopathic pure red cell anemia. Unknown cause
4.Inherited ; Diamond-Blackfan syndrome; occur in young infants <1 yr, associated with face,cleft palate,renal,eye (as cataract) anomalies, microcephaly.
Usually RBCs are macrocytic anemia.